Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive and refractory subtype of breast cancer, often occurring in younger patients with poor clinical prognosis. Given the current lack of specific targets for effective intervention, the development of better treatment strategies remains an unmet medical need. Over the last decade, the field of extracellular vesicles (EVs) has grown tremendously, offering immense potential for clinical diagnosis/prognosis and therapeutic applications. While TNBC-EVs have been shown to play an important role in tumorigenesis, chemoresistance and metastasis, they could be repurposed as potential biomarkers for TNBC diagnosis and prognosis.
- triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
- extracellular vesicles (EV)
- exosome
- nanomedicine
- blood-brain barrier (BBB)
- cancer
- biomarkers
- nanoscale drug delivery system (NDDS)
- solid tumour
1. Treatment Approaches in TNBC
2. The Innate Properties of EVs as Cancer Therapeutics
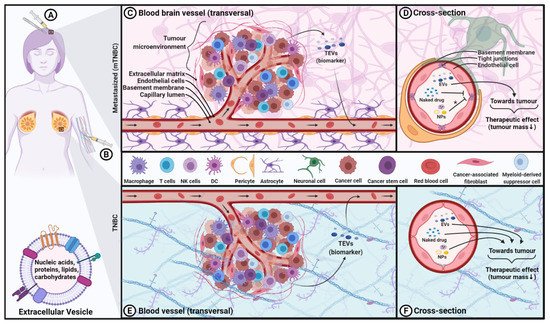
3. Using EVs as Diagnostic/Prognostic Biomarkers for TNBC
Paradoxically, EVs can also be used as biomarkers of certain pathophysiological conditions, including cancer, since the EVs’ molecular constituents usually mirror the characteristics of their parental cells [39,44,54,71][39][44][54][71]. For example, tumour and stromal cells present in the TME were found to release EVs containing oncogenic material that was transferred to nearby cells, consequently increasing tumorigenesis, tissue invasion and metastasis, as well as stimulating angiogenesis, proliferation and immune system evasion mechanisms [72,73,74,75][72][73][74][75]. For instance, tumour-derived EVs (TEVs) from TNBC cells carrying CCL5 on their surface were shown to influence the behaviour of TME resident macrophages, rendering them pro-metastatic in nature, which ultimately led to a TME favourable for tumorigenesis [74,76][74][76]. Furthermore, TEVs are mediators of malignant transformation via Wnt signaling, modulating the cancer stem cells’ equilibrium [77]. This pathophysiological mechanism may be fed by TEVs derived from cancer stem cells [78]. With this in mind, the application of TEVs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers is under clinical investigation. Currently, only one clinical trial has been registered investigating this avenue (NCT04523389) for early detection of colorectal cancer; more will certainly emerge in the next decade. One of the many pathological functions of TEVs is their ability to transfer a malignant phenotype to healthy cells and establish a fertile local and distant TME that promotes tumorigenesis and prometastatic niches, leading to metastatic TNBC [40,78,79,80,81][40][78][79][80][81]. TEVs may alter the transcriptome of receiving cells [82], in addition to modifying the immune response and other physiological functions, which consequently contribute to tumorigenesis and sustain tumour-related angiogenesis [74,83,84,85][74][83][84][85]. TNBC-TEVs increase the potential for pre-metastatic niche formation with distinct protein properties that proportionally increase cell motility, suggesting that TEVs are likely contributors to metastasis [86]. TEVs also facilitate chemoresistance in TNBC. For example, breast cancer TEVs (BC-TEVs) were found to export DOX into the extracellular environment and contribute to chemoresistance [87]. Besides this direct interaction with the drugs, TNBC-TEVs may have the potential to mediate the horizontal transfer of drug efflux pumps, including the ATP-binding cassette transporter between tumour cells [88]. Similarly, BC-TEVs from resistant breast MCF-7 cancer cells were shown to transfer hormones/metformin/tamoxifen chemoresistance capabilities to drug-sensitive MCF-7 cells [89]. Other examples of TNBC-TEVs transferring chemoresistance to healthy cells also exist [90]. Since TEV-mediate acquired hormonal resistance against these types of hormone-targeting therapeutics (cornerstone for treating ER+ and PR+ BC), this can be problematic and may worsen the clinical outcomes in hormone-sensitive BC [89,91][89][91]. MCF-7-EVs were also found to upregulate Wnt 5a in macrophages, which reciprocally produced EVs that enhanced tumorigenesis by enabling malignant invasion via the β-catenin-independent Wnt signaling pathway in cancerous cells [92]. BC cells under hypoxic and acidic conditions were found to upregulate EV secretion, which might contribute to tumorigenesis [73,81][73][81]. Although the BC cell line MCF-7 is non-TNBC classified because it expresses ER+PR+, it would be interesting to see if the above observations apply to TNBC. While TEVs have been reported and reviewed extensively for their role in many pathologies, they are also considered as diagnosis/prognosis biomarkers for TNBC after being repurposed [40,44,71,93,94][40][44][71][93][94]. There is of great interest in early detection of solid cancer via lesser invasive medical interventions. For example, EVs can be retrieved from liquid biopsies, which include biological fluids such as serum, urine, ascites fluids and pleural effusion [37[37][40][95],40,95], and analyzed with the appropriate method to establish a diagnosis. This is possible because of their systematic presence in most physiological fluids, prominent stability in circulation and the fact that they mirror their parental cell phenotypic profile and molecular characteristics [38,96][38][96]. In other words, TNBC-TEVs will reflect the phenotypic traits and molecular pathology of the parental TNBC cells, thereby bearing a TNBC-specific cargo that can be used as diagnostic/prognostic biomarkers. In turn, TEVs can inform on the cancer molecular pathological state to develop future drug treatment [73]. One study even reveals how these non-invasive liquid biopsies can discriminate between the different subtypes of BC based on the distinctiveness of the TEV-proteome and metabolome [97,98][97][98]. Indeed, many studies have identified miRNAs in TEVs that can be used as biomarkers for the diagnosis/prognosis of TNBC, among other types of BC [99]. MicroRNA (miRNA/miR) are small (roughly 20 nucleotides long) non-coding RNA that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Their functional role has been linked to a diverse range of pathophysiological effects, such as the acquisition of chemoresistance, reduction in chemosensitivity, metastatic potential and vascular permeability and promotion of tumorigenesis [100]. Many miRNAs are involved in BC pathophysiology where TEVs transfer miRNAs from one cell to another, affecting epithelial–mesenchymal transition (miR-105, miR-122 and miR-939), tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis (let-7a miRNA, miR-21, miR-92b, miR-130a, miR-149, miR-181c, miR-200, miR-328, miR-423-5p, miR-602 and miR-1246) and the transfer of chemoresistance abilities (miR-21, miR-221/222, miR-423-5p, miR-770 and miR-1246) [100,101,102][100][101][102]. Similar functional miRNAs (miR-17, miR-30a, miR-100 and miR-222), contributing to the horizontal transfer of cargo, allowing for chemoresistance, were found in MCF-7-EVs [103]. The miRNA pattern obtained from the TEVs derived from HER2+ BC and TNBC was shown to be different, implying an important feature of precise subtype identification among the different BC subtypes [104]. TNBC-TEVs encapsulating known RNA species as cargo with diagnosis/prognostic purposes are summarized in Table 1.| Cargo | Parental Cell Origin | Reported Effect and Outcomes in TNBC | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA Species | |||
