Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Jessie Wu and Version 1 by Nicholas Tolwinski.
The WNT signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signal transduction pathway that regulates a wide range of cellular functions during development and adulthood. It controls multiple aspects of development, including cell proliferation, cell fate determination, apoptosis, cell migration and cell polarity during development and stem cell maintenance in adults. Inappropriate activation of the WNT pathway is also a major factor in human oncogenesis.
- WNT
- RNF43
- Cancer
1. Introduction
The first WNT gene, then known as int-1 (mouse mammary tumor virus integration site 1), was isolated from mouse mammary tumors in 1982 [5][1]. Int-1 turned out to be highly conserved across multiple species and especially similar to the Drosophila gene wingless (Wg) a gene found to be involved in wing development, segmentation and formation of body axis during flight development [6,7,8,9][2][3][4][5]. The name WNT comes from a fusion of wg and int [10,11][6][7]. Most animals have several WNT genes with mice and humans encoding 19 WNT genes, seven in Drosophila and five in Caenorhabditis elegans (C.elegans) [6][2].
The WNT proteins are secreted, lipid-modified glycoproteins, usually 350–400 amino acids in length [12][8]. WNT proteins act as ligands interacting with Frizzled (FZD) receptors on the cell surface to activate intracellular signaling pathways [6,12,13][2][8][9]. Frizzled receptors are seven-pass transmembrane proteins (similar to G-protein coupled receptors or GPCRs) that act as primary receptors for WNT signals. In addition to the interaction between WNT ligands and FZD receptors, a variety of co-receptors, such as, the low-density lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP) may be required to mediate WNT signaling [14,15][10][11]. Upon activation, a signal is transduced by the pathway activating protein Disheveled (Dsh or Dvl) [13,16][9][12]. Dsh proteins have highly conserved protein domains comprised of an amino-terminal DIX domain (named for Dsh and Axin), a central PDZ domain (named for postsynaptic density-95, discs-large and zonula occludens-1) and a carboxy-terminal DEP domain (named for Dsh, Egl-10 and pleckstrin). Dsh acts as a key switch in WNT signaling where, depending on which of the three domains is activated, the WNT signal can be branched off into multiple downstream pathways [16][12]. The resulting pathways can be categorized into the canonical WNT pathway (β-catenin dependent pathway) and the non-canonical WNT pathways (β-catenin independent pathways) which include polarity and the WNT/Ca2+ pathway [15][11].
Canonical pathway: The stability of cytoplasmic β-catenin is mediated by a multimeric protein complex known as the destruction complex formed by the scaffolding proteins (Axin) [17][13], the tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) [18,19][14][15], glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) and casein kinase 1 (CK1). In the absence of canonical WNT ligands, β-catenin binds to the destruction complex and is phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK-3. Phosphorylated β-catenin is then ubiquitinated and subsequently degraded through the proteasome (Figure 1) [14,20,21,22][10][16][17][18].
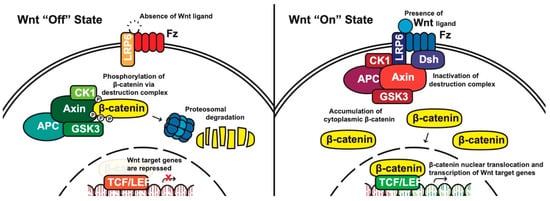
Figure 1. The canonical WNT pathway in on and off states. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1, casein kinase 1; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor; LRP6, lipoprotein receptor related protein 6; FZD/Fz, Frizzled; Dsh, Disheveled.
In the presence of canonical WNT ligands, β-catenin phosphorylation and degradation is inhibited. Gene expression downstream of canonical WNT signaling is regulated by controlling the amount of the transcriptional co-activator β-catenin. When WNT ligands bind to FZD receptors and LRP co-receptors, a cascade of events is initiated, resulting in the disassembly of the destruction complex stabilizing β-catenin [22][18]. The signaling cascade is initiated when Dsh is activated through the DIX and PDZ domain, and the FZD-associated Disheveled (Dsh) protein then binds to Axin; Axin then inhibits GSK-3 phosphorylation of β-catenin in the destruction complex. Axin and the destruction complex are thus recruited to the plasma membrane forming signalosomes [23][19]. β-catenin accumulates in the cytoplasm and localizes to the nucleus where it forms a nuclear complex with DNA-bound T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor (TCF/LEF) transcription factor, resulting in the activation of WNT-responsive genes [14,16,20,24][10][12][16][20].
Non-canonical pathways: In contrast to the β-catenin-dependent canonical pathway, WNT proteins are able to activate additional signaling pathways that are independent of β-catenin. These pathways are called non-canonical pathways, which can be further categorized into two distinct branches, the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway and the WNT/Ca2+ pathway (Figure 2).
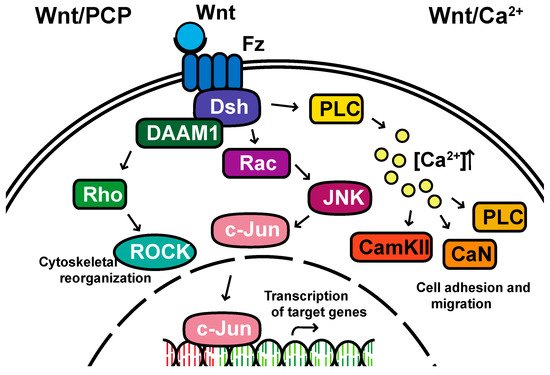
Figure 2. The non-canonical planar cell polarity and Calcium pathways. DAAM1, Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1; Rac; ROCK, Rho-associated kinase; JNK, Jun kinase; PLC, Phospholipase C; CamKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II.
