Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Sabrin R. M. Ibrahim and Version 2 by Dean Liu.
Two new benzophenones and five known metabolites were purified from Garcinia mangostana ((GM) pericarps. They were characterized by various spectral techniques. Compounds 6 and 7 displayed AAI activity. They also exhibited highly negative docking scores, when complexed with 5TD4. Their complexes with the α-amylase were found to be stable over the course of 50 ns. These results supported the previous reports that GM can potentially represent an appealing treatment of diabetes and its related disorders.
- benzophenones
- Garcinia mangostana
- Clusiaceae
- Diabetes
- Alpha-amylase
1. Introduction
GarciniaGarcinia mangostana mangostana ((GM) purple mangosteen, mangosteen, mangkhut, queen of fruits) is a tropical fruit that is widely cultivated in Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, India, Cambodia, Malaysia, Netherlands Antilles, Sri Lanka, Philippines, Colombia, Central America, and tropical Africa [1][15]. This fruit has gained increasing acceptance due to its pleasant sweet-sour taste and distinctive aroma. It is also a rich source of nutrients and health-promoting phytochemicals, including carotenoids, ascorbic acid, oxygenated and prenylated xanthones, flavonoids, anthocyanins, phenolic acids, and benzophenones which possess a wide extent of bioactivities [2][3][4][5][6][7][8][16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In Southeast Asia, it is used as a traditional medicine for treating dysentery, abdominal pain, suppuration, wound infections, and chronic ulcers [9][10][11][23,24,25]. Various in-vivo and in-vitro studies proved that GM pericarp extracts (GME) had substantial insulin-sensitizing and glucose-lowering potentials [12][13][26,27]. GME displayed a hypoglycemic potential via increasing the insulin-producing β-cells’ population, which was attributed to their antioxidant-phenolic metabolites [13][27]. Adnyana et al. reported that α-mangostin and the pericarp extract of GM had a concentration-dependent α-amylase inhibitory potential [14][28]. Moreover, GM bettered the STZ (streptozotocin)-produced impairment to β-cells and pancreatic glands through enhancing insulin production and amending the sensitivity to insulin decrease in diabetic mice [15][29]. Besides, it retarded the glucose absorption via suppressing the enzymes accountable for carbohydrates hydrolysis such as α-amylase and α-glucosidase [16][30]. Interestingly, many GM xanthones have been reported as α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors as they lessened postprandial hyperglycemia by prohibiting the absorption of glucose [17][18][19][20][21][2,3,4,12,31]. A clinical study by Watanabe et al. reported that GME supplementation for 26 weeks resulted in improving glucose hemostasis and increasing insulin sensitization in obese insulin-resistant female patients [22][32]. TheOur previous studies of GM reported the isolation of xanthones, flavonoids, and phenolics with cytotoxic, vasodilatation, hepato-protective, antioxidant, and glycation end-product and α-amylase inhibitory capacities [4][5][6][10][11][21][23][24][18,19,20,24,25,31,33,34]. In continuing of theour goal to discover structurally diverse bio-metabolites from GM, this work described the purification and structural elucidation of two new benzophenone derivatives, along with five known metabolites from its EtOAc-soluble extract (Figure 1). They were elucidated unambiguously by NMR and MS techniques, in addition to comparing their data with the known related compounds. Their α-amylase inhibition capacity was estimated. Additionally, docking studies and molecular dynamics (MDs) simulations towards α-amylase were carried out.
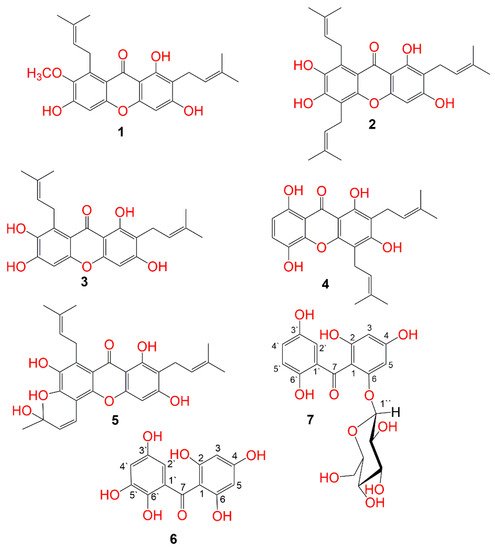
Figure 1. Structures of the isolated compounds (1–7).
