Separation is a critical process to isolate a particular compound, whether it is a natural product or a synthetic product. Studies of a compound’s characteristics and elucidation structure provides reliable results for pure compounds because there is no interference from other compounds. The primary source of difficulty in a separation process is the high similarity between two or more compounds, such as racemic and homologous mixtures. Liquid chromatography has proven to be an effective solution to those problems. The key to liquid chromatography separation is a sustainable retention and elution process. Stationary phases are essential for separating compounds in liquid chromatography. Various liquid chromatography columns of both preparative and quantitative types have been used and continue to develop. This revisewarch will discuss the separation mechanism in liquid chromatography.
- liquid chromatography
- stationary phase
- separation mechanism
1. Introduction
Separation is a critical process to isolate a particular compound, whether it is a natural product or a synthetic product. Studies of a compound’s characteristics and elucidation structure provides reliable results for pure compounds because there is no interference from other compounds. The primary source of difficulty in a separation process is the high similarity between two or more compounds, such as racemic and homologous mixtures. Liquid chromatography has proven to be an effective solution to those problems. The key to liquid chromatography separation is a sustainable retention and elution process. Stationary phases essential for separating compounds in liquid chromatography. Various liquid chromatography columns of both preparative and quantitative types have been used and continue to develop. For this reason, multiple studies and publications related to liquid chromatography can be found and accessed easily.2. The Principle of Separation of Compounds in Liquid Chromatography
Separation using liquid chromatography is possible because of the different interactions between the compounds present in the sample with the stationary and the mobile phases in the liquid chromatography system (Figure 1). Stationary phases can be developed to enable compound separation based on several modes, such as (A) differences in the affinity to the compounds, (B) differences in the strength of electrostatic forces with the target compounds, and (C) size differences of target compounds. One or more of these modes of interaction will result in compound separation using liquid chromatography. Choosing the appropriate columns, whether commercial or under development, could be somewhat confusing for a user. Understanding the modes of interaction will be helpful to assist users in selecting the appropriate columns for a particular type of analyte.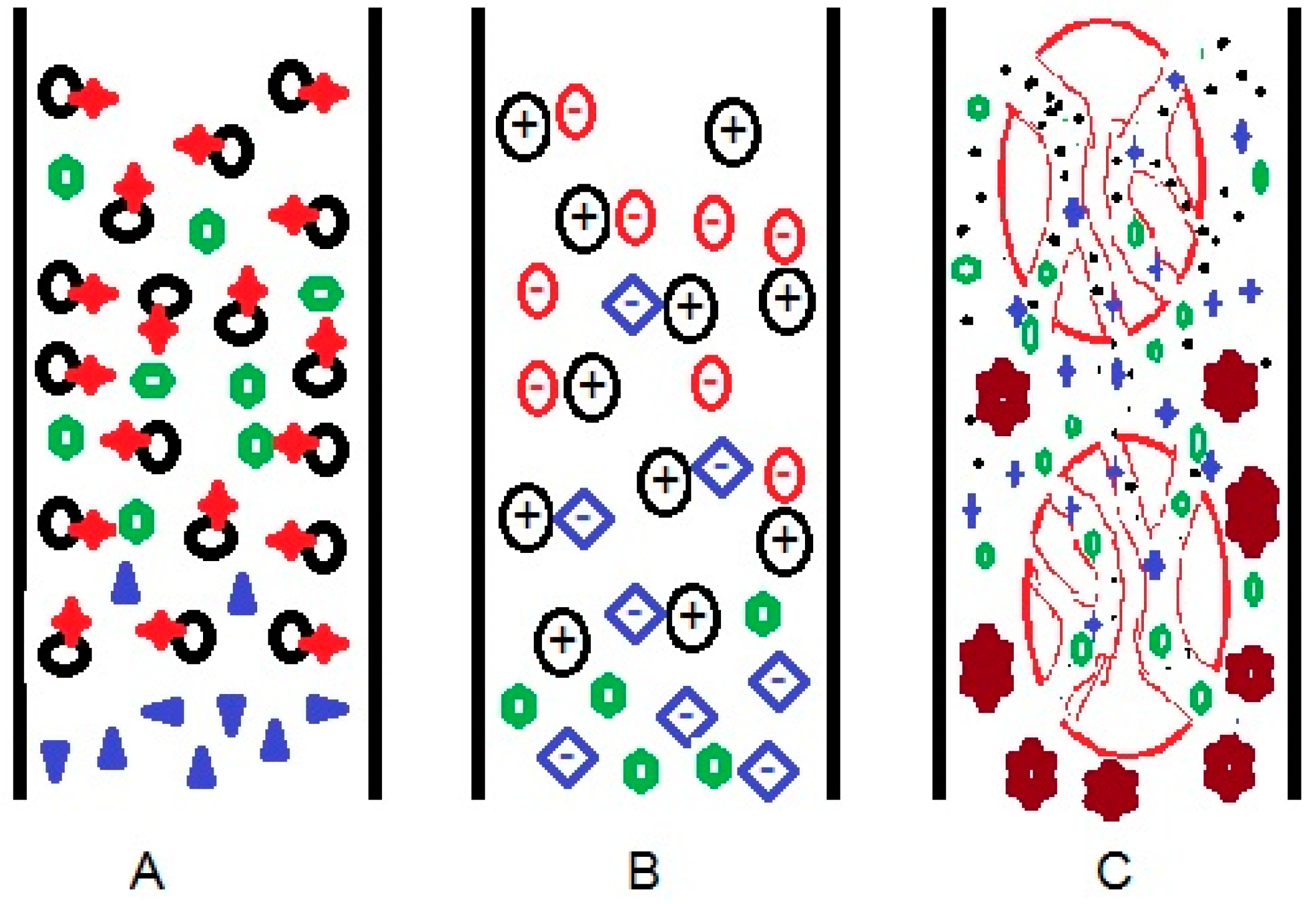 Figure 1. Scheme of physical interactions between column and target molecules, based on (A) affinity, (B) electrostatic forces, and (C) size difference in liquid chromatography systems.
Figure 1. Scheme of physical interactions between column and target molecules, based on (A) affinity, (B) electrostatic forces, and (C) size difference in liquid chromatography systems.| Mode of Liquid Chromatography | Separation Principle | Stationary Phase | Analyte | Mobile Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse-phase chromatography | Affinity | Silica modified with octadecyl acrylate and 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine [38] | PAHs | Methanol |
