Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Diego Franco and Version 7 by Conner Chen.
The upstroke phase of the cardiac action potential (AP) is mainly coordinated by cardiac sodium channels, which are immediately activated and generate a fast Na+ inward current, through the membrane, after membrane depolarization. In atrial and ventricular myocytes, the sodium current (INa) is principally governed by cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel 1.5 (Nav1.5) with a tinny contribution of NaV1.8. The human Nav1.5 channel is composed of a pore-forming α-subunit (227-kDa) and one or more auxiliary β-subunit (30-kDa).
- cardiac sodium channel
- gene regulation
1. Introduction
The upstroke phase of the cardiac action potential (AP) is mainly coordinated by cardiac sodium channels, which are immediately activated and generate a fast Na+ inward current, through the membrane, after membrane depolarization [1]. In atrial and ventricular myocytes, the sodium current (INa) is principally governed by cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel 1.5 (Nav1.5) with a tinny contribution of NaV1.8 [2]. The human Nav1.5 channel is composed of a pore-forming α-subunit (227-kDa) and one or more auxiliary β-subunit (30-kDa) [3]. SCN5A gene with 80 kb length is located on chromosome 3p21 and consists of 28 exons which encode a protein of 2016 amino acid, the α-subunit of Nav1.5 channel [4]. This protein contains four homologous sites (DI–DIV), each composed of six transmembrane segments organized into two functional modules. Segments from one to four (S1–S4) generate the voltage-sensing module (VS), and segments five and six (S5–S6) jointly with P-loop create the pore module (PM). Finally, we can find an α-helical S4–S5 linker, whose function is to bind these two structures, the voltage-sensing and the pore modules. Moreover, there are intracellular linkers that are in charge of DI–DII, DII–DIII, and DIII–DIV binding, and more concretely, the DIII–DIV linker is the controller of pore closing, acting as a fast inactivation gate [5]. The VS and PM modules of the Nav1.5 constitute preferred therapeutic targets for the treatment of several cardiac sodium channelopathies. Particularly, flecainide, as well as other class IC antiarrhythmic drugs, bind to the central cavity of the pore and block sodium permeation directly [5]. The class IA antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., procainamide) and the class IB antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., lidocaine) might act on a smaller surface of the central cavity of the pore as well [5]. However, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and PUFA analogs have been shown to be antiarrhythmic by inhibiting Nav1.5 channel currents, probably through acting on the voltage-sensing S4 segments that control inactivation in these channels [6][7][6,7].
2. Genomic Regulation of the Cardiac Sodium Channel
2.1. Genetic Code of SCN5A
Nav1.5 channel expression and function may be impaired due to variations in the genomic sequence of SCN5A, including missense, nonsense, splice-altering, and frame shift truncation [8][9][22,23]. These variations cause different cardiac diseases because of a loss- or gain-of-function and occasionally both, generating overlapped phenotypes [10][24]. For example, Brugada Syndrome (BrS) [10][11][12][24,25,26], progressive cardiac conduction disease (Lev-Lenegre disease) [13][14][27,28], and sick sinus syndrome [15][16][29,30] are some diseases caused by loss-of-function mutations in SCN5A. However, long QT syndrome type 3 (LQTS3) [10][17][24,31] and multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions (MEPPC) [18][19][20][32,33,34] are due to gain-of-function mutations in SCN5A. Finally, a combination of gain- and loss-of-function mutations are associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) [21][22][35,36] and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) [20][22][23][24][34,36,37,38]. Some of these channelopathies are widely described in Section 4 of this review. Additionally, several SCN5A missenses can generate dominant-negative variants affecting Nav1.5 trafficking or gating at the cell surface [39,40,41]. A recent study demonstrated that most of SCN5A missense that generate loss-of-function variants exert a dominant-negative effect that confers a high burden of BrS [42]. Finally, post-translational modifications affecting Nav1.5 have an impact on the use of antiarrhythmic drugs, making these data quite relevant for future drug design [43].
2.2. Regulation of SCN5A Transcription
2.2.1. Epigenetic Regulation of SCN5A
Regulation of
SCN5A
by Distinct Regulatory Elements and Histones
Gene transcriptional activation is not only modulated by transcription factors; in this process, the role of distinct regulatory elements (RE) is also important, as well as how these REs interact with chromatin, depending on DNA accessibility. Several authors have identified different roles of an enhancer cluster in the SCN5A-SCN10A locus, which modulate SCN5A gene expression [30][31][32][44,45,46]. RE-1 and RE-5 are located in an SCN10A and SCN5A intron, respectively, and RE-6, located downstream of SCN5A, contains genetic variants associated with PR intervals and QRS duration [30][31][33][34][44,45,47,48]. Moreover, Christoffels’ lab [35][49] has recently demonstrated that there are several downstream SCN5A REs acting as cardiac-specific “super enhancers”, concretely the intergenic region composed by RE6-9, which possess an extensive association with Histone H3 lysine (K) 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) [36][50]. RE6-9 has the ability to fine-tune Scn5a-Scn10a chromatin architecture modulating Scn5a expression. In addition, it has been identified that some single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in an enhancer region are able to regulate transcription factor binding and modulate gene expression. In particular, major alleles of rs6801957 and rs10428132 lead to SCN5A gene expression, while minor alleles cannot due to a loss of a T-box protein binding site [37][38][51,52]. Furthermore, an enrichment of H3K27ac and Histone H3 lysine (K) 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) near of SCN5A promoter region in striated muscles regulates normal expression of Scn5a and improve the re-expression of SCN5A in denervated muscle [35][39][40][49,53,54]. Moreover, Lamin A/C (encoded by LMNA) is a component of the nuclear lamina, and its K219T mutation has been described to trigger a change in the distribution of the histone marks. Concretely, H3K9me and H3K27me, which are transcriptional repressive histone marks, and H3K4me3, which acts as transcriptional active histone mark, generate cardiac conduction defects through SCN5A inhibition and reduced INa density [41][55].
Regulation of
SCN5A
by Transcription Factors
During biosynthesis, SCN5A transcription is regulated by several transcription factors. Sometimes this transcription step can be enhanced or decreased, i.e., TBX5 has a binding site downstream of the SCN5A gene, and several authors have demonstrated that TBX5 knockout presents a decreased density of Nav1.5 that leads to arrhythmias and eventually sudden cardiac death [42][43][44][56,57,58]. Additionally, GATA4 and GATA5 have their binding site in the SCN5A promoter and intron 1 region. These transcription factors activate the SCN5A gene in human left ventricles, whereas heterozygous mutants for GATA4+/− show short PR intervals [45][46][47][59,60,61]. Moreover, MEF2C has its binding site in the SCN5A promoter region and enhances SCN5A transcription [48][49][62,63]. Finally, IRX3 gain-of-function upregulates SCN5A mRNA levels [50][51][64,65], whereas, on the contrary, FOXO1 and Snail negatively regulate SCN5A mRNA levels [52][53][54][55][56][66,67,68,69,70] (Figure 1).
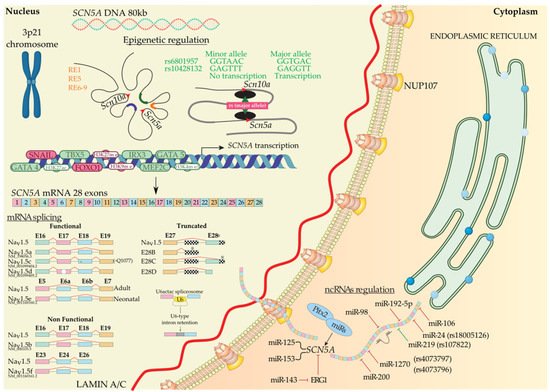

Figure 1. SCN5A biosynthesis: chromosomal localization, gene transcriptional activation modulated by regulatory elements, transcription factors, histones, and SNPs. Functional, non-functional, and truncated isoforms derived from mRNA splicing, mechanism of the U6-type intron retention, and post-transcriptional regulation mediated by ncRNAs. Alternative exon sequences, intronic or exonic sequences outside the open reading frame (squared), and stop codons (asterisks) are indicated.
