Today, dendrimers are the main nanoparticle applied to drug delivery systems. The physicochemical characteristics of dendrimers and their versatility structural modification make them attractive to applied as a platform to bioactive molecules transport. Nanoformulations based on dendrimers enhance low solubility drugs, arrival to the target tissue, drugs bioavailability, and controlled release. This review describes the latter approaches on the transport of bioactive molecules based on dendrimers. The review focus is on the last therapeutic strategies addressed by dendrimers conjugated with bioactive molecules. A brief review of the latest studies in therapies against cancer and cardiovascular diseases, as well as future projections in the area, are addressed.
- dendrimers
- polymeric materials
- biopolymers
https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030570
1. Introduction
Today, most pathologies, whether chronic or not, are treated through oral, mucosal, dermal, and transdermal administration of drugs. Most of the effects of the drugs used to cure diseases have a high percentage of inhibition of the target agents that generate the pathology or significantly reduce the symptoms of it. The problem with some drugs is that they must be administered in high doses, to reach a positive therapeutic, but the higher doses usually result in unwanted side effects [1][2][3][4]. These side effects are because some drugs that have low bioavailability, so they must be administered in high doses. For this reason, in the last decades, the challenge has been focused on the investigation of the targeted drug delivery systems [5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]. There is a large variety of organic systems that have been considered as drug delivery systems, such as micelles, liposomes, and polymeric nanoparticles. All these systems must meet some requirements to be applied as the drug carrier agents, namely nanoscale size, biocompatible, bioresorbable, water solubility, and monodisperse structure [13][14][15][16]. Among these synthetic nanostructures, dendrimers have been one of the most studied in the last twenty years.
Dendrimers are very attractive macromolecules, both from the challenge proposed by their design and chemical synthesis and from the range of applications they have given in different areas. They are three-dimensional structures highly branched and radially symmetrical (
). They have three very well defined structural regions, a central junction structure (core) with multiple internal repeating units covalently linked to the nucleus (called generations, G), and finally, a terminal chemical structure that forms the multifunctional surface of a dendrimer [17]. These attractive macromolecular architectures were reported in the late 70’s by Vögtle et al. and have been the subject of numerous studies since then. In later years Tomalia, Newkome, and Frechet, independently, reported two new synthetic routes to obtain dendrimersoma [18][19]. The chemical architecture of the dendrimers overcome other polymers (linear, branched or cross-linked) since they have attributes like monodisperse structures (desirable for applications in nanomedicine), control over macromolecular growth, multifunctional surface structure, internal cavities available to host small molecules, increased solubilization, among many other advantages that enable them to be used in several fields. Nanomedicine is one of the applications in which dendrimers have been studied and tested, using as a nanocarrier bioactive molecules, imaging agents, or transfection of genes.
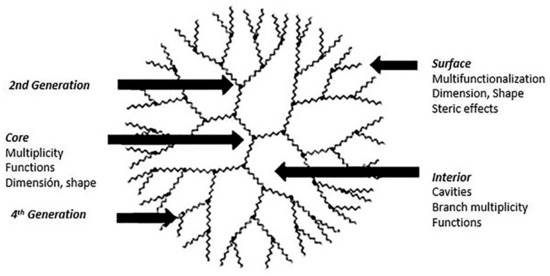
Schematic representation of a dendrimer of fourth-generation. This scheme was provided thanks to Reference [20].
In the last ten years, numerous publications, over 29 thousand articles, and more than 6 thousand reviews (source: WOS, January 09–2020) have been published on a drug delivery system based on dendrimers. The present review primarily focuses on progress carried out in the last few years in dendrimers and their applications as drug delivery systems. Here, we will give an overview of the dendrimer types and their properties, and in a second part give we will present pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies which have been done regarding the transport and control release of bioactive molecules based on dendrimers. Finally, the latest studies concerning the release of drugs based on dendrimers focused on cancer and cardiovascular diseases and prospects are reported.
2. Dendrimers to Drug Delivery Systems Applications
As mentioned earlier, thousands of reviews and articles have been published in the last decade on transport and contracted release of drugs by nanoparticles. These delivery systems have been of a relevant interest from industry to academic researches. The challenges in drug delivery systems are focused on solving the inefficient distribution of the drugs to the target tissues and the side effects improvement after drug administration that can influence both pharmacokinetic profiles as the biodistribution of them. The dendrimers, as we have said before, constitute a class of nanoparticles with physicochemical characteristics that make them very attractive in nanomedicine applications, more specifically as drug delivery systems (DDS). As previously mentioned, these extraordinary dendritic macromolecules have an improved membrane permeability and tumor retention effects [21][22][23], due to their suitable structural properties and size control.
