Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Irena Baranowska-Bosiacka and Version 2 by Bruce Ren.
CXCL1 is one of the most important chemokines, part of a group of chemotactic cytokines involved in the development of many inflammatory diseases. It activates CXCR2 and, at high levels, CXCR1. The expression of CXCL1 is elevated in inflammatory reactions and also has important functions in physiology, including the induction of angiogenesis and recruitment of neutrophils.
- CXCL1
- MGSA
- Gro-α
- CXCR2
- inflammation
- cancer
- tumor
- chemokine
- neutrophil
1. Introduction
Intercellular signaling is an essential part of the functioning of a multicellular organism, involving the flow of information between different cells through either direct contact or via factors secreted outside the cell: simple compounds such as lactate [1], or large structures such as extracellular vesicles [2]. One group of factors responsible for intercellular signaling is chemokines, a group of about 50 chemotactic cytokines grouped according to the conserved N-terminal cysteine motif: CXC chemokines (α-chemokines), CC chemokines (β-chemokines), C chemokines (γ-chemokines) and CX3C chemokines (δ-chemokines) [3].
2. The Name ‘CXCL1’
CXCL1 was first described in the 1980s as an auto-stimulatory melanoma mitogen, to which it owes one of its first names: melanoma growth-stimulatory activity (MGSA) [4][5]. Another historical name of CXCL1 is neutrophil-activating peptide-3 (NAP-3), a term associated with its ability to induce neutrophil chemotaxis [5][6]. In subsequent years, CXCL1 was shown to be a product of the growth-regulated gene (Gro) [6][7][7,8]. Since then, CXCL1 has functioned under two names: MGSA and growth-regulated (or -related) oncogene (GRO) [7][8][9][8,9,10]. In the early 1990s, two more chemokines were identified that were very similar to GRO [10][11]. They were named GRO-β and GRO-γ, now known as CXCL2 and CXCL3 [11][12]. GRO itself was given the additional symbol α (GRO-α); another variant of this name is GRO-1 [8][10][9,11]. With the discovery of more CXC chemokines, a new and more systematic nomenclature was required. For this reason, a new classification was introduced based on the chemokine sub-family name and the number of the chemokine. Thus, GRO-α was named small inducible cytokine sub-family B, member 1 (SCYB1), and then CXCL1 [11][12].
CXCL1 has two important motifs in its sequence. One is the CXC motif (9–11 amino acids), which assigns this chemokine to CXC chemokines (or α-chemokines) [7][8]. The second is the ELR motif (6–8 amino acids), also located at the N-terminus, which makes CXCL1 one of the ELR+ CXC chemokines, currently also known as CXC motif chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) receptor agonists [12][13][13,14].
3. CXCL1: Gene and Transcriptional Regulation
3.1. 4q12–q13 CXC Chemokine Gene Cluster
The CXCL1 gene is localized in the 4q12–q13 CXC chemokine gene cluster [11][14][12,15]. This region includes the closely located loci of other CXC sub-family chemokines, including CXCL2/GRO-β, CXCL3/GRO-γ, CXCL4/PF-4, CXC motif chemokine ligand 4 variant-1 (CXCL4L1), CXCL5/ENA-78, CXCL6/GCP-2, CXCL7/PPBP/NAP-2, and CXCL8/IL-8 [15][16][17][4,16,17]. It also contains the CXC motif chemokine ligand 1 pseudogene 1 (CXCL1P1) previously described as a growth-regulated oncogene δ-pseudogene (GRO-δ) [18]. Near the cluster, at 4q21, are the ligands of CXCR3 and CXCL13 [15][17][4,17]. Very often the 4q12–q13 gene cluster is amplified in cancer, particularly in Barrett neoplasia [19]. In breast cancer, 7.5% of primary tumors have a CXCL1 gene amplification. The frequency of CXCL1 amplification increases with disease progression [20]. The amplification of the CXCL1 gene is observed in 20% cases of breast cancer metastasis [20]. The duplication of the 4q12–q13 CXC chemokine gene cluster is associated with a higher incidence of cancer, and is particularly found in individuals from melanoma-prone families [21].