| let-7a miRNA, miR-328, miR-130a, miR-149, miR-602, and miR-92b | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis | [105] |
| miR-21 and miR-1246 | TNBC and BC patient serum | Promotes invasion, metastasis and chemoresistance | [106][107] |
| miR-27b, miR-335, miR-376c, miR-382, miR-433, and miR-628 | TNBC patient serum | Various effect; high-throughput screening for miRNAs in TNBC-TEVs | [108] |
| miR-7e, miR-10b, miR-32, miR-106b and miR-138 | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes invasion and metastasis | [109] |
| miR-101 and miR-373 | TNBC patient serum | Downregulates ER expression and inhibits camptothecin-induced apoptosis | [110] |
| miR-105 | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes invasion and metastasis by specifically targeting tight junction protein Promotes angiogenesis |
[111] |
| miR-122 | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes metastasis and the establishment of a pre-metastatic niche | [112] |
| miR-134 | Hs578T | Reduces cancer aggressiveness and increases drug sensitivity | [113] |
| miR-137 and miR-496 | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes proliferation and invasion | [114] |
| miR-181c | MDA-MB-231-luc-D3H2LN | Promotes invasion and metastasis by disrupting the integrity of the BBB | [115] |
| miR-200 | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes metastasis and the establishment of a pre-metastatic niche | [116] |
| miR-223 | Macrophages | Promotes invasion via a positive feedback loop using EV communication platform | [117] |
| miR-423-5p | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes chemoresistance | [118] |
| miR-770 | MDA-MB-231 MDA-MB-468 |
Suppresses the DOX-resistance mechanism | [119] |
| miR-939 | MDA-MB-231 | Regulates VE-cadherin in endothelial cells, which enhances cancer cell’s trans-endothelial migration | [120] |
| circPSMA1 | MDA-MB-231 | Facilitates tumorigenesis, metastasis and migration via miR-637/Akt1/β-catenin (cyclin D1) axis | [121] |
| lncRNA XIST | TNBC patient serum | Increases tumour recurrence | [122] |
| Proteins | |||
| UCHL1 | Various TNBC cell lines, various PDX, TNBC patient-serum | Stimulates migration, extravasation and promotes tumor progression | [123] |
| CD151 | MDA-MB-231 and TNBC patient-serum | Stimulates migration and invasion | [124] |
| EGFR | MDA-MB-231 | Stimulates invasion | [125] |
| Survivin | MDA-MB-231 | Promotes tumour survival | [126] |
4. Novel Treatment Avenues Using EVs for TNBC
| Cargo Type | Cargo | Parental Cell | Receiving Cell | Reported Effect and Outcomes | Refs. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small molecules | DOX | Immature DCs | MDA-MB-231 MCF-7 |
Inhibiting tumour growth without overt toxicity | [146] | ||||
| DOX | MDA-MB-231 and STOSE ovarian cancer | MDA-MB-231 and STOSE ovarian cancer | EV-DOX is less toxic and allows treating mice at a higher concentration, reducing the volume of the tumour. | [147] | |||||
| PTX and DOX | Macrophages | MDA-MB231 | Enhancing anti-proliferation effect | [148] | |||||
| Curcumin | B16 (melanoma), TS/A (adenocarcinoma), and 4T.1 | NK cells | Restoring the strongest effect to the cytotoxic function of NK cells | [149] | |||||
| β-Elemene | MCF-7 | MCF-7/Docetaxel MCF-7/Adriamycin | Significantly reversing the BC chemoresistance | [150] | |||||
| Erastin | HFL-1 (normal human lung fibroblast) | MDA-MB231 | Robust accumulation of erastin and increasing killing effect | [151] | |||||
| Nucleic acids | TPD52-siRNA | HEK293T | SKBR3 MDA-MB231 |
siRNA downregulation of gene expression by 70% of cancer cells although no conclusion was drawn on the effect of this silencing | [152] | ||||
| VEGF-siRNA and let-7a miRNA | Primary DCs | MDA-MB-231 | Selectively targeting nucleolin-positive tumour tissues and inhibiting tumour growth | [153] | |||||
| let-7a miRNA | HEK293 cells | HCC70 | Significantly inhibiting tumour growth | [154] | |||||
| miR-127, miR-197, miR-222, and miR-223 | Bone marrow stroma | MDA-MB-231 | Enhancing anti-proliferation effect | [155] | |||||
| miR-142-3p inhibitor | MSCs | 4T1 (mouse) | Efficiently delivering anti-miR-142-3p and restraining cancer proliferation | Low[156] | |||||
| [ | 55 | ] | [56][244] | miR-9 and miR-155 | MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | Remarkably downregulating PTEN and DUSP14 in tumour cells | [157] | |
| Complexity of production, isolation and characterization. | Varied | Varied | Varied | [37][230][244][245][246] | miR-381 | MSCs | MDA-MB-231 | Reducing cancer metastatic behaviours | [158] |
| miR-496 | MCF10A | MDA-MB-231 | Exerting a tumour suppressive role by targeting Del-1 | [114] | |||||
| miR-424-5p | Adipose tissue-derived-MSCs | MDA-MB-231 | Promoting apoptosis of TNBC by suppressing PD-L1 signaling | [159] | |||||
| Membrane-embedded molecules | Human IL-3Rα/CD123 Mab | Human TEC (thymic epithelial cells) | MDA-MB-231 | Reducing cell viability and cell migration | [160] | ||||
| HER2 | BT-474 | MDA-MB-231 | Receptor HER2 conferred on the surface of TNBC cells allowing for anti-HER2 antibody delivery therapy | [161] |
4.1. TNBC Treatment with EV-NDDS Containing Therapeutically Relevant Small Molecules
Mab: monoclonal antibody; MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, HCC70 and 4TI (mouse) are TNBC (ER-PR-HER2-) cell lines; MCF-7 and SKBR3 are ER+PR+HER2- cell lines; MSCs: mesenchymal stromal/stem cells; PTX: paclitaxel; DOX: doxorubicin.
4.1. TNBC Treatment with EV-NDDS Containing Therapeutically Relevant Small Molecules
4.2. TNBC Treatment with EVs Containing Therapeutically Relevant Nucleic Acids
4.3. TNBC Treatment with EVs Containing Therapeutically Relevant Membrane-Embedded Molecules
4.4. TNBC Treatment with EVs Derived from Cytotoxic Effector Cells (NK and CD8+ T Cells)
4.5. TNBC Treatment with EV-NDDS-Based Cancer Vaccines
| Trial (National Clinical Trial ID) | Phase | Condition | Interventions |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03362060 | I | TNBC Metastatic TNBC |
Drug: Pembrolizumab Biological: PVX-410 |
| NCT02826434 | I | BC | Biological: PVX-410 Biological: Durvalumab Drug: Hiltonol |
| NCT04105582 | I | TNBC BC |
Biological: Neo-antigen pulsed DCs |
| NCT02316457 | I | TNBC | Biological: IVAC_W_bre1_uID Biological: IVAC_W_bre1_uID/IVAC_M_uID |
| NCT03199040 | I | TNBC Metastatic TNBC |
Drug: Durvalumab Biological: Neoantigen DNA vaccine Device: TDS-IM system (Inchor Medical Systems) |
| NCT04024800 | II | TNBC | Biological: AE37 Peptide vaccine Biological: Pembrolizumab |
Pembrolizumab: FDA-approved anti-PD-1 antagonist monoclonal antibody; PVX-410 and AE37: investigational peptide therapeutic as cancer vaccine. IVAC_W_bre1_uID: Individualized Cancer Immunotherapy patient-specific liposome complexed RNA tailored to the antigen-expression profile of any given patient’s tumour. IVAC_M_uID: Individualized Cancer Immunotherapy treatment with de novo synthesized RNAs targeting up to 20 individual tumour mutations. TDS-IM system: a dermal DNA vaccine delivery system.