Dendrimers as DDS can improve key points in transport and biodistribution such as prolongation of the drug circulation time, enhance drug solubility, enhance tumor permeation and retention, protection of the drug from surroundings, and the ability to target diseased tissue, among others. As a strategy to minimize the cytotoxicity of PAMAM dendrimers, the positive surface charge of its surface has been modified with carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) [24][25][26]. Considering that, CMCS is an amphoteric polymer, sensitive pH, and taking doxorubicin as a model drug for cancer, it is that the formulation of a nanoparticle between PAMAM dendrimer and CMCS based on electrostatic conjugation, can transport the drug and release it into the target tissue (23A). It is known that there is a slight difference between physiological pH (7.4) and extracellular pH of tumor cells (6.5), (
2B) so PAMAM dendrimers decorated with CMCS showed promising in vitro results of doxorubicin release at pH 6.5.
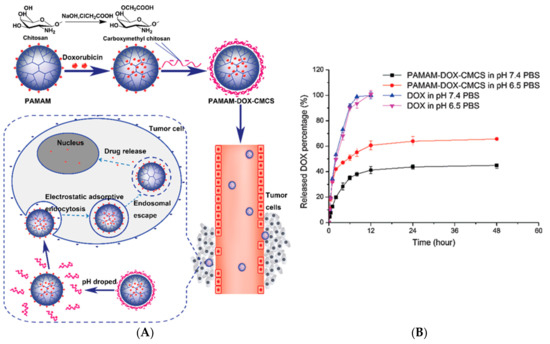
(
) Schematic representation of electrostatic conjugation of PAMAM dendrimers with carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) and the PAMAM-Doxorubicin-CMCS complex circulation through bloodstream and tumor microenvironment. (
) In vitro doxorubicin release with and without PAMAM-CMCS complex at pH 7.4 and pH 6.5. This Figure was provided thanks to Reference [24].
Thus, dendrimer-drug conjugates used as pharmacological strategies can be decorated depending on the target tissue, the pathology of interest, and the type of drug to be transported. Otto et al. studied the solubility and dissolution properties of furosemide/PAMAM dendrimers complexes with different generations containing amino and ester terminal groups [25]. Pharmacokinetic assessments in vivo show that the dendrimer complexes improved the bioavailability of the drug compared to the free drug. Other drug reported with low solubility, rifampicin (RIF) an antibiotic to the tuberculosis treatment [27]
and important side effects since it suffers a hydrolysis reaction under gastric conditions was studied. Results of stability and drug-load capacity of the RIF-PAMAM complexes under different pH conditions were carried out by theoretical and experimental methods [28]. Studies demonstrated that twenty molecules of RIF per G4-PAMAM were determined according the results reported by molecular dynamic simulation tools. A theoretical study was carried out at two pH conditions, neutral and acid. At low pH, RIF molecules were quickly released to the solvent bulk, otherwise at neutral pH the RIF-PAMAM complex was more stable (
3). Taking into account that drugs release strongly depends on the pH, may impose restrictions to administration way, namely in the case of oral administration due to the low pH of the stomach. Nevertheless, preliminaries studies have shown that PAMAM dendrimers have the potential for pulmonary inhalation, which may be advantageous in the case of respiratory diseases treatment [29][30]. These studies allow us determine what kind of dendrimer it is necessary to synthetize, according to the type of the target tissue and the type of drug will be transported.
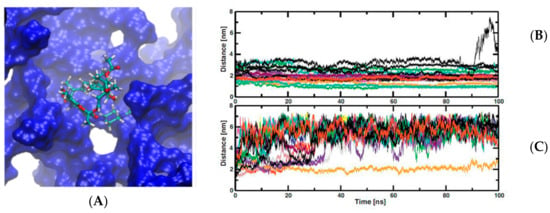
(
) a rifampicin (RIF) molecule inside one cavity of PAMAM dendrimer from molecular dynamic trajectory. (
,
) charts time of simulations against distance between center of mass of RIF molecules and dendrimer center of mass. (
) at neutral pH and (
) at low pH. This Figure was provided thanks to Reference [28].
