You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 3 by Vicky Zhou and Version 2 by Vicky Zhou.
Biochar is a biological material for environmental remediation due to its low-cost precursor (waste), low toxicity, and diversity of active sites, along with their facile tailoring techniques. Due to its versatility, biochar has been employed as an adsorbent, catalyst (for activating hydrogen peroxide, ozone, persulfate), and photocatalyst. Biochar could also be applied in remediation of organic pollutants in water.
- biochar
- adsorption
- H2O2 activation
- O3 activation
- peroxymonosulfate activation
- peroxydisulfate activation
- photocatalysis
- organic pollutants
1. Introduction
Over the past few years, the rapid growth of various industries has led to the release of toxic pollutants to the environment. In particular, various refractory pollutants such as antibiotics, phenolic compounds, dyes, and heavy metals are detected in numerous water bodies and soil [1][2][3][4][5]. In particular, pollution due to refractory pollutants in water bodies is of emerging concern due to its greater mobility compared to soil. While these pollutants pose a threat to public health, they also disrupt the microbial ecosystem [6][7]. For instance, the release of trace antibiotics will lead to the development of multidrug-resistant strains, which will result in less effective clinical treatment effects of conventional antibiotics [7]. Phenolic compounds such as chlorophenols are toxic and may induce carcinogenic and mutagenic effects. In order to alleviate this problem, methods such as adsorption [8], membrane separation [9], and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) [10] can be used to treat the wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. Generally, adsorption and membrane separation involve the separation of pollutants and water without destroying the pollutants, while AOPs utilizes reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation for organics mineralization.
Recently, biochar has gained attention in various environmental remediation applications. Biochar can be obtained by the direct carbonization of organic wastes in an oxygen-deficient environment. Compared with other carbon-based materials, some of the advantages of using biochar for environmental remediation include low production cost (cheap raw materials), relatively simple preparation methods (facile pyrolysis of biomass), and eco-friendly (waste recovery). Furthermore, the properties of biochar can be engineered more easily (compared with other carbon allotropes) by changing the synthesis parameters (e.g., synthesis temperature and duration) [11][12], careful selection of biomass as a precursor [13], and functionalization (e.g., heteroatom doping, oxygen tuning, and defects) [14][15].
Numerous reviews on the use of biochar in specific environmental applications are available [16][17][18][19][20][21][22], howbeit, with modest emphasis on comparing biochar performance and the mechanism of treating organic pollutants under different systems for finding superior applications of biochar and to fully realize its potential. For instance, Dai et al. [21] discussed the employment of biochar as an adsorbents for organic pollutants, however, without discussing biochar potential in other pollutant remediation systems. Similarly, Zhou et al. [19] and Zhao et al. [23] reviewed biochar as AOPs catalyst and persulfate activator, respectively, without comparison against other systems (e.g., adsorption, O3 activation).
2. Applications of Biochar in Environmental Remediation
2.1. Adsorption
Adsorption is a common technique to remove organic pollutants. Due to its relatively low operational cost, adsorption is widely utilized for water remediation. Table 1 presents an overview of the performance of biochar as an adsorbent for various organic pollutants. The criteria for an effective adsorbent include having high SSA and porosity along with the abundance of active sites. Generally, the adsorption process relies on the liquid–solid intermolecular attraction between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, which leads to the accumulation of solute molecules on the adsorbent surface [24]. The adsorption mechanisms between the biochar and organic pollutant occur through physical and chemical interactions, including H-bonding, hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic attraction, π-π EDA interactions, complexes adsorption, Lewis acid–base interactions, pore filling, partition uncarbonized fraction, dipole–dipole interactions, Coulombic attraction, spectrometer exchange, and acceptor interactions [22]. The adsorption process undertaken is controlled by the nature of the adsorbate, biochar properties, and operational condition (i.e., pH, pressure of water matrix, rate). The adsorption process is divided into three stages. First, there is external mass transfer of organic pollutants from the aqueous solution to the biochar surface (external diffusion), which is followed by the diffusion of organic molecules into the pores of biochar (internal diffusion) and ending with the adsorptive interactions (Figure 1) [14][25].