5. EVs versus Synthetic NPs
The nanomedicine field is evolving rapidly, with ongoing research and development focused on improving the delivery of targeted therapeutics for tailored treatments and personalized medicine. Among those nanomedicine products, synthetic NPs have been revolutionary by paving the way forward as they enhance the delivery and bioavailability of chemotherapeutic drugs and improve their immunotherapy efficacy [182,183,184][199][200][201]. The term nanoparticle is defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry as a particle of any shape falling in the nanometre scale [185][202]. Interestingly, small EVs fall into the nanosized range (<100 nm or <200 nm for small EVs, according to the minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV) 2018 guidelines); however, they contrast with synthetic NPs as they are biologically derived from cells and not synthetically made [37]. Indeed, therapeutically relevant NPs are nearly always artificially produced and synthesized using wet chemistry methods (referred to as synthetic NPs in this review), with the exception of viruses and virus-like particles (VLP) (such as plant-based particles), which would be considered non-synthetic NPs. In contrast, EVs are isolated from biological fluids (urine, saliva, serum, etc.) released by cells or obtained from cell culture medium in the laboratory setting and therefore display innate biological diversity [186][203]. Consequently, the term “synthetic” will be placed in front of NPs (i.e., using wet chemistry) to distinguish the NPs accurately at play. Mainly three classes of synthetic NPs are known: polymeric NPs (e.g., polymersome, dendrimer), inorganic NPs (e.g., silica, iron oxide) and lipid-based NPs (e.g., liposomes, micelles) [187][204]. Conversely, synthetic NPs range in size, in material composition (metal, lipids, polymers, etc.), in their 3D configuration (sphere, rod, etc.) and in the type of coating on their surface (functional group presentation, antibody presentation, etc.) [183,188][200][205]. Their nanoscale size renders them able to interact with the cell surface and intracellular targets without modifying their properties and behaviours [184][201]. Polymeric synthetic NPs are biodegradable and commonly coated with a hydrophilic polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG), to improve the circulation lifetime and biodistribution [184,189,190,191][201][206][207][208]. Therefore, synthetic NPs can encapsulate hydrophobic drugs to increase the compound’s bioavailability without increasing the dosage. However, an immune response is mountable against PEG, limiting the repetitive administration of PEG-coated synthetic NPs [61,62,187,192][61][62][204][209]. For that reason, other molecules are under evaluation as alternatives over PEG to extend the circulation lifetime while keeping immunogenicity at bay [191][208]. The pharmacokinetic properties of the synthetic NP-NDDS can be optimized by formulating different combinations of particle size, dosage, surface properties and the timely release of therapeutic agents to specific sites. As such, successful synthetic NP-NDDS often have a high drug-loading capacity to reduce the number of matrix materials required for administration [183][200], combined with efficient drug loading and drug release characteristics and should not be immunogenic unless used as a vaccine. The reported administration routes of synthetic NPs include various parenteral routes, such as transdermal (also including intraocular), inhalation and injection, in addition to enteral routes, mainly oral [190,193,194,195][207][210][211][212]. Synthetic NP-NDDS can be manufactured to address some of the clinical challenges faced with BC treatment [196][213]. For example, Abraxane (a formulation of albumin-bound paclitaxel) and Doxil/Myocet/Lipo-Dox (a formulation of liposomal doxorubicin made by different manufacturers) have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of BC [197][214]. Indeed, synthetic NPs accumulate and get trapped in the tumour because of the abnormal vasculature and poor lymphatic drainage of the tumour-induced angiogenesis. The EPR effect, previously described, permits synthetic NPs to be utilized as a NDDS where they would target tumour cells while minimally impacting other organs simply by remaining near the tumour [198,199][215][216]. Their surfaces can be modified to incorporate functional domains to regulate their interactions with target cells [190][207]. They can also be programmed to release agents and compounds of interest (i.e., chemotherapy drugs) within the local environment of their target cells [188,200][205][217]. Most recently, synthetic NPs encapsulating tumour antigens, immune adjuvants and cytokines have shown efficacy in clinical trials [188][205], demonstrating their application as NDDS. However, most synthetic NPs cannot transport drugs across the BBB through the systemic circulation without incorporating the ligands (e.g., apolipoprotein E) necessary for receptor-mediated uptake [201][218]. Thus, engineering synthetic NPs by adding specific ligands can improve their clinical application for brain diseases and disorders [201][218]. Among all the known, therapeutically relevant synthetic NPs, liposomes are the most similar to EVs due to their morphological and materialistic structure (lipid-based) resemblances. With modifications to their surface with free ligands, liposomes can be synthesized to cross the BBB and circumvent the aforementioned limitation [202][219]. The comparison between naked drug delivery, synthetic NP delivery and EV delivery systems has been reviewed elsewhere [70,203,204,205,206,207][70][220][221][222][223][224]. The similarities and differences between EV-NDDS, NP-NDDS and naked drug delivery systems are highlighted in Table 4.| Component | EV-NDDS | Synthetic NP-NDDS | Naked Drug | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inherent ability to cross the BBB and cross from the bloodstream into the brain. | Yes | No * | No | [225][226][227][228][229] |
| Susceptibility to the EPR effect (accumulation in tumour tissue). | Yes | Yes | No | [230][231][232] |
| Ability to cross cellular barrier. | Yes | Varied | Low | [232][233] |
| Improve intracellular penetration. | Yes | Yes | Varied | [234][235][236] |
| Targeted delivery (tissue or cell type specific) and co-delivery of multiple agents. | Yes | Yes | N/A | [225][237] |
| Application versatility (vaccine vehicle, immunotherapy, regenerative medicine, etc.). | Yes | Yes | N/A | [230][238] |
| Improved pharmacological properties such as solubility, in vivo stability (circulating half-life), pharmacokinetic profile, protection of biologic drugs from premature release and degradation. | Yes | Yes | N/A | [13][239][234][240] |
| Therapeutic index improvement either by increasing the efficacy or decreasing unwanted side effects. | Yes | Yes | N/A | [241][242] |
| Cargo diversity (nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, drugs, etc.). | Yes | Yes | N/A | [37][231] |
| Relative dosing. | Low | Low | High | [13][243] |
| Susceptibility to sheer force during nebulization, lyophilization and other extreme handling processes. | Low | Low | ||
| Prevention of antidrug antibodies formation. | Varied | Varied | N/A | [62][247][242] |
| Responsiveness to the TME. | No | No | N/A | [37][248][249] |
| Environmental toxicity. | Low | Varied | Varied | [250][251] |
| Clinical toxicity. | Low | Varied | High | [241][252][253] |
| Potency after systemic delivery, biodistribution and biocompatibility. | High | Varied * | Low | [254][232][255] |
| Drug release versatility. | High | High | N/A | [242][256] |
| Engineering potential (composition, targeted delivery, selective packing, etc.). | High | High | N/A | [257][240][245] |
| Diagnostic potential. | Yes | Potentially | N/A | [44][242] |
| Ability to evade immune detection. | Varied | Varied | N/A | [41][258] |
| Potential to cause graft-vs.-host disease (GvHD). | Depends on producer cell | Unlikely | N/A | [259] |
| Intrinsic diversity. | High | Low | N/A | [37][230] |
6. Future Directions of EV Application as Therapeutics and NDDS
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33.
- Ensenyat-Mendez, M.; Llinàs-Arias, P.; Orozco, J.I.J.; Íñiguez-Muñoz, S.; Salomon, M.P.; Sesé, B.; DiNome, M.L.; Marzese, D.M. Current Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes: Dissecting the Most Aggressive Form of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 681476.
- Marra, A.; Trapani, D.; Viale, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Curigliano, G. Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: Intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 54.
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767.
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.W.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Identifies Novel Subtypes and Targets of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698.
- Liu, Y.-R.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Xu, X.-E.; Yu, K.-D.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Zuo, W.-J.; Hao, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, G.-Y.; et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis identifies novel molecular subtypes and subtype-specific RNAs of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 33.
- Desmedt, C.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Wirapati, P.; Buyse, M.; Larsimont, D.; Bontempi, G.; Delorenzi, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Sotiriou, C. Biological Processes Associated with Breast Cancer Clinical Outcome Depend on the Molecular Subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5158–5165.
- Engel, C.; Rhiem, K.; Hahnen, E.; Loibl, S.; Weber, K.E.; Seiler, S.; Zachariae, S.; Hauke, J.; Wappenschmidt, B.; Waha, A.; et al. Prevalence of pathogenic BRCA1/2 germline mutations among 802 women with unilateral triple-negative breast cancer without family cancer history. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 265.
- Seong, M.-W.; Korean Hereditary Breast Cancer Study Group; Kim, K.H.; Chung, I.Y.; Kang, E.; Lee, J.W.; Park, S.K.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.E.; Oh, S.J.; et al. A multi-institutional study on the association between BRCA1/BRCA2 mutational status and triple-negative breast cancer in familial breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 63–69.
- Howard, F.M.; Olopade, O.I. Epidemiology of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 8–16.
- Won, K.; Spruck, C. Triple-negative breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1245–1261.
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674.
- Bansal, S.S.; Goel, M.; Aqil, F.; Vadhanam, M.V.; Gupta, R.C. Advanced Drug Delivery Systems of Curcumin for Cancer Chemoprevention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1158–1171.
- Honda, Y.; Aruga, T.; Yamashita, T.; Miyamoto, H.; Horiguchi, K.; Kitagawa, D.; Idera, N.; Goto, R.; Kuroi, K. Prolonged survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis from breast cancer: Contributing factors and treatment implications. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 713–718.
- Lin, N.U.; Claus, E.; Sohl, J.; Razzak, A.R.; Arnaout, A.; Winer, E.P. Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: High incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer 2008, 113, 2638–2645.
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284.
- Jia, D.; Li, L.; Andrew, S.; Allan, D.; Li, X.; Lee, J.; Ji, G.; Yao, Z.; Gadde, S.; Figeys, D.; et al. An autocrine inflammatory forward-feedback loop after chemotherapy withdrawal facilitates the repopulation of drug-resistant breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2932.
- Papadimitriou, M.; Mountzios, G.; Papadimitriou, C.A. The role of PARP inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer: Unraveling the wide spectrum of synthetic lethality. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 67, 34–44.
