Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Fazlina Nordin and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
The chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) protein is composed of two domains: (a) The extracellular tumour-antigen receptor that specifically recognises tumour-associated antigens (TAA) on the cell-surface membrane of cancer cells (e.g., CD19 on B-cells); and (b) the intracellular signal transduction domain, which stimulates the engineered cell’s proliferation and function.
- CAR
- chimeric antigen receptor
- CAR-T cell
- CAR-NK cell
1. Introduction
Cellular immunotherapy, also known as adoptive cell therapy, has shown significant progress and advances utilising engineered immune cells to eliminate cancer. A notable contributor to immunotherapy is the expression of chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) on the surface of immune cells, mostly T-cells and natural killer (NK) cells. This form of cancer treatment involves the use of “living drugs” [1] because the patient’s cells or cells from donors are genetically engineered and processed for cancer treatment. Hence, the specificity and activity of the engineered immune cell are directed, in this case, towards tumour cells [2]. CAR-T cell therapy has been studied extensively over the years, and currently, there are approximately 1000 clinical trials. CAR-NK cell therapy has also attracted a great deal of interest in recent years to overcome the limitations of CAR-T cells. However, CAR therapies may have limited therapeutic potential, especially in solid malignancies (toxicity, escape of antigen, limited stability, etc.). This has paved the way for more studies to improve the efficacy of CAR immune cells, and one of the methods is the introduction of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) as biological vehicles [3][4][5][6][7]. A biological molecule delivery system may sustain the anti-tumour response of CAR immune cells [8].
Cellular immunotherapy, also known as adoptive cell therapy, has shown significant progress and advances utilising engineered immune cells to eliminate cancer. A notable contributor to immunotherapy is the expression of chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) on the surface of immune cells, mostly T-cells and natural killer (NK) cells. This form of cancer treatment involves the use of “living drugs” [1] because the patient’s cells or cells from donors are genetically engineered and processed for cancer treatment. Hence, the specificity and activity of the engineered immune cell are directed, in this case, towards tumour cells [2]. CAR-T cell therapy has been studied extensively over the years, and currently, there are approximately 1000 clinical trials. CAR-NK cell therapy has also attracted a great deal of interest in recent years to overcome the limitations of CAR-T cells. However, CAR therapies may have limited therapeutic potential, especially in solid malignancies (toxicity, escape of antigen, limited stability, etc.). This has paved the way for more studies to improve the efficacy of CAR immune cells, and one of the methods is the introduction of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) as biological vehicles [3,4,5,6,7]. A biological molecule delivery system may sustain the anti-tumour response of CAR immune cells [8].
2. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
The CAR protein is composed of two domains: (a) The extracellular tumour-antigen receptor that specifically recognises tumour-associated antigens (TAA) on the cell-surface membrane of cancer cells (e.g., CD19 on B-cells); and (b) the intracellular signal transduction domain, which stimulates the engineered cell’s proliferation and function [1][9]. The extracellular domain is the antigen-binding site of monoclonal antibodies (scFv, sdab, etc.), while the intracellular domain is a combination of natural TCR complex and co-stimulatory molecules [1][9][10]. Modifications made to the intracellular signal transduction domain give rise to several generations of CARs [10]. The design of CARs to treat cancer relies on specific TAA while the signalling and co-stimulatory domains depend on the immune cell used [11]. The expression of CARs on cell surfaces relies on gene transfer technology, mainly viral-based gene transfer. This includes the use of alpha-retroviruses, gamma-retroviruses and lentiviruses for gene engineering. Non-viral methods involve DNA-based transposons or the direct transfer of mRNA by electroporation [12]. Researchers will discuss two of the most common CAR-immune cells involved in cancer treatment, including a brief description of the therapeutic mechanism of each intrinsic immune cell, their sources and the production process of the CAR-immune cells. It is also important to note that genetically engineered immune cells carry out the same cytotoxic mechanisms as unmodified immune cells. The presence of CARs facilitates the binding to specific TAA in order for cytotoxic activities to be directed to the respective tumour [11].2.1. CAR-T Cells
T-cells are responsible for the body’s cell-mediated immune responses and play a significant role in identifying antigens of tumour cells, proliferating to a great number and performing cytotoxicity upon appropriate signals. However, the genetic instability in tumour cells causes these cells to not have the required immunogenic markers for T-cell recognition. Mutations in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes, the immunosuppressive microenvironment and the expression of negative co-stimulatory molecules disrupt intrinsic T-cell antitumour activity. Prior to the development of CAR-T cells, researchers developed T-cells that expressed tumour-specific TCRs [13]. However, TCR-engineered T-cells have limited modifications in their cellular and molecular mechanism, hence this treatment is still subjected to human leukocyte antigen restriction, the negative regulatory factors of the tumour microenvironment and requires sufficient expression of MHC [10][13]. Consequently, the limitations of this method