Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Conner Chen and Version 1 by Jose Ramon Botella.
Environmental cues have a critical impact on plant growth and development. As sessile organisms, plants exhibit extraordinary plasticity and have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to adapt and mitigate the adverse effects of environmental fluctuations. Heterotrimeric G proteins (G proteins), composed of α, β, and γ subunits, are universal signaling molecules mediating the response to a myriad of internal and external signals. In this review, we summarize and discuss the current knowledge on the roles of the different G protein subunits in response to abiotic stress and suggest future directions for research.
- Heterotrimeric G proteins
- Plant abiotic stress
- Plant signal transduction
- Plant signaling
- Drought stress
- Salt stress
- tmeperature stress
1. Introduction
Environmental cues have a critical impact on plant growth and development [1]. In the face of increasing environmental pollution and climate change, we are experiencing increased incidence of abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, heat, cold, heavy metals, ozone, and UV-B radiation affecting crop yields and increasing demands on plant plasticity [2,3,4][2][3][4]. Heterotrimeric guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins), composed of α, β, and γ subunits, are a family of highly conserved signaling molecules involved in multiple biological processes [5,6,7,8,9,10][5][6][7][8][9][10]. G proteins transduce signals from membrane receptors synchronizing development and triggering responses to multiple stresses. In animal systems, the Gα subunit is bound to GDP in the inactive state, which is replaced by GTP upon activation by G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) leading to dissociation of Gα from the Gβγ dimer and activation of independent signaling pathways by each of the two functional subunits.
Plant G proteins have evolved a number of important differences with their animal counterparts [11,12,13][11][12][13]. Plants lack GPCRs and G proteins are associated with receptor-like kinases and regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins [11,14,15][11][14][15]. Aside from the canonical animal looking subunits, plants possess several atypical subunits with important structural and biochemical differences. As an example, extra-large Gα subunits (XLGs) contain a Gα-like C-terminal domain fused to a non-conserved N-terminal region. XLGs are involved in plant defense, root development, and stress responses [16,17,18][16][17][18]. Plants also contain extra-large Gγ subunits with transmembrane and extracellular domains with important roles in crop productivity [19,20,21,22,23][19][20][21][22][23]. Finally, some plant Gγ subunits lack the isoprenylation motif present in all known animal Gγs [24]. Most importantly, plant G proteins do not necessarily use the GDP-GTP switch for activation/deactivation of the signaling cycle with both canonical Gα and XLG subunits being able to signal in a GTP-independent manner [25,26][25][26]. A mutant Arabidopsis canonical Gα subunit, unable to bind guanine nucleotides, successfully complemented several Gα knockout phenotypes, including morphological abnormalities, such as reduced leaf and hypocotyl lengths, and stomatal opening sensitivity to ABA, suggesting that these traits are nucleotide exchange-independent. In contrast the hypersensitivity to ABA during seed germination as well as the reduced stomata density shown by knockout mutants could not be restored to WT levels by the mutant Gα, suggesting that they require GTP binding. The extra-large Gα subunit XLG2 has also proven to function in a GTP-independent manner [25,26][25][26]. A vast majority of G protein studies have been performed in the model system Arabidopsis thaliana, which contains a canonical Gα subunit (GPA1), three extra-large Gα subunits (XLG1, XLG2 and XLG3), one Gβ subunit (AGB1), two type A Gγ subunits (AGG1 and AGG2), and one atypical type C Gγ subunit (AGG3). Plant G proteins are involved in multiple aspects of plant growth, including seed germination, seedling development, plant morphology, stomatal movement, biotic and abiotic stresses [5,7,27,28,29,30,31,32][5][7][27][28][29][30][31][32]. Among their multiple functions, numerous studies have shown that G protein signaling plays an essential role in plant responses to abiotic stresses.
2. G Protein Signaling in the Response to Drought Stress
Globally, drought is the most significant abiotic stress affecting agricultural production [33]. Terrestrial plants lose water mainly through stomata, therefore precise control of guard cell opening is a critical mechanism to reduce water loss [34]. Even in ideal conditions, plants need to balance CO2 acquisition with water loss to maximize photosynthesis. In Arabidopsis thaliana, G proteins are involved in a variety of pathways that regulate stomatal closure in response to drought stress, including abscisic acid (ABA), extracellular calmodulin (ExtCaM), and the brassinosteroid-ethylene pathways [35,36,37][35][36][37]. In addition, G protein regulation of leaf developmental processes determines stomatal density, thus affecting the ability of plants to withstand drought conditions [38,39][38][39].