The sequences of the chemokine genes in the 4q12–q13 CXC chemokine gene cluster are similar and located close to each other, which suggests that these genes originated as a result of duplication [15][4]. In general, all CXC chemokines from this gene cluster can be divided into two groups [3], CXCL6 and CXCL8 (which, at similar concentrations, activate both CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors), and CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, and CXCL7 (which, at about 1 nM concentration, activate CXCR2; and at a concentration about 100 times higher, activate CXCR1) [3][22][23][24][25][3,22,23,24,25]. Each of the groups consists of chemokines that share the same properties and activate the same receptor at similar concentrations. Nevertheless, significant differences do occur in the action of individual chemokines, as the expression and secretion of each chemokine is sometimes separately regulated and depends on the cell type [26]. For this reason, to understand the interaction of all representatives of this gene cluster, it is necessary to understand the regulation of each CXC chemokine.
At this point, it should be noted that the ancestor of today’s mammals (cretaceous period, separation of placental mammals from marsupials) had far fewer CXC chemokine genes. These genes were duplicated, and today, this gene cluster has seven CXC chemokine genes in mice and nine in humans [15][4]. The opossum has only three chemokine genes, and birds have between two and three depending on the species. While the accumulation of genetic changes in individual CXC chemokine genes occurred independently of each other, duplication may have occurred multiple times at different times. Therefore, mouse lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine (LIX) is as similar to rat LIX (a different species) as the human CXCL5 is to human CXCL6 (same species/genome) [27]. Therefore, a given human CXC chemokine cannot be unambiguously assigned to a mouse or rat CXC chemokine from this cluster. While it may be that in one disease or laboratory model a given chemokine in a human or mouse/rat is upregulated, when studying a second disease the expression of the given chemokine will be upregulated only in one species [28]. For this reason, the role of human CXCL1 in a given disease cannot be compared with rat cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1) [29] or mouse keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC) [30][31][30,31] without performing experiments on samples from human patients.
Importantly, given the arrangement of the genes on chromosomes, the human CXCL1 gene does not correspond to the murine KC gene, but to the murine dendritic cell inflammatory protein-1 (DCIP-1) gene [15][4]. Even though the murine KC gene corresponds to the human CXCL3, CXCL5 and CXCL7 genes, in many papers, CXCL1 and KC are used interchangeably. For this reason, in this review, thwe researchers distinguish murine KC from human CXCL1.
3.2. CXCL1: Promoter
The CXCL1 gene consists of four exons and three introns. The exons and introns have a total length of 1845 bp [32]. Preceding the transcription start site is a TATA box (at a locus from −30 to −24 bp) preceded by numerous sequences to which various transcriptional activators and transcriptional repressors are attached.
Due to the significance of CXCL1 in inflammatory responses, the most important method for the induction of expression of this chemokine is the activation of NF-κB. At a locus −78 to −66 bp is the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) binding site [33][34][35][36][33,34,35,36]. The NF-κB p50/p65 heterodimer attaches to it, inducing CXCL1 expression [37]. Therefore, through NF-κB activation, CXCL1 expression is increased by cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) [37][38][37,38], tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [37][38][37,38] and interleukin-17 (IL-17) [39][40][41][39,40,41]. Importantly, the activation of NF-κB by the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) occurs via the NF-κB activator 1 (Act1) → TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) → transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) pathway [39][40][39,40]. The main effect of IL-17 on CXCL1 expression is an increase in the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [42][43][42,43]. In cancer cells, basal NF-κB activation is high, which results in high basal CXCL1 expression [35]. Therefore, in cancer cells, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α can only increase the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [37]. CXCL1 can also increase its own expression via NF-κB activation, a mechanism that is important in cancer [7][44][45][8,44,45]. The effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines on CXCL1 expression is important because of inflammatory responses in malignant tumors. Depending on the type of cancer, there is an upregulation in pro-inflammatory cytokines, e.g., TNF-α [46] and IL-17 [47][48][47,48], which are involved in tumorigenesis.