The non-canonical PCP pathway regulates a variety of cellular behaviors including planar cell polarity, cell movements during gastrulation and cell migration of neural crest cells [25,26,27,28][21][22][23][24]. This PCP pathway is activated through the binding of WNT ligands to the FZD receptor independently of the LRP [16][12]. The non-canonical pathways do not need to utilize the majority of canonical pathway components including WNT itself, but most do involve Dsh and specifically the PDZ and DEP domains and the Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1 (DAAM 1). This links FZD and Dsh to the small GTPases Rho, and Rho further activates Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), thus leading to cytoskeletal reorganization [29][25]. Dsh utilizes the DEP domain to form a complex with Rac GTPase, independent of the DAAM 1, then stimulates Jun kinase (JNK) activity and mediates profilin binding to actin [16,28,29][12][24][25]. The polarity signaling pathway is likely best described as a collection of WNT-dependent and WNT-independent effects on cellular organization both within a cell sheet and within the cell itself, showing an intricate interplay between polarity and adhesion [30,31,32,33,34,35][26][27][28][29][30][31].
A second branch of non-canonical WNT signaling is termed the WNT/Ca2+ pathway. The role of the WNT/Ca2+ pathway is to regulate the release of the intracellular Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum [36,37][32][33] and modulate signaling for dorsal axis formation and PCP signaling for gastrulation cell movements, cell adhesion, migration and tissue separation during gastrulation [15,38][11][34]. Similar to other WNT pathways, the activation of the WNT/Ca2+ pathway requires the binding of the WNT ligands to the FZD receptor. The activated FZD receptor directly interacts and activates the heterotrimeric G-proteins, leading to an increase in the intracellular Ca2+ concentration [15][11]. The released Ca2+ then activates calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII), calcineurin or Protein Kinase C [36][32].
2. The Importance of WNT Signaling
Since the identification of the WNT gene more than 30 years ago, various avenues of research have shown roles in myriad processes. The WNT pathway is most famously known for its involvement in hereditary familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), where a mutated APC tumor suppressor gene fails to regulate β-catenin regulation, allowing tumor cells to progress towards malignancy [39,40][35][36]. Among many functions during development, mutations in the WNT pathway disrupt segment polarity in Drosophila embryos [41][37], regulate cardiac development in mice [42][38] and many other developmental processes in vertebrates and invertebrates [43][39].
Beyond embryonic development and cancer progression, the WNT pathway has emerged as a key contributor to Alzheimer’s and metabolic diseases. For example, amyloid-β (Aβ) neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease results in downregulated WNT signaling [44][40], which suggests that downregulated WNT may play an important role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s. WNT signaling has also been linked to metabolic disorders (reviewed by Sethi et al. [45][41]), where dysregulated WNT is hypothesized to be responsible for obesity and insulin resistance.
Given the vital role that WNT signaling plays in a variety of diseases, this review aims to summarize recent advances in WNT signaling to provide a thorough understanding of WNT signaling in disease.
3. WNT Signaling in Aging
Aging can be defined as the time-related progressive accumulation of detrimental changes that are associated with increasing susceptibility to disease and death [46][42]. In general, aging is a complex biological process associated with a decline in efficiency of physiological processes which include biological function on the molecular, cellular and tissue level [47][43]. These physiological processes reduce the efficiency of body metabolism, resulting in the disruption of body functional processes and ultimately death. There are a variety of different mechanisms that are thought to participate in the aging process. The WNT signaling pathway is one pathway that may contribute to aging.
Senescence contributes to tissue aging [48][44] through inhibition of cell differentiation, apoptosis and cell division [49,50][45][46], and one of the functions of WNT signaling is to maintain proliferation of tissue stem cells. Ye et al. reported that the canonical WNT2 ligand and downstream canonical WNT-signals are repressed in senescent human cells [49][45], where downregulation of WNT signaling activates senescence-associated heterochromatin focus (SAHF) assembly, a specialized domain of facultative heterochromatin that represses expression of proliferation-promoting genes, thereby contributing to senescence-associated cell cycle arrest [51][47]. The formation of SAHF is dependent on GSK3β activity, where increased GSK3β activity decreases the level of β-catenin in senescent cells, suggesting that the canonical WNT pathway is repressed in senescent human fibroblasts [49][45].
Another example of the detrimental effect of WNT signaling on aging comes from a mouse model of accelerated aging. The authors utilized klotho knockout mice that exhibit many age-related disorders [52][48]. Klotho is a transmembrane protein that acts as an anti-aging hormone [53][49]. Klotho binds to WNT proteins and reduces β-catenin levels leading to lower levels of WNT signaling which contributes to stem cell depletion and aging [52,54][48][50].
Hair graying is another hallmark of the aging process. One mouse study found that β-catenin expression is significantly elevated in the skin of aged mice through WNT10b/β-catenin signaling promoting melanocyte stem cell differentiation. The authors concluded that the increase in WNT signaling is insufficient to induce hair regeneration but may promote melanocyte stem cell differentiation resulting in a decreased number of melanocyte stem cells and eventually hair graying [55][51].
In contrast, a number of studies have also suggested that WNT signaling has positive effects on aging. In one study, Chen et al. reported that β-catenin plays an important role in the early phase of fracture healing. Several WNTs (e.g., WNT4, WNT10b and LRP6) were expressed during fracture repair showing activation of WNT/β-catenin signaling through a TCF-dependent transcription reporter in both bone and cartilage formation during fracture repair [56][52]. Another study found that activation of WNT signaling is required to regenerate hair follicles in wounded mice [57][53] raising the possibility of therapy using modulators of the WNT pathway to improve bone healing or treating hair loss. As with most WNT studies, these results show a complex role for WNT as it has both positive and negative consequences for aging [58][54].