2.1. Dendrimer as Drug Delivery Systems to Cancer Treatments
The different kinds of cancer that afflict the population are the leading cause of death worldwide. Despite the significant advances in medicine, there are still many challenges to be achieved in the treatment of cancer, to name a few, namely to decrease the side effects of some drugs [31][32], drug solubility improvement [33], drug-resistant cancer cell [34], and achieve a transport and targeted release of the drug [35][
]. Some of these advances focus on the use of dendritic nanoparticles as vehicles for the targeted transport of drugs against various types of cancer [36].
Studies about hepatic cancer have determined that asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) is specifically overexpressed on tumor cells, and shown high binding affinity with glycoproteins [37][38]. The above can be considered as an advantage because key parts of the glycoproteins can be obtained and grafted on the surface of nanoparticles (NP) to promote high-efficiency binding to hepatic tumor cells. N-acetylgalactosamine (NAcGal) ligands on a NP surface achieves selective intake into hepatic cancer cells [39][40][41]. Moreover, Kurivilla et al. synthesized G5-dendrimers containing NAcGal ligands tri-valent (NAcGal3) attached to the surface through a PEG linker and measured their ability to achieve hepatic cancer cells in comparison to mono-valent ligands [42] (
2).
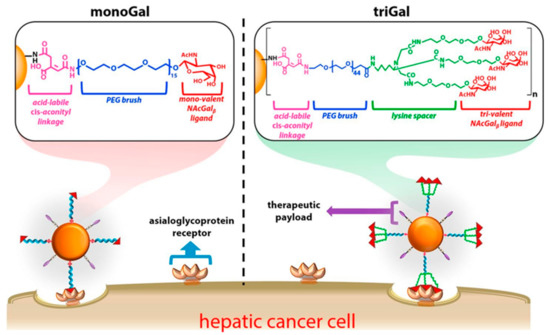
2 Schematic representation of G5-PAMAM dendrimer functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG brush) connecting to both nono-valent and tri-valent N-acetylgalactosamine (NAcGal), and folate as a linkage. This scheme was provided thanks to Reference [42].
Metallodendrimers based on ruthenium to incorporate metals into dendritic scaffolds has been synthetize (
3) and characterize [43]. Several complexes based on ruthenium are in clinical phases against cancer therapies, however some complexes have had cytotoxicity problems. Evaluations of IC50 for metallodendrimers, organometallic complexes of ruthenium (Rucp) and cisplatin (cisPt) (a anticancer drug approval by FDA) in several of the carcinogenic cell lines were performed. The IC50 values for the metallodendrimers were the lowest compared to Rucp and cisPt. These results demonstrate that a lower concentration of metallodendrimer is needed to achieve 50% inhibition of cancer cell growth compared to Rucp and cisPt.
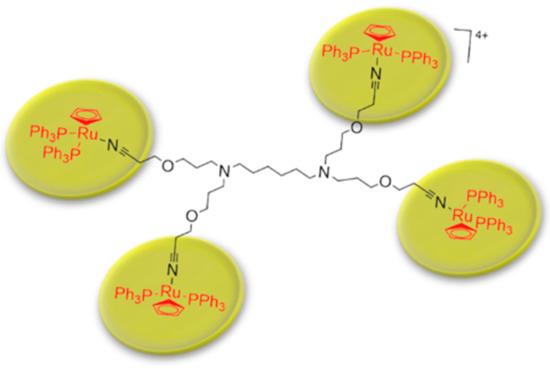
Schematic representation of metallodendrimer base on poly(alkylidenimine) dendrimer core containing nitrile groups and functionalized with [Ru(η
-C
H
)(PPh
)
Cl] compound. This scheme was provided thanks to Reference [43].
Several studies have shown that the direct administration of chemotherapeutic drugs for lung cancer significantly improves the exposure and residence of the drug in comparison with intravenous administration treatments. PEGylated polylysine dendrimers, conjugated to doxorubicin (DOX) to promote the controlled and prolonged exposure of lung-resident cancer to the cytotoxic drug, have been studied. The results show that PEGylated polylysine dendrimers have great potential as inhalable chemotherapeutic nanoformulations, improving the exposure of lung tumor to a cytotoxic drug [44]. Likewise, conjugates of DOX linked to PEGylated G4-polylysine dendrimer were studied to determine drug delivery kinetics, intravenous, and pulmonary pharmacokinetics in rats [45]. Cathepsin B-cleavable peptides were used to drug-linker since the extracellular and lysosomal expression of this enzyme is highly upregulated by cancer cells.
