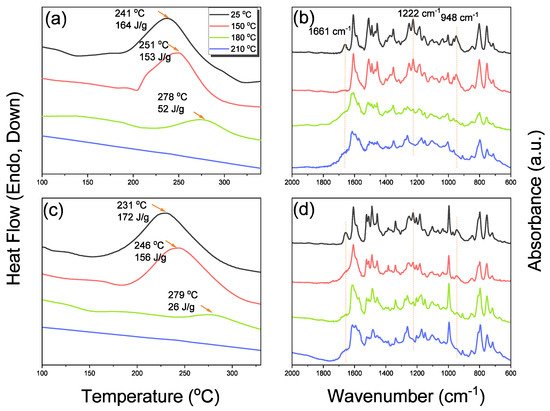
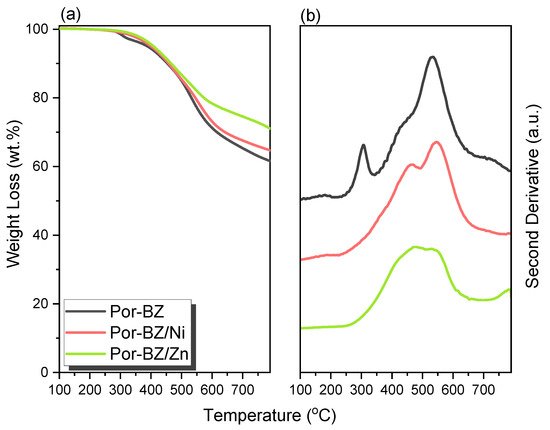
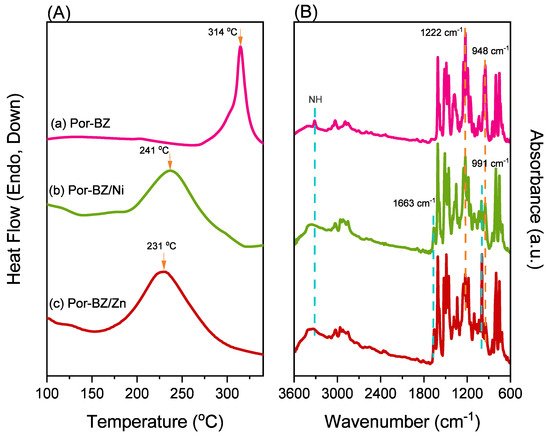
New porphyrin-functionalized benzoxazine (Por-BZ) in high purity and yield was synthesized in this study based on 1H and 13C NMR and FTIR spectroscopic analyses through the reduction of Schiff base formed from tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin (TAPP) and salicylaldehyde and the subsequent reaction with CH2O. Thermal properties of the product formed through ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of Por-BZ were measured using DSC, TGA and FTIR spectroscopy. Because of the rigid structure of the porphyrin moiety appended to the benzoxazine unit, the temperature required for ROP (314 °C) was higher than the typical Pa-type benzoxazine monomer (ca. 260 °C); furthermore, poly(Por-BZ) possessed a high thermal decomposition temperature (Td10 = 478 °C) and char yield (66 wt%) after thermal polymerization at 240 °C. An investigation of the thermal and luminescence properties of metal–porphyrin complexes revealed that the insertion of Ni and Zn ions decreased the thermal ROP temperatures of the Por-BZ/Ni and Por-BZ/Zn complexes significantly, to 241 and 231 °C, respectively. The metal ions acted as the effective promoter and catalyst for the thermal polymerization of the Por-BZ monomer, and also improved the thermal stabilities after thermal polymerization.