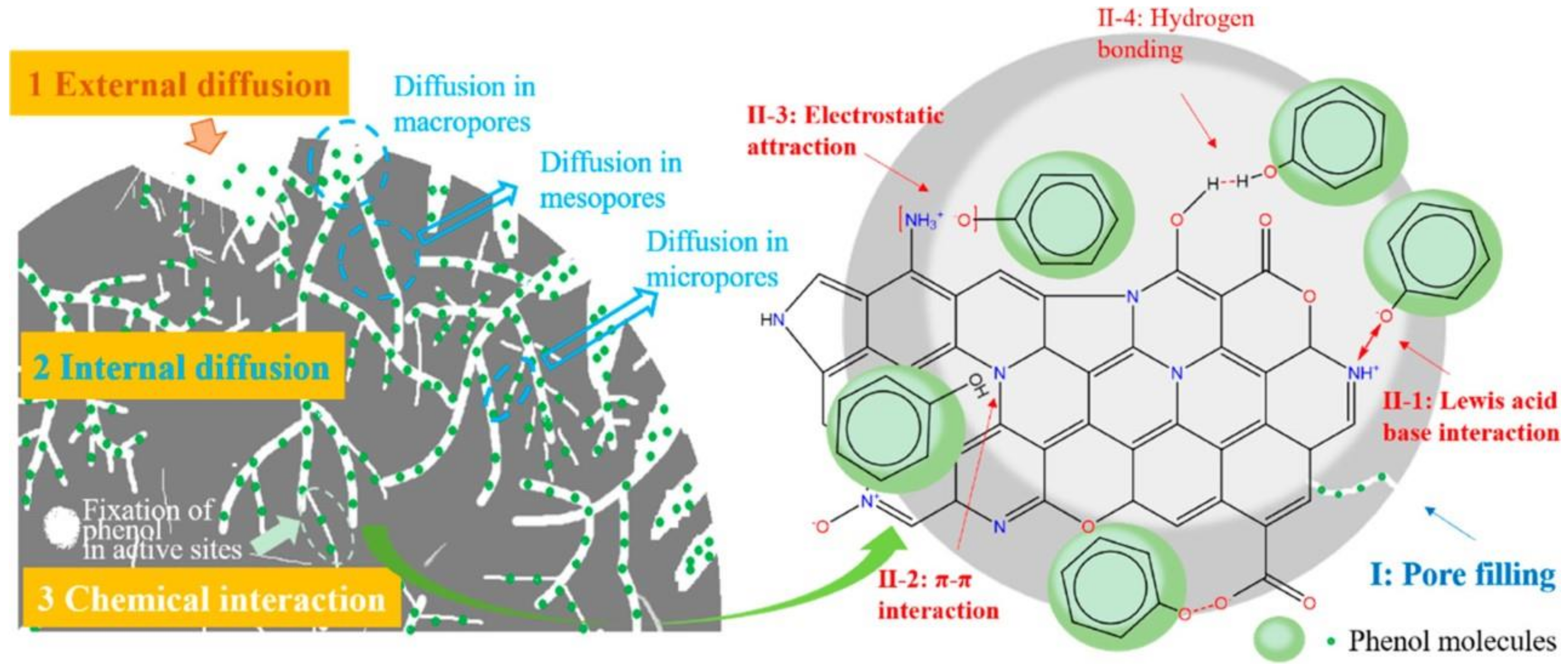

Figure 1. Mechanism of phenol adsorption by N-doped biochar. Reprinted with permission from Li et al. [14]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.
Table 1. An overview of biochar preparation and performance in adsorption of organic pollutants.
| Biochar Precursor and Synthesis |
Performance | Removal Mechanism | Ref | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| [26] | ||||||
|
|
| [27] | ||||||
|
|
|
•− can be achieved through the activation of PS such as peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and peroxydisulfate (PDS). Table 4 provides an overview on biochar performance in PS activation to remove organic pollutants.