2.2.2. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of SCN5A
Regulation of
SCN5A
by Alternative Splicing
After transcription, precursor mRNA copes with splicing and post-transcriptional modification to generate mature mRNA and finally translation into protein. Alternative splicing generate multiple functional (Nav1.5a, Nav1.5d, Nav1.5e, and Nav1.5c) and non-functional (Nav1.5b, Nav1.5f, and truncated) Nav1.5 variants [57][11]. Nav1.5a isoform is characterized by the deletion of exon 18. This isoform is only present in small rodents and, compared with full-length Nav1.5, leads to altered electrophysiological kinetics properties. There is no evidence of Nav1.5a expression in human cardiac cells [57][58][11,71]. Another alternative spliced variant of SCN5A generates Nav1.5c isoform, which has been identified as the most abundant isoform in humans. Nav1.5c is characterized by a 5′-trinucleotide deletion in exon 18, concretely a CAG—Glu (Q) in 1077 position, affected by the splicing machinery and generating a Nav1.5 variant that contains 2015 polypeptides instead of 2016. It has been identified that the electrophysiological properties of Nav1.5 and Nav1.5c are indistinguishable [58][59][71,72]. Nav1.5d is another Nav1.5 variant, where 120 bp fragment is deleted from exon 17. This Nav1.5d isoform is present in the fetal and adult human heart and has altered channel kinetics due to a reduction of open channel probability [58][60][61][71,73,74]. Finally, the last functional Nav1.5 variant is Nav1.5e and is generated by alternative splicing on exon 6. It can be found Nav1.5e with 5′-exon 6 in neonatal (exon 6a) or 3′-exon 6 (exon 6b) in any adult mammalian heart [4][62][4,75]. Nav1.5e contains a K211 residue, instead of D211 residue in Nav1.5, being responsible for slower kinetics of the channel [63][76]. Navd1.5b is a non-functional Nav1.5 variant and is generated by the deletion of exon 17 and exon 18. Heterologous expression reveals that exon 17 encodes an essential Nav1.5 region that confers functionality to the channel [61][64][74,77]. This splice variant is present in mouse hearts, but there is no evidence of this variant in other mammals’ hearts [61][74]. On the other hand, deletion of exon 24 of Nav1.5 generates Nav1.5f variant; this isoform is highly detected in rat heart and human brain but not in the human heart [65][66][78,79]. Electrophysiological experiments evidenced that Nav1.5f is a non-functional variant [58][71]. Finally, it has been identified three C-terminal truncated spliced variants, E28B, E28C, and E28D, that generate reduced protein levels and no functional Na+ currents in the normal fetal and adult human heart [67][80]. In another layer of complexity, in a very recent study, it has been evidenced that minor introns modulate gene families at a post-transcriptional level. Concretely, U6actac, which is a minor spliceosome component, modulates Nav1.5 and Cav1.2 protein levels through the removal of minor introns in Scn5a and Cacna1c, regulating electrophysiological properties of cardiomyocytes [68][81].
Regulation of SCN5A by Non-Coding RNAs
SCN5A mRNA degradation or translational repression can be mediated by microRNAs. It has been widely demonstrated that microRNAs exert their function controlling the development of several cardiac arrhythmogenic diseases; however, there is not much information about the SCN5A/Nav1.5 post-transcriptional control by microRNAs despite being an important modulator of cardiac arrhythmias [82,83,84,85]. A few years ago, data from our laboratory demonstrated that miR-98, miR-106, miR-200, and miR-219 directly regulated human SCN5A, while miR-125 and miR-153 regulate it indirectly, being evidenced that miR219 and miR200 modulate Scn5a expression in an opposite way in HL1 cardiomyocytes. Concretely, miR-200 decreases, while miR-219 increases Scn5a expression. Moreover, miR-219 is able to increase Nav1.5 protein levels leading to the subsequent rise in INa [86]. In another study, we elucidated a complex regulatory network where Pitx2 transcription factor and microRNAs are involved, being able to modulate ion channel expression in atrial fibrillation [87,88,89]. Additionally, Zhao et al. [90] demonstrated that miR-192-5p exerts its function, reducing Nav1.5 expression and INa density in humans. It has also been evidenced that SCN5A expression can be indirectly modulated through ERG1 mediated regulation by miR-143 [91]. Furthermore, a miR-24 binding site is generated in the coding sequence of SCN5A by the SNP rs1805126, decreasing SCN5A expression and INa density [92]. Finally, it has been evidenced that some SNPs can generate new miRNAs binding sites at the SCN5A 3′UTR region. Previous work in our lab demonstrated that rs4073797 and rs4073796 polymorphisms create a new miR-1270 binding site in SCN5A 3′UTR, which imbalance Scn5a expression. Moreover, rs107822C localized upstream of miR-219a precursor impairs miR-219a expression deregulating SCN5A/Nav1.5 levels [93]. Although INa is the most relevant during cardiac AP, the functional role of microRNAs controlling SCN5A expression is poorly described. Quite recently, a new class of RNAs has emerged, i.e., long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are long RNA molecules with >200 nt length and scarce protein-coding properties, but being able to modulate several biological processes and thus participating in pathogenesis [94,95]. It has been demonstrated that some lncRNAs modulate cardiac AP regulating the slow component of the delayed rectifier potassium current (IKS) or transient outward potassium current (Ito), concretely, lncRNA-Kcna2as and lncRNA-MALAT1, respectively [96,97], and more recently, it has been elucidated that lncDACH1 modulate Nav1.5 protein distribution through dystrophin binding which determines Nav1.5 membrane anchoring [98]. Studies about how cardiac AP can be modulated by lncRNA need to be further developed, as these molecular mechanisms could reveal a potential therapeutic work line.
3. Non-Genomic Regulation of the Cardiac Sodium Channel
Being an ion channel, Nav1.5 is first synthesized as a primary protein chain that is subsequently folded in order to acquire the pore-forming three-dimensional conformation [57][11]. This tertiary structure is then assembled with its beta subunits, most likely (β1), and trafficked through the Golgi apparatus to be targeted to the corresponding cell membrane compartments [69][99]. Along this whole process, Nav1.5 went through distinct non-genomic regulatory modifications and quality control steps conferring its unique conformational and functional identity as a voltage-gated sodium channel [57][70][11,100]. These steps are ensured by a growing set of regulatory proteins that have been demonstrated to covalently or non-covalently interact with Nav1.5 [71][101]. In addition to the interacting proteins, Nav1.5 function has been demonstrated to be influenced by wider intracellular (oxidative stress, metabolic stress, electrolyte homeostasis, etc.) and extracellular (pH, temperature, hormones, etc.) factors. All these factors are discussed subsequently in this review.
3.1. Regulation of Na
v
1.5 Biosynthesis and Post-Translational Modifications
3.1.1. Regulation of Nav1.5 Translation and ER Retention
The translation of Nav1.5 starts in the cytosol and then pursue into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Anchoring the ribosome with the elongating Nav1.5 polypeptide chain to the ER occurs when a signal peptide is recognized by the signal recognition particle (SRP) that targets the active ribosome to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Unlike cytosolic proteins, which have their signal peptide generally within the amino terminal, ion channels contain numerous signal sequences that are not restricted to the amino terminal [72][102]. Although the signal sequences of some ion channels such as Kv1.3 and CFTR have been already mapped to the second transmembrane spanning domain, almost 200 amino acids downstream from the NH2 terminal [72][102], that of Nav1.5 are not yet identified. Once anchored, the ribosome translocates the elongating polypeptide chain into the ER lumen [73][103]. As a transmembrane protein, the nascent Nav1.5 is soon pushed to the ER membrane, where it is anchored and retained [73][103]. The ER retention is thought to occur when specific ER retention motifs embedded in the elongating Nav1.5 polypeptide (most likely in the DI-DII linker of the sodium channel [74][104]) binds a cytosolic signal recognition particle (endoplasmic reticulum recognition particle, ERRP), that then directs the Nav1.5-ERRP complex to receptors within the ER membrane [75][76][77][105,106,107]. The complex Nav1.5-ERRP is then trapped within the ER, ensuring that the newly formed channel does not leave the ER membrane before finishing the folding and assembly steps [72][102]. At this level, several regulatory proteins and residues are reported to bind to this complex and facilitate the folding and maturation of the nascent protein [57][72][75][76][77][78][79][80][11,102,105,106,107,108,109,110] (Figure 2).