| Affinity | Silica modified with octadecyl acrylate and N-methylmaleimide [39] | PAHs and tocopherols | Mixed of methanol and water | |
| Affinity | Silica modified with N-Boc-phenylalanine and cyclohexylamine [40] | Phytohormones | Mixed of phosphate buffer and acetonitrile | |
| Affinity | Zr6O4(OH)4 MOF modified with 2-amino-terephthalic acid or 4,4′-biphenyl-dicarboxylic acid [41] | PAHs and aromatics compound | Mixed of methanol and water | |
| Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography | Ionic | Silica modified with (2-(methacryloyloxy)-ethyl)dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl)ammonium hydroxide or 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine [42] | Mixed of toluene, formamide, dimethylformamide, and thiourea | Mixed of water and acetonitrile |
| Affinity | Amino silica modified with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and acrylamide derivatives [34] | Nucleosides, organic acids, and β-agonists | Mixed of acetonitrile and ammonium formate solution | |
| Affinity | Silica modified with EGDMA and maltose [32] | Nucleobases and nucleotides | Mixed of water and acetonitrile | |
| Affinity | Silica modified with vinyl silsesquioxane and dithiothreitol [43] | |||
| Ionic and affinity | Silica modified with pyrazinedicarboxylic anhydrate [44] | Oligosaccharides, alkaloid, and organic acid groups | Mixed of acetonitrile and ammonium formate solution | |
| Mixed-mode chromatography | Ionic and affinity | Silica modified with 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine [35] | Protein and lysozyme | Mixed of acetonitrile, ammonium formate solution, KH2PO4 solution, NaCl solution |
| Ionic and affinity | Silica modified with octadecyl and diol groups [8] | Aristolochic acid and derivatives | Mixed of formic acid and acetonitrile | |
| Ionic and affinity | Silica modified with glutathione [26] | Protein | Mixed of water, formic acid, acetonitrile | |
| Ionic and affinity | poly(12-methacryloyl dodecylphosphatidic acid-co- ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) [45] | Ketone aromatic, phenol and derivatives, small organic compounds | Mixed of ammonium formate solution and acetonitrile | |
| Affinity | Amino silica modified with octadecyl and carbon dots [31] | PAHs, nucleosides, and nucleobases | Mixed of water and methanol, acetonitrile, and ammonium acetate solution | |
| Affinity chromatography | Ionic and affinity | Agarose modified with 2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole [46] | Protein | NaOH solution |
| Ionic and affinity | Sepharose modified with ligand complex [3] | Protein with histidine | Mixed of Tris buffer, sodium chloride, and imidazole | |
| Ionic and affinity | Silica modified with N-methylimidazolium ionic liquid [28] | Protein | Mixed of acetonitrile, trifluoroacetic acid, NaClO4 solution, KH2PO4 solution, and NaCl solution | |
| Ionic and affinity | Amino silica modified with glutaraldehyde [47] | Protein | Phosphate buffer | |