led to the development of genetically engineered T-cells expressing the recombinant receptor CAR in place of TCR. This enables specific targeting of cancer antigens and is MHC-independent [9][13]. T-cells that are genetically engineered to express CARs are often obtained from the peripheral blood of the patient via leukapheresis or phlebotomy followed by apheresis [13]. The CAR gene is transduced into the T-cells and the expansion of T-cells is observed ex vivo [10][13]. Purification is carried out, and the validation of its quality and sterility is required [14]. Lymphodepletion is carried out in patients prior to CAR-T cells administration [13]. Treatment of haematological malignancies using CAR-T cell therapy has shown significant achievements over the years. However, there are still challenges that need to be resolved before it can be used as a dominant therapeutic choice in cancer treatment. Other concerns such as its serious side effects should also be highlighted and resolved. Some known side effects are cytokine release syndrome (CRS) [15][16][17], immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) [18][19], cytopenia [20][21], tumour lysis syndrome and off-tumour on-target toxicity [9][22][23].2.2. CAR-NK Cells
Alternatively, research on genetically engineered natural killer (NK) cells that express CARs is of great interest because CAR-T cell therapy has its known limitations, such as suppression by regulatory T-cells (Tregs) [24]. It is also suggested that CAR-NK cells may be more beneficial than CAR-T cells as they are not suppressed by Tregs. When NK cells are activated, they can carry out cytotoxic activities without prior tumour antigen priming, which is essential for T-cell activation [24][25]. They release cytotoxic granules of perforin and granzyme, which causes target cell lysis [26][27]. In addition, NK cells also release tumour necrosis factor molecules (TNF), which increase death-ligand expression (TRAIL/FasL) on the NK cell surface that can be recognised by death receptors of tumour cells and initiate the caspase pathway of cell apoptosis [24][26][28]. Furthermore, NK cells secrete interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which causes the recruitment of other immune effectors such as macrophages and dendritic cells to carry out alternative anti-tumour activities [27][29]. Another immune response of NK cells is its ability to kill cancers cells by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). CD16 plays a key role in ADCC [27]. It recognises and binds to the Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies opsonised on the surface of tumour cells [27][30]. An advantage of NK cells over T-cells is that they do not stimulate graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Their allogeneic behaviour gives them potential as off-the-shelf therapies in the near future [31]. NK cells also do not cause severe toxicities such as CRS and ICANS [32]. The efficient intrinsic abilities of NK cells aptly complement suitable CAR structures. The initial CAR structures used in engineered NK cells were similar to the CARs that were designed for T-cell-based therapy (2. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
The CAR protein is composed of two domains: (a) The extracellular tumour-antigen receptor that specifically recognises tumour-associated antigens (TAA) on the cell-surface membrane of cancer cells (e.g., CD19 on B-cells); and (b) the intracellular signal transduction domain, which stimulates the engineered cell’s proliferation and function [1,9]. The extracellular domain is the antigen-binding site of monoclonal antibodies (scFv, sdab, etc.), while the intracellular domain is a combination of natural TCR complex and co-stimulatory molecules [1,9,10]. Modifications made to the intracellular signal transduction domain give rise to several generations of CARs [10]. The design of CARs to treat cancer relies on specific TAA while the signalling and co-stimulatory domains depend on the immune cell used [11]. The expression of CARs on cell surfaces relies on gene transfer technology, mainly viral-based gene transfer. This includes the use of alpha-retroviruses, gamma-retroviruses and lentiviruses for gene engineering. Non-viral methods involve DNA-based transposons or the direct transfer of mRNA by electroporation [12]. We will discuss two of the most common CAR-immune cells involved in cancer treatment, including a brief description of the therapeutic mechanism of each intrinsic immune cell, their sources and the production process of the CAR-immune cells. It is also important to note that genetically engineered immune cells carry out the same cytotoxic mechanisms as unmodified immune cells. The presence of CARs facilitates the binding to specific TAA in order for cytotoxic activities to be directed to the respective tumour [11].2.1. CAR-T Cells
T-cells are responsible for the body’s cell-mediated immune responses and play a significant role in identifying antigens of tumour cells, proliferating to a great number and performing cytotoxicity upon appropriate signals. However, the genetic instability in tumour cells causes these cells to not have the required immunogenic markers for T-cell recognition. Mutations in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes, the immunosuppressive microenvironment and the expression of negative co-stimulatory molecules disrupt intrinsic T-cell antitumour activity. Prior to the development of CAR-T cells, researchers developed T-cells that expressed tumour-specific TCRs [13]. However, TCR-engineered T-cells have limited modifications in their cellular and molecular mechanism, hence this treatment is still subjected to human leukocyte antigen restriction, the negative regulatory factors of the tumour microenvironment and requires sufficient expression of MHC [10,13]. Consequently, the limitations of this method led to the development of genetically engineered T-cells expressing the recombinant receptor CAR in place of TCR. This enables specific targeting of cancer antigens and is MHC-independent [9,13].
