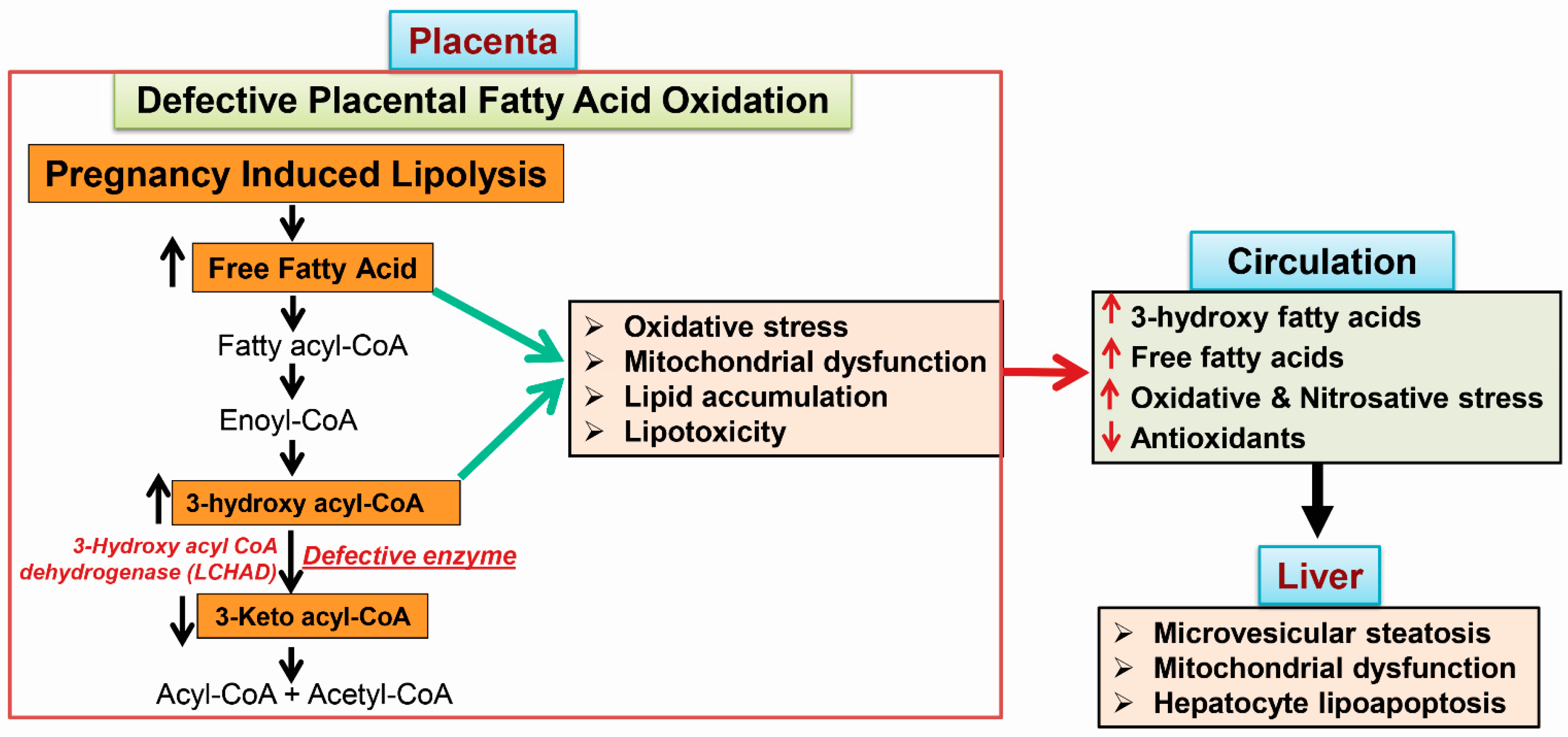
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), a catastrophic illness for both the mother and the unborn offspring, develops in the last trimester of pregnancy with significant maternal and perinatal mortality. AFLP is also recognized as an obstetric and medical emergency. Maternal AFLP is highly associated with a fetal homozygous mutation (1528G>C) in the gene that encodes for mitochondrial long-chain hydroxy acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD). The mutation in LCHAD results in the accumulation of 3-hydroxy fatty acids, such as 3-hydroxy myristic acid, 3-hydroxy palmitic acid and 3-hydroxy dicarboxylic acid in the placenta, which are then shunted to the maternal circulation leading to the development of acute liver injury observed in patients with AFLP.