- Schirrmacher, V. From chemotherapy to biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side effects of systemic cancer treatment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 407–419.
- Nanda, R.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Dees, E.C.; Berger, R.; Gupta, S.; Geva, R.; Pusztai, L.; Pathiraja, K.; Aktan, G.; Cheng, J.D.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2460–2467.
- Emens, L.A.; Cruz, C.; Eder, J.P.; Braiteh, F.; Chung, C.; Tolaney, S.M.; Kuter, I.; Nanda, R.; Cassier, P.A.; Delord, J.-P.; et al. Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Biomarker Analyses of Atezolizumab Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Phase 1 Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 74–82.
- Miles, D.; Gligorov, J.; André, F.; Cameron, D.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.; Xu, B.; Wardley, A.; Kaen, D.; Andrade, L.; et al. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 994–1004.
- Quagliariello, V.; De Laurentiis, M.; Cocco, S.; Rea, G.; Bonelli, A.; Caronna, A.; Lombari, M.; Conforti, G.; Berretta, M.; Botti, G.; et al. NLRP3 as Putative Marker of Ipilimumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity in the Presence of Hyperglycemia in Estrogen-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7802.
- Navarrete-Bernal, M.G.C.; Cervantes-Badillo, M.G.; Martínez-Herrera, J.F.; Lara-Torres, C.O.; Gerson-Cwilich, R.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Ibarra-Sánchez, M.D.J.; Esparza-López, J.; Montesinos, J.J.; Cortés-Morales, V.A.; et al. Biological Landscape of Triple Negative Breast Cancers Expressing CTLA-4. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1206.
- Weiss, J.; Glode, A.; Messersmith, W.A.; Diamond, J. Sacituzumab govitecan: Breakthrough targeted therapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2019, 19, 673–679.
- Bardia, A.; Mayer, I.A.; Diamond, J.R.; Moroose, R.L.; Isakoff, S.J.; Starodub, A.N.; Shah, N.C.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Kalinsky, K.; Guarino, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Trop-2 Antibody Drug Conjugate Sacituzumab Govitecan (IMMU-132) in Heavily Pretreated Patients With Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2141–2148.
- Mediratta, K.; El-Sahli, S.; D’Costa, V.; Wang, L. Current Progresses and Challenges of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3529.
- Keenan, T.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Role of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 479–489.
- Vikas, P.; Borcherding, N.; Zhang, W. The clinical promise of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, ume 10, 6823–6833.
- Dees, S.; Ganesan, R.; Singh, S.; Grewal, I.S. Emerging CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2409–2421.
- Xie, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Yao, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, F. CAR T-cell therapy for triple-negative breast cancer: Where we are. Cancer Lett. 2020, 491, 121–131.
- Li, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J. Immunotherapeutic interventions of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 147.
- Lyons, T.G. Targeted Therapies for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 82.
- Waldman, A.D.; Fritz, J.M.; Lenardo, M.J. A guide to cancer immunotherapy: From T cell basic science to clinical practice. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 651–668.
- Wrzesinski, C.; Paulos, C.M.; Gattinoni, L.; Palmer, D.; Kaiser, A.; Yu, Z.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Restifo, N.P. Hematopoietic stem cells promote the expansion and function of adoptively transferred antitumor CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 492–501.
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Restifo, N.P.; Yang, J.C.; Morgan, R.A.; Dudley, M.E. Adoptive cell transfer: A clinical path to effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2008, 8, 299–308.
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750.
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579.
- Munshi, A.; Mehic, J.; Creskey, M.; Gobin, J.; Gao, J.; Rigg, E.; Muradia, G.; Luebbert, C.C.; Westwood, C.; Stalker, A.; et al. A comprehensive proteomics profiling identifies NRP1 as a novel identity marker of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell-derived small extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 401.
- Jia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jayasinghe, U.; Luo, X.; Wei, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiong, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; et al. Exosome: Emerging biomarker in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41717–41733.
- Batista, I.; Quintas, S.; Melo, S. The Interplay of Exosomes and NK Cells in Cancer Biology. Cancers 2021, 13, 473.
- Cruz, L.; Romero, J.A.A.; Iglesia, R.P.; Lopes, M.H. Extracellular Vesicles: Decoding a New Language for Cellular Communication in Early Embryonic Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6.
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H. Engineered Exosomes: A Promising Drug Delivery Strategy for Brain Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1.
- Goh, C.Y.; Wyse, C.; Ho, M.; O’Beirne, E.; Howard, J.; Lindsay, S.; Kelly, P.; Higgins, M.; McCann, A. Exosomes in triple negative breast cancer: Garbage disposals or Trojan horses? Cancer Lett. 2020, 473, 90–97.
- Ronquist, K.G. Extracellular vesicles and energy metabolism. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 488, 116–121.
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345.
- Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Grizzle, W.; Sun, D.; Zhang, S.; Axtell, R.C.; Ju, S.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Steinman, L.; et al. Treatment of Brain Inflammatory Diseases by Delivering Exosome Encapsulated Anti-inflammatory Drugs From the Nasal Region to the Brain. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1769–1779.
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K., Jr.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278.
- Saeedi, S.; Israel, S.; Nagy, C.; Turecki, G. The emerging role of exosomes in mental disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 122.
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.; Melo, S.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503.
- Parada, N.; Romero-Trujillo, A.; Georges, N.; Alcayaga-Miranda, F. Camouflage strategies for therapeutic exosomes evasion from phagocytosis. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 31, 61–74.
- Morris, E.C.; Neelapu, S.S.; Giavridis, T.; Sadelain, M. Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 199.
- Bunggulawa, E.J.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; Wang, N.; Durkan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 81.
- Gobin, J.; Muradia, G.; Mehic, J.; Westwood, C.; Couvrette, L.; Stalker, A.; Bigelow, S.; Luebbert, C.C.; Bissonnette, F.S.-D.; Johnston, M.J.W.; et al. Hollow-fiber bioreactor production of extracellular vesicles from human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells yields nanovesicles that mirrors the immuno-modulatory antigenic signature of the producer cell. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 127.
- Yuan, F.; Li, Y.-M.; Wang, Z. Preserving extracellular vesicles for biomedical applications: Consideration of storage stability before and after isolation. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1501–1509.
- Trenkenschuh, E.; Richter, M.; Heinrich, E.; Koch, M.; Fuhrmann, G.; Friess, W. Enhancing the Stabilization Potential of Lyophilization for Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2021, 2100538.
- De Jong, B.; Barros, E.R.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Rigalli, J.P. Recent Advances in Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems and Their Potential in Precision Medicine. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1006.
- Jafari, D.; Shajari, S.; Jafari, R.; Mardi, N.; Gomari, H.; Ganji, F.; Moghadam, M.F.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A. Designer Exosomes: A New Platform for Biotechnology Therapeutics. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 567–586.
- Murphy, D.E.; De Jong, O.G.; Brouwer, M.; Wood, M.J.; Lavieu, G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: Natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–12.
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, H.; He, Q.; Wu, Z.; Liao, W.; Yuan, M. Application of the Nano-Drug Delivery System in Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 489.
- Ishida, T.; Ichihara, M.; Wang, X.; Yamamoto, K.; Kimura, J.; Majima, E.; Kiwada, H. Injection of PEGylated liposomes in rats elicits PEG-specific IgM, which is responsible for rapid elimination of a second dose of PEGylated liposomes. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 15–25.
- Verhoef, J.J.F.; Carpenter, J.F.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Schellekens, H. Potential induction of anti-PEG antibodies and complement activation toward PEGylated therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1945–1952.
- Dams, E.T.; Laverman, P.; Oyen, W.J.; Storm, G.; Scherphof, G.L.; Van Der Meer, J.W.; Corstens, F.H.; Boerman, O.C. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1071–1079.
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591.
- Walker, S.; Busatto, S.; Pham, A.; Tian, M.; Suh, A.; Carson, K.; Quintero, A.; Lafrence, M.; Malik, H.; Santana, M.X.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8001–8017.
- Ohno, S.-I.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ueda, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Fujita, K.; Mizutani, T.; Ohgi, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Systemically Injected Exosomes Targeted to EGFR Deliver Antitumor MicroRNA to Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 185–191.
- Yang, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhu, J.; Kang, C.; Chiang, C.-L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Kuang, T.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; et al. Functional exosome-mimic for delivery of siRNA to cancer: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2016, 243, 160–171.
- Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Corona, G.; Caligiuri, I.; Canzonieri, V.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. Exosomes increase the therapeutic index of doxorubicin in breast and ovarian cancer mouse models. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2431–2441.