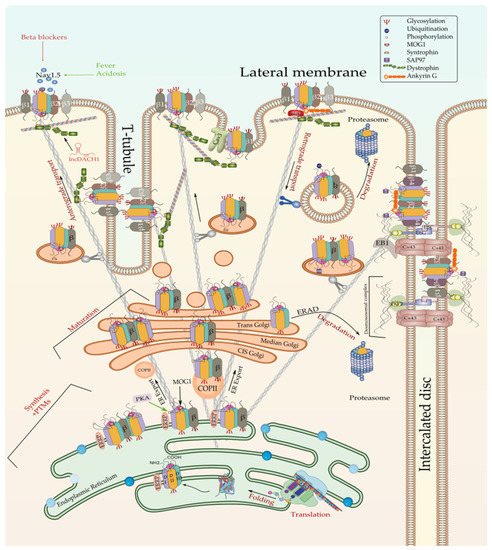

Figure 2. Biosynthesis and degradation pathways of Nav1.5. Only one of the possible scenarios where Nav1.5 assembles with one or more β-subunits early at the ER is depicted here. Furthermore, one possible scenario where ERAD-dependent degradation exclusively affects α subunit rather than α-β assembly is shown here since no information is currently available about the detailed process. ERRP—endoplasmic reticulum retention protein; β—beta subunit; PKA—protein kinase A; MOG1—RAN guanine nucleotide release factor; COPII—coat protein complex II; ERAD—ER-associated degradation; Cx43—connexin 43; PKP2—plakophilin 2; DSG—desmoglein; DSC—desmocollin; EB1—end-binding 1; Cav3—caveolin 3; PTMs—post-translational modifications.
The correct folding of the newly synthesized Nav1.5 channels is commonly thought to be a condition for their forward trafficking to the cell membrane and their proper gating function. This notion has been tested by the exploration of Nav1.5 trafficking-deficient mutants such as R282H, A124D, and V1378M that, due to folding defects, they failed to exit the ER and thus to reach the cell membrane [81][82][111,112]. Although the importance of this step in the life cycle of any ion channel, very scarce information is currently available about the mechanism of Nav1.5 folding and its regulation. Nonetheless, it is currently established that one of the prerequisites for proper Nav1.5 folding is core-glycosylation, as will be discussed later in this review [113]. In addition, molecular chaperone proteins such as protein disulfide isomerases (PDI), ER oxidoreductases (ERO), 70 kDa heat shock proteins (Hsp70), 90 kDa heat shock proteins (Hsp90), as well as calnexin and calreticulin, have been demonstrated to regulate the folding of the nascent proteins and the ER-associated degradation of the misfolded proteins [84][85][86][87][88][114,115,116,117,118]. However, their implication in the Nav1.5 folding process has not been specifically studied yet. Interestingly, Nav1.5 H558R polymorphism has been shown to have a corrective effect on the misfolded R282H mutant by restoring its trafficking to the cell membrane and thus limiting the misfolding of the mutant through a physical interaction [111,119].
Some antiarrhythmic drugs such as mexiletine, quinidine, and flecainide proved their efficiency rescuing the trafficking of some misfolded Nav1.5 variants, thus playing the role of pharmacological chaperones [82][90][112,120]. In addition, curcumin, a major constituent of turmeric known to block the ER calcium pump, has also been reported as effective in rescuing the INa current of L325R misfolded Nav1.5 channels [26][40]. Low temperature has also been demonstrated to trigger the rescue of misfolded Nav1.5 mutants [90][120], probably through slowing the folding process, which prevents protein misfolding and aggregation [91][121].
3.1.2. Co-Translational and Post-Translational Regulation of Nav1.5
N-Linked Glycosylation of Nascent Na
v
1.5
One of the earliest modifications that the Nav1.5 undergoes co-translationally once inserted into the ER is the N-glycosylation [69][83][99,113]. This quality control step has been first evidenced in the rat heart by Cohen and Levitt, who have found that glycosylation increases Nav1.5 mass by only 5%, compared to 25–30% increases observed in other voltage-gated sodium channel isoforms [92][122]. Glycosylation initiates in the ER and terminates in the Golgi [83][93][113,123]. In the ER, glycosylation initiates when glycan (Glc3Man9GlcNAc2) is dissociated from a lipid derivative by oligosaccharyl transferase (OST) and bind to the amide nitrogen of asparagine (N) localized in the extracellular side of the nascent Nav1.5 protein [70][94][100,124]. Although no validated “map” of the N-glycosylation sites has been published yet for Nav1.5, 13 potential external N-glycosylation sites have been identified in human Nav1.5 [95][125], and at least 14 putative N-linked glycosylation sites have been reported in the rat cardiac sodium channel [92][122]. The N-glycosylation of the newly formed cardiac sodium channel has been reported to be a prerequisite for proper Nav1.5 folding and subsequent surface expression as well as an assembly with its β subunits [69][83][96][99,113,126]. According to Arakel et al., Nav1.5 maturation strongly depends on the presence of the auxiliary β1 that binds to the pore-forming α subunit and promotes its glycosylation and its trafficking to the cell membrane [97][127].
In this context, N-glycosylated Nav1.5 is thought to undergo subsequent serial de-glucosylation steps and extreme quality controls involving the ER-resident chaperones, which will ensure that only correctly folded and fully glycosylated channels can be trafficked [83][93][98][113,123,128]. Interestingly, Mercier et al. found that early N-glycosylated Nav1.5 channels generated in the ER could reach the cell membrane through an unconventional trafficking pathway bypassing the Golgi stacks while functional channels are trafficked through the conventional pathway that is Golgi-dependent [83][113]. In addition, ER-resident chaperones such as Calnexin and Calreticulin have been reported to play a crucial role in controlling ion channels folding and efficient export to the Golgi [99][100][101][129,130,131]. However, there is no evidence of physical interaction of Calnexin and Nav1.5 despite their proven co-localization in the ER [102][103][132,133]. While properly folded Nav1.5 are trafficked forward to the cis-Golgi where they will be fully maturated, misfolded Nav1.5 are retained in the ER to be later degraded, most likely through the activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway and/or ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway that is linked to the cytoplasmic ubiquitin-proteasome pathway [104][105][106][134,135,136].
Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation of Na
v
1.5
In addition to N-linked glycosylation, Nav1.5 undergoes phosphorylation as a post-translational modification [107][137]. Thirty years ago, Shubert et al. brought the first evidence of Nav1.5 phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA) through the activation of the β-adrenergic system by isoproterenol, which led to an increased level of cAMP, which in turn reduced Na+ current (INa) [108][138]. These findings were further confirmed by a subsequent study by Frohnwieser and his co-worker, who showed that combined cytosolic injection of cAMP and a PKA activator increased INa suggesting a modulatory effect of PKA on human Nav1.5 [109][139]. The same study demonstrated that this modulatory effect of PKA is conferred by the DI–DII intracellular linker of Nav1.5. In this regard, it has been reported that the rat Nav1.5 protein sequence harbors two distinct sites for PKA phosphorylation that were mapped to serine positions S526 (525 in human) and S529 (528 in human) [70][110][111][112][100,140,141,142]. These sites are localized in the cytosolic loop interconnecting DI and DII of Nav1.5, where the three putative RXR-type (R479KR481, R533RR535, and R659QR661) ER retention motifs have been localized too [74][107][113][104,137,143]. Zhou et al. have previously demonstrated that PKA activation promotes trafficking of channels to the plasma membrane [113][143]. In the same context, Scott et al. have shown that a PKA-PKC mediated phosphorylation of NMDA receptor masks its ER retention motifs leading thus to its release from the ER and exportation to the cell membrane [114][144]. Taken together, these findings suggest a similar mechanism where the phosphorylation of Nav1.5 at S525 and S528 by PKA leads to changes in the Nav1.5 conformation that masks the ER retention signals and eases the trafficking of the channel to the cell membrane [112][115][142,145]. This is consistent with the idea that proper folding of Nav1.5 unmasks its ER retention motifs and facilitates its forward trafficking to the Golgi apparatus [76][106].
In an antagonistic way to PKA, Nav1.5 is downregulated by protein kinase C (PKC)-mediated phosphorylation which leads to a reduced channel density at the cell surface and INa decay [116][146]. Although ten different PKC isoforms have been identified in human ventricular myocytes and in different animal species [117][147], isoform-specific activation/inhibition studies suggested εPKC isoform as the key player in the PKC-mediated regulation of Nav1.5 and INa [118][119][148,149]. Nonetheless, PKCδ-mediated Nav1.5/INa downregulation either directly through phosphorylation at S1503 or indirectly through elevated mitoROS production has been reported [120][150]. In addition, a minor role of αPKC reducing INa through angiotensin II has also been described [121][151]. As a direct mechanism, the PKC (particularly εPKC) effect on Nav1.5 and INa has been partially attributed to the phosphorylation of a conserved serine S1503 of the DIII-DIV cytosolic linker of Nav1.5 [122][123][152,153]. However, intracellular metabolic changes have been described as a mediator of PKC activation and PKC-mediated phosphorylation of Nav1.5 [120][150]. In this regard, high intracellular levels of NADH have been described as triggers of PKC, thus leading to overproduction of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mitoROS) and INa decay [124][125][126][154,155,156]. This effect has been demonstrated to be mediated by glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 (GPD1L) [127][157] and could be reversed by NAD+-mediated PKA activation [124][128][129][130][154,158,159,160]. Interestingly, Fouda et al. have demonstrated that PKA and PKC phosphorylation pathways could be activated by Cannabidiol and Estradiol and that this activation could rescue the high glucose-induced changes in Nav1.5 properties [131][132][161,162].