Table 4. An overview of biochar preparation and performance in PS activation for organic pollutants removal.
cb− can reduce O2 to generate •O2− whereas hvb+ can react with the OH− to generate •OH. Nonetheless, •O2− can only be generated when the CB potential is more negative than the reduction potential of O2/•O2− (−0.33 eV). As for •OH formation, the VB potential edge of the photocatalyst must be sufficiently positive to oxidize hydroxide ions or adsorbed H2O to form •OH (OH−/•OH: +2.38 eV, H2O/•OH: +2.72 eV) [62][63][64].
Recently, biochar has been found to have a semiconductor-like structure and serves as an active carbonaceous photocatalyst. Table 5 provides the performance and mechanism of biochar as a photocatalyst to remove organic pollutants.
Table 5. An overview of biochar preparation and performance as photocatalyst activation for organic pollutants removal.
| Biochar Precursor and Synthesis |
Performance | Removal Mechanism | Ref | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| [65] | |||||||||||||||
|
|
| [65] | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| [ | 28] | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
| [66] |
|
|
| [29] | |||||||||||
|
|
| [30] | |||||||||||||||
|
|
| [31] | |||||||||||||||
|
|
| [32] | |||||||||||||||
|
|
| [33] |
2.2. H2O2 Activation
Chemical oxidants such as H2O2, persulfate (PS), and O3 are capable of treating organic effluents. However, due to their relatively mild oxidative potentials, catalytic activation using biochar to generate reactive species is desirable. The activation process follows an electron transfer regime between the activator (biochar) and the oxidant, and these activation mechanisms are influenced by the properties of the peroxide (O-O) bond (i.e., bond distance and dissociation energy). Among the common oxidants, H2O2, with a redox potential of 1.76 V vs. NHE [34], is highly preferable in water treatment because its decomposition products are only oxygen and hydrogen, which is considered environmentally friendly to water treatment [35]. The H2O2 structure encompasses an O-O bond distance of 1.460 Å with a dissociation energy of 377 kJ/mol. In a biochar/H2O2 system, the electron transfer process from biochar to H2O2 molecules induces the breakage of the O-O or O-H bond for subsequent ROS formations. Table 2 overviews the performance and mechanism of H2O2 activation by biochar catalysts.
45]. Nonetheless, enhanced ozonation can be achieved by catalytic activation for escalated ROS generation and faster O3 decomposition. Table 3 provides an overview on the performance and mechanism of biochar in O3 activation.
Table 2. An overview of biochar preparation and performance in H2O2 activation for organic pollutants removal.
- Synergistic removal by adsorption with other AOPs methods may provide constructive results. Nonetheless, the optimization of adsorption contribution is crucial to avoid undesirable competition over biochar active sites and hinder removal performance.
- Specific tailoring of biochar active sites that are unlikely to be affected with pH changes and/or can produce species that are resistant to changing pH (i.e., nonradical pathways) can endow the biochar with better performance over different water matrixes.
| Biochar Precursor and Synthesis |
Performance | Removal Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Table 3. An overview of biochar preparation and performance in O3 activation for organic pollutants removal.