4. WNT Signaling in Cancer
The WNT pathway plays a complex role in cancer development. Often, mutations of key components are associated with processes like uncontrollable cell proliferation, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis. This section will discuss the main WNT components that have been investigated in oncology and will review the current progress of their roles in cancer development (Figure 3).
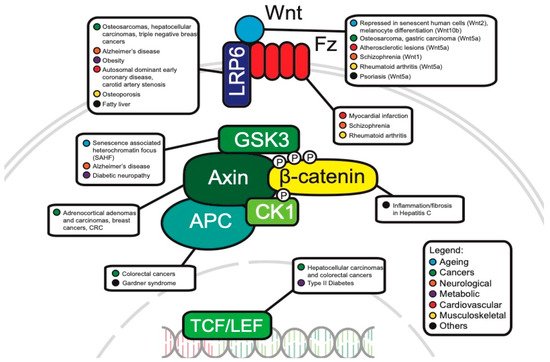
Figure 3. Canonical WNT pathway components associated with disease.
Frequent APC mutations in colorectal cancer: The APC protein is an important component of the destruction complex in canonical WNT signaling. In addition to this role, APC is also essential for the rapid transition of Axin immediately after WNT stimulation and facilitates the association of Axin and co-receptor LRP6/Arrow in Drosophila [59][55].
As APC negatively regulates the canonical WNT pathway, it is likely that it can act as a tumor suppressor. Consistent with this idea, APC mutations, which are present in approximately ~80% of colorectal cancers, are indeed mostly loss of function and/or truncating mutations [60,61][56][57]. These APC mutations frequently occur in the mutation cluster region (MCR) between codons 1285 and 1513 which accounts for only 10% of the entire coding region [62][58]. To illustrate this, a study concluded that 28 out of 43 (65%) somatic mutations in colorectal cancer cells occur in the MCR [62][58]. These mutations can inhibit β-catenin ubiquitination and cause uncontrollable transcription [63][59]. Interestingly, an analysis of 630 human sporadic colorectal cancer tumors revealed that different APC mutations can result in different levels of canonical WNT signaling, and each region of the large intestine has its own optimal threshold of WNT signaling for tumorigenesis [60][56]. APC mutations also occur in the germline and are present in up to 85% of patients with classical familial adenomatous polyposis (CFAP). Most germline mutations are also truncating (e.g., frameshift, nonsense) [64][60], confirming APC’s tumor suppressor role.
The prevalence of APC mutations in colorectal cancers suggest APC as a powerful target for therapy. TASIN-1 (truncated APC selective inhibitor-1) was identified as a molecule that could specifically kill cells with truncated APC’s. TASIN-1′s administration into xenograft and mouse models has shown its effectiveness in tumor suppression and its specificity in killing cells with truncated APC’s while sparing normal cells in vivo [65][61]. Considering the high frequency of mutated APC in patients with colorectal cancer, further studies are needed to investigate APC’s molecular mechanism in β-catenin degradation, its use as a potential biomarker and other possible therapeutic targeting approaches.
AXIN1/2: Axin proteins (AXIN1 and AXIN2) are important scaffold proteins that help assemble the β-catenin destruction complex [66][62]. AXIN1/2 act as negative regulators of β-catenin levels and tumor suppressor proteins. This is consistent with the finding that the overexpression of AXIN1 inhibits cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [67][63]. However, the role of AXIN1/2 as a tumor suppressor through the canonical WNT pathway remains controversial, as other findings have suggested that most human Axin1 mutated HCCs do not show a β-catenin activation program. These HCCs might have occurred independently of the WNT/β-catenin pathway and instead involved other pathways like YAP and Notch [68][64].
AXIN2 has been shown to behave as both a tumor suppressor and an oncogene. Its mutations are also observed in various cancers. Chapman et al. observed genetic changes (mostly deletions) of AXIN2 in 7% of human adrenocortical adenomas tumor samples and 17% of adrenocortical carcinomas tumor samples [69][65]. Consistent with the idea that AXIN2 might act as a tumor suppressor, AXIN2 downregulation is associated with poorer overall survival of patients with breast cancer [70][66]. However, in vivo findings also suggest AXIN2 as tumor-promoting, as it upregulates the transcriptional repressor, SNAI1, leading to increased EMT and metastatic activity in colorectal cancers in mice [71][67]. As these contradictory studies provide only preliminary evidence of the functional significance of Axin in canonical WNT pathways, future studies aimed towards exploring Axin’s expression in different cancers and its mechanism in affecting tumor progression should be conducted. The contradictory findings in cancer are not surprising as Axin’s role in development is complex [72][68].
LRP5/6: LRP5 and LRP6 in the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family are single-pass transmembrane coreceptors in the WNT canonical signaling pathway. The FZD receptor may form a WNT-induced FZD–LRP6 (or LRP5) complex with these coreceptors. After WNT ligands bind to these receptors, the β-catenin signaling is initiated [73,74][69][70].
LRP5 has contradictory roles in cancer progression as well. When osteosarcoma cells are transfected with dominant negative, soluble LRP5 (sLRP5), epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is reversed, suggesting wildtype LRP5′s role in promoting EMT and metastasis [75][71]. However, Horne et al. observed an opposite effect in which dominant-negative LRP5 failed to block osteosarcoma cell formation, suggesting LRP’s role as a tumor suppressor [76][72].