Importantly, not far from the PKA phosphorylation sites in Nav1.5 DI–DII linker, there is a Ca2+/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II (CaMKII) phosphorylation site as well, which was mapped to S516 [133][163]. This CaMKII phosphorylation site is not the only one in Nav1.5 since Ashpole et al. have identified four extra potential sites; all of them are localized in DI–DII linker, suggesting linker I as a hotspot for Nav1.5 phosphorylation [133][163]. However, a recent study by Herren et al. identified 23 sites along Nav1.5 intracellular regions that could be phosphorylated by CaMKII in human Nav1.5 [134][164]. More recently, Burel et al. identified two further CaMKII phosphorylation sites localized in the C-terminal region of Nav1.5 [135][165]. Several studies have shown that Nav1.5 is regulated by CaMKII and that activation of this kinase increases the so-called pathogenic late cardiac sodium current INaL [136][166]. Interestingly, El Refaey et al. demonstrated that INaL could also be regulated by B56α, the key regulatory subunit of the PP (protein phosphatase) 2A holoenzyme [137][167]. This phosphatase is targeted by ankyrin-G to the Nav1.5-CaMKII -βIV spectrin axis at the ID where it is thought to dephosphorylate Nav1.5 at S571 in the DI-DII linker via B56α balancing, thus the CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of the cardiac sodium channel. According to a study by Deschênes et al., inhibition of CaMKII slowed Nav1.5 channel current decay, produced a depolarizing shift in fast inactivation, and slowed entry into inactivated states [138][168].
Nav1.5 is also phosphorylated by Tyrosine kinases. In this regard, phosphorylation of Nav1.5 by the Src family Tyrosine kinase Fyn has been first reported by Ahern and co-workers, who have demonstrated that this kinase acts by increasing the rates of recovery from fast-inactivated states, thus impairing the steady-state inactivation of Nav1.5 [139][169]. Fyn kinase acts most likely on Tyr1495 of Nav1.5 not far from the Ile-Phe-Met (IFM) motif of DIII–DIV linker that is known to modulate the rapid inactivation process of the channel [5]. In the heart, Fyn tyrosine kinases are reported to co-localize with Nav1.5 channels at adherens junctions, where they modulate electrical coupling and propagation of action potential [140][141][170,171]. Iqbal et al. found that the major Nav1.5 splice variants Q1077 and delQ1077 are differentially phosphorylated by Fyn kinase, which results in coordinated steady-state rapid inactivation kinetics for smooth electrical activity of the heart [142][172]. The same researchers suggested a multistep mechanism by which Fyn kinases bind and modulate Nav1.5. This mechanism starts by the association of Fyn kinase to proline-rich regions in the DI–DII linker and C-terminal region of Nav1.5, which activates the phosphorylation of neighboring tyrosine residues in the N-terminal region (Y68, Y87, and Y112), DIII–DIV linker (Y1494, Y1495), and C-terminal region (Y1811, Y1889) [139][142][143][169,172,173]. Particularly, Y1494 and Y1495 of the DIII–IV linker have been demonstrated to play an essential role in the anchoring of Ca2+/Calmodulin to the Nav1.5 inactivation gate, and thus Fyn-mediated phosphorylation of the two Tyrosine residues has been suggested to reduce or abolish calmodulin binding and to impair the interaction of the side chain with the inactivation gate receptor [144][174].
Additionally, Nav1.5 has been reported to be dephosphorylated by the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (PTPH1), which interacts with the Nav1.5 PDZ domain binding site at the C-terminal region [101]. PTPH1–mediated dephosphorylation of Nav1.5 modulates its gating by shifting the steady-state inactivation towards hyperpolarized potentials [175].
Arginine Methylation
Beltran-Alvarez and co-workers evidenced for the first time that Nav1.5 is post-translationally modified by arginine methylation at three residues (R513, R526, and R680) within the Nav1.5 DI–DII linker [146][176]. This modification is catalyzed by arginine methyltransferases (PRMT) PRMT-3 and PMRT-5 and leads to an increased expression of Nav1.5 in cell surface [147][177]. Studying the PTMs of Nav1.5 in end-stage heart failure patients, the same team demonstrated that methylation of R526 is the major quality control step of any Nav1.5 arginine or lysine residue [148][178].
N-Terminal and Lysine Acetylation
Another PTM during the Nav1.5 life cycle is the acetylation process. Two types of acetylation have been reported so far: reversible and irreversible. The first type is mediated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) which exert N-terminal acetylation of a Nav1.5 lysine residue leading to enhanced trafficking of Nav1.5 and therefore to an increased INa current [149][179], whereas the second type of acetylation is mediated by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs), where a Nav1.5 alanine residue is acetylated and has been reported as a Nav1.5 degradation signal [147][177]. Interestingly, native Nav1.5 channels purified from end-stage heart failure patients were reported to lack the initiation of methionine and be acetylated at the resulting initial alanine residue [148][178]. Recently, Vikram et al. showed that Nav1.5 undergoes reversible lysine acetylation. For instance, sirtuin 1 deacetylase (Sirt1), an NAD+-dependent lysine deacetylase, has been demonstrated to regulate Nav1.5 channels by deacetylating lysine residue 1479 (K1479) in the DIII–DIV linker, which promotes Nav1.5 cell surface expression and increases INa [150][180]. Interestingly, the murine model of cardiac Sirt1 deficiency presents fatal cardiac conduction defects as a result of K1479 hyperacetylation, which decreases Nav1.5 cell surface expression and reduces INa. These arrhythmogenic substrates are similar to those characterizing human Nav1.5 loss-of-function cardiac arrhythmias suggesting that Nav1.5 Sirt1-mediated deacetylation is crucial for the proper function of the cardiac sodium channel. It is noteworthy that the authors of this study raised an interesting point regarding the role of the functional interaction and interplay between different PTMs fine-tune regulating the Nav1.5 channel expression and function. In this regard, it has been suggested that Nav1.5 is regulated by Sirt1-mediated interaction between lysine acetylation and the ubiquitination in one hand and NAD+ dependent interplay between PKC-mediated phosphorylation and Sirt1-mediated deacetylation in another hand [150][180].
SUMOylation
Although more than 25 years have passed since the discovery of SUMOylation, a post-translational modification conjugating a small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) molecule to a lysine residue in the substrate protein [151][181], very scarce information are currently available about the regulation of Nav1.5 by SUMOylation. For instance, only one study, that of Plant et al., has reported that one of the mechanisms underlying INaL elevation in response to acute cardiac hypoxia is the quick SUMOylation of Nav1.5 channels at the cell surface [152][182]. Particularly, SUMOylation of K442 residue has been reported to contribute to the pathological increasing of INaL and action potential prolongation through activation of Nav1.5 channels when they should normally be inactivated.
S-Nitrosylation
S-nitrosylation, a PTM consisting of the covalent binding of a nitrogen monoxide (NO) moiety to the thiol side chain of cysteine in the target protein, has recently gained progressive attention as a crucial quality control step that is required for the proper function of a given protein [153][183]. In the cardiomyocytes, NO is produced by neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) [154][184]. nNOS mediated S-nitrosylation of Nav1.5 has been demonstrated to maintain INaL [155][185]. Interestingly, nNOS has been shown to interact with Nav1.5 via its regulating protein α1-syntrophin, which acts as a scaffolding protein bringing together Nav1.5 with nNOS and plasma membrane Ca-ATPase (PMCA4b) (an inhibitor of nNOS activity) [156][186]. Therefore, LQTS-associated α1-syntrophin mutation has been demonstrated to break the SNTA1- PMCA4b association neutralizing, thus the nNOS inhibition and increasing Nav1.5 S-nitrosylation, which in turn increase INaL currents [156][186]. A similar effect has been observed with a decreased caveolin 3(Cav3) expression, which has been shown to enhance S-nitrosylation of Nav1.5 through increasing the nNOS activity, which increased INaL in cardiomyocytes [157][187]. However, a very recent study by Wang and co-workers suggested an indirect mechanism by which S-nitrosylation modulates the cardiac sodium channel expression and function. For instance, NO has been demonstrated to down-regulate SCN5A expression and Nav1.5 function through S-nitrosylation of regulatory transcription factor FOXO1 [158][188]. These findings increase our current understanding of the role of redox and free radicals in the regulation of Nav1.5 function (see [100] for further review).