| Biochar Precursor and Synthesis |
Performance | Removal Mechanism | Ref | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar Precursor and Synthesis | |||||||||||||||||||
| Performance | Removal Mechanism | Ref | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| [36] | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
|
|
| [37] | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| [ | 49 | ] |
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| [50] |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| [38] | |||||||||||||||
|
| [48] |
|
2.4. PS Activation
Recently, sulfate radical (SO4•−)-based AOPs (SR-AOPs) have gained attention for organic pollutant degradation. Generally, SO4
|
| [51] | |||||||||||
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| [ | 52 | ] |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
| [ | 53] |
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| [41] | |||||||
| [54] |
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
| [42] | |||||||||
|
|
| [55] |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
2.3. O3 Activation
O3 is widely used for wastewater disinfection due to its high redox potential (E° = 2.08 V). Ozone may also directly oxidize organic pollutants with the targeting of C=C or N=N bonds [44]. However, direct ozonation is limited by selective interactions with organic molecules under acidic conditions. Additionally, O3 direct reaction with some organics such as saturated carboxylic acids and inactivated aromatics is slow, making it difficult to achieve complete mineralization [
| |||||||||
|
|
| [56] | ||||||
|
|
| [15] | ||||||
|
|
| [57] | ||||||
|
|
| [58] |
2.5. Photocatalysis
Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants has been extensity studied in the last few decades. Typically, metals oxides such as TiO2, ZnO, and BiVO4 have been commonly used as a photocatalyst for environmental application. During photocatalytic reactions, the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the photocatalyst is crucial to activate the photocatalyst and produce ROS, which can be used to degrade organic pollutants. The energy of the absorbed light irradiation must be greater or equal to the bandgap energy (Eg) of that photocatalyst in order to excite the electrons from the conduction band (CB) to the valence band (VB) [59]. When the excited electrons (ecb−) migrate to CB, positive holes (hvb+) will be formed in VB. Then, the electron/hole pair will migrate to the surface of the semiconductor to react with the adsorbed substrates. Generally, ecb− will react with the electron acceptors adsorbed on the catalyst surface to reduce it, whereas hvb+ will react with electron donors on the catalyst surface to oxidize it [60][61]. Dissolved O2 and OH− ions in water can interact as electron acceptors and electron donors, respectively. The e3. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Thus far, biochar, as a carbonaceous material with various active sites, has been successfully utilized in the decontamination of organic pollutants from water by different applications. Among the numerous applications of biochar in wastewater treatment, adsorption, H2O2 activation, O3 activation, PS activation, and photocatalysis hold the superlative potential in the treatment of organic pollutants. These applications were compared with respect to performance, mechanism of removal with emphasis on pollutant–biochar interactions and biochar active sites’ involvement, tolerance to changes in water pH, stability of biochar after consecutive cycles of pollutant treatment, and economic factors. Each application has its own advantages and limitations. Adsorption is superior in terms of simplicity of operational procedures, ability to remove oxidation-resistant pollutants, and cost-wise. AOPs utilize more active sites of biochar and are able to mineralize organics pollutants or form less resistant organic by-products, so they can be treated by conventional methods. All AOPs have their own advantages. For instance, PS activation is effective in utilizing all of the biochar active sites along with having a monopoly on the capability to produce SO4•−. H2O2 is a safe oxidant with nonharmful decomposition products (hydrogen and oxygen). O3 is a strong oxidant with various activation pathways. Photocatalysis does not require the use of any oxidant. Nonetheless, limitations are present in each application. (i) The low durability of biochar active sites during AOPs is repeatedly reported. In addition, (ii) the performance of pristine biochar for environmental remediation of organic pollutants is often slow with low efficiency. (iii) The cost of light source during photocatalytic reactions is a drawback. (iv) Adsorption is unable to mineralize or degrade organic pollutants. (v) Biochar–pollutant and biochar–oxidant interactions are highly influenced by water pH changes, hindering its application in real wastewater. To enhance biochar performance in environmental remediation, several suggestions can be made:
-
The fabrication of robust biochar with high graphitization and aromaticity degree can prevent poor durability. In addition, compositing with polymers can protect the active site of biochar from cannibalistic reactions and can also simplify the separation of the catalyst.
-
Heteroatom (i.e., N, S, B, F, P) doping is often found to have a fruitful effect on the performance of biochar in environmental remediation. However, co-doping and triple-doping are rarely reported. Hence, more studies are needed on multi-doped biochar, with systematic investigations on the interactions between the multi-dopants within the biochar structure and its effect on the biochar performance. Moreover, as heteroatomic doping of biochar can be achieved by in situ and post-treatment methods, a comparison between the two techniques is needed to determine the most efficient method.
-
For photocatalytic applications, LED lamps can be used instead of conventional light sources to avoid an additional cost of electricity and better utilization of energy.
