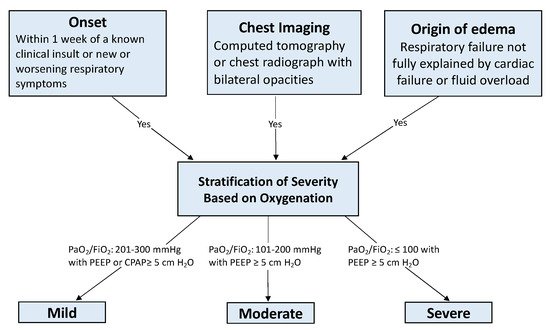
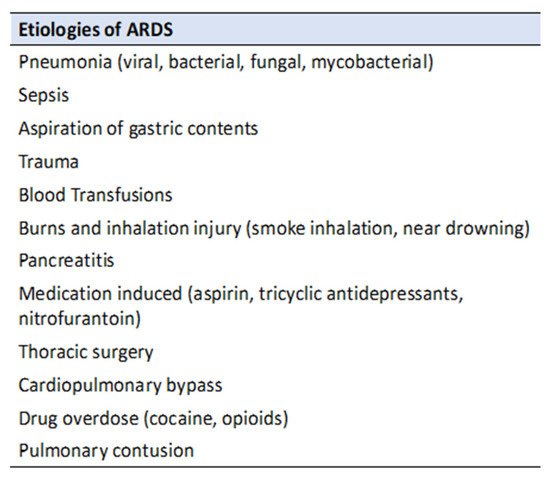
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is an acute, severe lung injury that is characterized by inflammatory cascades, hypoxemia, and diffuse lung involvement. In 1967, Acute respiratory distress syndrome remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients despite advancements in the field. Mechanical ventilatory strategies are a vital component of ARDS management to prevent secondaryRDS was first described as an acute hypoxic lung injury with infectious and traumatic triggers, similar to neonatal congestive atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. Since then, several definitions of ARDS have been established, but the Berlin definition is the latest and most widely accepted. The diagnostic criteria are summarized as an acute injurious lung event with diffuse bilateral lung injury and improve patient outcomesopacities of non-cardiogenic origin on imaging.
- acute respiratory distress syndrome
- ARDS
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Ventilator
- PEEP
- Tidal Volume
1. Introduction