2. Purification of Compounds
The MeOH extract was suspended in H2O and partitioned between n-hexane and EtOAc. The EtOAc fraction was successively treated utilizing Sephadex, SiO2, and RP-18 columns to provide two new (6 and 7) and five known metabolites (1–5) (Figure 1). These metabolites were identified based on the spectral analyses and comparison with literature.
3. Structural Assignment of Compounds 6 and 7
Compound 6 was separated as a light-yellow powder and provided an FeCl3 positive test, revealing its phenolic nature. Its HRESIMS demonstrated a pseudo-molecular peak at m/z 279.0515 [M+H]+ (calcd for C13H11O7, 279.0505), consistent with a molecular formula C13H10O7. This formula required nine degrees of unsaturation. The UV revealed bands at 206, 296, and 318 nm, suggesting 6 to have a benzophenone skeleton [25][44]. Characteristic bands at 3317, 1623, and 1601 and 1589 cm−1 for chelated OH, carbonyl, and aromatic C=C functionalities, respectively were observed in the IR spectrum [26][45]. The 13C and HSQC spectra showed 13 carbon resonances, comprising four aromatic methines and nine quaternary carbons, including one carbonyl at δC 200.6 (C-7) and six for oxygen-linked carbons (Table 1). In the 1H NMR of 6, the appearance of an aromatic signal at δH 5.83 (2H, brs, H-3, 5), relating with the carbon at δC 95.8 (C-3, 5) in the HSQC suggested the presence of a symmetrically substituted phloroglucinol ring (ring A) in 6 [26][45]. This was confirmed by the HMBC-cross-peaks of H-3/C-2, C-1, C-4, and C-5 and H-5/C-1, C-3, C-4, and C-6. Moreover, the 1H NMR signals at δH 6.52 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-2`) and 6.36 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-4`) were attributed to two m-coupled aromatic protons. They had HSQC-cross-peaks to the carbons at δC 107.4 (C-2`) and 112.1 (C-4`). This was consistent with the existence of a hydroxyquinol moiety (1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted phenyl, ring B). In the HMBC, the cross-peaks of H-2`/C-4` and C-6` and H-4`/C-2`, C-5`, and C-6` assured this moiety (Figure 2). The link of rings A and B via the carbonyl group to provide the benzophenone core was established based on HMBC correlations from H-3 and H-5/C-7 and H-2`/C-7 and C-1. Based on the fore-mentioned evidences, the structure of 6 was elucidated and named garcimangophenone A.
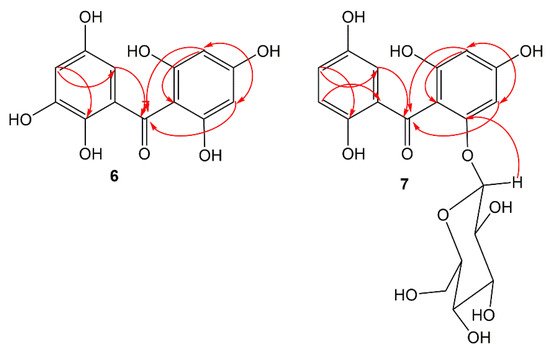
Figure 2. Some key HMBC correlations of compounds 6 and 7.