References
- Anh, H.Q.; Le, T.P.Q.; Da Le, N.; Lu, X.X.; Duong, T.T.; Garnier, J.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Zhang, S.; Oh, N.H.; Oeurng, C.; et al. Antibiotics in surface water of East and Southeast Asian countries: A focused review on contamination status, pollution sources, potential risks, and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142865.
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691.
- Choong, Z.-Y.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lisak, G.; Lim, T.-T.; Oh, W.-D. Multi-heteroatom-doped carbocatalyst as peroxymonosulfate and peroxydisulfate activator for water purification: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 426, 128077.
- Offiong, N.-A.O.; Inam, E.J.; Etuk, H.S.; Ebong, G.A.; Inyangudoh, A.I.; Addison, F. Trace Metal Levels and Nutrient Characteristics of Crude Oil-Contaminated Soil Amended with Biochar–Humus Sediment Slurry. Pollutants 2021, 1, 119–126.
- Offiong, N.A.O.; Inam, E.J.; Etuk, H.S.; Essien, J.P.; Ofon, U.A.; Una, C.C. Biochar and humus sediment mixture attenuates crude oil-derived PAHs in a simulated tropical ultisol. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1930.
- Bharagava, R.N.; Saxena, G.; Mulla, S.I.; Patel, D.K. Characterization and Identification of Recalcitrant Organic Pollutants (ROPs) in Tannery Wastewater and Its Phytotoxicity Evaluation for Environmental Safety. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 75, 259–272.
- van Duin, D.; Paterson, D.L. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Community: Trends and Lessons Learned. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 377–390.
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of adsorption process for effective removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995.
- Fonseca Couto, C.; Lange, L.C.; Santos Amaral, M.C. A critical review on membrane separation processes applied to remove pharmaceutically active compounds from water and wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 156–175.
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemöller, M. Advanced oxidation process-mediated removal of pharmaceuticals from water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 189–207.
- Suliman, W.; Harsh, J.B.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Fortuna, A.M.; Dallmeyer, I.; Garcia-Perez, M. Influence of feedstock source and pyrolysis temperature on biochar bulk and surface properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 84, 37–48.
- Chandra, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Influence of temperature and duration of pyrolysis on the property heterogeneity of rice straw biochar and optimization of pyrolysis conditions for its application in soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1123–1139.
- Meng, H.; Nie, C.; Li, W.; Duan, X.; Lai, B.; Ao, Z.; Wang, S.; An, T. Insight into the effect of lignocellulosic biomass source on the performance of biochar as persulfate activator for aqueous organic pollutants remediation: Epicarp and mesocarp of citrus peels as examples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123043.
- Li, Y.; Xing, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S. Nitrogen-Doped Hierarchical Porous Biochar Derived from Corn Stalks for Phenol-Enhanced Adsorption. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 12459–12468.
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Si, Q.; Sseguya, F.; Ren, N. Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: An electron transfer mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 160, 405–414.
- Do Minh, T.; Song, J.; Deb, A.; Cha, L.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M. Biochar based catalysts for the abatement of emerging pollutants: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124856.
- Liang, L.; Xi, F.; Tan, W.; Meng, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 2021, 3, 255–281.
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022.
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; et al. New notion of biochar: A review on the mechanism of biochar applications in advannced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129027.
- Luo, K.; Pang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Lei, M.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Q. A critical review on the application of biochar in environmental pollution remediation: Role of persistent free radicals (PFRs). J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 108, 201–216.
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xing, C.; Cui, Q.; Sun, Q. The adsorption, regeneration and engineering applications of biochar for removal organic pollutants: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 12–27.
- Gasim, M.F.; Lim, J.-W.; Low, S.-C.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Oh, W.-D. Can biochar and hydrochar be used as sustainable catalyst for persulfate activation? Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132458.
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Burgeoning prospects of biochar and its composite in persulfate-advanced oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124893.
- Nageeb, M. Adsorption Technique for the Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water and Wastewater. In Organic Pollutants—Monitoring, Risk and Treatment; InTech: London, UK, 2013.