- acute fatty liver of pregnancy
- 3-hydroxy fatty acids
- lipoapoptosis
- fatty acid oxidation
1. Maternal Liver Disease Associated with Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects
1.1. Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
1.2. The Incidence of AFLP and LCHAD Mutations
1.3. 3-Hydroxy Fatty Acid Accumulation
2. Metabolic Phenotypes Associated with 3-Hydroxy Fatty Acid Accumulation
2.1. Hypoglycemia in AFLP and Hormonal Regulation
2.2. Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (MTP)-Deficient Mice Develop Intra Uterine Growth Retardation (IUGR), Neonatal Hypoglycemia, and Sudden Death
2.3. MTP Heterozygous Mice Develop Hepatic Insulin Resistance
3. Mechanisms of 3-Hydroxy Fatty Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity
3.1. Placental Damage in AFLP Patients
3.2. Subcellular Damage and Oxidative Injury
3.3. 3-Hydroxy Fatty Acid-Induced Hepatocyte Lipoapoptosis
Abbreviations
| AFLP | acute fatty liver of pregnancy |
| ALT | alanine amino transferase |
| AST | aspartate amino transferase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| CPT2 | carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 |
| DHA | docosa hexaenoic acid |
| FoxO | forkhead family of transcription factor class O |
| GGT | γ-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| LCHAD | long chain hydroxy acyl-CoA dehydrogenease |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinases |
| MTP | mitochondiral trifunctional protien |
| PUMA | p35-upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| TCA cycle | tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| 3-HFA | 3-hydroxy fatty acid |
| 3-HMA | 3-hydroxy myristic acid |
| 3-HOA | 3-hydroxy octanoic acid |
| 3-HPA | 3-hydroxy palmitic acid |
References
- Ibdah, J.A. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: An update on pathogenesis and clinical implications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7397–7404.
- Ibdah, J.A. Role of genetic screening in identifying susceptibility to acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 494–495.
- Yang, Z.; Yamada, J.; Zhao, Y.; Strauss, A.W.; Ibdah, J.A. Prospective screening for pediatric mitochondrial trifunctional protein defects in pregnancies complicated by liver disease. JAMA 2002, 288, 2163–2166.
- Yang, Z.; Lantz, P.E.; Ibdah, J.A. Post-mortem analysis for two prevalent β-oxidation mutations in sudden infant death. Pediatr. Int. 2007, 49, 883–887.
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Bennett, M.J.; Strauss, A.W.; Ibdah, J.A. Fetal genotypes and pregnancy outcomes in 35 families with mitochondrial trifunctional protein mutations. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 715–720.
- Goel, A.; Ramakrishna, B.; Zachariah, U.; Ramachandran, J.; Eapen, C.E.; Kurian, G.; Chandy, G. How accurate are the swansea criteria to diagnose acute fatty liver of pregnancy in predicting hepatic microvesicular steatosis? Gut 2011, 60, 138–139.
- Kingham, J.G. Swansea criteria for diagnosis of acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Gut 2010.
- Goel, A.; Jamwal, K.D.; Ramachandran, A.; Balasubramanian, K.A.; Eapen, C.E. Pregnancy-related liver disorders. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 151–162.
- Goel, A.; Nair, S.C.; Viswabandya, A.; Masilamani, V.P.; Rao, S.V.; George, A.; Regi, A.; Jose, R.; Zachariah, U.; Subramani, K.; et al. Preliminary experience with use of recombinant activated factor VII to control postpartum hemorrhage in acute fatty liver of pregnancy and other pregnancy-related liver disorders. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 32, 268–271.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Thangaraj, K.R.; Eapen, C.E.; Ramachandran, A.; Mukhopadhya, A.; Mathai, M.; Seshadri, L.; Peedikayil, A.; Ramakrishna, B.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Liver injury in acute fatty liver of pregnancy: Possible link to placental mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Hepatology 2010, 51, 191–200.
- Ibdah, J.A.; Dasouki, M.J.; Strauss, A.W. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Variable expressivity of maternal illness during pregnancy and unusual presentation with infantile cholestasis and hypocalcaemia. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999, 22, 811–814.