2.1. G Protein Involvement in the
Arabidopsis
ABA Signaling Pathway
ABA has an essential role in response to drought stress affecting ion fluxes to promote stomata closure and inhibiting stomata opening to enhance plant survival chances [39]. Although the general consensus is that G proteins are involved in Arabidopsis ABA signaling and drought response, there is some discrepancy about the roles of the individual subunits.
Arabidopsis gpa1 (Gα) mutants show a WT response to ABA promotion of stomatal closure but are defective in ABA-mediated inhibition of inward K+ channels and pH-independent ABA activation of anion channels. As a result, gpa1 mutants are hyposensitive to inhibition of stomatal opening by ABA and have higher rates of water loss in excised leaves than WT plants [35,40][35][40]. A key component of the ABA response in guard cells is the influx of calcium ions (Ca2+) into the cell through activation of Ca2+ channels by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by the membrane-bound NADPH oxidases AtrbohD and AtrbohF. Zhang et al. (2011) reported that ABA-mediated activation of Ca2+ channel of guard cells in Arabidopsis gpa1 (Gα) mutants was defective, while ABA-induced ROS synthesis was also disrupted [41]. The authors proposed that GPA1 is required for guard cell ROS production in response to ABA functioning upstream of the NADPH oxidases, AtrbohD and AtrbohF. Addition of exogenous H2O2 restored ion channel activation suggesting that GPA1 deficiency inhibits Ca2+ channel activation and ROS production due to disruption of ABA signaling (Figure 1). GPA1 has been proven to interact with RD20/CLO3, a member of the calcium-binding protein family caleosin [42]. RD20/CLO3 transcript levels are strongly induced by drought, salt, and abscisic acid and the rd20/clo3 exhibit decreased tolerance to drought and salt stresses, prompting the suggestion that RD20/CLO3 acts as a stress-signaling hub controlling multiple plant stress response mechanisms [43,44][43][44]. Disruption of the calcium-binding capacity of RD20/CLO3 abolishes the in vivo interaction with GPA1 assays. Comparative analysis of rd20/clo3, gpa1 single mutants, and rd20/clo3gpa1 double mutant suggested that RD20/CLO3 is a negative regulator of GPA1 [42]. ABA activates the synthesis of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a signaling sphingolipid involved in the control of guard cell turgor by inhibition of inward K+ channels and activation of slow anion channels to promote stomatal closure and inhibit stomatal opening [45,46][45][46]. In gpa1 mutants, ABA-induced inhibition of guard cell inward potassium channels and pH-independent ABA activation of anion channels are disrupted [35[35][47],47], and S1P is unable to regulate guard cell ion channels and initiate stomatal closure, indicating that GPA1 acts downstream of S1P to mediate stomatal closure by regulating downstream guard cell ion channel activity, thereby increasing drought tolerance in Arabidopsis [47]. G proteins have also been proposed to regulate the activity of the outward-rectifying potassium efflux GORK channels, an essential component of the stress-induced K+ loss from the cytosol based on the presence of a conserved consensus protein sequence for G protein binding motif in the GORK protein sequence, although no experimental proof of the interaction has been provided [48]. Phospholipases mediate hormonal signaling in the response to multiple stresses and are involved in ABA signaling [49]. Interestingly, the Arabidopsis phospholipase Dα1 (PLDα1) contains a motif with homology to the known Gα-interacting DRY motif found in animal G protein coupled receptors [50]. Interaction studies showed that PLDα1 interacts with GPA1 through the DRY1 motif, and the interaction has important biochemical implications. PLDα1 activity is inhibited by the addition of GPA1 while GTP abolished the inhibitory effect of GPA1 as well as the binding of PLDα1 with GPA1 [50]. PLDα1 mediates ABA effects on stomatal movements through a bifurcating signaling pathway involving a protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) in one of the branches and GPA1 in the other branch [51]. It was proposed that phosphatidic acid (PA), the product of PLDα1 as well as PLDα1 itself interact with GPA1 to mediate ABA inhibition of stomatal opening. All the above results suggest that GPA1 is a positive regulator of the drought response in Arabidopsis.