Similarly, LRP6′s role in cancer progression has been controversial. A total of 45% of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells have overexpressed LRP6 and as a result, increased β-catenin levels, suggesting LRP6 as tumor-promoting [77][73]. Consistent with this finding, overexpression of LRP6 is also found in triple negative breast cancers. When LRP6 is knocked-down in triple negative breast cancer cells, tumor growth is suppressed in vivo [78][74]. LRP’s also seem to have a promoting role in breast cancer metastasis to bone. TM40D-MB breast cells which are highly metastatic to bone have higher mRNA levels of LRP5, LRP6 and β-catenin, as compared to TM40D cells, which are breast cancer cells that are non-bone metastatic [79][75]. However, contrary to previous studies, Ren et al. reported the novel role of LRP5/6 as suppressing metastasis. This study showed that LRP5/6 downregulation is crucial for metastasis in mouse breast cancer models [80][76], suggesting that the binding of LRP5/6 to FZD inhibits the FZD-regulated non-canonical pathway and its further tumor metastasis.
Therapeutic targeting of LRP5/6 shows promising results. Mesd, a specialized chaperone that binds to LRP5/6 on the cell surface, inhibits LRP5/6 ligands and suppresses downstream WNT/β-catenin signaling in prostate cancer [81][77]. Niclosamide, another inhibitor targeting LRP6 on the cell surface, also induces cancer cell apoptosis [81][77]. Future studies can aim to discover new therapeutic approaches targeting LRP5/6 and other members in the LDLR family. Other LDLR family members like LRP8 and LRP10 are also good potential targets to be further investigated given that previous studies have showed their involvement in breast cancers and hepatocellular carcinomas, respectively [82,83][78][79].
WNT 5A: The WNT5A ligand binds to certain receptors (e.g., ROR2, ROR1, etc.) and activates non-canonical WNT signaling pathways [84][80]. Mutations of WNT5A have been shown to associate with cancer development, possibly through noncanonical WNT signaling pathways [84][80]. For example, WNT5A promotes cancer through binding its receptor ROR2 and enhancing human osteosarcoma invasiveness [85][81]. WNT5A expression induces EMT in a PKC-dependent pathway in human melanoma cell lines [86][82], suggesting that the increased ability of cells to undergo EMT promotes their invasiveness. Kanzawa et al. reported that the expression of WNT5A in human gastric carcinoma-derived MKN-7 cells promoted cancer cell invasiveness by upregulating a transcription factor involved in EMT, namely SNAI1. This study also suggested that WNT5A may play a role in creating favorable tumor microenvironments and inducing cancer stem cell properties [87][83]. Aside from its role of promoting cell invasion, WNT5A drives pseudo-senescence in melanoma cancer cells. When exposed to stress, pseudo-senescent cells display classical senescence markers, but are highly invasive, metastatic and resistant to therapy. In response to stressors, tumor cells with knocked down WNT5A do not display this pseudo-senescent phenotype, whereas highly expressed WNT5A tumor cells do, suggesting WNT5A’s role in promoting cancer cell adaptiveness under stress [88][84]. WNT5A has also been shown to be involved with cancer cell metabolism and inflammation [89][85]. Future studies should investigate other WNT ligands (e.g., WNT11) and their roles in cancer progression through non-canonical pathways with the hope of providing novel targets for therapies.
RNF43: Ring finger protein 43 (RNF43) is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that degrades WNT receptors such as FZD and LRP5/6. It serves as a negative regulator of the WNT pathway. The mechanisms of WNT signaling suppression are different between non-canonical and canonical pathways. In non-canonical pathways, the suppression involves the interaction between RNF43′s C-terminal cytoplasmic region and Dsh’s PDZ domain. Suppression of the canonical pathway involves FZD’s extracellular protease-associated domain, cysteine-rich domain and the intracellular ring finger domain of RNF43 [90][86]. A recent study has suggested a novel way that RNF43 suppresses the pathway in the nucleus where a physical interaction between RNF43 and TCF4 translocates TCF4 to the nuclear membrane, inhibiting TCF4 transcriptional activity [91][87].
RNF43 acts as a tumor suppressor. When 185 human colorectal tumor samples were analyzed, there were RNF43 somatic mutations in over 18% of colorectal adenocarcinomas and endometrial carcinomas. This study also showed that most RNF43 mutations (73%–75% of non-silent mutations) found were truncating, confirming that RNF43 acts as a tumor suppressor [92][88]. RNF43 mutations were also found in pancreatic cancers [93][89] and mucinous ovarian carcinomas [94][90]. However, few studies have been conducted to explore the role of RNF43 in these cancers, so further studies are needed to investigate how certain mutations in RNF43 can possibly lead to the development of these cancers.
TCF4/TCF7L2: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (TCF/LEF) transcription factors are the downstream effectors of the WNT pathway. When WNT ligands bind to upstream receptors, β-catenin is released from the cytoplasmic destruction complex and moves to the nucleus, where it associates with TCFs to regulate the transcription of target genes [95][91].
TCF4, one of the most studied members of the TCL/LEF family, seems to have contradictory roles as both tumor-promoting and tumor-suppressing. TCF4 was originally believed to be tumor-promoting. Van De Wetering et al. demonstrated that dominant-negative TCF4, which fails to bind to β-catenin, halted cell proliferation in colorectal cells [96][92]. However, Angus-Hill et al. reported TCF4 as tumor-suppressing as its loss of function increased proliferation in colon tumors in mice [97][93]. This controversy may be resolved by considering that TCL/LEF undergoes alternative splicing, and the isoforms produced may differ in functional domain composition. Thus, these TCL/LEF isoforms will differ in DNA binding and target gene activation [98][94]. To illustrate this, Tsedensodum et al. identified 14 TCF4 isoforms from four hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Functional analysis showed that one isoform, TCF-4K is tumor growth promotive, and another isoform, TCF-4J, is tumor growth suppressive. Strikingly, these two isoforms only differ by five amino acids [99][95]. These data suggest that the variants caused by alternative splicing may be a reason to explain the contradictory role of TCF4 [100][96]. Further studies should elucidate the roles of TCF in cancer and development [101][97], taking into consideration not only the downstream target genes’ roles, but also the different isoforms that result from alternative splicing. Based on this understanding, more effective therapeutic approaches can be developed to aim for certain isoforms that cause malignant phenotypes.