T-cells that are genetically engineered to express CARs are often obtained from the peripheral blood of the patient via leukapheresis or phlebotomy followed by apheresis [13]. The CAR gene is transduced into the T-cells and the expansion of T-cells is observed ex vivo [10,13]. Purification is carried out, and the validation of its quality and sterility is required [14]. Lymphodepletion is carried out in patients prior to CAR-T cells administration [13].
Treatment of haematological malignancies using CAR-T cell therapy has shown significant achievements over the years. However, there are still challenges that need to be resolved before it can be used as a dominant therapeutic choice in cancer treatment. Other concerns such as its serious side effects should also be highlighted and resolved. Some known side effects are cytokine release syndrome (CRS) [15,16,17], immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) [18,19], cytopenia [20,21], tumour lysis syndrome and off-tumour on-target toxicity [9,22,23].
2.2. CAR-NK Cells
Alternatively, research on genetically engineered natural killer (NK) cells that express CARs is of great interest because CAR-T cell therapy has its known limitations, such as suppression by regulatory T-cells (Tregs) [24]. It is also suggested that CAR-NK cells may be more beneficial than CAR-T cells as they are not suppressed by Tregs. When NK cells are activated, they can carry out cytotoxic activities without prior tumour antigen priming, which is essential for T-cell activation [24,25]. They release cytotoxic granules of perforin and granzyme, which causes target cell lysis [26,27]. In addition, NK cells also release tumour necrosis factor molecules (TNF), which increase death-ligand expression (TRAIL/FasL) on the NK cell surface that can be recognised by death receptors of tumour cells and initiate the caspase pathway of cell apoptosis [24,26,28]. Furthermore, NK cells secrete interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which causes the recruitment of other immune effectors such as macrophages and dendritic cells to carry out alternative anti-tumour activities [27,29]. Another immune response of NK cells is its ability to kill cancers cells by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). CD16 plays a key role in ADCC [27]. It recognises and binds to the Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies opsonised on the surface of tumour cells [27,30]. An advantage of NK cells over T-cells is that they do not stimulate graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Their allogeneic behaviour gives them potential as off-the-shelf therapies in the near future [31]. NK cells also do not cause severe toxicities such as CRS and ICANS [32]. The efficient intrinsic abilities of NK cells aptly complement suitable CAR structures.
The initial CAR structures used in engineered NK cells were similar to the CARs that were designed for T-cell-based therapy (
Figure 1) [27]. Consequently, the CAR structures lacked specificity for NK cells as these CARs were tailormade for T-cells. Therefore, their signalling and co-stimulatory domains were more optimum for the T lymphocyte signalling pathways including the CD3zeta (signalling domain) and 4-1BB or CD28 (co-stimulatory domain). It is necessary to investigate the co-stimulatory domains that are better equipped and more specific for NK cell signalling in order to maximise its efficacy [24][27]. NK-specific co-stimulatory domains such as DNAX-activation protein 10 (DAP10), DAP12 and 2B4 showed greater cytotoxicity and increased IFN-γ secretion [27]. Moreover, CAR-NK cells are incorporated with inducible caspase 9 (iCas9) to eliminate the CAR-NK cells after their antitumour activities [33]. NK cells from the peripheral blood of donors, human NK92 cell lines, umbilical cord blood and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) are suitable for the generation of CAR-NK, with each source having its advantages and limitations [27].