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10.
- Elsharkasy, O.M.; Nordin, J.Z.; Hagey, D.W.; De Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Vader, P. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 332–343.
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59.
- Ramírez-Ricardo, J.; Leal-Orta, E.; Martínez-Baeza, E.; Ortiz-Mendoza, C.M.; Breton-Mora, F.; Herrera-Torres, A.; Elizalde-Acosta, I.; Cortes-Reynosa, P.; Thompson-Bonilla, R.; Salazar, E.P. Circulating extracellular vesicles from patients with breast cancer enhance migration and invasion via a Src-dependent pathway in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1932–1948.
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, L.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes in cancer: Small particle, big player. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 83.
- Piao, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, E.H.; Woo, J.; Zhang, M.; Moon, W.K. Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7398–7410.
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.-C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492.
- Rabe, D.; Walker, N.; Rustandy, F.; Wallace, J.; Lee, J.; Stott, S.; Rosner, M. Tumor Extracellular Vesicles Regulate Macrophage-Driven Metastasis through CCL5. Cancers 2021, 13, 3459.
- Koch, R.; Demant, M.; Aung, T.; Diering, N.; Cicholas, A.; Chapuy, B.; Wenzel, D.; Lahmann, M.; Güntsch, A.; Kiecke, C.; et al. Populational equilibrium through exosome-mediated Wnt signaling in tumor progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 2189–2198.
- Wang, H.-X.; Gires, O. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in breast cancer: From bench to bedside. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 54–64.
- Deepak, K.; Vempati, R.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Dasari, V.R.; Nagini, S.; Rao, D.; Malla, R.R. Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104683.
- Kruger, S.; Elmageed, Z.A.; Hawke, D.H.; Wörner, P.M.; Jansen, D.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Alt, E.U.; Izadpanah, R. Molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles from breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 44.
- King, H.W.; Michael, M.Z.; Gleadle, J.M. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 421.
- Melo, S.A.; Sugimoto, H.; O’Connell, J.T.; Kato, N.; Villanueva, A.; Vidal, A.; Qiu, L.; Vitkin, E.; Perelman, L.T.; Melo, C.A.; et al. Cancer Exosomes Perform Cell-Independent MicroRNA Biogenesis and Promote Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 707–721.
- Ye, S.-B.; Li, Z.-L.; Luo, D.-H.; Huang, B.-J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zhang, X.-S.; Cui, J.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Li, J. Tumor-derived exosomes promote tumor progression and T-cell dysfunction through the regulation of enriched exosomal microRNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5439–5452.
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891.
- Jabbari, N.; Akbariazar, E.; Feqhhi, M.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Rezaie, J. Breast cancer-derived exosomes: Tumor progression and therapeutic agents. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6345–6356.
- Harris, D.A.; Patel, S.H.; Gucek, M.; Hendrix, A.; Westbroek, W.; Taraska, J.W. Exosomes Released from Breast Cancer Carcinomas Stimulate Cell Movement. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117495.
- Shedden, K.; Xie, X.T.; Chandaroy, P.; Chang, Y.T.; Rosania, G.R. Expulsion of small molecules in vesicles shed by cancer cells: Association with gene expression and chemosensitivity profiles. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4331–4337.
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957.
- Semina, S.E.; Scherbakov, A.M.; Vnukova, A.A.; Bagrov, D.V.; Evtushenko, E.G.; Safronova, V.M.; Golovina, D.A.; Lyubchenko, L.N.; Gudkova, M.V.; Krasil’Nikov, M.A. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of Cancer Cell Resistance to Antiestrogen Drugs. Molecules 2018, 23, 829.
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Cavalli, I.J.; Malheiros, D.; de Souza Fonseca Ribeiro, E.M.; Cavalli, L.R. Extracellular vesicles from triple-negative breast cancer cells promote proliferation and drug resistance in non-tumorigenic breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 713–723.
- Nasrazadani, A.; Thomas, R.A.; Oesterreich, S.; Lee, A.V. Precision Medicine in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 144.
- Menck, K.; Klemm, F.; Gross, J.C.; Pukrop, T.; Wenzel, D.; Binder, C. Induction and transport of Wnt 5a during macrophage-induced malignant invasion is mediated by two types of extracellular vesicles. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2057–2066.
- Tao, S.-C.; Guo, S.-C. Role of extracellular vesicles in tumour microenvironment. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 163.
- Mathew, M.; Zade, M.; Mezghani, N.; Patel, R.; Wang, Y.; Momen-Heravi, F. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2825.
- Andre, F.; Schartz, N.E.; Movassagh, M.; Flament, C.; Pautier, P.; Morice, P.; Pomel, C.; Lhomme, C.; Escudier, B.; Le Chevalier, T.; et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet 2002, 360, 295–305.
- Yamamoto, T.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T. Latest advances in extracellular vesicles: From bench to bedside. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 746–757.
- Rontogianni, S.; Synadaki, E.; Li, B.; Liefaard, M.C.; Lips, E.H.; Wesseling, J.; Wu, W.; Altelaar, M. Proteomic profiling of extracellular vesicles allows for human breast cancer subtyping. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 325.
- Hoshino, A.; Kim, H.S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K.E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; et al. Extracellular vesicle and particle biomarkers define multiple human cancers. Cell 2020, 182, 1044–1061.e18.
- O’Brien, K.; Rani, S.; Corcoran, C.; Wallace, R.; Hughes, L.; Friel, A.; McDonnell, S.; Crown, J.; Radomski, M.W.; O’Driscoll, L. Exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer cells can transfer phenotypic traits representing their cells of origin to secondary cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1845–1859.
- Takahashi, R.-U.; Miyazaki, H.; Ochiya, T. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 598–616.
- Qattan, A. Novel miRNA Targets and Therapies in the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Microenvironment: An Emerging Hope for a Challenging Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8905.
- Wei, Y.; Lai, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. Exosomal miR-221/222 enhances tamoxifen resistance in recipient ER-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 423–431.
- Chen, W.-X.; Liu, X.-M.; Lv, M.-M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Zhong, S.-L.; Ji, M.-H.; Hu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wu, J.-Z.; et al. Exosomes from drug-resistant breast cancer cells transmit chemoresistance by a horizontal transfer of MicroRNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95240.
- Stevic, I.; Müller, V.; Weber, K.; Fasching, P.A.; Karn, T.; Marmé, F.; Schem, C.; Stickeler, E.; Denkert, C.; Van Mackelenbergh, M.; et al. Specific microRNA signatures in exosomes of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy within the GeparSixto trial. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 179.
- Kruger, S.; Elmageed, Z.A.; Hawke, D.H.; Wörner, P.M.; Jansen, D.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Alt, E.U.; Izadpanah, R. Molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles from breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 44.
- Hannafon, B.N.; Trigoso, Y.D.; Calloway, C.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Lum, D.H.; Welm, A.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Blick, K.E.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.Q. Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 90.
- Wang, M.; Ji, S.; Shao, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A. Effect of exosome biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer patients. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 20, 906–911.
- Stevic, I.; Müller, V.; Weber, K.; Fasching, P.A.; Karn, T.; Marmé, F.; Schem, C.; Stickeler, E.; Denkert, C.; Van Mackelenbergh, M.; et al. Specific microRNA signatures in exosomes of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy within the GeparSixto trial. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 179.
- Singh, R.; Pochampally, R.; Watabe, K.; Lu, Z.; Mo, Y.-Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 256.
- Eichelser, C.; Stückrath, I.; Müller, V.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Wikman, H.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Increased serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9650–9663.
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515.
- Fong, M.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Alontaga, A.Y.; Chandra, M.; Ashby, J.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Li, S.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 183–194.
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789.
- Lee, S.J.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, E.A.; Park, N.J.-Y.; Park, J.-Y.; Lee, I.H.; et al. MicroRNA-496 inhibits triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation by targeting Del-1. Medicine 2021, 100, e25270.
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lötvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain metastatic cancer cells release microRNA-181c-containing extracellular vesicles capable of destructing blood–brain barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716.
- LE, T.N.M.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.; Basar, E.; Perdigão-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. miR-200–containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5109–5128.
- Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Yu, B.; Su, F.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.-D.; Song, E. Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 117.
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, H. Cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-231 Cell-derived Exosomes Increase the Resistance of Recipient Cells in an Exosomal miR-423-5p-dependent Manner. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 804–814.
- Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Q. MiR-770 suppresses the chemo-resistance and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer via direct targeting of STMN1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 14.