- Duan, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, C.; Li, J. Adsorption of 17β-estradiol from aqueous solutions by a novel hierarchically nitrogen-doped porous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 700–708.
- Guo, R.; Yan, L.; Rao, P.; Wang, R.; Guo, X. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped biochar derived from peanut shell with enhanced adsorption capacity for diethyl phthalate. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113674.
- Zhang, X.; Gang, D.D.; Zhang, J.; Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Holmes, W.E.; Zappi, M.E.; Yao, H. Insight into the activation mechanisms of biochar by boric acid and its application for the removal of sulfamethoxazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 424, 127333.
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Sirajudheen, P.; Karthikeyan, P.; Meenakshi, S. Fabrication of sulfur-doped biochar derived from tapioca peel waste with superior adsorption performance for the removal of Malachite green and Rhodamine B dyes. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100920.
- Giri, B.S.; Sonwani, R.K.; Varjani, S.; Chaurasia, D.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Chaturvedi, P.; Yadav, S.; Katiyar, V.; Singh, R.S.; Pandey, A. Highly efficient bio-adsorption of Malachite green using Chinese Fan-Palm Biochar (Livistona chinensis). Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132282.
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanism of Bisphenol A by Magnetic Biochar. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1075.
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wei, J.; Luo, L.; Lei, M.; Tang, L. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 266–273.
- Chen, T.; Luo, L.; Deng, S.; Shi, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, O.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L. Sorption of tetracycline on H3PO4 modified biochar derived from rice straw and swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 431–437.
- Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G.; Javed, A. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin sorption on chitosan/biochar hydrogel beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569.
- Lim, J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Substrate oxidation enhances the electrochemical production of hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 958–964.
- Li, W.; Bonakdarpour, A.; Gyenge, E.; Wilkinson, D.P. Production of Hydrogen Peroxide for Drinking Water Treatment in a Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer at Near-Neutral pH. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 044502.
- Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wei, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Enhanced H2O2 activation and sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fe-impregnated biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123921.
- Luo, K.; Yang, Q.; Pang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Lei, M.; Huang, Q. Unveiling the mechanism of biochar-activated hydrogen peroxide on the degradation of ciprofloxacin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 520–530.
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Wan, J.; Qin, L.; Zeng, Y. Influence of morphological and chemical features of biochar on hydrogen peroxide activation: Implications on sulfamethazine degradation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73186–73196.
- Sun, P.; Hua, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Tan, Q.; Shen, G. Insights into the mechanism of hydrogen peroxide activation with biochar produced from anaerobically digested residues at different pyrolysis temperatures for the degradation of BTEXS. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147718.
- Li, J.; Pan, L.; Yu, G.; Xie, S.; Li, C.; Lai, D.; Li, Z.; You, F.; Wang, Y. The synthesis of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst using sewage sludge biochar and its application for ciprofloxacin degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1284–1292.
- Huang, D.; Luo, H.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, R.; Deng, R.; Xue, W.; Gong, X.; et al. Nonnegligible role of biomass types and its compositions on the formation of persistent free radicals in biochar: Insight into the influences on Fenton-like process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 353–363.
- Park, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Xiao, R.; Tafti, N.; DeLaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Degradation of Orange G by Fenton-like reaction with Fe-impregnated biochar catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 368–376.
- Yi, Y.; Tu, G.; Eric Tsang, P.; Fang, Z. Insight into the influence of pyrolysis temperature on Fenton-like catalytic performance of magnetic biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122518.
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water. An Overview. Water 2019, 12, 102.
- Mehrjouei, M.; Müller, S.; Möller, D. A review on photocatalytic ozonation used for the treatment of water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 209–219.
- Zhang, F.; Wu, K.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Preis, S.V.; Wu, H.; Wei, C. Ozonation of aqueous phenol catalyzed by biochar produced from sludge obtained in the treatment of coking wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 376–386.
- Chen, C.; Yan, X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yoza, B.A.; Wang, X.; Kou, Y.; Ye, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.X. Activated petroleum waste sludge biochar for efficient catalytic ozonation of refinery wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2631–2640.