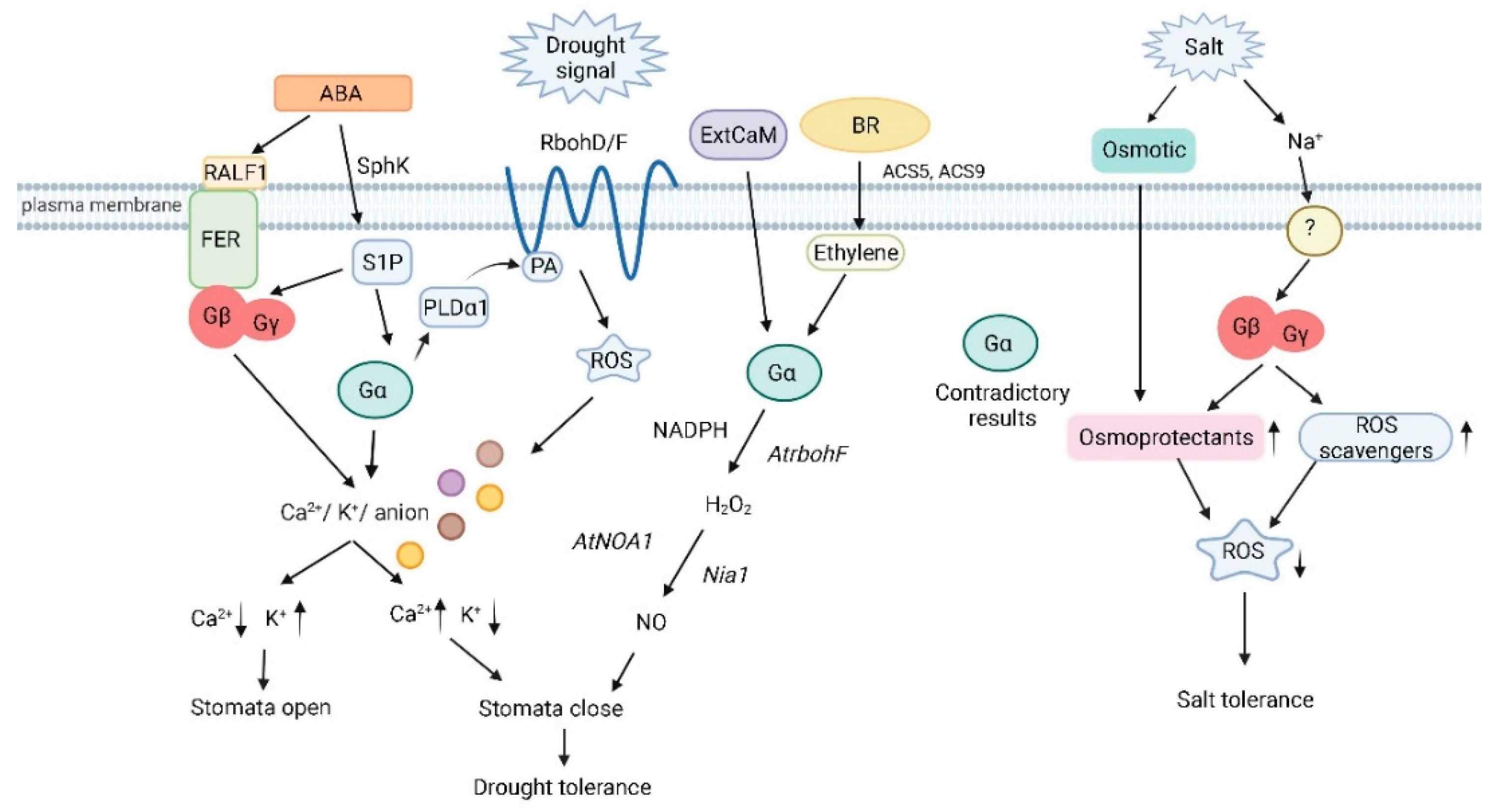

Figure 1. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling in plant drought and salinity stress (Created with BioRender.com on 17/03/2022). Gα deficiency inhibits Ca2+ channel activation and ROS production due to disruption of ABA signaling. Gα acts downstream of S1P to regulate stomatal closure by modulating inward K+ channels and slow anion channels. PA and PLDα1 interact with Gα to mediate ABA inhibition of stomatal opening. Binding of PA to Rboh at the N-terminal cytoplasmic region results in the production of ROS. Stomatal regulation by the RALF-FER pathway is associated with Gβ. Gα participates in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure of guard cells by regulating NO synthesis, and NO synthesis is dependent on H2O2 produced by NADPH oxidases through the action of the nitrate reductase Nia1. BR induces the expression of ACS5 and ACS9 to initiate ethylene synthesis, which signals through Gα to synthesize H2O2 and before the nitric synthase NOA1 induces the production of NO. Several groups have proven the involvement of Gα in salt stress although the results are contradictory with positive as well as negative roles being proposed for this subunit. Gβ regulates the combination of osmotic and ionic stresses during salt stress by increasing levels of proteins involved in ROS detoxification and osmoprotectant compounds. SphK: sphingosine kinase; RALF1: rapid alkalinization factor 1; FER: receptor-like kinase FERONIA; S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate; PLDα1: phospholipase D α1; PA: phosphatidic acid; RbohD/F: NADP oxidases RbohD and RbohF; ROS: reactive oxygen species; ExtCaM: extracellular calmodulin; AtNOA1: nitric oxide; Nia1: nitrate reductase.