In some cases, NF-κB can decrease CXCL1 expression. In hepatocytes, there is an important NF-κB p50/p50 homodimer that binds to the CXCL1 promoter to recruit the co-repressor histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) [49]. This results in reduced CXCL1 expression, which is important for preventing chronic liver disease.
The NF-κB binding site also contains the AT motif (the exact locus is −74 bp and −73 bp), which can attach a high-mobility group, AT-hook 1 (HMGA1) (previous name: high-mobility group-I(Y) (HMGI(Y))) [34][50][34,50]. This protein is important for the full activation of the CXCL1 promoter [34].
In the induction of CXCL1 expression by the exposure of cells to TNF-α, the formation of an NF-κB complex with cut-like homeobox 1 (CUX1) is important, and is much more intensely induced in the simultaneous exposure to IL-17 and TNF-α [51]. This complex attaches to the CXCL1 gene promoter at the NF-κB binding site in the −94 bp to −84 bp region of the CXCL1 promoter, i.e., where the binding site for CUX1 is located, leading to an increase in CXCL1 expression. This process is significant in rheumatoid arthritis, which is marked by high concentrations of IL-17 and TNF-α at disease sites [51].
The CXCL1 gene promoter also contains the immediate upstream region (IUR) at loci −93 bp to −78 bp (Figure 1) [50][52][50,52]. This region is directly upstream of the NF-κB binding site [33][34][35][36][33,34,35,36] and can attach to the human CUT homeodomain protein/CCAAT displacement protein (CDP) [53]. Then, CDP disrupts the interaction with the NF-κB of CREB-binding protein (CBP) or p300/CBP-association factor (PCAF) [52]. As CBP and PCAF are coactivators important for the function of NF-κB [54], CDP decreases the expression of CXCL1, which depends on NF-κB [52][53][52,53]. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP1) can also attach to the IUR [55][56][55,56], although only in the inactive state of PARP1. This inhibits the binding of NF-κB to the CXCL1 promoter, and thus the expression of this gene. In contrast, activated PARP1 loses its ability to bind to the IUR, which results in NF-κB binding to the CXCL1 promoter and an increase in CXCL1 expression [56]. The involvement of PARP1 is important in melanoma tumorigenesis; in normal melanocytes, PARP1 is inactive and inhibits CXCL1 expression, while in melanomas PARP1 is active.
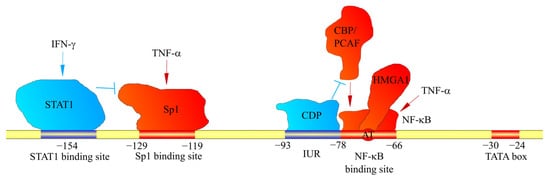

Figure 1. Factors affecting CXCL1 gene transcription. The CXCL1 promoter contains binding sites for factors that bind to these sites. They either increase (shown in red) or decrease (shown in blue) CXCL1 expression. In particular, the CXCL1 promoter contains a binding site for STAT1 and Sp1. STAT1 and Sp1 activated by IFN-γ and TNF-α, respectively, attach to these sites. Sp1 increases CXCL1 expression; however, STAT1 inhibits Sp1 binding to the CXCL1 promoter. Another mechanism regulating CXCL1 expression is IUR, a region that directly borders the NF-κB binding site. CDP binds to IUR, which inhibits the recruitment of CBP and PCAF coactivators by NF-κB. This prevents the induction of CXCL1 expression by NF-κB.
Locus −129 bp to −119 bp is the specificity protein 1 (Sp1) and specificity protein 3 (Sp3) binding site [34][50][34,50], important in the basal expression of CXCL1 and the induction of CXCL1 expression by IL-17 and TNF-α [41][57][41,57]. This site is also crucial for regulation of the expression of CXCL1 by the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) signal transducer, and the activator of transcription (STAT)1 can also inhibit CXCL1 expression. In particular, in peritoneal mesothelial cells, upon exposure of these cells to IFN-γ, STAT1 binds to the −154 bp region upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, which results in a decreased expression of CXCL1 [57] and reduced binding of Sp1 to the CXCL1 promoter. STAT1 may also increase the expression of CXCL1. However, its effect will depend on the selected cell model and the factor acting on these cells. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells, there is an induction of CXCL1 expression by IL-35 [58], which is associated with the direct binding of the STAT1/STAT4 heterodimer to the CXCL1 promoter.