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Qiu, S.; Sun, L.; Yuan, X.; Xia, D. Catalytic ozonation oxidation of ketoprofen by peanut shell-based biochar: Effects of the pyrolysis temperatures. Environ. Technol. 2020.
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, T.; Mei, M.; Chen, S.; Li, J. Peroxydisulfate activation by digestate-derived biochar for azo dye degradation: Mechanism and performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119687.
- Jin, Z.; Xiao, S.; Dong, H.; Xiao, J.; Tian, R.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L. Adsorption and catalytic degradation of organic contaminants by biochar: Overlooked role of biochar’s particle size. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126928.
- Chen, Y.P.; Zheng, C.H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.R. Removal of chlortetracycline from water using spent tea leaves-based biochar as adsorption-enhanced persulfate activator. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131770.
- Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, W.; Yan, B.; Yu, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, G.; Hou, L.; Wang, S. Tunable active sites on biogas digestate derived biochar for sulfanilamide degradation by peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126794.
- Zhong, Q.; Lin, Q.; He, W.; Fu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Study on the nonradical pathways of nitrogen-doped biochar activating persulfate for tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119354.
- Avramiotis, E.; Frontistis, Z.; Manariotis, I.D.; Vakros, J.; Mantzavinos, D. Oxidation of Sulfamethoxazole by Rice Husk Biochar-Activated Persulfate. Catalysts 2021, 11, 850.
- Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Si, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, H.; Ren, N. B-doped graphitic porous biochar with enhanced surface affinity and electron transfer for efficient peroxydisulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125119.
- Oh, W.-D.; Jannah Zaeni, J.R.; Lisak, G.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Leong, K.-H.; Choong, Z.-Y. Accelerated organics degradation by peroxymonosulfate activated with biochar co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130313.
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Ma, F.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Catalytic Removal of Aqueous Contaminants on N-Doped Graphitic Biochars: Inherent Roles of Adsorption and Nonradical Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8649–8658.
- Ho, S.H.; Chen, Y.-d.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y.; Cao, G.; Ma, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.-q. N-doped graphitic biochars from C-phycocyanin extracted Spirulina residue for catalytic persulfate activation toward nonradical disinfection and organic oxidation. Water Res. 2019, 159, 77–86.
- Abdellah, M.H.; Nosier, S.A.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Mubarak, A.A. Photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue using TiO2/UV system enhanced by air sparging. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 3727–3735.
- Byrne, J.A.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Polo-López, I.; Sharma, P.K.; Vennard, A.S.M. A review of heterogeneous photocatalysis for water and surface disinfection. Molecules 2015, 20, 5574–5615.
- Mahlambi, M.; Ngila, C.; Mamba, B. Recent Developments in Environmental Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants: The Case of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles-A Review. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 790173.
- Arimi, A.; Günnemann, C.; Curti, M.; Bahnemann, W.D. Regarding the Nature of Charge Carriers Formed by UV or Visible Light Excitation of Carbon-Modified Titanium Dioxide. Catalysts 2019, 9, 697.
- Pirhashemi, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A. Preparation of novel nanocomposites by deposition of Ag2WO4 and AgI over ZnO particles: Efficient plasmonic visible-light-driven photocatalysts through a cascade mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13447–13460.
- Rashid, J.; Parveen, N.; Iqbal, A.; Awan, S.U.; Iqbal, N.; Talib, S.H.; Hussain, N.; Akram, B.; Ulhaq, A.; Ahmed, B.; et al. Facile synthesis of g-C3N4(0.94)/CeO2(0.05)/Fe3O4(0.01) nanosheets for DFT supported visible photocatalysis of 2-Chlorophenol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10202.
- Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhou, D. Photogeneration of reactive oxygen species from biochar suspension for diethyl phthalate degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 214, 34–45.
- Xiao, Y.; Lyu, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, K.; Sun, H. Effects of ball milling on the photochemistry of biochar: Enrofloxacin degradation and possible mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123311.
More