Lipoxidation
Lipoxidation refers to the establishment of covalent adducts between reactive products of lipid peroxidation and macromolecules such as proteins, phospholipids, and DNA [159][189]. Recently, lipoxidation gained interest as a post-translational modification of the cardiac sodium channel that gives further evidence on the regulation of Nav1.5 by oxidative stress [160][190]. Nonetheless, little information is currently available about the mechanism of Nav1.5 regulation by lipoxidation. In this respect, in vitro data by Nakajima and co-worker provided the first evidence that Nav1.5 is post-translationally modified by lipoxidation during oxidant injury and that sodium channel dysfunction evoked by lipid peroxidation could be prevented by scavenging Isoketals (IsoKs), which are the most reactive products of lipoxidation [161][191].
Methionine Oxidation
A previous study by Quiñonez et al. demonstrated that skeletal Nav1.4 fast inactivation could be impaired by oxidizing at least two methionine residues in the channel [162][192]. These findings have been supported in cardiac Nav1.5 as well, where oxidative modification of the methionine within the IFM motif has been shown to lead to a drastic loss of Nav1.5 inactivation [163][193]. Interestingly, Nav1.5 channels and INa currents have been reported to be indirectly modulated by CaMKII, the activation of which depends on the oxidation of its own methionine residues [164][194].
Palmitoylation
Palmitoylation (also called S-acylation) is the PTM of protein cysteines with saturated fatty acids that modify protein hydrophobicity and thereby influence their function [165][195]. Palmitoylation has been reported to regulate ion channel’s function, most likely through controlling their trafficking and cell membrane expression [69][166][99,196]. An early study by Schmidt et al. showed that Nav1.5 is subject to palmitoylation [69][99]. However, palmitoylation has been demonstrated to slightly influence cell surface expression of Nav1.5 and rather significantly impact channel availability by regulating the voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation in both HEK293 cells and cardiomyocytes [167][197]. Additionally, cysteine residues predicted to be palmitoylated in Nav1.5 are mapped to the DII–DIII linker of the channel by prediction algorithms [167][197].
3.1.3. Regulation of the ER-to-Golgi Trafficking
Well folded and assembled proteins are supposed to cross the ER-Golgi space in vesicle budding guided by cytoskeletal proteins [168][198]. Studying the subcellular distribution of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 in HEK293 Cells and canine cardiac myocytes, Zimmer et al. noticed an accumulation of the intracellular channels within the ER and a lower channel density in the Golgi apparatus. Thereby, they proposed that ER plays the role of an intracellular reservoir where sodium channels are transiently stored [169][199]. As discussed previously, stimulation of PKA likely results in the activation of the ER-to-Golgi trafficking, which in turn leads to a rapid increase of the channel density in the cell membrane [74][104]. However, the whole mechanisms underlying the ER exit of Nav1.5 to the Golgi is not yet fully deciphered, and current advances in this topic show that not only the PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the Nav1.5 ER retention sites is what facilitates its ER-Golgi exportation. That is, several proteins and enzymes have been reported to bind to Nav1.5 once retained to the ER and enhance its release. In this context, Wu et al. have identified the Ran-guanine nucleotide release factor (RANGRF or MOG1) as a cofactor of Nav1.5, which by binding to its intracellular loop DII–DIII facilitates its cell surface expression [170][200]. Using the DII–DIII linker of Nav1.5, in yeast two-hybrid analyses, the team demonstrated that MOG1 is crucial for the optimal expression of Nav1.5 and promotes its ER export and intracellular trafficking to the plasma membrane [170][200]. These findings are consistent with Chakrabarti et al. study, which showed that silencing of MOG1 expression by small interfering RNAs caused retention of Nav1.5 in the ER, reduced Nav1.5 plasma membrane expression, and disrupted the Nav1.5 targeting to the cell surface, in particular, to the caveolin-enriched microdomains (caveolae) [171][201]. A subsequent mutational study performed by Yu et al. further revealed that mutations in the amino acids E83, D148, R150, and S151 of MOG1 disrupt its interaction with Nav1.5 and significantly reduce the cardiac sodium channel trafficking to the cell surface, suggesting that these amino acids are important for the MOG1-Nav1.5 binding and interaction [172][9]. The same team found that MOG1-mediated trafficking and function of Nav1.5 requires the interaction of MOG1 with two small GTPases SAR1A and SAR1B and that the knockdown of both enzymes abolishes the function of MOG1 [173][202]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that activation of SAR1 leads to the recruitment and internalization of Nav1.5 cargo into the coated transition vesicle COPII-coated vesicles that will ensure its ER-to-Golgi trafficking [173][202]. The Nav1.5 ER export is also controlled by Dynamitin as demonstrated by Chatin et al., who have proved, using a yeast two-hybrid system, that Dynamitin (C-terminal domain), interacted with the Nav1.5 DI–DII linker between amino acids 417 and 444 and that this interaction is crucial for the Nav1.5 cell-surface density probably through controlling the ER-to-Golgi trafficking [174][203].
3.1.4. Regulation of Nav1.5 Maturation and Golgi Export
Once in the Golgi, N-glycosylated Nav1.5 undergoes additional mannose trimming and terminal glycosylation where acetyl-glucosamine, oligosaccharides, and finally sialic acid residues are sequentially added as the protein crosses the distinct Golgi cisternae. It has been demonstrated that glycosylation regulates voltage-gated sodium channels (including Nav1.5) gating, inactivation, and recovery process during cardiac AP by interfering with the electric field near the gating sensors [175][176][177][178][179][204,205,206,207,208]. Hence, it has been suggested that extracellular sialic acid residues, which are negatively charged at physiological pH, modulate the sensitivity of the Nav1.5 voltage sensor domains to the transmembrane electrical potential fluctuation [180][209]. Particularly, sialic acid residues localized to DI S5-S6 have been demonstrated to regulate the sialic acid-dependent gating of Nav1.5 [95][125].
Mature Nav1.5 (fully glycosylated) are exported from the Golgi apparatus, which acts as a major secretory sorting hub that targets newly synthesized proteins to their final subcellular destinations [181][210]. Although the current knowledge on the exact mechanisms regulating the Nav1.5 export from the Golgi and trafficking to the cell membrane is still limited, a recent study by Ponce-Balbuena and co-workers reported that Nav1.5 Golgi export is driven by a trafficking signal localized in its terminal COOH region. This signal corresponds to a binding site of the adaptor protein complex 1 (AP1) mapped to Nav1.5’s Y1810 residue. AP1-marked Nav1.5 will be then incorporated into clathrin-coated vesicles that will migrate to the cell membrane where the channel will be anchored [182][211]. The same team showed that the Nav1.5 cross the Golgi-cell membrane space by a common anterograde trafficking pathway as Kir2.1. These findings support previous studies demonstrating that both ion channels form a channelosome that shares common trafficking, targeting, anchoring, recycling, and degradation pathways [183][184][212,213].
3.1.5. Regulation of the Nav1.5 Targeting to the Cell Membrane
Over the last few years, it became widely accepted that not all the Nav1.5 proteins synthesized in one cardiomyocyte undergo the same regulatory steps till reaching their final localization in the cell membrane [185][214]. After years of debate and controversial studies about the subcellular distribution of the cardiac sodium channel, the new cellular imaging techniques excluded the idea of an exclusive expression of Nav1.5 at the ID [141][186][171,215] and gave way to a more conceivable model that suggests a multi-pool aggregation of Nav1.5 along with the cellular membrane compartments including the LM and the T-tubules [187][188][189][216,217,218]. Being in one membrane domain or the other put the Nav1.5 in distinct microenvironments composed of different interacting proteins that regulate its gating function and biophysical properties. Above all these interacting proteins, beta subunits are without doubt the ones that most gained interest in this field over the last few decades as their presence and function are dependent on the presence of the pore-forming α-subunit (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
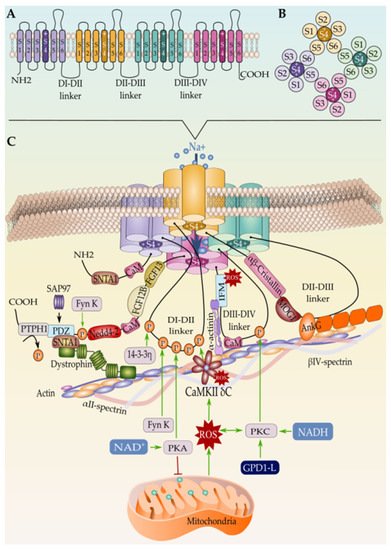

Figure 3. (A) Schematic representation of the Nav1.5 secondary structure, (B) the intracellular view of the channel, and (C) the tertiary structure along with the interacting proteins. Only proteins with known binding sites in Nav1.5 are represented here. Mechanism of Nav1.5 regulation by the mitochondrial reactive oxygen species ROS is represented as well.