) [27]. Consequently, the CAR structures lacked specificity for NK cells as these CARs were tailormade for T-cells. Therefore, their signalling and co-stimulatory domains were more optimum for the T lymphocyte signalling pathways including the CD3zeta (signalling domain) and 4-1BB or CD28 (co-stimulatory domain). It is necessary to investigate the co-stimulatory domains that are better equipped and more specific for NK cell signalling in order to maximise its efficacy [24,27]. NK-specific co-stimulatory domains such as DNAX-activation protein 10 (DAP10), DAP12 and 2B4 showed greater cytotoxicity and increased IFN-γ secretion [27]. Moreover, CAR-NK cells are incorporated with inducible caspase 9 (iCas9) to eliminate the CAR-NK cells after their antitumour activities [33]. NK cells from the peripheral blood of donors, human NK92 cell lines, umbilical cord blood and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) are suitable for the generation of CAR-NK, with each source having its advantages and limitations [27].
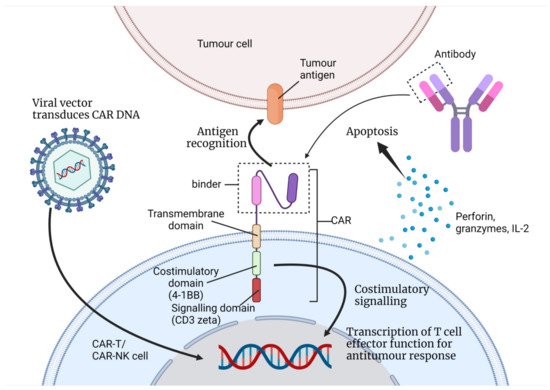

Figure 1. This figure illustrates how a T-cell/NK cell can be engineered to express CAR with its binder from monoclonal antibodies (single-chain variable fragment in the figure) as the antigen-binding receptor. This is a second-generation CAR with its single co-stimulatory domain (4-1BB or CD28) and its signalling domain (CD3zeta) [13]. A viral vector is used to transfer the DNA that codes for CAR into the nucleus of the immune cell. When the CAR receptor recognises the tumour antigen, the signal is amplified and transferred to the nucleus. This initiates a series of antitumour responses; the immune cell may proliferate and secrete cytokines, perforins, etc. (Created with BioRender.com).
The production process of CAR-NK cells is rather similar to that of CAR-T cells. However, CAR-NK cells require further expansion and activation prior to infusion. It is necessary to produce CAR-NK cells that are homogenous, GMP-compliant and show a similar maturity stage. Common approaches include incubation with feeder cells, for example, the Wilms tumour cell line, irradiated K562 cells, or human B-lymphoblastoid cell line 721.221 [27]. Overall, the differences between CAR-T and CAR-NK cells are summarised in
This figure illustrates how a T-cell/NK cell can be engineered to express CAR with its binder from monoclonal antibodies (single-chain variable fragment in the figure) as the antigen-binding receptor. This is a second-generation CAR with its single co-stimulatory domain (4-1BB or CD28) and its signalling domain (CD3zeta) [13]. A viral vector is used to transfer the DNA that codes for CAR into the nucleus of the immune cell. When the CAR receptor recognises the tumour antigen, the signal is amplified and transferred to the nucleus. This initiates a series of antitumour responses; the immune cell may proliferate and secrete cytokines, perforins, etc. (Created with BioRender.com).
The production process of CAR-NK cells is rather similar to that of CAR-T cells. However, CAR-NK cells require further expansion and activation prior to infusion. It is necessary to produce CAR-NK cells that are homogenous, GMP-compliant and show a similar maturity stage. Common approaches include incubation with feeder cells, for example, the Wilms tumour cell line, irradiated K562 cells, or human B-lymphoblastoid cell line 721.221 [27]. Overall, the differences between CAR-T and CAR-NK cells are summarised in
Table 1
, while the similarities between the two CAR cells are discussed in
Table 2
.