Compound 7 was separated as an amorphous brown powder. It displayed bands at 3342 (OH), 1632 (C=O), and 1608 and 1578 (C=C) cm−1 in the IR and at 209, 286, and 308 nm, respectively, in the UV spectrum. It had a molecular formula C19H20O11, which was specified from the observed pseudo-molecular ion peak in HRESIMS at m/z 425.1078 (calcd for 425.1084 for C19H21O11), requiring ten degrees of unsaturation. A characteristic fragment ion peak at m/z 262.0433 [M+H-hexose]+ was observed in the HRESIMS, indicating 7 had a hexose moiety. In the 13C and HSQC, 19 carbon signals were observed, including one methylene, ten methines, and eight quaternary carbons five of them for oxygenated aromatic carbons at 163.8 (C-2), 161.7 (C-4), 159.5 (C-6), 154.2 (C-3`), and 155.8 (C-6`). Compound 7 had one degree of unsaturation and 146 mass units more than 6. Its NMR spectral data were comparable with those of 6, except for the 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted benzene unit in 6 that had been replaced by 1,2,5-trisubstituted benzene unit in 7. In 1H and 13C NMR signals for a symmetrically-substituted phloroglucinol (ring A) at δH 6.06 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-3)/δC 98.1 (C-3) and 6.21 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-5)/δC 95.7 (C-5) were observed, which was further assured by the HMBC-cross-peaks of H-3/C-1, C-2, C-4, and C-5 and H-5/C-1, C-3, and C-4. Additionally, a doublet signal at δH 4.88 (J = 7.6 Hz, H-1``) for an anomeric proton, having HSQC cross-peak to the carbon at δC 101.6 characterized the β-D-glucopyranosyl unit in 7 [27][46]. The other sugar signals at δH 2.92 (H-1``)/δC 74.6 (C-1``), 3.30 (H-3``)/δC 77.8 (C-3``), 3.29 (H-4``)/δC 71.0 (C-4``), 3.32 (H-5``)/δC 78.2 (C-5``), and 3.86 and 3.69 (H-6``)/δC 62.5 (C-6``) were observed in the 1H and 13C NMR spectra. Further, the HMB-cross-peaks of H-3``and H-2``/C-1``, H-4``/C-2`` and C-6``, H-5``/C-3`` and C-6``, and H-6``/C-4`` and C-5`` established the β-D-glucopyranosyl unit. The HMBC cross-peak of H-1`` to C-6 (δC 159.5) indicated the connectivity of glucose moiety at C-6 of ring A. Furthermore, 1H NMR spectrum also displayed three coupled aromatic protons, resonating at δH 6.96 (H-2`), 7.18 (H-4`), and 7.22 (H-5`). They had HSQC cross-peaks to the carbons at δC 114.2, 121.4, and 120.4, respectively, which characterized the existence of a hydroquinone moiety in 7 (ring B) [25][26][44,45]. This was further secured based on the observed HMBC cross-peaks of H-5`/C-1` and C-3`, H-4`/C-2` and C-6`, and H-2`/C-4` and C-6` (Figure 2). The connectivity of the carbonyl group (δC 199.3, C-7) at C-1 and C-1` of rings A and B, respectively, was established by the HMBC correlations of H-3, H-5, and H-2` to C-7. Therefore, the structure of 7 was established as depicted and named garcimangophenone B.
4. Identification of Known Metabolites
5. α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity
Benzophenones are known to have diverse bioactivities such as antioxidant, antibacterial, cytotoxic, antitrypanosomal, and leishmanicidal activities [32][33][34][35][51,52,53,54]. However, there are limited reports regarding the AAI potential of Garcinia’s benzophenones. Therefore, the AAI potential of the new benzophenone derivatives (6 and 7), along with compound 5 was assessed. The results showed that compounds 7 and 6 demonstrated noticeable AAI potential (IC50 9.3 and 12.2 µM, respectively), compared with acarbose (IC50 6.4 µM). These results are in good agreement with the previous study by Akoro et al. that reported the potent AAI effect of gakolanone, a benzophenone derivative reported from G. kola [36][55]. On the other hand, 5 displayed moderate activity with an AAI (IC50 16.1 µM). It is noteworthy that previous studies revealed the AAI potential of 1–4 [17][18][19][2,3,4].
6. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Studies
The hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkage in starch is catalyzed by the α-amylase enzyme [37][56]. The α-amylase active site consists of five major subsites that are necessary for the binding of longer substrates [38][57]. Three residues in the active site, Asp 300, Asp 197, and Glu 233 are important for the catalysis. The catalytic nucleophile, Asp 197, forms a covalent bond with the glucosyl in the S-1 subsite. The Glu233 is the acid-base catalyst as it protonates the leaving group and deprotonates the water. The Glu300 is also essential for positioning the catalytic water for hydrolysis [39][58].