| Ionic chromatography | Ionic | Bentonite modified with chitosan and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) [11] | Cr(III) and Cr(VI) solution | Nitric acid solution for Cr(III) and ammonia solution for Cr(VI) |
| Ionic | Polystyrene-methacrylate derivatives modified with poly(amidoamine) [10] | Small anions like nitrate, sulfates, bromide, etc. | NaOH solution | |
| Chiral chromatography | Size and affinity | Polysaccharide modified with 3-chloro-4-methylphenylcarbamate [48] | Paroxetine hydrochloride groups | Mixed of supercritical CO2, methanol, and ammonium acetate solution |
| Affinity | Isopropylcarbamate cyclofructan 6 groups [49] | Methionine groups | Mixed of methanol, acetonitrile, acetic acid, and triethylamine | |
| Size | Silica modified with 3,3′- phenyl-1,1′-binaphthyl-18-crown-6-ether [50] | Amino acids and peptides | Mixed of perchloric acid solution, acetonitrile, and methanol | |
| Affinity | Poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) coated with chitosan [9] | Benzoin | Mixed of water and acetonitrile | |
| Electrochromatography | Size and ionic | Poly(POSS-co-META-co-DMMSA) [18] | Benzoic acid, nucleosides, bases, glycopeptides | Mixed of phosphate buffer, triethylamine, and acetonitrile |
| Affinity | Silica modified with a metal-organic framework (MOF) [20] | Benzenes and derivatives | Mixed of phosphate buffer and acetonitrile | |
| Size exclusion chromatography | Size | Poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) [51] | Protein | Mixed of water and acetonitrile |
References
- Zeng, R.; Jin, B.-K.; Yang, Z.-H.; Guan, R.; Quan, C. Preparation of a modified crosslinked chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blended affinity membrane for purification of His-tagged protein. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47347.
- Eldin, M.S.M.; Rahman, S.A.; El Fawal, G.F. Novel immobilized Cu2+-aminated poly (methyl methacrylate) grafted cellophane membranes for affinity separation of His-Tag chitinase. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 135–151.
- Riguero, V.; Clifford, R.; Dawley, M.; Dickson, M.; Gastfriend, B.; Thompson, C.; Wang, S.-C.; O’Connor, E. Immobilized metal affinity chromatography optimization for poly-histidine tagged proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1629, 461505.
- Huberman, L.B.; Wu, V.W.; Kowbel, D.J.; Lee, J.; Daum, C.; Grigoriev, I.V.; O’Malley, R.C.; Glass, N.L. DNA affinity purification sequencing and transcriptional profiling reveal new aspects of nitrogen regulation in a filamentous fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2009501118.
- Hovhannisyan, R.H.; Carstens, R.P. Affinity chromatography using 2′ fluoro-substituted RNAs for detection of RNA-protein interactions in RNase-rich or RNase-treated extracts. BioTechniques 2009, 46, 95–98.
- Busby, K.N.; Fulzele, A.; Zhang, D.; Bennett, E.J.; Devaraj, N.K. Enzymatic RNA Biotinylation for Affinity Purification and Identification of RNA–Protein Interactions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2247–2258.
- Moravcová, D.; Planeta, J. Monolithic Silica Capillary Columns with Improved Retention and Selectivity for Amino Acids. Separations 2018, 5, 48.
- Wang, Q.; Ye, M.; Xu, L.; Shi, Z.-G. A reversed-phase/hydrophilic interaction mixed-mode C18-Diol stationary phase for multiple applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 182–190.