Cis-diamminodichloridoplatinum (II) (CDDP) is a anticancer drug used for the treatment of lung cancer. This drug intercalates into the cellular DNA, forming DNA adducts resulting in apoptosis [46]. A novel strategy chemotherapeutic combination for lung cancer was developed based on a folic acid (FA) conjugated polyamidoamine dendrimer. This formulation was proposed for co-delivery of siRNA against human antigen R and cis-diamine platinum (CDDP) to folate receptor-α (FRA) overexpressing (H1299) lung cancer cell [47] (
4). Studies reveal that folic acid-conjugated dendrimers generate considerable DNA damage and apoptosis cell death compared to non-functionalized nanoparticles with FA.
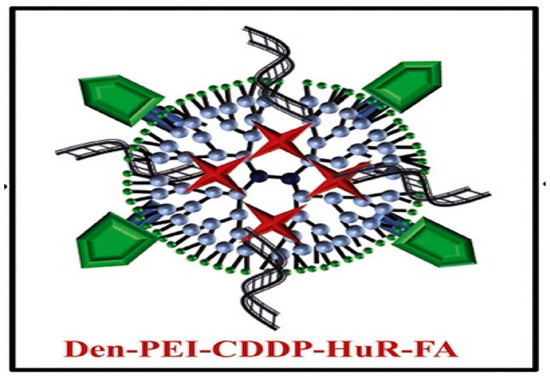
Therapeutic nanoformulation based on polyethyleneimine dendrimer functionalized with folic acid (FA), human antigen R (HuR), and cis-diamine platinum (CDDP). This scheme was provided thanks to Reference [47].
While positively charged dendrimers possess considerable cellular cytotoxicity, other strategies have been proposed to formulate dendritic nanoparticles. The formulation of dendrimers negatively charged on the surface has been proposed as a way to increase the viability of healthy tissues. Negatively charged poly(amido amine)-2,3-dimethylmaleic monoamine (PAMAM-DMA) dendrimers were prepared by Cao et al. [48], which possess the capacity to change their load in response to acid pH, present in a tumor environment. Low cytotoxicity in the normal/neutral environment was observed for negatively charged PAMAM-DMA dendrimers. Co-administration of DOX plus G5-PAMAM-DMA in mice bearing MCF-7 tumors enhanced the efficacy of tumor growth inhibition compared with the administration of free DOX.
Li et al. [49] has developed a novel and practical photothermal hydrogel, based on platinum nanoparticles encapsulated with dendrimer (DEPts) dextran. Photothermal hydrogel allowed repeating the photothermal therapy (PTT) and reduced the toxicity induced by long-term retention. The hydrogel represented an excellent photothermal effect and excellent biocompatibility. It was able to remain in tumors for days to allow repeated PTT, leading to complete tumor regression. Additionally, anti-Flt1 antibody-conjugated polyethylene glycol (PEG)-cored poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers improve the effectiveness of the gemcitabine against pancreatic cancer. Tissues, such as the liver and the bone marrow, which are known to have high vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–Flt1 pathway activity, were targeted by gemcitabine when delivered through anti-Flt1 antibody-conjugated PAMAM dendrimers [50]. The advantage of using chemotherapeutic agents complexed with dendrimers not only improve anticancer efficacy but also assist in the elimination of the tumor-induced myeloid cells.
Undoubtedly it can be said that transport systems for cancer drugs based on dendrimers are the most studied and published [51][52][53][54][55][56]. This high interest is due to its versatility to mold them to the need of the system under study. A large number of works every year are published on these drug nanocarriers.