PTK7: Another gene linking the various types of WNT signaling to cancer is the gene PTK7, an orphan receptor linked to a variety of cancers as a highly upregulated biomarker [102][98]. PTK7 was originally discovered as a colon carcinoma kinase-4 upregulated in cancer tissue [103][99]. Its function remained unclear until the ortholog was discovered as a neuronal pathfinding gene in Drosophila (known as off-track in flies) [104][100] and subsequently shown to be a planar polarity gene during mouse development [105][101]. The mechanism of action remains controversial with WNT and non-canonical functions proposed [105[101][102][103][104],106,107,108], but the use of PTK7 in cancer treatment could well be under way [109][105].
WNT pathway as a tumor suppressor: Although WNT is usually referred to as an oncogenic pathway, it can also function in quite the opposite direction depending on cellular context. This has primarily been studied in malignant melanoma, where activation of WNT reduces cell proliferation and can actually function as a tumor suppressor. Overall, the main lesson from these studies is that context is crucial, namely depending on what transforming factor is driving oncogenicity since WNT activation can lead to unexpected consequences [110,111,112][106][107][108].
References
- Nusse, R.; Varmus, H.E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 1982, 31, 99–109.
- Nusse, R. Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 28–32.
- Oliva, C.A.; Montecinos-Oliva, C.; Inestrosa, N.C. Wnt Signaling in the Central Nervous System: New Insights in Health and Disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 153, 81–130.
- Sharma, R.P.; Chopra, V.L. Effect of the Wingless (wg1) mutation on wing and haltere development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 1976, 48, 461–465.
- Nusslein-Volhard, C.; Wieschaus, E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 1980, 287, 795–801.
- Wodarz, A.; Nusse, R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 59–88.
- Nusse, R.; Brown, A.; Papkoff, J.; Scambler, P.; Shackleford, G.; McMahon, A.; Moon, R.; Varmus, H. A new nomenclature for int-1 and related genes: The Wnt gene family. Cell 1991, 64, 231.
- Cadigan, K.M.; Nusse, R. Wnt signaling: A common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3286–3305.
- Pfister, A.S.; Kuhl, M. Of Wnts and Ribosomes. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 153, 131–155.
- He, X.; Semenov, M.; Tamai, K.; Zeng, X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Arrows point the way. Development 2004, 131, 1663–1677.
- Komiya, Y.; Habas, R. Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis 2008, 4, 68–75.
- Habas, R.; Dawid, I.B. Dishevelled and Wnt signaling: Is the nucleus the final frontier? J. Biol. 2005, 4, 2.
- Zeng, L.; Fagotto, F.; Zhang, T.; Hsu, W.; Vasicek, T.J.; Perry, W.L., III; Lee, J.J.; Tilghman, S.M.; Gumbiner, B.M.; Costantini, F. The mouse Fused locus encodes Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway that regulates embryonic axis formation. Cell 1997, 90, 181–192.
- Minde, D.P.; Anvarian, Z.; Rudiger, S.G.; Maurice, M.M. Messing up disorder: How do missense mutations in the tumor suppressor protein APC lead to cancer? Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 101.
- Minde, D.P.; Radli, M.; Forneris, F.; Maurice, M.M.; Rudiger, S.G. Large extent of disorder in Adenomatous Polyposis Coli offers a strategy to guard Wnt signalling against point mutations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77257.
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26.
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Semenov, M.; Han, C.; Baeg, G.H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, X. Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell 2002, 108, 837–847.
- Rao, T.P.; Kühl, M. An Updated Overview on Wnt Signaling Pathways. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1798–1806.
- Bilić, J.; Huang, Y.-L.; Davidson, G.; Zimmermann, T.; Cruciat, C.-M.; Bienz, M.; Niehrs, C. Wnt Induces LRP6 Signalosomes and Promotes Dishevelled-Dependent LRP6 Phosphorylation. Science 2007, 316, 1619.
- Tolwinski, N.S.; Wieschaus, E. A nuclear escort for β-catenin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 579–580.
- Kestler, H.A.; Kuhl, M. From individual Wnt pathways towards a Wnt signalling network. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1333–1347.
- Matsui, T.; Raya, A.; Kawakami, Y.; Callol-Massot, C.; Capdevila, J.; Rodriguez-Esteban, C.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Noncanonical Wnt signaling regulates midline convergence of organ primordia during zebrafish development. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 164–175.
- De Calisto, J. Essential role of non-canonical Wnt signalling in neural crest migration. Development 2005, 132, 2587–2597.
- Veeman, M.T.; Axelrod, J.D.; Moon, R.T. A second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 367–377.
- Habas, R.; Kato, Y.; He, X. Wnt/Frizzled activation of Rho regulates vertebrate gastrulation and requires a novel Formin homology protein Daam1. Cell 2001, 107, 843–854.
- Colosimo, P.F.; Tolwinski, N.S. Wnt, Hedgehog and junctional Armadillo/beta-catenin establish planar polarity in the Drosophila embryo. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e9.
- Kaplan, N.A.; Liu, X.; Tolwinski, N.S. Epithelial polarity: Interactions between junctions and apical-basal machinery. Genetics 2009, 183, 897–904.
- Colosimo, P.F.; Liu, X.; Kaplan, N.A.; Tolwinski, N.S. GSK3beta affects apical-basal polarity and cell-cell adhesion by regulating aPKC levels. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 115–125.