- Ibdah, J.A.; Bennett, M.J.; Rinaldo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Gibson, B.; Sims, H.F.; Strauss, A.W. A fetal fatty-acid oxidation disorder as a cause of liver disease in pregnant women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1723–1731.
- Ibdah, J.A.; Yang, Z.; Bennett, M.J. Liver disease in pregnancy and fetal fatty acid oxidation defects. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 71, 182–189.
- Ibdah, J.A.; Zhao, Y.; Viola, J.; Gibson, B.; Bennett, M.J.; Strauss, A.W. Molecular prenatal diagnosis in families with fetal mitochondrial trifunctional protein mutations. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 396–399.
- van Eerd, D.C.; Brusse, I.A.; Adriaens, V.F.; Mankowski, R.T.; Praet, S.F.; Michels, M.; Langeveld, M. Management of an LCHADD patient during pregnancy and high intensity exercise. JIMD Rep. 2017, 32, 95–100.
- Haglind, C.B.; Stenlid, M.H.; Ask, S.; Alm, J.; Nemeth, A.; Dobeln, U.; Nordenstrom, A. Growth in long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2013, 8, 81–90.
- Rakheja, D.; Bennett, M.J.; Rogers, B.B. Long-chain l-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase deficiency: A molecular and biochemical review. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 815–824.
- Shekhawat, P.; Bennett, M.J.; Sadovsky, Y.; Nelson, D.M.; Rakheja, D.; Strauss, A.W. Human placenta metabolizes fatty acids: Implications for fetal fatty acid oxidation disorders and maternal liver diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E1098–E1105.
- Ch’ng, C.L.; Morgan, M.; Hainsworth, I.; Kingham, J.G. Prospective study of liver dysfunction in pregnancy in southwest wales. Gut 2002, 51, 876–880.
- Rathi, U.; Bapat, M.; Rathi, P.; Abraham, P. Effect of liver disease on maternal and fetal outcome—A prospective study. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 26, 59–63.
- Bartha, J.L.; Visiedo, F.; Fernandez-Deudero, A.; Bugatto, F.; Perdomo, G. Decreased mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in placentas from women with preeclampsia. Placenta 2012, 33, 132–134.
- Ding, X.; Yang, Z.; Han, Y.; Yu, H. Fatty acid oxidation changes and the correlation with oxidative stress in different preeclampsia-like mouse models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109554.
- Han, Y.W.; Yang, Z.; Ding, X.Y.; Yu, H. Differences in liver injury and trophoblastic mitochondrial damage in different preeclampsia-like mouse models. Chin. Med. J(Engl). 2015, 128, 1627–1635.
- Dani, R.; Mendes, G.S.; Medeiros, J.L.; Peret, F.J.; Nunes, A. Study of the liver changes occurring in preeclampsia and their possible pathogenetic connection with acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 292–294.
- Nedoszytko, B.; Sieminska, A.; Strapagiel, D.; Dabrowski, S.; Slomka, M.; Sobalska-Kwapis, M.; Marciniak, B.; Wierzba, J.; Skokowski, J.; Fijalkowski, M.; et al. High prevalence of carriers of variant c.1528G>C of hadha gene causing long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (LCHADD) in the population of adult kashubians from north poland. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187365.
- Barycki, J.J.; O’Brien, L.K.; Strauss, A.W.; Banaszak, L.J. Glutamate 170 of human l-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase is required for proper orientation of the catalytic histidine and structural integrity of the enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36718–36726.
- Sykut-Cegielska, J.; Gradowska, W.; Piekutowska-Abramczuk, D.; Andresen, B.S.; Olsen, R.K.; Oltarzewski, M.; Pronicki, M.; Pajdowska, M.; Bogdanska, A.; Jablonska, E.; et al. Urgent metabolic service improves survival in long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency detected by symptomatic identification and pilot newborn screening. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 185–195.
- Joost, K.; Ounap, K.; Zordania, R.; Uudelepp, M.L.; Olsen, R.K.; Kall, K.; Kilk, K.; Soomets, U.; Kahre, T. Prevalence of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in estonia. JIMD Rep. 2012, 2, 79–85.