2.2. Dendrimer as Drug Delivery Systems to Cardiovascular Treatments
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality around the world. CVDs include diseases to heart, vascular diseases of brain and diseases of blood vessels, and are responsible for over 17.3 million deaths per year [57]. This pathology is associated with the upregulation of inflammatory genes. Gene silencing using RNA interference is a technic to regulate gene expression in CVDs, but the lack of efficient delivery systems has prevented its correct application. An important hormonal system involved in CVDs is the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). Angiotensin II (Ang II), a peptide of eight amino acids regulates the main effects of RAAS [58]. Therefore, overexpression of Ang II can cause a series of complications that can lead to heart failure. Due to these reasons, the inhibition of Ang II activation is an objective within the therapies for CVDs [59]. Liu et al. formulated a nanocarrier to complex siRNA and a cell penetration peptide (CPP) that allows improving the internalization of complexed siRNA within cardiomyocytes [60]. PEG segment was included in the structure to reduce the PAMAM toxicity. The results display that CPP conjugated with dendrimer was non-toxic and efficient to the siRNA delivery system. Bioinformatic analysis showed that the molar ratio of union between Ang-(1-7) and PAMAM-OH dendrimer as 2:1. Molecular dynamics simulation analysis revealed that the ability of neutral PAMAM-OH to protect Ang-(1-7) and form stable complexes. In short, the complex Ang-(1-7)/PAMAM-OH is an efficient administration method for Ang-(1-7), since it improves the anti-atrophic activity of this peptide in skeletal [61].
Myocardial ischemia can be addressed through gene therapy of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to promote therapeutic angiogenesis. However, the unregulated expression of VEGF and the use of viral vectors have stopped angiogenic therapy. Won et al. developed and evaluated a bioreducible polymer dendrimer-type, PAM-ABP to conjugate with a VEGF plasmid, pb-SP-ODD-VEGF [62]. This complex base on a dendrimer shows great potential as a therapy for the treatment of myocardial ischemia and infarction.
3. Conclusions
Dendrimers are multifunctional macromolecules that can be used in several fields. The nano-size, tunable surface, interaction with cell membranes, interaction with drugs, interior cavities, among other features, make dendrimers excellent candidates for drug delivery systems (DDS). Due to their chemical versatility, dendrimers have been applied to the transport of various types of bioactive molecules, namely drug-type molecules and genes. In the last decade, the use of dendrimer as DDS has been reported approximately one thousand publications, according to the WOS database. Mainly, the highest number of researches in the area of DDS using dendrimers has been for cancer diseases. A large number of studies reported for lung cancer involving dendrimers have been reported. In past years, the DDS for lung cancer has combined strategies, conjugating drugs in dendrimers, as well as gene agents for cell recognition. In addition, dendrimers are being studied as DDS in cardiovascular diseases. Due to low bioavailability and low cellular transfection of some bioactive molecules, formulations have been prepared to inhibit agents that affect cardiovascular pathologies, e.g., angiotensin has been conjugated with dendrimers to form stable complexes [63]. The controlled release of therapeutic agents and decreasing of side effects are challenges that are continuously being addressed by researchers. In conclusion, dendrimers are amazing macromolecular platforms that can be modified depending on the chemical nature of the drug that will be transported and also the target tissue. The physicochemical properties of dendrimers are important to study to understand the transport and release of drugs, as well as internalization and intracellular traffic.
References
- Servati, N.; Priano, J.; Vilar, J.; Schiel, J. A cool side effect of valproic acid administration: Single dose-induced hypothermia. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 2129.e3–2129.e4.
- Mello-Andrade, F.; Cardoso, C.G.; E Silva, C.R.; Chen-Chen, L.; De Melo-Reis, P.R.; De Lima, A.P.; Oliveira, R.; Ferraz, I.B.M.; Grisolia, C.K.; Almeida, M.A.P.; et al. Acute toxic effects of ruthenium (II)/amino acid/diphosphine complexes on Swiss mice and zebrafish embryos. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1082–1092.
- Tian, F.; Lin, X.; Valle, R.P.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Gu, N. Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimer as a Respiratory Nanocarrier: Insights from Experiments and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5364–5371.
- Lei, J.; Rosenzweig, J.M.; Mishra, M.K.; AlShehri, W.; Brancusi, F.; McLane, M.; Almalki, A.; Bahabry, R.; Arif, H.; Rozzah, R.; et al. Maternal dendrimer-based therapy for inflammation-induced preterm birth and perinatal brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6106.
- Khan, A.R.; Liu, M.; Khan, M.W.; Zhai, G. Progress in brain targeting drug delivery system by nasal route. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 364–389.
- Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Wen, L.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Viennois, E.; Merlin, D. A Hyaluronidase-Responsive Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System for Targeting Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7208–7218.
- Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.; Qian, Z. Microneedles-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1581–1597.
- Printz, C. Researchers develop drug delivery system to slow and control tumors. Cancer 2016, 122, 3751.