Like gpa1 mutants, Arabidopsis agb1 (Gβ) mutants have been reported to be hyposensitive to ABA inhibition of stomatal opening while displaying wild-type ABA promotion of stomatal closure [40]. Although this result suggests that AGB1 has a positive role in drought stress, overexpression of AGB1 failed to increase ABA sensitivity over WT levels [40]. Further support for a positive role of AGB1 in drought stress comes from studies of the FERONIA pathway which is involved in the regulation of stomatal movement by ABA [52,53][52][53]. Immunoprecipitation experiments using anti-AGB1 antibodies and plasma membrane enriched protein extracts identified the receptor-like kinase FERONIA (FER) as an AGB1 interactor [54]. FER ligands include the rapid alkalinization factor (RALF) family of polypeptides and the authors demonstrated that RALF1 inhibits stomatal opening and promotes stomatal closure [54]. Stomatal regulation by the RALF-FER pathway is G protein-dependent and is absent in agb1 mutants. In addition to AGB1, AGG gamma subunits and XLGs, but not GPA1 are involved in RALF1-mediated stomatal signaling, perhaps using Ca2+ as a second messenger [54]. A study by a different group also reported that agb1 mutants were hypersensitive to drought compared to WT plants [55]. Plant Gβ subunits positively regulate drought tolerance by increasing ROS detoxification. In open contrast with the above results, Xu et al. (2015) reported that Arabidopsis agb1 mutants have enhanced drought tolerance suggesting that AGB1 might be a negative regulator of the drought response [56]. The same study found that AGB1 can physically interact with the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) AtMPK6, a member of several MAPK cascades with multiple roles in plant development, including regulation of mitotic activity in the root apical meristem [56], regulation of shoot branching, hypocotyl gravitropism, and lateral root formation [57], jasmonate signaling [58], and most importantly, regulation of ABA stomatal responses [59]. Upregulation of four ABA-responsive genes, AtMPK6, AtVIP1, AtMYB44, and RD29A, was greatly increased in agb1 mutants compared to WT plants [56]. In addition, agb1 mutants showed increased transcription of ABA and proline biosynthesis genes upon drought treatment suggesting that AGB1 inhibits the synthesis of these two essential players in plant drought tolerance [56].
AGB1, does not function in isolation and forms obligate dimers with Gγ subunits [7]. Arabidopsis has three Gγ subunits, AGG1, AGG2, and AGG3 with AGG1 and two showing all the hallmarks of animal Gγs and AGG3 containing plant specific features such as a transmembrane and extracellular domains [19,60,61,62][19][60][61][62]. Similar to the observations in gpa1 and agb1 mutants [35[35][40],40], Arabidopsis agg3 mutants stomatal opening and inward K+ currents were hyposensitive to ABA, while ABA-mediated promotion of stomatal closure was wild-type [19]. agg1 and agg2 mutants showed a WT behavior [63], suggesting that AGG3 is the only Gγ subunit participating in the ABA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis guard cells. Similarly, Camelina sativa, a close relative of A. thaliana, overexpressing AGG3 showed hyposensitivity to ABA in seed-related traits but were hypersensitive to ABA in stomatal responses, resulting in increased drought stress tolerance [64].