- Di Modica, M.; Regondi, V.; Sandri, M.; Iorio, M.; Zanetti, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Casalini, P.; Triulzi, T. Breast cancer-secreted miR-939 downregulates VE-cadherin and destroys the barrier function of endothelial monolayers. Cancer Lett. 2016, 384, 94–100.
- Yang, S.-J.; Wang, D.-D.; Zhong, S.-L.; Chen, W.-Q.; Wang, F.-L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.-X.; Xu, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.-D.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal circPSMA1 facilitates the tumorigenesis, metastasis, and migration in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) through miR-637/Akt1/β-catenin (cyclin D1) axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 420.
- Lan, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Sun, Q. Serum exosomal lncRNA XIST is a potential non-invasive biomarker to diagnose recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7602–7607.
- Liu, S.; González-Prieto, R.; Zhang, M.; Geurink, P.P.; Kooij, R.; Iyengar, P.V.; Van Dinther, M.; Bos, E.; Zhang, X.; Le Dévédec, S.; et al. Deubiquitinase Activity Profiling Identifies UCHL1 as a Candidate Oncoprotein That Promotes TGFβ-Induced Breast Cancer Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1460–1473.
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Pi, H.; Li, Z.; Yao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; et al. Proteomic Landscape of Exosomes Reveals the Functional Contributions of CD151 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100121.
- Higginbotham, J.N.; Beckler, M.D.; Gephart, J.D.; Franklin, J.L.; Bogatcheva, G.; Kremers, G.-J.; Piston, D.W.; Ayers, G.D.; McConnell, R.E.; Tyska, M.J.; et al. Amphiregulin Exosomes Increase Cancer Cell Invasion. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 779–786.
- Kreger, B.T.; Johansen, E.R.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. The Enrichment of Survivin in Exosomes from Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Paclitaxel Promotes Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2016, 8, 111.
- Sulaiman, A.; Wang, L. Bridging the divide: Preclinical research discrepancies between triple-negative breast cancer cell lines and patient tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113269–113281.
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215.
- Liu, S.; González-Prieto, R.; Zhang, M.; Geurink, P.P.; Kooij, R.; Iyengar, P.V.; Van Dinther, M.; Bos, E.; Zhang, X.; Le Dévédec, S.; et al. Deubiquitinase Activity Profiling Identifies UCHL1 as a Candidate Oncoprotein That Promotes TGFβ-Induced Breast Cancer Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1460–1473.
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Pi, H.; Li, Z.; Yao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; et al. Proteomic Landscape of Exosomes Reveals the Functional Contributions of CD151 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100121.
- Higginbotham, J.N.; Beckler, M.D.; Gephart, J.D.; Franklin, J.L.; Bogatcheva, G.; Kremers, G.-J.; Piston, D.W.; Ayers, G.D.; McConnell, R.E.; Tyska, M.J.; et al. Amphiregulin Exosomes Increase Cancer Cell Invasion. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 779–786.
- Kreger, B.T.; Johansen, E.R.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. The Enrichment of Survivin in Exosomes from Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Paclitaxel Promotes Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2016, 8, 111.
- Schwich, E.; Rebmann, V. The Inner and Outer Qualities of Extracellular Vesicles for Translational Purposes in Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 584.
- Loi, S.; Michiels, S.; Salgado, R.; Sirtaine, N.; Jose, V.; Fumagalli, D.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Bono, P.; Kataja, V.; Desmedt, C.; et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: Results from the FinHER trial. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1544–1550.
- Rody, A.; Holtrich, U.; Pusztai, L.; Liedtke, C.; Gaetje, R.; Ruckhaeberle, E.; Solbach, C.; Hanker, L.; Ahr, A.; Metzler, D.; et al. T-cell metagene predicts a favorable prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R15.
- Yeong, J.; Lim, J.C.T.; Lee, B.; Li, H.; Ong, C.C.H.; Thike, A.A.; Yeap, W.H.; Yang, Y.; Lim, A.Y.H.; Tay, T.K.Y.; et al. Prognostic value of CD8 + PD-1+ immune infiltrates and PDCD1 gene expression in triple negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 34.
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, J.-M.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, C.-W.; Yu, D.; et al. Activated T cell-derived exosomal PD-1 attenuates PD-L1-induced immune dysfunction in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4992–5001.
- Mori, H.; Kubo, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nishimura, R.; Osako, T.; Arima, N.; Okumura, Y.; Okido, M.; Yamada, M.; Kai, M.; et al. The combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15584–15592.
- García-Teijido, P.; Cabal, M.L.; Fernández, I.P.; Pérez, Y.F. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: The Future of Immune Targeting. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2016, 10s1, 34540.
- Syn, N.L.; Wang, L.; Chow, E.K.-H.; Lim, C.T.; Goh, B.-C. Exosomes in Cancer Nanomedicine and Immunotherapy: Prospects and Challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 665–676.
- Yim, N.; Ryu, S.-W.; Choi, K.; Lee, K.R.; Lee, S.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Shaker, M.R.; Sun, W.; Park, J.-H.; et al. Exosome engineering for efficient intracellular delivery of soluble proteins using optically reversible protein–protein interaction module. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12277.
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.Á.; Lötvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; EL Andaloussi, S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 492.
- Zhu, L.; Kalimuthu, S.; Gangadaran, P.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, H.W.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Exosomes derived from natural killer cells exert therapeutic effect in melanoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2732–2745.
- Shoae-Hassani, A.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Behfar, M.; Mohseni, R.; Mortazavi-Tabatabaei, S.A.; Asgharzadeh, S. NK Cell–derived Exosomes From NK Cells Previously Exposed to Neuroblastoma Cells Augment the Antitumor Activity of Cytokine-activated NK Cells. J. Immunother. 2017, 40, 265–276.
- Gao, D.; Jiang, L. Exosomes in cancer therapy: A novel experimental strategy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 2165–2175.
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390.
- Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Corona, G.; Caligiuri, I.; Canzonieri, V.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. Exosomes increase the therapeutic index of doxorubicin in breast and ovarian cancer mouse models. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2431–2441.
- Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.S.; Li, S.M.; Bago, J.R.; Klyachko, N.L.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Therapy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 15, 487–500.
- Zhang, H.-G.; Kim, H.; Liu, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Grizzle, W.E.; Kimberly, R.; Barnes, S. Curcumin reverses breast tumor exosomes mediated immune suppression of NK cell tumor cytotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1116–1123.
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.-D.; Yao, Y.-F.; Zhong, S.-L.; Zhao, J.H.; Tang, J.H. β-Elemene Reverses Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer Cells by Reducing Resistance Transmission via Exosomes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 2274–2286.
- Yu, M.; Gai, C.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Lv, S.; Li, W. Targeted exosome-encapsulated erastin induced ferroptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3173–3182.
- Limoni, S.K.; Moghadam, M.F.; Moazzeni, S.M.; Gomari, H.; Salimi, F. Engineered Exosomes for Targeted Transfer of siRNA to HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 187, 352–364.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, L.; Chen, T.; Hong, A.; Wang, X. Nucleolin-targeted Extracellular Vesicles as a Versatile Platform for Biologics Delivery to Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1360–1372.
- Ohno, S.-I.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ueda, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Fujita, K.; Mizutani, T.; Ohgi, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Systemically Injected Exosomes Targeted to EGFR Deliver Antitumor MicroRNA to Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 185–191.
- Lim, P.K.; Bliss, S.A.; Patel, S.A.; Taborga, M.; Dave, M.A.; Gregory, L.A.; Greco, S.J.; Bryan, M.; Patel, P.S.; Rameshwar, P. Gap Junction–Mediated Import of MicroRNA from Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Can Elicit Cell Cycle Quiescence in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1550–1560.
- Naseri, Z.; Oskuee, R.K.; Jaafari, M.R.; Forouzandeh, M. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-142-3p inhibitor reduces tumorigenicity of breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, ume 13, 7727–7747.
- Kia, V.; Paryan, M.; Mortazavi, Y.; Biglari, A.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Evaluation of exosomal miR-9 and miR-155 targeting PTEN and DUSP14 in highly metastatic breast cancer and their effect on low metastatic cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 5666–5676.
- Shojaei, S.; Hashemi, S.M.; Ghanbarian, H.; Sharifi, K.; Salehi, M.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Delivery of miR-381-3p Mimic by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer Aggressiveness; an In Vitro Study. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 1027–1038.
- Zhou, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Yamamoto, T.; Xiao, Z.; Ochiya, T. Delivery of miR-424-5p via Extracellular Vesicles Promotes the Apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 TNBC Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 844.