- den Boer, M.E.; Wanders, R.J.; Morris, A.A.; Ijist, L.; Heymans, H.S.; Wijburg, F.A. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Clinical presentation and follow-up of 50 patients. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 99–104.
- Thiel, C.; Baudach, S.; Schnackenberg, U.; Vreken, P.; Wanders, R.J. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Neonatal manifestation at the first day of life presenting with tachypnoea. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999, 22, 839–840.
- Tuuli, I.; Emilia, A.; Jussi, T.; Risto, L.; Tiina, T.; Leena, L. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency—A follow-up emg study of 12 patients. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 38–44.
- Tyni, T.; Kivela, T.; Lappi, M.; Summanen, P.; Nikoskelainen, E.; Pihko, H. Ophthalmologic findings in long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency caused by the G1528C mutation: A new type of hereditary metabolic chorioretinopathy. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 810–824.
- Tyni, T.; Majander, A.; Kalimo, H.; Rapola, J.; Pihko, H. Pathology of skeletal muscle and impaired respiratory chain function in long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency with the G1528C mutation. Neuromuscul. Disord. 1996, 6, 327–337.
- Tyni, T.; Paetau, A.; Strauss, A.W.; Middleton, B.; Kivela, T. Mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation in the human eye and brain: Implications for the retinopathy of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 744–750.
- Tyni, T.; Pihko, H. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 237–245.
- Tonin, A.M.; Amaral, A.U.; Busanello, E.N.; Gasparotto, J.; Gelain, D.P.; Gregersen, N.; Wajner, M. Mitochondrial bioenergetics deregulation caused by long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids accumulating in lchad and MTP deficiencies in rat brain: A possible role of mptp opening as a pathomechanism in these disorders? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1658–1667.
- Tonin, A.M.; Ferreira, G.C.; Grings, M.; Viegas, C.M.; Busanello, E.N.; Amaral, A.U.; Zanatta, A.; Schuck, P.F.; Wajner, M. Disturbance of mitochondrial energy homeostasis caused by the metabolites accumulating in LCHAD and MTP deficiencies in rat brain. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 825–831.
- Tonin, A.M.; Grings, M.; Busanello, E.N.; Moura, A.P.; Ferreira, G.C.; Viegas, C.M.; Fernandes, C.G.; Schuck, P.F.; Wajner, M. Long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids accumulating in LCHAD and MTP deficiencies induce oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 930–936.
- Jones, P.M.; Moffitt, M.; Joseph, D.; Harthcock, P.A.; Boriack, R.L.; Ibdah, J.A.; Strauss, A.W.; Bennett, M.J. Accumulation of free 3-hydroxy fatty acids in the culture media of fibroblasts from patients deficient in long-chain l-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase: A useful diagnostic aid. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 1190–1194.
- Cecatto, C.; Godoy Kdos, S.; da Silva, J.C.; Amaral, A.U.; Wajner, M. Disturbance of mitochondrial functions provoked by the major long-chain 3-hydroxylated fatty acids accumulating in MTP and LCHAD deficiencies in skeletal muscle. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 36, 1–9.
- Cecatto, C.; Hickmann, F.H.; Rodrigues, M.D.; Amaral, A.U.; Wajner, M. Deregulation of mitochondrial functions provoked by LCHFA accumulating in LCHAD and MTP deficiencies in rat heart: Mpt pore opening as a potential contributing pathomechanism of cardiac alterations in these disorders. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 4714–4726.
- Eskelin, P.M.; Laitinen, K.A.; Tyni, T.A. Elevated hydroxyacylcarnitines in a carrier of lchad deficiency during acute liver disease of pregnancy—A common feature of the pregnancy complication? Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 100, 204–206.
- Gutierrez Junquera, C.; Balmaseda, E.; Gil, E.; Martinez, A.; Sorli, M.; Cuartero, I.; Merinero, B.; Ugarte, M. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy and neonatal long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 103–106.
- Jones, P.M.; Butt, Y.; Bennett, M.J. Accumulation of 3-hydroxy-fatty acids in the culture medium of long-chain l-3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) and mitochondrial trifunctional protein-deficient skin fibroblasts: Implications for medium chain triglyceride dietary treatment of LCHAD deficiency. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 783–787.