- Turato, C.; Balasso, A.; Carloni, V.; Tiribelli, C.; Mastrotto, F.; Mazzocca, A.; Pontisso, P. New molecular targets for functionalized nanosized drug delivery systems in personalized therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 184–197.
- Wang, F.; Porter, M.; Konstantopoulos, A.; Zhang, P.; Cui, H. Preclinical development of drug delivery systems for paclitaxel-based cancer chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 100–118.
- Selvakumaran, S.; Muhamad, I.I. Evaluation of kappa carrageenan as potential carrier for floating drug delivery system: Effect of cross linker. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 323–331.
- Saini, K.; Prabhuraj, R.S.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. Development of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles of Tunable Pore Diameter for Superior Gemcitabine Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 3084–3096.
- Miguel Espinoza, S.; Patil, H.I.; San Martin Martinez, E.; Casanas Pimentel, R.; Ige, P.P. Poly-epsilon-caprolactone (PCL), a promising polymer for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: Focus on nanomedicine in cancer. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 85–126.
- Halder, S.; Ogino, M.; Seto, Y.; Sato, H.; Onoue, S. Improved biopharmaceutical properties of carvedilol employing α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-based self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1838–1844.
- Sala, M.; Diab, R.; Elaïssari, A.; Fessi, H. Lipid nanocarriers as skin drug delivery systems: Properties, mechanisms of skin interactions and medical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 1–17.
- Patty, P.J.; Wattimena, S.C. lipid vesicles: physical properties and application as nanocarriers in drug delivery systems. Int. J. Health Med. Curr. Res. 2017, 2, 716–722.
- Vergara-Jaque, A.; Comer, J.; Monsalve, L.; González-Nilo, F.D.; Sandoval, C. Computationally Efficient Methodology for Atomic-Level Characterization of Dendrimer–Drug Complexes: A Comparison of Amine- and Acetyl-Terminated PAMAM. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6801–6813.
- Tomalia, D.A.; Fréchet, J.M.J. Discovery of dendrimers and dendritic polymers: A brief historical perspective. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 2719–2728.
- Lee, C.C.; A Mackay, J.; Fréchet, J.M.J.; Szoka, F.C. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517–1526.
- Majoral, J.-P.; Caminade, A.-M. Dendrimers containing heteroatoms (si, p, B, ge, or bi). Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 845–880.
- LaVan, M.; Knipp, G. Effects of Dendrimer-Like Biopolymers on Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions and Drug Permeability Across Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2459–2471.
- Falanga, A.; Lombardi, L.; Tarallo, R.; Franci, G.; Perillo, E.; Palomba, L.; Galdiero, M.; Pontoni, D.; Fragneto, G.; Weck, M.; et al. The intriguing journey of gH625-dendrimers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9106–9114.
- Chan, C.-O.; Jing, J.; Xiao, W.; Tan, Z.; Lv, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, S. Enhanced Intestinal Permeability of Bufalin by a Novel Bufalin-Peptide-Dendrimer Inclusion through Caco-2 Cell Monolayer. Molecules 2017, 22, 2088.
- Qi, X.; Qin, J.; Fan, Y.; Qin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xiaole, Q.; Jiayi, Q.; Yuchao, F.; Xiaoxue, Q.; et al. Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Modified Polyamidoamine Dendrimer Enables Progressive Drug Targeting of Tumors via pH-Sensitive Charge Inversion. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 667–678.
- Otto, D.P.; De Villiers, M.M. All-atomistic molecular dynamics (AA-MD) studies and pharmacokinetic performance of PAMAM-dendrimer-furosemide delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 545–555.
- Mehrizi, T.Z.; Ardestani, M.S.; Khamesipour, A.; Hoseini, M.H.M.; Mosaffa, N.; Anissian, A.; Ramezani, A. Reduction toxicity of Amphotericin B through loading into a novel nanoformulation of anionic linear globular dendrimer for improve treatment of leishmania major. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 125.
- Burman, W.J.; Gallicano, K.; Peloquin, C.; Burman, W.J. Comparative Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Rifamycin Antibacterials. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 327–341.
- Bellini, R.G.; Guimarães, A.P.; Pacheco, M.A.; Dias, D.M.; Furtado, V.R.; De Alencastro, R.B.; Horta, B.A. Association of the anti-tuberculosis drug rifampicin with a PAMAM dendrimer. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 60, 34–42.