Regulation of Na
v
1.5 by β-Subunits
The β subunit family consists of four different proteins β1–4 encoded by four genes, SCN1B–SCN4B, respectively, with β1 alternatively spliced into two isoforms, β1A and β1B [190][219]. TAs mentioned earlier in this review, the β-subunits, most likely β1-subunits, assemble with Nav1.5 at the endoplasmic reticulum and influence its maturation and trafficking to the plasma membrane [97][191][127,220]. Alpha-beta subunits assembly is either covalent (β2 or β4) or non-covalent (β1 or β3) [192][221]. Particularly, β 4-Nav1.5 covalent association is ensured by an extracellular cysteine–cysteine single disulfide bond [193][194][222,223], while β2 does not form a disulfide linkage at this position with Nav1.5 as recently specified [5], whereas β1 and β3 non-covalently interact with Nav1.5 through the channels DIV and DIII voltage gating domain respectively [195][224].
Despite the structural similarities between β2/β4 on one hand and β1/β3 on the other hand, their expression differs from one cellular sub-domain to another. Inside the cardiomyocyte, β3 are expressed at the T-tubules and β4 at the ID, while β1 and β2 are found at both locations [186][196][197][215,225,226]. Zimmer et al. have suggested that, unlike β2, β1 associates to Nav1.5 early at the ER, and both α and β1 subunits are trafficked together to their final destination at the cell membrane [198][227]. Subsequent studies revealed that β1-subunits enhance the α-subunits dimerization and promote the dominant-negative effect of trafficking defective mutants [199][228]. β2 has been reported to promote surface localization of Nav1.5 [200][229]. Importantly, β3 subunits have been demonstrated to bind to Nav1.5 in multiple sites and promote the formation of α subunit oligomers, including trimers [201][230]. However, β4 has been reported as a modulator of Nav1.5 kinetic and gating properties by increasing INa [202][231]. Taken together, these findings are consistent with the idea that the distinct sodium channel β subunits provide support for the pore-forming subunit, facilitate the trafficking of the mature channel to the different membrane domains, and modulate the gating function of Nav1.5 by increasing the INa [203][204][205][206][207][232,233,234,235,236]. More details regarding the regulation of Nav1.5 by β subunits in the context of sodium channelopathies are discussed in Section 4 of this review.
The Na
v
1.5 and the Intercalated Disc Interactome
As suggested by the Delmar research team, several evidence point to the fact that the ID is not a hub of proteins playing independent functions within the cardiomyocyte, but rather a network of molecules interacting together in order to fulfill a specific function (AP propagation, cell-to-cell coupling, cardiac excitability, etc.) that cannot be accomplished if this “interactome” is impaired [208][237]. As a component of the ID proteins, Nav1.5 has been demonstrated to be in the heart of this interactome by physically and functionally associating to several proteins belonging to this macromolecular complex.
In this context, it is currently well known that Nav1.5 targeted to the ID are “tagged” with synapse-associated protein 97 (SAP97), a scaffolding MAGUK ((membrane-associated guanylate kinase) protein that is abundantly expressed in human and rat ventricular myocardium [209][238]. SAP97 has been introduced as the determinant of the Nav1.5 ID pool as it plays an important role in targeting Nav1.5 along with Kir2.1 to this cell membrane domain [209][210][238,239]. Both channels were structurally evidenced to co-assemble to SAP97 by their C-terminal domains [209][211][238,240]. For Nav1.5, it is assumed that the last three amino-acids (serine–isoleucine–valine or SIV motif) of the C-terminal region form a PDZ (postsynaptic density protein (PSD95), Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor (Dlg1), and zonula occludens-1 protein (zo-1) domain binding motif) that interacts with the syntrophin–dystrophin complex at the cardiomyocyte LM and PDZ domains of SAP97 at the ID [189][218]. In the absence of the PDZ-domain-binding motif of Nav1.5 or SAP97, Nav1.5 expression at the cell surface decreased, thus leading to a reduction in the cardiac INa in vitro [212][241]. However, a subsequent study by the same team demonstrated that in vivo ablation of SAP97 did not change Nav1.5 localization and function, but it did decrease the cardiac potassium currents [213][242]. The authors of these studies justified this discrepancy by the fact that SAP97 silencing in vitro is induced in adult cardiomyocytes while in vivo, it is a constitutive ablation present early in development, which may impact protein expression and interactions.
In addition, the Nav1.5-SAP97-Kir2.1 complex has been demonstrated to reach the ID through the microtubule highway [103][209][210][214][133,238,239,243]. Although the exact mechanism by which Nav1.5 is targeted to the ID is not yet fully discovered, part of it is already elucidated. A few years ago, Agullo-Pascual et al. proved for the first time that the microtubule plus-end tracking protein “end-binding 1” (EB1) is captured to the IDs by connexin 43 (cx43), which facilitates the cargo delivery, including Nav1.5 [215][244]. These findings are consistent with Marchal and co-workers’ recent study in which they have further proved that EB1 modulates Nav1.5 trafficking to the IDs and that loss of EB1 function leads to reduced INa and conduction slowing [216][245]. Moreover, EB1 has been previously demonstrated to bind directly to CLASP2 (cytoplasmic linker associated protein 2) and form a complex at the microtubule plus-end, promoting thus microtubule polymerization and stabilization [217][246]. Interestingly, inhibiting the GSK3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3β)-mediated phosphorylation of CLASP2 enhanced the EB1–CLASP2 interaction, which in turn led to an increased Nav1.5 delivery at the ID of cardiomyocytes and an increased INa [216][245]. Furthermore, Rhett et al. have shown that in addition to its known localization at the gap junction where it interacts with zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) [218][219][247,248], Cx43 also co-localizes with ZO-1 in the zone surrounding the gap junction, conventionally termed as perinexus and that Cx43 but not ZO-1 interact with Nav1.5 at this zone in physiological conditions [220][249]. In vivo and in vitro assays show that Nav1.5 expression and function are reduced as a result of Cx43 expression/function decrease, thus giving more evidence that Cx43 is required for a proper Nav1.5 function at the ID [221][250].
Importantly, Nav1.5 and Cx43 interaction at the perinexus is thought to be mediated by scaffolding proteins SAP97 and Ankyrin G (AnkG) as their interaction has been reported [212][222][241,251]. In the cardiovascular system, ankyrins are critical components of ion channels and transporter signaling complexes, and their dysfunction has been linked with abnormal ion channel and transporter membrane organization and fatal human arrhythmias [223][252]. Although both ankyrin-B (AnkB, encoded by ANK2) and ankyrin-G (ANK3) have been found to be expressed in the myocardium, only ankyrin-G has been shown to interact with Nav1.5 [224][253]. Specifically, AnkG is necessary for normal expression of Nav1.5 and acts as a coordinating signaling center, functionally coupling Nav1.5 gating with upstream kinase and phosphatase enzymes and downstream cytoskeletal proteins [80][225][110,254]. AnkG is primarily expressed at the ID membrane and T tubules, where it co-localizes with Nav1.5 [112][142]. In vitro, it has been demonstrated that AnkG binds to Nav1.5 and that AnkG downregulation impaired the subcellular localization of Nav1.5 and reduced the INa current amplitude [226][227][255,256]. In vivo, Makara and his collaborators have demonstrated that AnkG plays an indispensable role in directing Nav1.5 and its regulatory protein CaMKII to the ID [225][228][254,257]. Mutational studies have further confirmed that disrupting the binding of AnkG to Nav1.5 impairs AnkG dependent targeting of the Na+ channel to the ID leading thus to a reduction in INa density and cardiac arrhythmias [224][225][229][253,254,258]. A recent study performed by Yang et al. has demonstrated that AnkG, but not AnkB, are expressed at the IDs and that masking Nav1.5 binding sites in AnkG using competitive peptides caused a decrease in sodium channel current (INa) and targeting defects of the Na+ channels to the ID, but not to LM [184][213]. However, a more recent study by Cavus and collaborators specified that only canonical AnkG isoforms have this regulatory effect on Nav1.5 and that noncanonical (giant) AnkG isoforms mediated electrical dysfunction is independent of Nav1.5 [230][259].