- Neuman-Laniec, M.; Wierzba, J.; Irga, N.; Zaborowska-Soltys, M.; Balcerska, A. LCHAD (long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase) deficiency as a cause of sudden death of a three months old infant. Med. Wieku Rozwoj. 2002, 6, 221–226.
- Bellig, L.L. Maternal acute fatty liver of pregnancy and the associated risk for long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency in infants. Adv. Neonatal. Care 2004, 4, 26–32.
- Dhar, M.; Sepkovic, D.W.; Hirani, V.; Magnusson, R.P.; Lasker, J.M. Omega oxidation of 3-hydroxy fatty acids by the human CYP4F gene subfamily enzyme CYP4F11. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 612–624.
- Tesfaye, N.; Seaquist, E.R. Neuroendocrine responses to hypoglycemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1212, 12–28.
- Halldin, M.U.; Forslund, A.; Von Dobeln, U.; Eklund, C.; Gustafsson, J. Increased lipolysis in LCHAD deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 39–46.
- Haglind, C.B.; Nordenstrom, A.; Ask, S.; von Dobeln, U.; Gustafsson, J.; Stenlid, M.H. Increased and early lipolysis in children with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency during fast. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 315–322.
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Ingham, S.A.; Mohr, A.M.; Wehrkamp, C.J.; Ray, A.; Roy, S.; Cazanave, S.C.; Phillippi, M.A.; Mott, J.L. Saturated free fatty acids induce cholangiocyte lipoapoptosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1942–1956.
- Listenberger, L.L.; Han, X.; Lewis, S.E.; Cases, S.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Triglyceride accumulation protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3077–3082.
- Ibdah, J.A.; Paul, H.; Zhao, Y.; Binford, S.; Salleng, K.; Cline, M.; Matern, D.; Bennett, M.J.; Rinaldo, P.; Strauss, A.W. Lack of mitochondrial trifunctional protein in mice causes neonatal hypoglycemia and sudden death. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1403–1409.
- Ahmed, K.T.; Almashhrawi, A.A.; Rahman, R.N.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Liver diseases in pregnancy: Diseases unique to pregnancy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7639–7646.
- Bonnet, D.; Martin, D.; Pascale De, L.; Villain, E.; Jouvet, P.; Rabier, D.; Brivet, M.; Saudubray, J.M. Arrhythmias and conduction defects as presenting symptoms of fatty acid oxidation disorders in children. Circulation 1999, 100, 2248–2253.
- Rector, R.S.; Morris, E.M.; Ridenhour, S.; Meers, G.M.; Hsu, F.F.; Turk, J.; Ibdah, J.A. Selective hepatic insulin resistance in a murine model heterozygous for a mitochondrial trifunctional protein defect. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2213–2223.
- Rector, R.S.; Payne, R.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Mitochondrial trifunctional protein defects: Clinical implications and therapeutic approaches. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1488–1496.
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Morris, R.T.; Laye, M.J.; Borengasser, S.J.; Booth, F.W.; Ibdah, J.A. Daily exercise increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents steatosis in otsuka long-evans tokushima fatty rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G619–G626.
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Uptergrove, G.M.; Morris, E.M.; Naples, S.P.; Borengasser, S.J.; Mikus, C.R.; Laye, M.J.; Laughlin, M.H.; Booth, F.W.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction precedes insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis and contributes to the natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an obese rodent model. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 727–736.
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Wei, Y.; Ibdah, J.A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 185–192.
- Oey, N.A.; den Boer, M.E.; Ruiter, J.P.; Wanders, R.J.; Duran, M.; Waterham, H.R.; Boer, K.; Van der Post, J.A.; Wijburg, F.A. High activity of fatty acid oxidation enzymes in human placenta: Implications for fetal-maternal disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2003, 26, 385–392.
- Oey, N.A.; den Boer, M.E.; Wijburg, F.A.; Vekemans, M.; Auge, J.; Steiner, C.; Wanders, R.J.; Waterham, H.R.; Ruiter, J.P.; Attie-Bitach, T. Long-chain fatty acid oxidation during early human development. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 755–759.
- Oey, N.A.; Ruiter, J.P.; Attie-Bitach, T.; Ijlst, L.; Wanders, R.J.; Wijburg, F.A. Fatty acid oxidation in the human fetus: Implications for fetal and adult disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 71–75.