- Lopatina, T.; Grange, C.; Cavallari, C.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; Lombardo, G.; Rosso, A.; Cedrino, M.; Pomatto, M.A.C.; Koni, M.; Veneziano, F.; et al. Targeting IL-3Rα on tumor-derived endothelial cells blunts metastatic spread of triple-negative breast cancer via extracellular vesicle reprogramming. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 90.
- Quinn, Z.; Mao, W.; Xia, Y.; John, R.; Wan, Y. Conferring receptors on recipient cells with extracellular vesicles for targeted drug delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 749–756.
- Sun, D.; Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.-G. A Novel Nanoparticle Drug Delivery System: The Anti-inflammatory Activity of Curcumin Is Enhanced When Encapsulated in Exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614.
- Luan, X.; Sansanaphongpricha, K.; Myers, I.; Chen, H.; Yuan, H.; Sun, D. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 754–763.
- Gong, C.; Tian, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Ding, X.; Qiang, L.; Li, G.; Han, Z.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Functional exosome-mediated co-delivery of doxorubicin and hydrophobically modified microRNA 159 for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 93.
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390.
- Yang, T.; Martin, P.; Fogarty, B.; Brown, A.; Schurman, K.; Phipps, R.; Yin, V.P.; Lockman, P.; Bai, S. Exosome Delivered Anticancer Drugs Across the Blood-Brain Barrier for Brain Cancer Therapy in Danio Rerio. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2003–2014.
- Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.S.; Li, S.M.; Bago, J.R.; Klyachko, N.L.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Therapy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 15, 487–500.
- Brosnan, E.M.; Anders, C.K. Understanding patterns of brain metastasis in breast cancer and designing rational therapeutic strategies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 163.
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233.
- Fritz, J.V.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Ghosal, A.; Wampach, L.; Etheridge, A.; Galas, D.; Wilmes, P. Sources and Functions of Extracellular Small RNAs in Human Circulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 301–336.
- Kim, K.M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Gorospe, M. RNA in extracellular vesicles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1413.
- Hickerson, R.P.; Vlassov, A.V.; Wang, Q.; Leake, D.; Ilves, H.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, E.; Contag, C.H.; Johnston, B.H.; Kaspar, R.L. Stability Study of Unmodified siRNA and Relevance to Clinical Use. Oligonucleotides 2008, 18, 345–354.
- Akinc, A.; Maier, M.A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X.; Hope, M.J.; Madden, T.D.; et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1084–1087.
- Wahlgren, J.; Karlson, T.D.L.; Brisslert, M.; Sani, F.V.; Telemo, E.; Sunnerhagen, P.; Valadi, H. Plasma exosomes can deliver exogenous short interfering RNA to monocytes and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e130.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, L.; Chen, T.; Hong, A.; Wang, X. Nucleolin-targeted Extracellular Vesicles as a Versatile Platform for Biologics Delivery to Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1360–1372.
- Lim, P.K.; Bliss, S.A.; Patel, S.A.; Taborga, M.; Dave, M.A.; Gregory, L.A.; Greco, S.J.; Bryan, M.; Patel, P.S.; Rameshwar, P. Gap Junction–Mediated Import of MicroRNA from Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Can Elicit Cell Cycle Quiescence in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1550–1560.
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789.
- Zhou, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Yamamoto, T.; Xiao, Z.; Ochiya, T. Delivery of miR-424-5p via Extracellular Vesicles Promotes the Apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 TNBC Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 844.
- Shojaei, S.; Hashemi, S.M.; Ghanbarian, H.; Sharifi, K.; Salehi, M.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Delivery of miR-381-3p Mimic by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer Aggressiveness; an In Vitro Study. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 1027–1038.
- Garg, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition—Activating transcription factors—Multifunctional regulators in cancer. World J. Stem Cells 2013, 5, 188–195.
- Lopatina, T.; Grange, C.; Cavallari, C.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; Lombardo, G.; Rosso, A.; Cedrino, M.; Pomatto, M.A.C.; Koni, M.; Veneziano, F.; et al. Targeting IL-3Rα on tumor-derived endothelial cells blunts metastatic spread of triple-negative breast cancer via extracellular vesicle reprogramming. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 90.
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24641.
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17.
- Prada, I.; Meldolesi, J. Binding and Fusion of Extracellular Vesicles to the Plasma Membrane of Their Cell Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1296.
- Quinn, Z.; Mao, W.; Xia, Y.; John, R.; Wan, Y. Conferring receptors on recipient cells with extracellular vesicles for targeted drug delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 749–756.
- Cai, Z.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, J. Activated T Cell Exosomes Promote Tumor Invasion via Fas Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5954–5961.
- Yan, W.; Jiang, S. Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 506–517.
- Wang, M.; Yin, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.-F. Current advances in T-cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2014, 6, 1265–1278.
- Lugini, L.; Cecchetti, S.; Huber, V.; Luciani, F.; Macchia, G.; Spadaro, F.; Paris, L.; Abalsamo, L.; Colone, M.; Molinari, A.; et al. Immune surveillance properties of human NK cell-derived exosomes. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2833–2842.
- Wu, C.-H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Fabbri, M.; Wayne, A.S.; Seeger, R.C.; Jong, A.Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from natural killer cells use multiple cytotoxic proteins and killing mechanisms to target cancer cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1588538.
- Seifalian, A.M.; Tan, A.; De La Peña, H. The application of exosomes as a nanoscale cancer vaccine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 889–900.
- Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, P.; Liang, Y.; Long, M.; Liu, H.; Mao, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the in vitro proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the activation of the ERK pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1843–1852.
- Wang, S.; Li, F.; Ye, T.; Wang, J.; Lyu, C.; Qing, S.; Ding, Z.; Gao, X.; Jia, R.; Yu, D.; et al. Macrophage-tumor chimeric exosomes accumulate in lymph node and tumor to activate the immune response and the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb6981.
- Zitvogel, L.; Regnault, A.; Lozier, A.; Wolfers, J.; Flament, C.; Tenza, D.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: Dendritic cell derived exosomes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 594–600.
- Escudier, B.; Dorval, T.; Chaput, N.; André, F.; Caby, M.-P.; Novault, S.; Flament, C.; Leboulaire, C.; Borg, C.; Amigorena, S.; et al. Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: Results of thefirst phase I clinical trial. J. Transl. Med. 2005, 3, 10.
- Gras Navarro, A.; Björklund, A.T.; Chekenya, M. Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Natural Killer Cells in Treatment of Solid Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 202.
- Federici, C.; Shahaj, E.; Cecchetti, S.; Camerini, S.; Casella, M.; Iessi, E.; Camisaschi, C.; Paolino, G.; Calvieri, S.; Ferro, S.; et al. Natural-killer-derived extracellular vesicles: Immune sensors and interactors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 262.
- Wolfers, J.; Lozier, A.; Raposo, G.; Regnault, A.; Théry, C.; Masurier, C.; Flament, C.; Pouzieux, S.; Faure, F.; Tursz, T.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 297–303.
- Hagan, C.T.; Medik, Y.B.; Wang, A.Z. Nanotechnology Approaches to Improving Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 139, 35–56.
- Mohanraj, V.J.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles—A review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2007, 5, 561–573.
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692.
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.H.; Park, K. Smart nanoparticles for drug delivery: Boundaries and opportunities. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 125, 158–164.
- Witwer, K.W.; Wolfram, J. Extracellular vesicles versus synthetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 103–106.
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124.
- Nam, J.; Son, S.; Park, K.S.; Zou, W.; Shea, L.D.; Moon, J.J. Cancer nanomedicine for combination cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 398–414.
- Dancy, J.G.; Wadajkar, A.S.; Connolly, N.P.; Galisteo, R.; Ames, H.M.; Peng, S.; Tran, N.L.; Goloubeva, O.G.; Woodworth, G.F.; Winkles, J.A.; et al. Decreased nonspecific adhesivity, receptor-targeted therapeutic nanoparticles for primary and metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax3931.
- Azarmi, S.; Roa, W.H.; Löbenberg, R. Targeted delivery of nanoparticles for the treatment of lung diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 863–875.
- Thanh, T.; Thi, H.; Pilkington, E.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Lee, J.S. The Importance of Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Alternatives for Overcoming PEG Immunogenicity in Drug. Polymers 2020, 3, 298.
- Wang, X.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H. Anti-PEG IgM elicited by injection of liposomes is involved in the enhanced blood clearance of a subsequent dose of PEGylated liposomes. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 236–244.