- Kaplan, N.A.; Tolwinski, N.S. Spatially defined Dsh-Lgl interaction contributes to directional tissue morphogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3157–3165.
- Kaplan, N.A.; Colosimo, P.F.; Liu, X.; Tolwinski, N.S. Complex interactions between GSK3 and aPKC in Drosophila embryonic epithelial morphogenesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18616.
- Schlessinger, K.; Hall, A.; Tolwinski, N. Wnt signaling pathways meet Rho GTPases. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 265–277.
- Kohn, A.D.; Moon, R.T. Wnt and calcium signaling: Beta-catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium 2005, 38, 439–446.
- Slusarski, D.C.; Pelegri, F. Calcium signaling in vertebrate embryonic patterning and morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2007, 307, 1–13.
- Pataki, C.A.; Couchman, J.R.; Brabek, J. Wnt Signaling Cascades and the Roles of Syndecan Proteoglycans. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 63, 465–480.
- Fodde, R. The APC gene in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 867–871.
- Kinzler, K.W.; Nilbert, M.C.; Su, L.K.; Vogelstein, B.; Bryan, T.M.; Levy, D.B.; Smith, K.J.; Preisinger, A.C.; Hedge, P.; McKechnie, D.; et al. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science 1991, 253, 661.
- Nusslein-Volhard, C.; Wieschaus, E.; Kluding, H. Mutations affecting the pattern of the larval cuticle inDrosophila melanogaster: I. Zygotic loci on the second chromosome. Wilehm Roux Arch. Dev. Biol. 1984, 193, 267–282.
- Tian, Y.; Cohen, E.D.; Morrisey, E.E. The importance of Wnt signaling in cardiovascular development. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2010, 31, 342–348.
- Logan, C.Y.; Nusse, R. The Wnt Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 781–810.
- De Ferrari, G.V.; Chacon, M.A.; Barria, M.I.; Garrido, J.L.; Godoy, J.A.; Olivares, G.; Reyes, A.E.; Alvarez, A.; Bronfman, M.; Inestrosa, N.C. Activation of Wnt signaling rescues neurodegeneration and behavioral impairments induced by beta-amyloid fibrils. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 195–208.
- Sethi, J.K.; Vidal-Puig, A. Wnt signalling and the control of cellular metabolism. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 1–17.
- Harman, D. The aging process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7124–7128.
- Cummings, S.R. The biology of aging. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2007, 7, 340–341.
- Campisi, J. Senescent Cells, Tumor Suppression, and Organismal Aging: Good Citizens, Bad Neighbors. Cell 2005, 120, 513–522.
- Ye, X.; Zerlanko, B.; Kennedy, A.; Banumathy, G.; Zhang, R.; Adams, P.D. Downregulation of Wnt signaling is a trigger for formation of facultative heterochromatin and onset of cell senescence in primary human cells. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 183–196.
- Reya, T.; Clevers, H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 2005, 434, 843–850.
- Zhang, R.; Poustovoitov, M.V.; Ye, X.; Santos, H.A.; Chen, W.; Daganzo, S.M.; Erzberger, J.P.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; Canutescu, A.A.; Dunbrack, R.L.; et al. Formation of MacroH2A-containing senescence-associated heterochromatin foci and senescence driven by ASF1a and HIRA. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 19–30.
- Liu, H.; Fergusson, M.M.; Castilho, R.M.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, J.; Malide, D.; Rovira, I.I.; Schimel, D.; Kuo, C.J.; et al. Augmented Wnt signaling in a mammalian model of accelerated aging. Science 2007, 317, 803–806.
- Kurosu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Clark, J.D.; Pastor, J.V.; Nandi, A.; Gurnani, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Chikuda, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 2005, 309, 1829–1833.
- White, B.D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Moon, R.T. Wnt Signaling: It Gets More Humorous with Age. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R923–R925.
- Zhang, Z.; Lei, M.; Xin, H.; Hu, C.; Yang, T.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Lian, X.; Deng, F. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes aging-associated hair graying in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69316–69327.
- Chen, Y.; Whetstone, H.C.; Lin, A.C.; Nadesan, P.; Wei, Q.; Poon, R.; Alman, B.A. Beta-catenin signaling plays a disparate role in different phases of fracture repair: Implications for therapy to improve bone healing. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e249.
- Ito, M.; Yang, Z.; Andl, T.; Cui, C.; Kim, N.; Millar, S.E.; Cotsarelis, G. Wnt-dependent de novo hair follicle regeneration in adult mouse skin after wounding. Nature 2007, 447, 316–320.
- DeCarolis, N.A.; Wharton, K.A., Jr.; Eisch, A.J. Which way does the Wnt blow? Exploring the duality of canonical Wnt signaling on cellular aging. Bioessays 2008, 30, 102–106.
- Tacchelly-Benites, O.; Wang, Z.; Yang, E.; Benchabane, H.; Tian, A.; Randall, M.P.; Ahmed, Y. Axin phosphorylation in both Wnt-off and Wnt-on states requires the tumor suppressor APC. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007178.
- Christie, M.; Jorissen, R.N.; Mouradov, D.; Sakthianandeswaren, A.; Li, S.; Day, F.; Tsui, C.; Lipton, L.; Desai, J.; Jones, I.T.; et al. Different APC genotypes in proximal and distal sporadic colorectal cancers suggest distinct WNT/beta-catenin signalling thresholds for tumourigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4675–4682.
- Powell, S.M.; Zilz, N.; Beazer-Barclay, Y.; Bryan, T.M.; Hamilton, S.R.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature 1992, 359, 235–237.