- Cong, H.; Xing, J.; Ding, X.; Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Yu, B. Preparation of porous sulfonated poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) microspheres and its application in hydrophilic and chiral separation. Talanta 2020, 210, 120586.
- Guo, D.; Lou, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y. Polystyrene-divinylbenzene-glycidyl methacrylate stationary phase grafted with poly (amidoamine) dendrimers for ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1456, 113–122.
- Amran, M.B.; Aminah, S.; Rusli, H.; Buchari, B. Bentonite-based functional material as preconcentration system for determination of chromium species in water by flow injection analysis technique. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04051.
- Zhang, R.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhou, W.; Ma, G.; Su, Z. Hydrophilic modification gigaporous resins with poly(ethylenimine) for high-throughput proteins ion-exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1343, 109–118.
- Bouvier, E.S.; Koza, S.M. Advances in size-exclusion separations of proteins and polymers by UHPLC. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 85–94.
- Sathitnaitham, S.; Suttangkakul, A.; Wonnapinij, P.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Vuttipongchaikij, S. Gel-permeation chromatography–enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method for systematic mass distribution profiling of plant cell wall matrix polysaccharides. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1776–1790.
- Perez-Moral, N.; Plankeele, J.-M.; Domoney, C.; Warren, F.J. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-size exclusion chromatography (UPLC-SEC) as an efficient tool for the rapid and highly informative characterisation of biopolymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 422–426.
- Kothencz, R.; Nagy, R.; Bartha, L.; Tóth, J.; Vágó, Á. Analysis of the interaction between polymer and surfactant in aqueous solutions for chemical-enhanced oil recovery. Part. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 887–890.
- Janco, M.; Iv, J.N.A.; Bouvier, E.S.P.; Morrison, D. Ultra-high performance size-exclusion chromatography of synthetic polymers: Demonstration of capability. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2718–2727.
- Huang, T.; Zhang, W.; Lei, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, C.; Wu, X. Rapid polymerization of polyhedral oligomeric siloxane-based zwitterionic sulfoalkylbetaine monolithic column in ionic liquid for hydrophilic interaction capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1659, 462651.
- Zong, R.; Wang, X.; Yin, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Xiang, Y.; Ye, N. Capillary coated with three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for separation of fluoroquinolones by open-tubular capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1656, 462549.
- Ji, B.; Yi, G.; Gui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Long, W.; You, M.; Xia, Z.; Fu, Q. High-Efficiency and Versatile Approach To Fabricate Diverse Metal–Organic Framework Coatings on a Support Surface as Stationary Phases for Electrochromatographic Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 41075–41083.
- Qiao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Shan, Y.; Dou, A.; Shi, X.; Xu, G. A novel surface-confined glucaminium-based ionic liquid stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/anion-exchange mixed-mode chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1360, 240–247.
- Hosseini, E.S.; Heydar, K.T. Preparation of two amide-bonded stationary phases and comparative evaluation under mixed-mode chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2888–2897.
- Ray, S.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H. Chromatographic evaluation of a newly designed peptide-silica stationary phase in reverse phase liquid chromatography and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography: Mixed mode behavior. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1266, 43–52.
- Hosseini, E.S.; Heydar, K.T. Silica modification with 9-methylacridine and 9-undecylacridine as mixed-mode stationary phases in HPLC. Talanta 2021, 221, 121445.
- Sun, M.; Feng, J.; Luo, C.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S. Benzimidazole modified silica as a novel reversed-phase and anion-exchange mixed-mode stationary phase for HPLC. Talanta 2013, 105, 135–141.
- Shen, A.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Wei, J.; Guo, Z.; Liang, X. Glutathione-based zwitterionic stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/cation-exchange mixed-mode chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 63–69.
- Wei, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. A new reversed-phase/strong anion-exchange mixed-mode stationary phase based on polar-copolymerized approach and its application in the enrichment of aristolochic acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1246, 129–136.
- Bai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Zhao, Q. Protein separation using a novel silica-based RPLC/IEC mixed-mode stationary phase modified with N-methylimidazolium ionic liquid. Talanta 2018, 185, 89–97.
- Gao, J.; Luo, G.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H. A new strategy for the preparation of mixed-mode chromatographic stationary phases based on modified dialdehyde cellulose. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460885.
- Hu, K.; Feng, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, A.; Zhang, S. Development of a V-shape bis(tetraoxacalixarenetriazine) stationary phase for High performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2014, 130, 63–70.