Furthermore, AnkG is thought to mediate the interaction between Cx43 and PKP2, thus connecting desmosomal proteins with the molecular complex that captures the microtubule plus-end at the ID, thus allowing for delivery of Nav1.5 [215][227][231][244,256,260]. This is consistent with the fact that loss of desmosomal integrity impacts cardiac conduction and leads to cardiac arrhythmias [231][232][233][260,261,262]. Accordingly, loss of Plakophilin-2 (PKP2), a crucial component of the cardiac desmosome, has been demonstrated to decrease INa in cardiac myocytes [234][263]. Similarly, loss of PKP2 expression in HL1 cells and in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) from a patient with PKP2 deficiency reduced INa amplitude [232][235][261,264]. Likewise, Rizzo et al. have demonstrated that desmoglein-2 (Dsg2), another desmosome protein, physically interacts with Nav1.5 at the ID of mouse cardiomyocytes in vivo [236][265]. They showed that mice models over-expressing a desmoglein-2 mutation present a wider intercellular space at the level of the ID, longer ventricular activation time, lower conduction velocity, lower upstroke velocity, and lower INa amplitude compared to wild type. Although no evidence of direct interaction between Desmoplakin (DSP) and Nav1.5 has been reported, RNAi-based Desmoplakin silencing in vitro resulted in a reduction in Nav1.5 expression at the ID of cardiomyocytes, an abnormal sub-cellular distribution of Cx43 and Nav1.5, INa decay, and slowed conduction velocity suggesting that DSP regulates Nav1.5 [237][266].
Similarly, AnkG is established as an adaptor protein that organizes, transports, and anchors Nav1.5 to the actin/spectrin cytoskeleton [238][239][240][267,268,269]. In fact, the AnkyrinG-Nav1.5 complex is believed to connect with the actin/α-spectrin cytoskeleton through CaMKII-βIV-spectrin interaction where the latter acts as a CaMKII-anchoring protein and thereby orchestrating the whole macromolecular complex; however, no evidence of direct interaction between Nav1.5 and βIV-spectrin has been found yet [226][255]. On the other hand, βIV-spectrin is assumed to control the CaMKII-dependent regulation of Nav1.5 at the ID, and loss of βIV-spectrin/CaMKII interaction precludes CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of Nav1.5 at Serine 571 in the DI–DII linker and abolishes the stress-induced activation of the pathogenic INa,L [241][242][270,271].
Remme’s team [243][272] has recently demonstrated that ID Nav1.5 physically interacts with coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR), a single-pass transmembrane cell adhesion molecule (CAM) [244][273]. Furthermore, they have demonstrated that CAR haploinsufficiency decreased INa amplitude at the ID, which in turn reduced sodium channel availability at this cell membrane compartment. Nav1.5–CAR interaction is only beginning to be understood, and thus, mechanisms underlying this interaction are still to be studied.
Our current understanding regarding the Nav1.5 auto-regulation is still limited. Over the last decades, several controversial studies emerged regarding the sodium channel α-α-subunits interaction and dimerization. However, Clatot and co-workers settled this controversy by demonstrating for the first time that trafficking-defective Nav1.5 exerts a dominant-negative effect on non-defective ones through α-α-subunits physical interaction at their N-terminal regions, precluding thus their cell surface expression [245][274]. Building on these findings, the team further evidenced that cardiac sodium channel α-subunits assemble as dimers with coupled gating and that this dimerization is mediated through an interaction site found within the DI-II linker of Nav1.5, between amino acids 493 and 517 [246][275]. Curiously, earlier studies have shown that 14-3-3 protein, a member of highly conserved cytosolic acidic proteins, physically interacts with the DI-II linker of Nav1.5 (between amino acid 417 and 467) at the ID and that this interaction facilitates the dimerization of cardiac sodium channels [247][276]. Strikingly, Clatot et al. identified a second 14-3-3 protein-Nav1.5 interaction site between amino acid 517–555 and demonstrated that co-operative gating behavior but not dimerization of α-subunits is dependent on 14-3-3-Nav1.5 interaction [246][275].
Na
v
1.5 and the Lateral Membrane’s Interactome
Nav1.5 targeting to the LM has been demonstrated to be mediated by the syntrophin–dystrophin complex [3,241]; however, a sub-pool of Nav1.5 at the LM, which is independent of syntrophin, has been recently characterized as well [277]. Dystrophin is known to indirectly mediate Nav1.5 expression at the LM through binding to Syntrophin adapter protein which physically associates to the PDZ domain-binding motif at the C-terminal region of Nav1.5 [3][212][248][249][250][3,241,278,279,280]. Interestingly, Matamoros et al. demonstrated that α1-syntrophin also interacts with the N-terminal region of Nav1.5 through an “internal” PDZ-like binding domain localized at this region which acts as “chaperone-like” domain that increases Nav1.5 density at the LM and INa [251][281]. The same mechanism has been validated for Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 that were demonstrated to reciprocally interact with Nav1.5 channels and modulate each other’s trafficking and expression [251][252][281,282].
Interestingly, Nav1.5 has been demonstrated to interact with CASK (calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine kinase), a member of the MAGUK protein family [253][283]. In several ways, CASK is considered an unconventional Nav1.5 regulator since it is the only MAGUK protein that is lateral membrane-specific and also the only Nav1.5 interacting protein that exerts a repressive effect on the functional expression of Nav1.5, most likely by preventing its early trafficking to the LM. In this regard, CASK has been demonstrated to decrease INa when the former is over-expressed and to increase INa when CASK is inhibited in vivo and in vitro [253][283].
In addition, Nav1.5 has been evidenced to interact with members of the Z-line scaffolding protein complex, such as α-actinin-2 and telethonin. While α-actinin-2 is currently known to physically interact with Nav1.5 through the channel DIII–DIV linker [254][284], the telethonin interaction site on Nav1.5 has not yet been identified [71][101]. α-actinin-2 is thought to positively regulate Nav1.5 by increasing its cell surface expression, most likely through promoting its anchoring to the contact zones between T-tubules and Z-lines and connecting the channel to the actin cytoskeleton network [254][284]. However, scarce information is available regarding the mechanism of Nav1.5 regulation by telethonin, although physical interaction between TCAP and Nav1.5 was evidenced by co-immunoprecipitation methods and mutations in the telethonin coding gene (TCAP) has been found to alter the channel-gating properties of Nav1.5 in patients with abnormal gut motility and Brugada syndrome [255][256][285,286].
Moreover, the role of fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs), a subset of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family [257][287], has been well elucidated modulating the neuron voltage-gated sodium channels [258][288]. However, their role in controlling cardiac sodium channel function is still poorly understood and subject to debate. In this respect, fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1B (FHF1B), also known as FGF12B, has been reported to regulate the biophysical properties and kinetics of Nav1.5 through its physical interaction (amino acids 1773–1832) with the Nav1.5 C terminal region [259][289]. Both in vitro data show that FHF1B interacts with Nav1.5, and this interaction results in hyperpolarizing shift in steady-state inactivation of this channel [259][289]. However, the opposite effect has also been reported where a depolarizing shift in the V1/2 of steady-state inactivation has been attributed to the FHF1B-Nav1.5 interaction [260][290]. Furthermore, FGF13 (FHF2), which is the major FHFs in adult mouse hearts, has been identified as a Nav1.5 interacting protein [260][290]. In the cardiomyocyte, FHF2 co-localizes with distinct Nav1.5 pools, i.e., the LM and ID suggesting an important role for FHF2 modulating Nav1.5 cell surface expression and function [261][291]. Like FGF12B, FGF13 physically binds to Nav1.5 through the channel’s C terminus region. In vivo, FGF13 knockdown altered Nav1.5 function resulting in a decreased INa current density, reduced Nav1.5 channel availability, slowed Nav1.5, and reduced INa current recovery from inactivation [260][290]. This effect of FGF13 is isoform-specific [262][292]. FHFs have also been implicated in voltage-gated sodium channel trafficking control. In this context, FGF14 has been reported as a modulator of Nav1.5 current densities in neurons and in the heart by impairing their biophysical properties or by controlling channel trafficking and cell surface expression in vitro [263][293].
