Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL disease or VHL syndrome) is a familial multisystem neoplastic disorder, stemming from germline disease-associated variants of the VHL tumor suppressor gene. VHL protein is involved in oxygen sensing and adaptive response to hypoxia through the EPO-VHL-HIF signaling axis. In recent years, numerous HIF-independent pathways of VHL have been identified, expanding the role of VHL throughout several cellular processes. In addition to VHL syndrome-associated tumors, VHL variations have also been associated with the development of eythrocytosis. Research indicated that there is a distinction between erythrocytosis-causing VHL variations and VHL variations causing VHL disease with tumor development. Therefore, elucidating the molecular background of the pathogenic effects of VHL variants could help determine the best approach to VHL disease management.
- VHL
- VHL disease
- Chuvash polycythemia
- genetic variation
- erythrocytosis
- pheochromocytoma
- renal cell carcinoma
- retinal hemangioblastoma
- hemangioblastoma
1. Introduction
2. VHL Canonical and Non-Canonical Functions
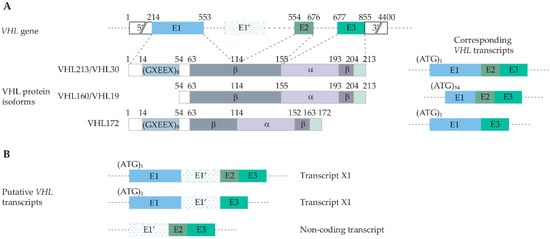
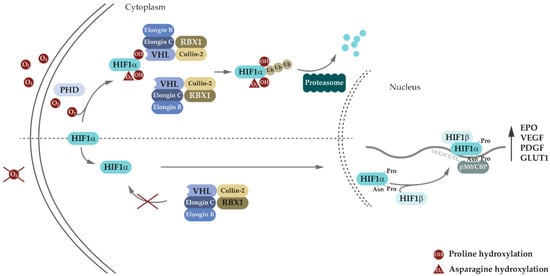
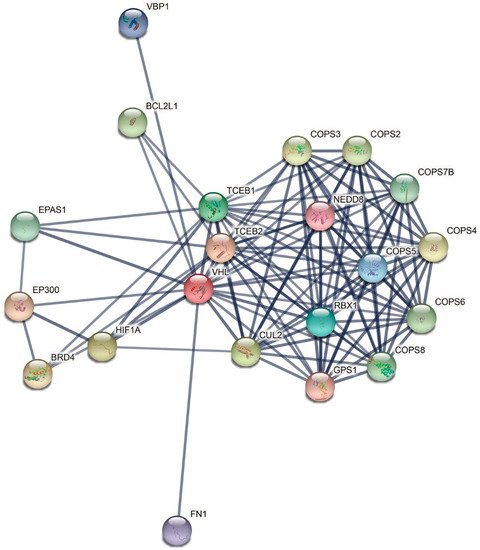
3. Genetic and Molecular Basis of VHL Disease
| Variant | Protein Change | Codon | VHL Type/Phenotype | Functional Consequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.191G>C | R64P | 64 | Type 2C | Increased aPKC JUNB levels; impaired binding to fibronectin. | [87][88][91,92] |
| c.194C>T | S65L | 56 | Type 2B | Impaired HIF1α binding; impaired HIF2α regulation. | [89][90][91][93,94,95] |
| c.208G>A | E70K | 70 | Type 1 | Impaired HIF1α binding. | [92][93][96,97] |
| c.233A>G | N78S | 78 | Type 1 | Impaired HIF1α regulation. | [94][95][98,99] |
| c.239G>A | S80N | 80 | Type 2C | No known consequence. | [94][98] |
| c.245G>C | R82P | 82 | Type 2B | Loss of function of VHL. | [96][100] |
| c.250G>C | V84L | 84 | Type 2C | No known consequence. | [94][98] |
| c.262T>A c.262T>C |
W88R | 88 | Hemangio- Blastoma 1 |
No known consequence. | [90][94] |
| c.269A>T | N90I | 90 | Type 2B | Impaired HIF1α regulation. | [90][94][97][98][94,98,101,102] |
| c.292T>C | Y98H | 98 | Type 2A | Impaired HIF1α regulation; defective microtubule stabilization. | [87][94][91,98] |
| c.292T>A | Y98N | 98 | Type 2B | Impaired HIF1α regulation; impaired GLUT1 suppression. | [97][101] |
| c.334T>A | Y112H | 112 | Type 2A | Impaired HIF1α regulation; decreased VHL stability. | [85][99][89,103] |
| c.334T>A | Y112N | 112 | Type 2B | Reduced stability of the Vhl-Elongin B/C complex; impaired HIF1α regulation; elevated HIF2α, GLUT1, and cyclin D1 expression in normoxic conditions. | [99][100][101][103,104,105] |
| c.334T>G | Y112D | 112 | Type 2C | No known consequence. | [94][98] |
| c.340G>C | G114R | 114 | Type 2B | Reduced stability of the Vhl-Elongin B/C complex. | [102][106] |
| c.349T>C c.349T>A |
W117R | 117 | Type 2B | Impaired HIF1α regulation; impaired binding to fibronectin; elevated HIF2α and GLUT1 expression in normoxic conditions. | [62][101][62[103],105,107] |
| c.355T>C c.357C>G c.357C>A |
F119L | 119 | Type 2B | Decreased VHL stability; impaired HIF1α regulation. | [104][108] |
| c.407T>C | F136S | 136 | Type 2B | No known consequence. | [94][98] |
| c.407T>A | F136Y | 136 | Type 2B | No known consequence. | [94][98] |
| c.408T>G | F136L | 136 | Type 2B | Decreased VHL stability; impaired HIF1α regulation. | [104][105][108,109] |
| c.482G>C | R161P | 161 | Type 2B | Reduced stability of the Vhl-Elongin B/C complex; defective microtubule stabilization. | [106][107][110,111] |
| c.482G>A | R161Q | 161 | Type 2A; Type 2B | Reduced VHL stability. | [108][112] |
| c.486C>G | C162W | 162 | Hemangio- Blastoma 1 |
Impaired HIF1α regulation. | [90][109][94,113] |
| c.499C>T | R167W | 167 | Type 2B | Decreased binding to Elongin B/C and Cullin-2; impaired ubiquitination and degradation of ESR1. | [62][110][62,114] |
| c.500G>A | R167Q | 167 | Hemangio- Blastoma 1 |
Decreased binding to Elongin C; impaired HIF2α regulation. | [90][111][112][94,115,116] |
| c.562C>G | L188V | Type 2C | Impaired binding to fibronectin; elevated RWWD3, aPKC, and JUNB levels. | [87][[114][9188][113],92,117,118] |