- Wu, Q.; Hou, X.; Lv, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H. Synthesis of octadecylamine-derived carbon dots and application in reversed phase/hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1656, 462548.
- Chu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W. Preparation and evaluation of maltose modified polymer-silica composite based on cross-linked poly glycidyl methacrylate as high performance liquid chromatography stationary phase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1036, 179–186.
- Wu, Q.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Lv, H. Amphipathic carbon quantum dots-functionalized silica stationary phase for reversed phase/hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta 2021, 226, 122148.
- Bo, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Jia, Z.; Dai, X.; Gong, B. Grafting copolymer brushes on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes silsesquioxane-decorated silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1659, 462627.
- Xiong, C.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yuan, C.; Wang, L. Preparation and evaluation of a hydrophilic interaction and cation-exchange chromatography stationary phase modified with 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1546, 56–65.
- Yu, J.; Wey, M.; Firooz, S.K.; Armstrong, D.W. Ionizable Cyclofructan 6-Based Stationary Phases for Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Using Superficially Porous Particles. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 821–832.
- Aral, T.; Aral, H.; Ziyadanoğulları, B.; Ziyadanoğulları, R. Synthesis of a mixed-model stationary phase derived from glutamine for HPLC separation of structurally different biologically active compounds: HILIC and reversed-phase applications. Talanta 2015, 131, 64–73.
- Mallik, A.K.; Noguchi, H.; Han, Y.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H. Enhancement of Thermal Stability and Selectivity by Introducing Aminotriazine Comonomer to Poly(Octadecyl Acrylate)-Grafted Silica as Chromatography Matrix. Separations 2018, 5, 15.
- Mallik, A.K.; Noguchi, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H. Facile preparation of an alternating copolymer-based high molecular shape-selective organic phase for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1555, 53–61.
- Aral, H.; Aral, T.; Ziyadanoğulları, B.; Ziyadanoğulları, R. Development of a novel amide-silica stationary phase for the reversed-phase HPLC separation of different classes of phytohormones. Talanta 2013, 116, 155–163.
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, C.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, F. Preparation, characterization, and performance evaluation of UiO-66 analogues as stationary phase in HPLC for the separation of substituted benzenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178513.
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Geng, H.; Yang, B. A polymer-based zwitterionic stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta 2020, 26, 120927.
- Lin, H.; Ou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Wu, M.; Zou, H. Facile Preparation of Zwitterionic Organic-Silica Hybrid Monolithic Capillary Column with an Improved “One-Pot” Approach for Hydrophilic-Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC). Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2721–2728.
- Jin, G.; Ding, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, D.; Guo, Z.; Liang, X. Synthesis and chromatographic evaluation of pyrazinedicarboxylic anhydride bonded stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461825.
- Peng, K.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Xia, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, F. Phosphatidic acid-functionalized monolithic stationary phase for reversed-phase/cation-exchange mixed mode chromatography. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100891–100898.
- Lu, H.-L.; Lin, D.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Yao, S.-J. Evaluation on adsorption selectivity of immunoglobulin G with 2-mercapto-1-methyl-imidazole-based hydrophobic charge-induction resins. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 119, 34–41.
- Hou, Y.; Lu, J.; Wei, D.; Lv, Y.; He, H.; Wang, C.; He, L. Establishment of substance P modified affinity chromatography for specific detection and enrichment of Mas-related G protein–coupled receptor X2. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1659, 462633.
- Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zuo, L.; Ma, X.; Shan, G. Separation of chiral and achiral impurities in paroxetine hydrochloride in a single run using supercritical fluid chromatography with a polysaccharide stationary phase. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 208, 114458.
- Hroboňová, K.; Moravčík, J.; Lehotay, J.; Armstrong, D.W. Determination of methionine enantiomers by HPLC on the cyclofructan chiral stationary phase. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 4577–4582.
- Kawamura, I.; Mijiddorj, B.; Kayano, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Ueda, K.; Sato, H. Separation of D-amino acid-containing peptide phenylseptin using 3,3′-phenyl-1,1′-binaphthyl-18-crown-6-ether columns. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140429.
- Sun, X.; Li, J.; Xu, L. Synthesis of penetrable poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) microsphere and its HPLC application in protein separation. Talanta 2018, 185, 182–190.