2.2. G Protein Involvement in the
Arabidopsis
ExtCaM Signaling Pathway
Cytosolic calcium [Ca2+]cyt is an important second messenger in plants and animals controlling multiple cellular responses [65]. In particular, [Ca2+]cyt levels can widely fluctuate in response to hormonal and environmental stimuli in guard cells to promote opening or closing of stomata [66]. Interestingly, a large proportion of the total Ca2+ is located outside the cell [Ca2+]ext and [Ca2+]ext levels can be perceived by sensors such as calcium-sensing receptors in the plasma membrane and extracellular calmodulin to stimulate multiple intracellular signaling pathways [36,67][36][67]. Activation of ExtCAM by [Ca2+]ext induces increases in [Ca2+]cyt and H2O2 leading to stomatal closure [36]. Experiments using G protein activity modulators suggested that G proteins were involved in the ExtCAM signaling pathway upstream of the increase in [Ca2+]cyt.
Confirming the pharmacological results, Arabidopsis gpa1 mutants were defective in ExtCaM-mediated induction of stomatal closure, while transgenic lines overexpressing a constitutively active Gα mutation (cGα) showed an enhanced ExtCaM response [36]. In addition to [Ca2+]cyt and H2O2, ExtCaM-triggered nitric oxide (NO) accumulation, mediated by AtNOA1, has a critical role in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure [68]. In gpa1 mutants, ExtCaM is unable to induce NO production, whereas NO levels are increased in cGα overexpressing plants, suggesting that ExtCaM-mediated NO accumulation is controlled by GPA1. Furthermore, overexpression of AtNOA1 rescued the phenotype of gpa1 mutants suggesting that GPA1 acts upstream of AtNOA1. Overall, the existing data suggests that ExtCaM-signaling involves GPA1-mediated H2O2 production followed by NO synthesis leading to stomatal closure. In addition, the pea Gβ subunit has also been implicated in the signaling pathway leading to NO-induced stomatal closure during heat and drought stress [69].
2.3. G Protein Involvement in the
Arabidopsis
Brassinosteroid-Ethylene Pathway
Aside from ABA, G proteins are involved in the signaling pathways of several other phytohormones [70]. Brassinosteroids (BR) and ethylene promote stomatal closure by induction of H2O2 and NO levels [37,71][37][71]. Ethylene-mediated induction of stomatal closure is dependent on GPA1 signaling as gpa1 mutants are defective in ethylene-induction of H2O2 and stomatal closure while transgenic lines expressing either WT or constitutively active cGα show an enhanced response to ethylene [71]. Three of the five known ethylene receptors, ETR1, ERS1, and EIN4 are involved in the guard cell responses to ethylene, while ETR2 and ERS2 do not seem to play an important role [71]. Pharmacological studies with Gα activators revealed a complicated picture with partial or total phenotypic rescue in the etr1, ers1, and ein4 mutant backgrounds. CTR1 acts immediately downstream of all ethylene receptors as a negative regulator of the ethylene response. ctr1 mutants showed elevated H2O2 levels and constitutive stomatal closure that could be reversed by incubation with Gα inhibitors, suggesting that GPA1 acts downstream from CTR1 [71]. Analysis of mutants for three downstream components of the ethylene response, ein2, ein3, and arr2 showed that Gα activators failed to induce stomatal closure thus positioning G proteins upstream of these elements of the ethylene response [71]. BR promotion of stomatal closure seems to be mediated by ethylene [37]. The bioactive 24-epibrassinolide (EBR) induces stomata closure by inducing ethylene synthesis, activation of Gα, and accumulation of H2O2 and NO. Incubation with EBR enhances the expression of the ethylene biosynthetic genes AtACS5 and AtACS9 resulting in ethylene synthesis, which in turn induces H2O2 synthesis through AtrbohF and subsequent NO synthesis finally triggering stomatal closure [37]. Shi et al. (2015) showed that EBR-induction of H2O2 and NO was defective in gpa1 mutants but enhanced in transgenic lines overexpressing the constitutively active cGα [37]. Additional mutant and pharmacological data positioned G proteins downstream of ethylene production but upstream of H2O2 and NO in this signaling pathway, consistent with the results of Ge et al. [71].
Although the BR-ethylene and the ExtCAM pathways seem to share the signaling downstream of GPA1, i.e., induction of H2O2 and NO synthesis, the signaling upstream of GPA1 and its activation mechanism are still unclear, specially taking into account that GPA1 does not necessarily follow the GTP/GDP activation/deactivation mechanism used in animal systems [25].