- polybenzoxazine
- ring-opening polymerization
- porphyrin
- metal complex
- thermal stability
1. Introduction
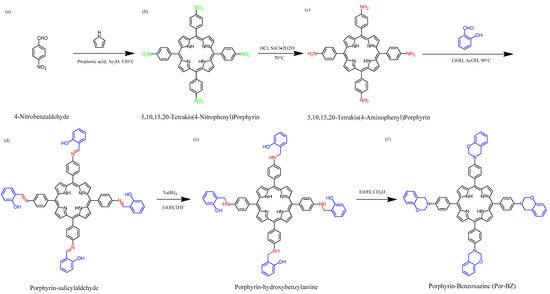
2. Metal Complexes of the Porphyrin-Functionalized Polybenzoxazine
2.1. Synthesis of TAPP
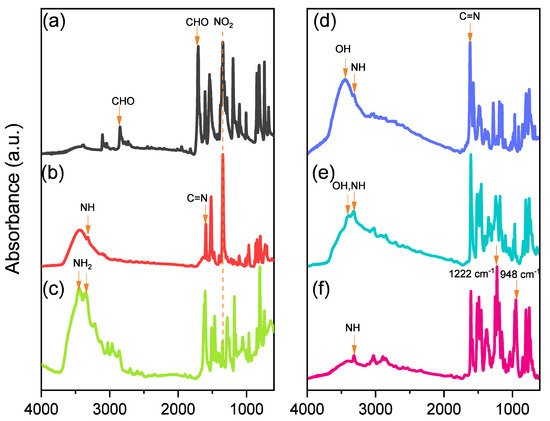
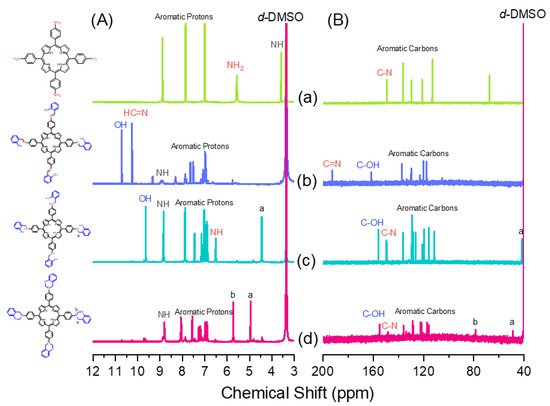
2.2. Synthesis of Por-BZ
2.3. Thermal Curing Polymerization of Por-BZ Monomer
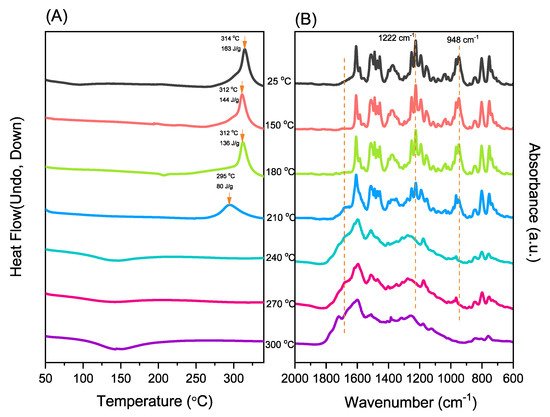
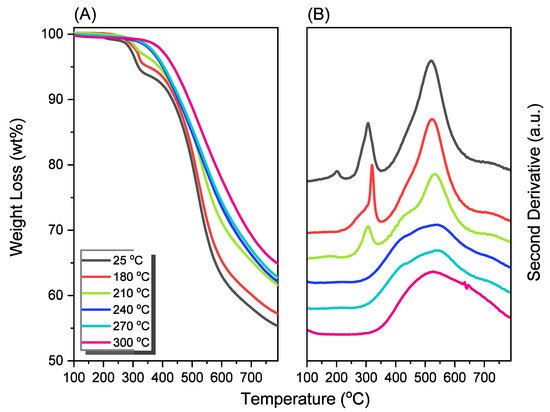
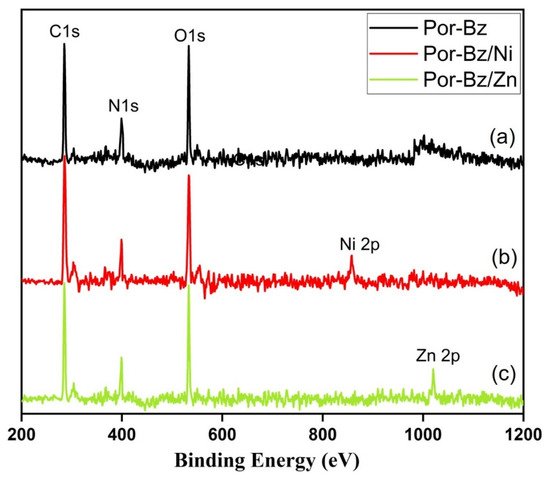
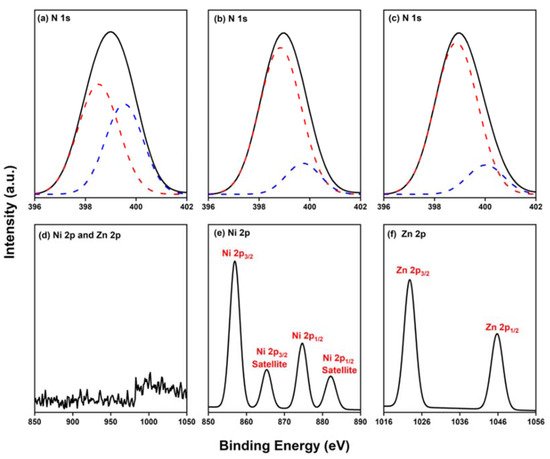
2.4. Characterization of Por-BZ/Metal Complex
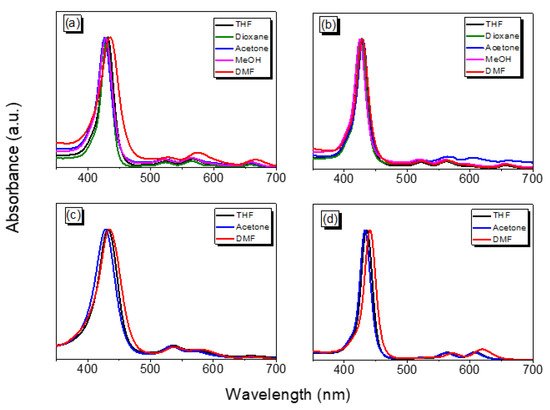