- Nasr, M.; Najlah, M.; D’Emanuele, A.; Elhissi, A. PAMAM dendrimers as aerosol drug nanocarriers for pulmonary delivery via nebulization. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 242–250.
- Dong, Z.; Hamid, K.A.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Polyamidoamine Dendrimers Can Improve the Pulmonary Absorption of Insulin and Calcitonin in Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1866–1878.
- Sharma, A.K.; Gothwal, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Alsaab, H.; Iyer, A.K.; Gupta, U. Dendrimer nanoarchitectures for cancer diagnosis and anticancer drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 314–326.
- Carrasco-Sanchez, V.; Vergara-Jaque, A.; Zuñiga, M.; Comer, J.; John, A.; Nachtigall, F.M.; Valdés, O.; Duran-Lara, E.F.; Sandoval, C.; Santos, L.S. In situ and in silico evaluation of amine- and folate-terminated dendrimers as nanocarriers of anesthetics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 73, 250–257.
- Choudhary, S.; Gupta, L.; Rani, S.; Dave, K.; Gupta, U. Impact of Dendrimers on Solubility of Hydrophobic Drug Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 17–23.
- Saw, P.E.; Park, J.; Jon, S.; Farokhzad, O.C. A drug-delivery strategy for overcoming drug resistance in breast cancer through targeting of oncofetal fibronectin. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Boil. Med. 2017, 13, 713–722.
- Sherje, A.P.; Jadhav, M.; Dravyakar, B.R.; Kadam, D. Dendrimers: A versatile nanocarrier for drug delivery and targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 707–720.
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, D.; Xu, X.; Gu, Z. Engineering Anticancer Amphipathic Peptide-Dendronized Compounds for Highly-Efficient Plasma/Organelle Membrane Perturbation and Multidrug Resistance Reversal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30952–30962.
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Diakur, J.; Wiebe, L. Targeted Delivery of Macromolecular Drugs: Asialoglycoprotein Receptor (ASGPR) Expression by Selected Hepatoma Cell Lines used in Antiviral Drug Development. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 299–302.
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Guo, R.; Wen, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Shen, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; et al. Lactobionic Acid-Modified Dendrimer-Entrapped Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Computed Tomography Imaging of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6944–6953.
- Kuruvilla, S.P.; Tiruchinapally, G.; Elazzouny, M.; Elsayed, M.E.H. N-Acetylgalactosamine-Targeted Delivery of Dendrimer-Doxorubicin Conjugates Influences Doxorubicin Cytotoxicity and Metabolic Profile in Hepatic Cancer Cells. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601046.
- Medina, S.H.; Chevliakov, M.V.; Tiruchinapally, G.; Durmaz, Y.Y.; Kuruvilla, S.P.; Elsayed, M.E. Enzyme-activated nanoconjugates for tunable release of doxorubicin in hepatic cancer cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4655–4666.
- Medina, S.H.; Tekumalla, V.; Chevliakov, M.V.; Shewach, D.S.; Ensminger, W.D.; El-Sayed, M.E. N-acetylgalactosamine-functionalized dendrimers as hepatic cancer cell-targeted carriers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4118–4129.
- Kuruvilla, S.P.; Tiruchinapally, G.; Kaushal, N.; Elsayed, M.E. Effect of N-acetylgalactosamine ligand valency on targeting dendrimers to hepatic cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 27–36.
- Gouveia, M.; Figueira, J.; Jardim, M.; Castro, R.; Tomás, H.; Rissanen, K.; Rodrigues, J. Poly(alkylidenimine) Dendrimers Functionalized with the Organometallic Moiety [Ru(η5-C5H5) (PPh3)2]+ as Promising Drugs Against Cisplatin-Resistant Cancer Cells and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. 2018, 23, 1471.
- Kaminskas, L.M.; McLeod, V.M.; Ryan, G.M.; Kelly, B.D.; Haynes, J.M.; Williamson, M.; Thienthong, N.; Owen, D.J.; Porter, C.J. Pulmonary administration of a doxorubicin-conjugated dendrimer enhances drug exposure to lung metastases and improves cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2014, 183, 18–26.
- Leong, N.J.; Mehta, D.; McLeod, V.M.; Kelly, B.D.; Pathak, R.; Owen, D.J.; Kaminskas, L.M.; Porter, C.J. Doxorubicin Conjugation and Drug Linker Chemistry Alter the Intravenous and Pulmonary Pharmacokinetics of a PEGylated Generation 4 Polylysine Dendrimer in Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2509–2513.