Furthermore, calmodulin (CaM), a ubiquitous Ca2+-sensing protein, has been reported to interact with Nav1.5 N- and C-terminal regions [264][265][266][267][294,295,296,297] and the DIII–IV linker [144][265][174,295]. This interaction has been demonstrated to enhance slow inactivation and modulate Nav1.5 gating [266][296], while disruption of CaM binding to Nav1.5 decreases channel activity and enhances the propensity for persistent Na+ current, all resulting from a switch in the NaV inactivation mechanism [267][297]. Nav1.5–CaM interaction has been further studied in a mutational context related to cardiac sodium channelopathies (See Section 4).
Finally, dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein-10 (DPP10), previously reported as a modulator of Kv4.3-current kinetics [268][298], has recently emerged as a new regulator of Nav1.5 [269][299]. In vivo, DPP10 has been reported to modulate Nav1.5 current kinetics as well by altering voltage dependence of Na+ current and upstroke velocity of the action potential [269][299].
The Caveolar Na
v
1.5
Cardiac sodium channels have also been localized to cardiomyocyte caveolae, which are specialized subsarcolemmal membrane compartments enriched in lipids and play a crucial role in vesicular trafficking and protein targeting to the cell surface [270][271][300,301]. Caveolar Nav1.5 is exposed to a very rich macromolecular complex encompassing fatty acids, ion channels (pacemaker channels, potassium channels, calcium channels, etc.), and signaling complexes (G-protein-coupled receptors, protein kinases, etc.). This microenvironment has been reported to regulate Nav1.5 function and membrane expression in a multilayers fashion [271][301].
The first layer is related to the biochemical properties of caveolae itself as a specialized lipid raft rich in fatty acids. In this regard, previous reports demonstrated that Nav1.5 is blocked by polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), suggesting that interaction of Nav1.5 with the caveolar lipids that also include PUFAs might have the same effect [272][273][302,303]. Nonetheless, the mechanism by which caveolar lipid rafts regulate Nav1.5 is not yet fully understood.
The second layer of caveolar Nav1.5 regulation is mediated by caveolins which are the major proteins of caveolae [271][301]. This mechanism was first reported by the Shibata group, which demonstrated that in addition to the indirect β-adrenergic regulation of Nav1.5, which is PKA-dependent, stimulation of the β-adrenergic pathway in the presence of a PKA inhibitor, activates G-protein (Gsα) cascade, which in turn leads to a rapid increase of INa [270][300]. A subsequent study by the same group suggested that caveolar Nav1.5 channels are stored at caveolae invaginations and that PKA-independent Gsα-dependant stimulation of the β-adrenergic pathway leads to the opening of caveolae, the exposition of Nav1.5 channels to the extracellular environment, which in turn increase INa [274][304]. This mechanism has been completely neutralized by anti-caveolin 3 antibodies dialyzed into the myocytes suggesting that caveolar Nav1.5 function is dependent on the Gsα-Caveolin 3 (Cav3) interaction [274][304]. Although Nav1.5 has been confirmed to interact with caveolin 3 in rodent and human cardiomyocytes [270][275][300,305], it is not yet clear if this interaction is direct or indirect. Several reports suggested that Cav3 modulates Nav1.5 function indirectly through inhibiting the nNOS, which is a part of the Nav1.5-SNTA1-PMCA4b macromolecular complex [305,306]. As mentioned earlier in this review, a decay in Cav3 expression has been demonstrated to [275][276]activate S-nitrosylation of Nav1.5 through increasing the local NO production, which increased INa,L in cardiomyocytes [187].
3.1.6. Regulation of Nav1.5 Degradation
Maintaining the balance between protein synthesis and degradation is crucial for the fine-tune regulation of Nav1.5 levels [277][307]. In fact, it is currently well established that internalization and degradation of Nav1.5 are regulated either by ubiquitination, covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties [278][308], or autophagy [279][309]. The first mechanism is mediated by the interaction of C-terminus PY motifs of Nav1.5 with the fourth tryptophan-rich domain (WW) of E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2, which leads to the labeling of Nav1.5 by ubiquitin residues that will be later recognized by the degradation machine [70][280][281][100,310,311]. Interestingly, yeast two-hybrid data demonstrated that the interaction between Nav1.5/αβ-Cristallin from one hand and αβ-Cristallin/Nedd4-2 from another hand reduced internalization of cell surface Nav1.5 and ubiquitination of Nav1.5 [282][312]. Similarly, serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase (SGK) has been reported to regulate Nav1.5 degradation by phosphorylating and inhibiting Nedd4-2 [283][313], whereas UBC9, a SUMO-conjugating enzyme, has been shown to promote Nav1.5 ubiquitination [284][314]. A very recent study by Liu et al. demonstrated that Nav1.5 ubiquitination would be downregulated by the association of FAT10, a small ubiquitin-like modifier, to the C-terminal lysine residues of Nav1.5, thus decreasing the binding of Nav1.5 to the Nedd4-2 and preventing its degradation [285][315].
Nedd4-2 has been reported as a direct target of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in epithelial cells [286][316]. However, a recent report by Liu X et al. attributed a Nedd4-2 independent Nav1.5 degradation mechanism to AMPK [279][309]. AMPK, through phosphorylating Nav1.5 T101 residue, facilitates the association of the channel to the autophagic adapter protein and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) and exposes the complex to the autophagic degradation machinery [279][309].
3.1.7. Effect of Gonadal Hormones on Nav1.5 Expression and Function
The male predominance of some sodium channelopathies such as Brugada syndrome has been extensively studied over the last few years, thus questioning a possible link between sex hormones and Nav1.5 [287][288][317,318]. However, comparing the expression levels of Nav1.5 between normal male and female human hearts showed no difference [289][319]. In addition, concentration-related block of Nav1.5 by estradiol showed that estradiol could not reduce the current of Nav1.5 [290][320], although a slight reduction in INa currents has been observed at a high concentration of estradiol in vitro [291][321]. Yang et al. have recently studied the expression levels and function of Nav1.5 in HEK293 cells co-expressing SCN5A (wild-type or BrS mutants R878C and R104W) and sex hormone receptors. They whereby showed that sex hormones have no effects on the expression level of SCN5A (either WT or mutant) and INa currents [292][322]. Similarly, gonadal hormones testosterone and estrogen showed no effect on fast INa in a canine model [293][323]. However, a recent study by Hu et al. demonstrated that estrogen through its rapid signal receptor GPER ameliorated the damaging effects of stress in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) model mimicking β-adrenergic overstimulation [324]. Taken [294]together, these findings demonstrate that our current knowledge on the regulation of Nav1.5 by sex hormones is still limited and that further studies in this regard are necessary.
3.1.8. Effect of Temperature and pH on Nav1.5 Expression and Function
Febrile states and acidosis are two environmental factors that have been extensively studied as non-genomic modulators of Nav1.5 function in health and disease. It is currently well known that Nav1.5 kinetic is temperature and pH-sensitive [295][325]. In this context, mild hypothermia has been described as an antiarrhythmic factor that maintains myocardial conduction during prolonged ischemia by sustaining Nav1.5 and Cx43 function [296][326], whereas hyperthermia has been described as a proarrhythmic factor, especially in combination with SCN5A mutations as is the case in Brugada syndrome [297][298][299][300][327,328,329,330]. Two mechanisms have been suggested so far for the temperature-dependent regulation of Nav1.5. The first one is a direct mechanism by which temperature accelerates the inactivation of only the wild-type Nav1.5 channels in heterozygous patients, which results in the misbalance between depolarization and repolarization currents and thus may lead to fever-induced arrhythmias [26][301][40,331]. The second mechanism is indirect by which temperature modulates the function of Nav1.5 interacting proteins, which in turn modulate Nav1.5 function as is the case of FGF13 [302][332].
Similarly, fluctuation of the extracellular pH has been demonstrated to influence the Nav1.5 function. For instance, acidic extracellular pH has been shown to modify wild-type Nav1.5 kinetics by destabilizing both the fast inactivated and the slow inactivated states of Nav1.5 [303][333]. In addition, it has been reported that extracellular protons disrupt charge immobilization which leads to the destabilization of the Nav1.5 fast-inactivation through direct interaction with outer ring carboxylates of the Nav1.5 DIII or DIV [304][334]. Particularly, His-880 and Cys-373 were identified as the key mediator of Nav1.5 sensitivity to pH fluctuation, where Cys-373 is responsible for isoform-specific proton modulation of use-dependent inactivation of Nav1.5 [305][335].