- Krishnan, V.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles for topical drug delivery: Potential for skin cancer treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 153, 87–108.
- Huang, R.; Boltze, J.; Li, S. Strategies for Improved Intra-arterial Treatments Targeting Brain Tumors: A Systematic Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1443.
- Wong, C.Y.; Al-Salami, H.; Dass, C.R. Cellular assays and applied technologies for characterisation of orally administered protein nanoparticles: A systematic review. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 585–599.
- Miller-Kleinhenz, J.M.; Bozeman, E.N.; Yang, L. Targeted nanoparticles for image-guided treatment of triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical significance and technological advances. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 797–816.
- Gadag, S.; Sinha, S.; Nayak, Y.; Garg, S.; Nayak, U.Y. Combination Therapy and Nanoparticulate Systems: Smart Approaches for the Effective Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 524.
- Sulaiman, A.; McGarry, S.; El-Sahli, S.; Li, L.; Chambers, J.; Phan, A.; Cote, M.; Cron, G.O.; Alain, T.; Le, Y.; et al. Co-targeting Bulk Tumor and CSCs in Clinically Translatable TNBC Patient-Derived Xenografts via Combination Nanotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1755–1764.
- Greish, K. Enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect for anticancer nanomedicine drug targeting. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 624, 25–37.
- Jiang, P.; Li, S.; Lai, J.; Zheng, H.; Lin, C.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y. Nanoparticle-Programmed Surface for Drug Release and Cell Regulation via Reversible Hybridization Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4467–4474.
- Zensi, A.; Begley, D.; Pontikis, C.; Legros, C.; Mihoreanu, L.; Wagner, S.; Büchel, C.; von Briesen, H.; Kreuter, J. Albumin nanoparticles targeted with Apo E enter the CNS by transcytosis and are delivered to neurones. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 78–86.
- Agrawal, M.; Ajazuddin; Tripathi, D.K.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Antimisiaris, S.G.; Mourtas, S.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Alexander, A. Recent advancements in liposomes targeting strategies to cross blood-brain barrier (BBB) for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 61–77.
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37.
- Somiya, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Drug delivery application of extracellular vesicles; insight into production, drug loading, targeting, and pharmacokinetics. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 73–92.
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760.
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71.
- Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. High drug-loading nanomedicines: Progress, current status, and prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, ume 12, 4085–4109.
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345.
- Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Grizzle, W.; Sun, D.; Zhang, S.; Axtell, R.C.; Ju, S.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Steinman, L.; et al. Treatment of Brain Inflammatory Diseases by Delivering Exosome Encapsulated Anti-inflammatory Drugs From the Nasal Region to the Brain. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1769–1779.
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K., Jr.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278.
- Saeedi, S.; Israel, S.; Nagy, C.; Turecki, G. The emerging role of exosomes in mental disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 122.
- Zensi, A.; Begley, D.; Pontikis, C.; Legros, C.; Mihoreanu, L.; Wagner, S.; Büchel, C.; von Briesen, H.; Kreuter, J. Albumin nanoparticles targeted with Apo E enter the CNS by transcytosis and are delivered to neurones. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 78–86.
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124.
- Miller-Kleinhenz, J.M.; Bozeman, E.N.; Yang, L. Targeted nanoparticles for image-guided treatment of triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical significance and technological advances. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 797–816.
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392.
- Heusermann, W.; Hean, J.; Trojer, D.; Steib, E.; Von Bueren, S.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Genoud, C.; Martin, K.; Pizzato, N.; Voshol, J.; et al. Exosomes surf on filopodia to enter cells at endocytic hot spots, traffic within endosomes, and are targeted to the ER. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 213, 173–184.
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760.
- Iinuma, H.; Maruyama, K.; Okinaga, K.; Sasaki, K.; Sekine, T.; Ishida, O.; Ogiwara, N.; Johkura, K.; Yonemura, Y. Intracellular targeting therapy of cisplatin-encapsulated transferrin-polyethylene glycol liposome on peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 130–137.
- Ishida, O.; Maruyama, K.; Tanahashi, H.; Iwatsuru, M.; Sasaki, K.; Eriguchi, M.; Yanagie, H. Liposomes Bearing Polyethyleneglycol-Coupled Transferrin with Intracellular Targeting Property to the Solid Tumors In Vivo. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1042–1048.
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10.
- Chu, P.-Y.; Tsai, S.-C.; Ko, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-H. Co-Delivery of Natural Compounds with a Dual-Targeted Nanoparticle Delivery System for Improving Synergistic Therapy in an Orthotopic Tumor Model. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23880–23892.
- Nam, J.; Son, S.; Park, K.S.; Zou, W.; Shea, L.D.; Moon, J.J. Cancer nanomedicine for combination cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 398–414.
- Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Swihart, M.; Prasad, P.N. Multifunctional nanoparticles as biocompatible targeted probes for human cancer diagnosis and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4655–4672.
- Sun, D.; Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.-G. A Novel Nanoparticle Drug Delivery System: The Anti-inflammatory Activity of Curcumin Is Enhanced When Encapsulated in Exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614.
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37.
- Gupta, D.; Zickler, A.M.; El Andaloussi, S. Dosing extracellular vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113961.
- Marbán, E. The Secret Life of Exosomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 193–200.
- Mudshinge, S.R.; Deore, A.; Patil, S.; Bhalgat, C.M. Nanoparticles: Emerging carriers for drug delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 129–141.
- Naahidi, S.; Jafari, M.; Edalat, F.; Raymond, K.; Khademhosseini, A.; Chen, P. Biocompatibility of engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 182–194.
- Thanh, T.; Thi, H.; Pilkington, E.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Lee, J.S. The Importance of Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Alternatives for Overcoming PEG Immunogenicity in Drug. Polymers 2020, 3, 298.
- Uthaman, S.; Huh, K.M.; Park, I.-K. Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles for cancer theragnostic applications. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 22.
- Yang, M.; Li, J.; Gu, P.; Fan, X. The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1973–1987.
- Qin, Y.; Long, L.; Huang, Q. Extracellular vesicles in toxicological studies: Key roles in communication between environmental stress and adverse outcomes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 1166–1182.
- Zhu, X.; Badawi, M.; Pomeroy, S.; Sutaria, D.S.; Xie, Z.; Baek, A.; Jiang, J.; Elgamal, O.A.; Mo, X.; Perle, K.; et al. Comprehensive toxicity and immunogenicity studies reveal minimal effects in mice following sustained dosing of extracellular vesicles derived from HEK293T cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1324730.
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759.
- Armstrong, J.P.; Stevens, M.M. Strategic design of extracellular vesicle drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 12–16.
- Dancy, J.G.; Wadajkar, A.S.; Connolly, N.P.; Galisteo, R.; Ames, H.M.; Peng, S.; Tran, N.L.; Goloubeva, O.G.; Woodworth, G.F.; Winkles, J.A.; et al. Decreased nonspecific adhesivity, receptor-targeted therapeutic nanoparticles for primary and metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax3931.
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 20.
- Beyer, S.; Moosmann, A.; Kahnt, A.S.; Ulshöfer, T.; Parnham, M.J.; Ferreirós, N.; Wagner, S.; Wacker, M.G. Drug Release and Targeting: The Versatility of Polymethacrylate Nanoparticles for Peroral Administration Revealed by Using an Optimized In Vitro-Toolbox. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 3986–3998.
- Piao, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, E.H.; Woo, J.; Zhang, M.; Moon, W.K. Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7398–7410.
- Fadeel, B. Hide and Seek: Nanomaterial Interactions with the Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 133.
- Lia, G.; Di Vito, C.; Cerrano, M.; Brunello, L.; Calcaterra, F.; Tapparo, M.; Giaccone, L.; Mavilio, D.; Bruno, B. Extracellular Vesicles After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Emerging Role in Post-Transplant Complications. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 422.
- Naahidi, S.; Jafari, M.; Edalat, F.; Raymond, K.; Khademhosseini, A.; Chen, P. Biocompatibility of engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 182–194.
- Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Swihart, M.; Prasad, P.N. Multifunctional nanoparticles as biocompatible targeted probes for human cancer diagnosis and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4655–4672.
- Scherphof, G.L.; Dijkstra, J.; Spanjer, H.H.; Derksen, J.T.P.; Roerdink, F.H. Uptake and Intracellular Processing of Targeted and Nontargeted Liposomes by Rat Kupffer Cells In Vivo and In Vitro. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1985, 446, 368–384.
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134.
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759.
- Meng, W.; He, C.; Hao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Zhu, G. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: Considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 585–598.