- Shi, S.; Tan, P.; Yan, B.; Gao, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Ma, Z. ER stress and autophagy are involved in the apoptosis induced by cisplatin in human lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2606–2614.
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Chemo-biologic combinatorial drug delivery using folate receptor-targeted dendrimer nanoparticles for lung cancer treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 373–384.
- Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, K.; Yan, H. Co-administration of a charge-conversional dendrimer enhances antitumor efficacy of conventional chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 371–377.
- Li, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y. A degradable hydrogel formed by dendrimer-encapsulated platinum nanoparticles and oxidized dextran for repeated photothermal cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2474–2480.
- Yoyen-Ermis, D.; Ozturk-Atar, K.; Kursunel, M.A.; Aydin, C.; Ozkazanç, D.; Gurbuz, M.U.; Uner, A.; Tulu, M.; Calis, S.; Esendagli, G.; et al. Tumor-Induced Myeloid Cells Are Reduced by Gemcitabine-Loaded PAMAM Dendrimers Decorated with Anti-Flt1 Antibody. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1526–1533.
- Zhong, Q. Co-Spray Dried Mannitol/Poly(amidoamine)-Doxorubicin Dry-Powder Inhaler Formulations for Lung Adenocarcinoma: Morphology, In Vitro Evaluation, and Aerodynamic Performance. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 531–540.
- Lu, Y.; Han, S.; Zheng, H.; Ma, R.; Ping, Y.; Zou, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, F. A novel RGDyC/PEG co-modified PAMAM dendrimer-loaded arsenic trioxide of glioma targeting delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5937–5952.
- Yamashita, S.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Bone-targeting dendrimer for the delivery of methotrexate and treatment of bone metastasis. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 818–828.
- Ma, J.; Yao, H. Dendrimer-paclitaxel complexes for efficient treatment in ovarian cancer: study on OVCAR-3 and HEK293T cells. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 219–225.
- Lin, L.; Fan, Y.; Gao, F.; Jin, L.; Li, D.; Sun, W.; Li, F.; Qin, P.; Shi, Q.; Shi, X.; et al. UTMD-Promoted Co-Delivery of Gemcitabine and miR-21 Inhibitor by Dendrimer-Entrapped Gold Nanoparticles for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1923–1939.
- Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, L.; Sahu, H.; Qayum, A.; Singh, S.K.; Nakhate, K.T.; Ajazuddin; Gupta, U. Chitosan Engineered PAMAM Dendrimers as Nanoconstructs for the Enhanced Anti-Cancer Potential and Improved In vivo Brain Pharmacokinetics of Temozolomide. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 9.
- Mendis, S.; Puska, P.; Norrving, B. World Health Organization, Federation WH, World Stroke Organization. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Dzau, V.J. Theodore Cooper Lecture: Tissue angiotensin and pathobiology of vascular disease: A unifying hypothesis. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1047–1052.
- Ma, T.K.; Kam, K.K.; Yan, B.P.; Lam, Y.-Y. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockade for cardiovascular diseases: current status. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1273–1292.
- Liu, J.; Gu, C.; Cabigas, E.B.; Pendergrass, K.D.; Brown, M.E.; Luo, Y.; Davis, M.E. Functionalized dendrimer-based delivery of angiotensin type 1 receptor siRNA for preserving cardiac function following infarction. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3729–3736.
- Márquez-Miranda, V.; Abrigo, J.; Rivera, J.C.; Araya-Durán, I.; Aravena, J.; Simon, F.; Pacheco, N.; González-Nilo, F.D.; Cabello-Verrugio, C. The complex of PAMAM-OH dendrimer with Angiotensin (1–7) prevented the disuse-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1985–1999.
- Won, Y.-W.; McGinn, A.N.; Lee, M.; Nam, K.; Bull, D.A.; Kim, S.W. Post-translational regulation of a hypoxia-responsive VEGF plasmid for the treatment of myocardial ischemia. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6229–6238.
- Akhtar, S.; El-Hashim, A.Z.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Attur, S.; Benter, I.F. Naked Polyamidoamine Polymers Intrinsically Inhibit Angiotensin II-Mediated EGFR and ErbB2 Transactivation in a Dendrimer Generation- and Surface Chemistry-Dependent Manner. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1575–1586.