2.4. G Protein Involvement in the Response to Drought Stress in Food Crops
Many rice G protein subunit genes, including the canonical Gα (RGA1), Gβ (RGB1), and two of the Gγ subunits, RGG1 and RGG2 are induced by drought stress, suggesting a possible role for G proteins in this stress [72,73,74,75][72][73][74][75]. ABA treatment also induced RGB1 expression while transcript levels for the atypical Gγ subunit DEP1 (also known as qPE9-1) decreased [76]. When transgenic lines containing DEP1 RNA interference constructs were analyzed, silencing of DEP1 resulted in enhanced drought tolerance in rice plants whereas silencing of AGB1 reduced drought tolerance [76]. Consistent with these results, simultaneous overexpression of RGB1 and AGG1 in rice increased the drought tolerance of the transgenic lines by potentiating plant the antioxidant machinery in stress situations [75]. On the other hand, the rga1-null mutant, also known as d1, showed improved drought resistance compared to WT plants, which was associated with increased stomatal conductance and low leaf temperature in the plants [77,78][77][78]. The finding that RGA1 was a negative regulator of mesophyll conductance, with d1 mutants showing improved photosynthesis, water use efficiency and drought tolerance supported a negative effect for RGA1 on drought. Taken together, the above results suggest that the Gα subunit RGA1 and the Gγ subunit DEP1 negatively regulate ABA signaling and drought adaptation, while the Gβ subunit RGB1 positively regulates the response to drought and ABA. Surprisingly, although the available evidence assigns antagonistic roles for Gα and Gβ in the drought response in rice and Arabidopsis, their roles seem to be opposite. The role of the remaining rice G protein subunits in drought resistance remains to be established.
Mulberry (Morus alba L.) is a drought-tolerant economic crop, and the roles of several mulberry G protein subunits in drought stress have been studied. Overexpression of MaGα in tobacco enhanced drought sensitivity [79]. Extensive analysis revealed that the antioxidant capacity of the transgenic plants was weakened and the content of H2O2 and O2- was increased. In contrast, overexpression of MaGβ and MaGγ (γ1 and γ2) increased the expression levels of glutathione peroxidase (POD) and antioxidant genes, and enhanced the drought tolerance of the plants, suggesting that G proteins could regulate drought adaptation by enhancing ROS detoxification [55,79,80][55][79][80]. The available evidence suggests that Gα has a negative regulatory effect on drought stress in mulberry, whereas Gβ and Gγ (γ1 and γ2) are positive regulators.
In contrast to rice and mulberry, the cucumber Gα subunit CsGPA1 appears to be a positive regulator of the drought stress response since downregulation of CsGPA1 by RNAi resulted in reduced drought tolerance in the transgenic lines [81]. Transgenic seedlings experienced higher water loss rates in leaves, perhaps as a result of the upregulation of several aquaporin genes, and when subjected to drought stress accumulated higher levels of H2O2 and malondialdehyde and decreased antioxidant enzyme activities than WT controls. In Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri), Gγ subunit expression show a mixed behavior in response to ABA, with some genes being upregulated while others show reduced expression [82]. In agreement with rice and mulberry, the pea Gβ subunit PsGβ is a positive regulator of the drought response with transgenic tobacco lines overexpressing PsGβ showing increased tolerance to drought stress [69]. The PsGβ-overexpressing lines showed increased NO production during drought stress leading to increased NO-induced stomatal closure. NO production was also enhanced in the transgenic lines in response to ABA and H2O2 treatment [69].
2.5. G Protein Involvement in Developmental Control of Drought Stress
Zhang et al. (2008) reported that Arabidopsis Gα is a positive regulator of stomatal development in cotyledons, with gpa1 mutants showing a reduction in stomatal density and transgenic lines overexpressing a constitutively active GPA1 subunit (GPA1QL) having increased stomatal density [83]. In contrast, agb1-2 mutants had increased stomatal density while transgenic lines overexpressing AGB1 contained decreased stomatal density. Stomatal density in gpa1 agb1 double mutants was the mean of the single gpa1 and agb1 mutants, suggesting that GPA1 and AGB1 regulate epidermal stomatal density in an antagonistic manner [83]. The amount of CO2 assimilated per unit of water lost by transpiration is known as transpiration efficiency (TE) and achieving an optimal ratio is essential for plant fitness, especially in C3 photosynthesis species [84]. Despite gpa1 mutants being defective in abscisic acid-induced inhibition of stomatal opening [35[35][40],40], they showed increased TE during drought stress and upon ABA treatment [38]. Stomatal density in fully developed gpa1 mutant leaves was almost half of those observed in WT while stomatal conductance was also reduced. The authors proposed that GPA1 acts as a negative regulator of TE by controlling stomatal conductance and density in leaves [38].