| Compound | Solvent | λabs (nm) (Soret Band) | λabs (nm) (Q Band) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAPP | THF | 524, 566, 602, 662 | 432 |
| Dioxane | 524, 564, 600, 660 | 430 | |
| Acetone | 522, 564, 600, 660 | 428 | |
| MeOH | 522, 564, 596, 656 | 426 | |
| DMF | 528, 574, 608, 666 | 436 | |
| Por-BZ | THF | 522, 562, 598, 658 | 428 |
| Dioxane | 522, 562, 598, 656 | 428 | |
| Acetone | 520, 560, 596, 654 | 424 | |
| MeOH | 522, 564, 606, 662 | 430 | |
| DMF | 522, 564, 600, 658 | 428 | |
| Por-BZ/Ni | THF | 535, 574, 657.5 | 432 |
| Acetone | 533.5, 571, 656.5 | 428 | |
| DMF | 538, 579, 660.5 | 434 | |
| Por-BZ/Zn | THF | 564, 608 | 436 |
| Acetone | 562, 606 | 432 | |
| DMF | 572, 620 | 440 |
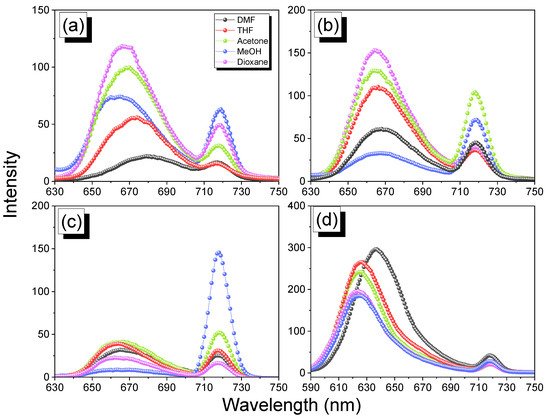
2.5. Thermal ROP of Por-BZ/Metal Complex