- Miyoshi, Y.; Nagase, H.; Ando, H.; Horii, A.; Ichii, S.; Nakatsuru, S.; Aoki, T.; Miki, Y.; Mori, T.; Nakamura, Y. Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: Mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1992, 1, 229–233.
- Polakis, P. The oncogenic activation of beta-catenin. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1999, 9, 15–21.
- Friedl, W.; Aretz, S. Familial adenomatous polyposis: Experience from a study of 1164 unrelated german polyposis patients. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2005, 3, 95–114.
- Zhang, L.; Theodoropoulos, P.C.; Eskiocak, U.; Wang, W.; Moon, Y.A.; Posner, B.; Williams, N.S.; Wright, W.E.; Kim, S.B.; Nijhawan, D.; et al. Selective targeting of mutant adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in colorectal cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 361ra140.
- Thorvaldsen, T.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Wenzel, E.M.; Stenmark, H. Differential Roles of AXIN1 and AXIN2 in Tankyrase Inhibitor-Induced Formation of Degradasomes and beta-Catenin Degradation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170508.
- Satoh, S.; Daigo, Y.; Furukawa, Y.; Kato, T.; Miwa, N.; Nishiwaki, T.; Kawasoe, T.; Ishiguro, H.; Fujita, M.; Tokino, T.; et al. AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 245–250.
- Abitbol, S.; Dahmani, R.; Coulouarn, C.; Ragazzon, B.; Mlecnik, B.; Senni, N.; Savall, M.; Bossard, P.; Sohier, P.; Drouet, V.; et al. AXIN deficiency in human and mouse hepatocytes induces hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of beta-catenin activation. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1203–1213.
- Chapman, A.; Durand, J.; Ouadi, L.; Bourdeau, I. Identification of genetic alterations of AXIN2 gene in adrenocortical tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1477–E1481.
- Dai, J.; Gao, H.; Xue, J.; Lin, W.; Zheng, L. The Association Between AXIN2 Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Breast Cancer in Chinese Women. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2019, 23, 393–400.
- Wu, Z.Q.; Brabletz, T.; Fearon, E.; Willis, A.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Weiss, S.J. Canonical Wnt suppressor, Axin2, promotes colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11312–11317.
- Qian, L.; Mahaffey, J.P.; Alcorn, H.L.; Anderson, K.V. Tissue-specific roles of Axin2 in the inhibition and activation of Wnt signaling in the mouse embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8692–8697.
- Roslan, Z.; Muhamad, M.; Selvaratnam, L.; Ab-Rahim, S. The Roles of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Proteins 5, 6, and 8 in Cancer: A Review. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 4536302.
- Janda, C.Y.; Waghray, D.; Levin, A.M.; Thomas, C.; Garcia, K.C. Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled. Science 2012, 337, 59.
- Guo, Y.; Zi, X.; Koontz, Z.; Kim, A.; Xie, J.; Gorlick, R.; Holcombe, R.F.; Hoang, B.H. Blocking Wnt/LRP5 signaling by a soluble receptor modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition and suppresses met and metalloproteinases in osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 964–971.
- Horne, L.; Avilucea, F.R.; Jin, H.; Barrott, J.J.; Smith-Fry, K.; Wang, Y.; Hoang, B.H.; Jones, K.B. LRP5 Signaling in Osteosarcomagenesis: A Cautionary Tale of Translation from Cell Lines to Tumors. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 438–444.
- Tung, E.K.; Wong, B.Y.; Yau, T.O.; Ng, I.O. Upregulation of the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and enhances cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36565.
- King, T.D.; Suto, M.J.; Li, Y. The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway: A potential therapeutic target in the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 13–18.
- Chen, Y.; Shi, H.Y.; Stock, S.R.; Stern, P.H.; Zhang, M. Regulation of breast cancer-induced bone lesions by beta-catenin protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42575–42584.
- Ren, D.N.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Yin, Y.; Wo, D.; Zhang, J.; Ao, L.; Chen, B.; Ito, T.K.; et al. LRP5/6 directly bind to Frizzled and prevent Frizzled-regulated tumour metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6906.
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Waud, W.R.; Piazza, G.A.; Li, Y. Niclosamide suppresses cancer cell growth by inducing Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29290.
- Lin, C.C.; Lo, M.C.; Moody, R.; Jiang, H.; Harouaka, R.; Stevers, N.; Tinsley, S.; Gasparyan, M.; Wicha, M.; Sun, D. Targeting LRP8 inhibits breast cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 165–173.
- Gonias, S.L.; Karimi-Mostowfi, N.; Murray, S.S.; Mantuano, E.; Gilder, A.S. Expression of LDL receptor-related proteins (LRPs) in common solid malignancies correlates with patient survival. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186649.
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473.
- Enomoto, M.; Hayakawa, S.; Itsukushima, S.; Ren, D.Y.; Matsuo, M.; Tamada, K.; Oneyama, C.; Okada, M.; Takumi, T.; Nishita, M.; et al. Autonomous regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasiveness by Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3197–3208.
- Dissanayake, S.K.; Wade, M.; Johnson, C.E.; O’Connell, M.P.; Leotlela, P.D.; French, A.D.; Shah, K.V.; Hewitt, K.J.; Rosenthal, D.T.; Indig, F.E.; et al. The Wnt5A/protein kinase C pathway mediates motility in melanoma cells via the inhibition of metastasis suppressors and initiation of an epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17259–17271.
- Kanzawa, M.; Semba, S.; Hara, S.; Itoh, T.; Yokozaki, H. WNT5A is a key regulator of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties in human gastric carcinoma cells. Pathobiology 2013, 80, 235–244.