| Differences | CAR-T Cells | CAR-NK Cells | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic immune cell | T cells | Derived from immune cells that are genetically engineered to express CARs | Natural killer (NK) cells Immortalised human NK cell lines |
| Source of immune cell | Peripheral blood of patient | Peripheral blood from donor Umbilical cord blood Differentiated pluripotent stem cells |
|
| Require expansion and activation prior to infusion | Surface expression of immune cell | T cell receptor (TCR), CD3 | CD56, CD16 |
| Shelf-life | Long-lived | Short-lived | |
| Antigen recognition | Require prior antigen recognition | Do not require prior priming with antigen | |
| Immune mechanisms | Stimulate apoptosis by activating the apoptotic signalling pathways within the cancer cells Cytokines enhance tumour clearance |
Eliminate cancer cells via ADCC due to CD16 expression Induce apoptosis of the tumour cells by secreting tumour necrosis factor (TNF) Produce interferon-gamma upon engagement |
|
| Intrinsic cells that are reprogrammed | CD4+, CD8+ | NK-92 cell (cell line) CD16+ CD56 dim (peripheral blood) CD16-CD56 bright (lymphoid tissues) |
|
| Receptor activated | NKG2D, NKG2C, NKp44, KIR | ||
| Co-stimulatory domain for specific CAR structures | CD28, CD137 (4-1BB), CD27, CD40, CD134 | DAP10, DAP12, 2B4 | |
| Potential side effects | Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) Risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD) due to allogenic source Tumour lysis syndrome Neurotoxicity On-target off-tumour toxicity Oncogenic insertional mutagenesis |
Lack evidence of serious toxicities such as CRS and ICANS Does not induce graft versus host disease (GVHD) |
| Similarities of CAR-T and CAR-NK Cells |
|---|
| Exhibit tumour cytotoxicity by releasing granzyme and perforin |
| Similar production protocols |
| Commonly used co-receptors: CD28, CD3z and 4-1BB |
| Independent of MHC |
| Utilise four generations of CARs and specific signalling/co-stimulatory domains |
| Common challenges: Trafficking to tumour sites, the immunosuppressive tumour environment, which is rich in immunosuppressive cytokines and metabolites |
| Amplification of the cytotoxicity activity via single-chain fragment variable (scFv) binding to respective tumour-associated antigen |
| Cytokines and chemokines release upon activation. (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL2, IL6, IL12, IL21) |
3. Application of CAR-T/CAR-NK Cells in Immunotherapy
Current Clinical Trials Involving CAR-T/CAR-NK Cells
CAR-T cell therapy has garnered much attention over the past decade as a cancer therapy, especially in haematological malignancies. There are currently a total of 988 studies being conducted worldwide on CAR -T cell therapy for various cancers. The exponential increase in studies in recent years proves the significance of CAR-related therapies. A total of 943 studies were classified as interventional (clinical trials). The majority of studies are being conducted in East Asia, totalling 512 trials, followed by the United States with 372 ongoing studies and Europe with 89 trials. The emergence of CAR-NK cell therapy as a subsequently promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment has led to several studies of CAR-NK cell efficacy. However, the number of studies registered is relatively low as it is still relatively new. Only a total of 29 studies on CAR-NK cell therapy are currently being conducted worldwide, with the majority of trials being performed in China (15 studies), followed by the United States (7 studies), Australia (1 study) and Germany (1 study). Studies are also being conducted for alternative candidates of CAR modification, which includes iNKT cells (one trial in China), macrophages (one trial each in the United States and Europe) and gamma delta T-cells (one trial in China and one trial in Malaysia) (Data obtained from3. Application of CAR-T/CAR-NK Cells in Immunotherapy
Current Clinical Trials Involving CAR-T/CAR-NK Cells
CAR-T cell therapy has garnered much attention over the past decade as a cancer therapy, especially in haematological malignancies. There are currently a total of 988 studies being conducted worldwide on CAR -T cell therapy for various cancers. The exponential increase in studies in recent years proves the significance of CAR-related therapies. A total of 943 studies were classified as interventional (clinical trials). The majority of studies are being conducted in East Asia, totalling 512 trials, followed by the United States with 372 ongoing studies and Europe with 89 trials.
The emergence of CAR-NK cell therapy as a subsequently promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment has led to several studies of CAR-NK cell efficacy. However, the number of studies registered is relatively low as it is still relatively new. Only a total of 29 studies on CAR-NK cell therapy are currently being conducted worldwide, with the majority of trials being performed in China (15 studies), followed by the United States (7 studies), Australia (1 study) and Germany (1 study). Studies are also being conducted for alternative candidates of CAR modification, which includes iNKT cells (one trial in China), macrophages (one trial each in the United States and Europe) and gamma delta T-cells (one trial in China and one trial in Malaysia) (Data obtained from
clinicaltrials.gov for trials registered by Q4 of 2021, accessed on 15 December 2021) [34].
CAR-T cell products that were approved to be used as drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Commission (EC) from 2017 onwards are Kymriah (Novartis), Yescarta (Kite Pharma, Gilead), Tecartus (Kite Pharma, Gilead) and Breyanzi (Juno Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company) [35].
for trials registered by Q4 of 2021, accessed on 15 December 2021) [39].
CAR-T cell products that were approved to be used as drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Commission (EC) from 2017 onwards are Kymriah (Novartis), Yescarta (Kite Pharma, Gilead), Tecartus (Kite Pharma, Gilead) and Breyanzi (Juno Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company) [40].