- Cunningham, P.; McDermott, L. Long chain pufa transport in human term placenta. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 636–639.
- Rahman, T.M.; Phillips, M.; Wendon, J. Rare fatal complications of acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Crit. Care 1999, 3, P186.
- Matern, D.; Schehata, B.M.; Shekhawa, P.; Strauss, A.W.; Bennett, M.J.; Rinaldo, P. Placental floor infarction complicating the pregnancy of a fetus with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 72, 265–268.
- Dwivedi, S.; Runmei, M. Retrospective study of seven cases with acute fatty liver of pregnancy. ISRN Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 2013, 730569.
- Costa, C.G.; Dorland, L.; Holwerda, U.; de Almeida, I.T.; Poll-The, B.T.; Jakobs, C.; Duran, M. Simultaneous analysis of plasma free fatty acids and their 3-hydroxy analogs in fatty acid β-oxidation disorders. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 463–471.
- Steinmann, D.; Knab, J.; Priebe, H.J. Perioperative management of a child with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2010, 20, 371–373.
- Ding, J.H.; Yang, B.Z.; Nada, M.A.; Roe, C.R. Improved detection of the G1528C mutation in LCHAD deficiency. Biochem. Mol. Med. 1996, 58, 46–51.
- Olpin, S.E.; Clark, S.; Andresen, B.S.; Bischoff, C.; Olsen, R.K.; Gregersen, N.; Chakrapani, A.; Downing, M.; Manning, N.J.; Sharrard, M.; et al. Biochemical, clinical and molecular findings in LCHAD and general mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2005, 28, 533–544.
- Innes, A.M.; Seargeant, L.E.; Balachandra, K.; Roe, C.R.; Wanders, R.J.; Ruiter, J.P.; Casiro, O.; Grewar, D.A.; Greenberg, C.R. Hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency presenting as maternal illness in pregnancy. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 47, 43–45.
- Kobayashi, T.; Minami, S.; Mitani, A.; Tanizaki, Y.; Booka, M.; Okutani, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ino, K. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy associated with fetal mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 799–802.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Thomas, S.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Basivireddy, J.; Pulimood, A.B.; Ramachandran, A.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Oxidative stress in the development of liver cirrhosis: A comparison of two different experimental models. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 947–957.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Eapen, C.E.; Pullimood, A.B.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Oxidative stress in experimental liver microvesicular steatosis: Role of mitochondria and peroxisomes. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1240–1249.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Thangaraj, K.R.; Eapen, C.E.; Ramachandran, A.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: An update on mechanism. Obstet. Med. 2011, 4, 99–103.
- Akazawa, Y.; Cazanave, S.; Mott, J.L.; Elmi, N.; Bronk, S.F.; Kohno, S.; Charlton, M.R.; Gores, G.J. Palmitoleate attenuates palmitate-induced bim and puma up-regulation and hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 586–593.
- Cazanave, S.C.; Mott, J.L.; Elmi, N.A.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Akazawa, Y.; Kahraman, A.; Garrison, S.P.; Zambetti, G.P.; Charlton, M.R.; et al. JNK1-dependent puma expression contributes to hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26591–26602.
- Cazanave, S.C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Rahmani, M.; Grant, S.; Durrant, D.E.; Klaassen, C.D.; Yamamoto, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Degradation of keap1 activates BH3-only proteins bim and puma during hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1303–1312.
- Malhi, H.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Gores, G.J. Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12093–12101.
- Martinez, A.K.; Glaser, S.S. Cholangiocyte lipoapoptosis: Implications for biliary damage during nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1809–1811.
- Natarajan, S.K.; Stringham, B.A.; Mohr, A.M.; Wehrkamp, C.J.; Lu, S.; Phillippi, M.A.; Harrison-Findik, D.; Mott, J.L. FoxO3 increases miR-34a to cause palmitate-induced cholangiocyte lipoapoptosis. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 866–875.
- Fan, C.Y.; Pan, J.; Usuda, N.; Yeldandi, A.V.; Rao, M.S.; Reddy, J.K. Steatohepatitis, spontaneous peroxisome proliferation and liver tumors in mice lacking peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. Implications for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α natural ligand metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15639–15645.