- Webster, M.R.; Xu, M.; Kinzler, K.A.; Kaur, A.; Appleton, J.; O’Connell, M.P.; Marchbank, K.; Valiga, A.; Dang, V.M.; Perego, M.; et al. Wnt5A promotes an adaptive, senescent-like stress response, while continuing to drive invasion in melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 184–195.
- Asem, M.S.; Buechler, S.; Wates, R.B.; Miller, D.L.; Stack, M.S. Wnt5a Signaling in Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 79.
- Tsukiyama, T.; Fukui, A.; Terai, S.; Fujioka, Y.; Shinada, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Ohba, Y.; Hatakeyama, S. Molecular Role of RNF43 in Canonical and Noncanonical Wnt Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2007–2023.
- Loregger, A.; Grandl, M.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Allgauer, M.; Degenhart, K.; Haselmann, V.; Oikonomou, C.; Hatzis, P.; Janssen, K.P.; Nitsche, U.; et al. The E3 ligase RNF43 inhibits Wnt signaling downstream of mutated beta-catenin by sequestering TCF4 to the nuclear membrane. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra90.
- Giannakis, M.; Hodis, E.; Jasmine Mu, X.; Yamauchi, M.; Rosenbluh, J.; Cibulskis, K.; Saksena, G.; Lawrence, M.S.; Qian, Z.R.; Nishihara, R.; et al. RNF43 is frequently mutated in colorectal and endometrial cancers. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1264–1266.
- Jiang, X.; Hao, H.X.; Growney, J.D.; Woolfenden, S.; Bottiglio, C.; Ng, N.; Lu, B.; Hsieh, M.H.; Bagdasarian, L.; Meyer, R.; et al. Inactivating mutations of RNF43 confer Wnt dependency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12649–12654.
- Zou, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, F.Y.; Huang, M.Z.; Li, W.; Yuan, X.Q.; Huang, O.P.; He, M. RNF43 mutations are recurrent in Chinese patients with mucinous ovarian carcinoma but absent in other subtypes of ovarian cancer. Gene 2013, 531, 112–116.
- Hrckulak, D.; Kolar, M.; Strnad, H.; Korinek, V. TCF/LEF Transcription Factors: An Update from the Internet Resources. Cancers 2016, 8, 70.
- Van de Wetering, M.; Sancho, E.; Verweij, C.; de Lau, W.; Oving, I.; Hurlstone, A.; van der Horn, K.; Batlle, E.; Coudreuse, D.; Haramis, A.P.; et al. The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 2002, 111, 241–250.
- Angus-Hill, M.L.; Elbert, K.M.; Hidalgo, J.; Capecchi, M.R. T-cell factor 4 functions as a tumor suppressor whose disruption modulates colon cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4914–4919.
- Cadigan, K.M.; Waterman, M.L. TCF/LEFs and Wnt signaling in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007906.
- Tsedensodnom, O.; Koga, H.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Nambotin, S.B.; Carroll, J.J.; Wands, J.R.; Kim, M. Identification of T-cell factor-4 isoforms that contribute to the malignant phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 920–931.
- Sumithra, B.; Saxena, U.; Das, A.B. Alternative splicing within the Wnt signaling pathway: Role in cancer development. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 1–13.
- Suresh, J.; Harmston, N.; Lim, K.K.; Kaur, P.; Jin, H.J.; Lusk, J.B.; Petretto, E.; Tolwinski, N.S. An embryonic system to assess direct and indirect Wnt transcriptional targets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11092.
- Dunn, N.R.; Tolwinski, N.S. Ptk7 and Mcc, Unfancied Components in Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling and Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 68.
- Mossie, K.; Jallal, B.; Alves, F.; Sures, I.; Plowman, G.D.; Ullrich, A. Colon carcinoma kinase-4 defines a new subclass of the receptor tyrosine kinase family. Oncogene 1995, 11, 2179–2184.
- Winberg, M.L.; Tamagnone, L.; Bai, J.; Comoglio, P.M.; Montell, D.; Goodman, C.S. The transmembrane protein Off-track associates with Plexins and functions downstream of Semaphorin signaling during axon guidance. Neuron 2001, 32, 53–62.
- Lu, X.; Borchers, A.G.; Jolicoeur, C.; Rayburn, H.; Baker, J.C.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. PTK7/CCK-4 is a novel regulator of planar cell polarity in vertebrates. Nature 2004, 430, 93–98.
- Peradziryi, H.; Tolwinski, N.S.; Borchers, A. The many roles of PTK7: A versatile regulator of cell-cell communication. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 524, 71–76.
- Peradziryi, H.; Kaplan, N.A.; Podleschny, M.; Liu, X.; Wehner, P.; Borchers, A.; Tolwinski, N.S. PTK7/Otk interacts with Wnts and inhibits canonical Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3729–3740.
- Linnemannstöns, K.; Ripp, C.; Honemann-Capito, M.; Brechtel-Curth, K.; Hedderich, M.; Wodarz, A. The PTK7-Related Transmembrane Proteins Off-track and Off-track 2 Are Co-receptors for Drosophila Wnt2 Required for Male Fertility. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004443.
- Damelin, M.; Bankovich, A.; Bernstein, J.; Lucas, J.; Chen, L.; Williams, S.; Park, A.; Aguilar, J.; Ernstoff, E.; Charati, M.; et al. A PTK7-targeted antibody-drug conjugate reduces tumor-initiating cells and induces sustained tumor regressions. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaag2611.
- Zimmerman, Z.F.; Moon, R.T.; Chien, A.J. Targeting Wnt Pathways in Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008086.
- Lucero, O.M.; Dawson, D.W.; Moon, R.T.; Chien, A.J. A re-evaluation of the “oncogenic” nature of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanoma and other cancers. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 12, 314–318.
- Anastas, J.N.; Moon, R.T. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 13, 11.
More