3.2.1. The Regulation of CXCL1 Expression by TGF-β and HGF
TGF-β reduces CXCL1 expression [59][60][59,60]. At locus −1247 bp, upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, is the TGF-β-inhibitory element (TIE), and at locus −560 bp is the SMAD-binding element (SBE) [61]. SMAD family member 4 (SMAD4) is the main factor in the signaling from the TGF-β receptor, but does not bind to these sites. Therefore, the effect of TGF-β on CXCL1 expression is indirect, likely reducing the activity of either NF-κB or other signaling pathways [61][62][61,62].
In contrast, in murine KC, a paralog for human CXCL1, there is a different mechanism by which TGF-β regulates the expression of this chemokine. At loci −249 bp to −246 bp and −144 bp to −141 bp, upstream of the transcription start site of the KC gene, are SBEs, which can bind SMAD2/3, reducing KC expression [63].
At the upstream transcription start site of the KC gene at loci −128 bp to −120 bp is the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-β (C/EBP-β) binding motif. Upon activation of c-Met by the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), C/EBP-β is activated and attaches to the C/EBP-β binding motif on the KC promoter, thus increasing the expression of this murine KC chemokine. Importantly, this mechanism only occurs in murine cells [63]. Based on the database, “https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene”; accessed dathe researcherse: 15 November 2021, we did not find any C/EBP-β binding motif according to the cited paper on mouse KC, i.e., 5′-TGGAGCAAG-3′ or any sequence complementary to it up to −2 kbp upstream of the human CXCL1 gene promoter. Therefore, theoretically, C/EBP-β does not directly affect the expression of human CXCL1. In addition, studies on human cells do not show that TGF-β and SMADs directly affect human CXCL1 expression [61]. Nevertheless, further studies on the mechanisms of regulation of CXCL1 expression by HGF and C/EBP-β in humans are required.
The regulation of CXCL1 expression by TGF-β is an important mechanism observed in cancer [61][63][61,63]. For example, SMAD4 expression is reduced in colorectal cancer cells, as it interferes with the action of TGF-β, and thus leads to an increase in CXCL1 expression in the cancer cell [61]. Notably, in a prostate cancer tumor, in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF), there is a decrease in TGF-β type II receptor (TβRII) expression [64]. This decreases the effect of TGF-β on these cells, and thus leads to the increased expression of CXCL1 in these cells. As CXCL1 is a chemotactic factor for neutrophils [65], an increase in CXCL1 expression in colorectal cancer tumors results in the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN), cells with pro-cancer properties [61][66][61,66]. Additionally, CXCL1 causes tumor cell migration, and consequently, metastasis [60].
3.2.2. Significance of p53 Transcription Factor Family in CXCL1 Expression
Gain-of-function and loss-of-function mutations of the TP53 gene are very common in cancer cells and lead to changes in the expression of various genes [67][68][67,68]. Loss-of-function TP53 mutations cause an increase in CXCL1 expression [69] due to reduced p53-induced inhibition of NF-κB activation [70][71][70,71]. If p53 loses its functions, there is an increase in NF-κB activity and in the expression of genes dependent on this transcription factor. This mechanism is not universal in all cells because in monocytes and macrophages, p53 together with NF-κB increase the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines [72]. In addition, the interaction of CXCL1 with p53 is complicated, as CXCR2 activation reduces p53 expression, this action is associated with protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt activation, which in turn activates murine double minute 2 (Mdm2) [73].
The gain-of-function TP53 mutations cause mutated p53 proteins to directly bind to the CXCL1 promoter, which results in an increased CXCL1 expression in the tumor cell [74][75][74,75]. The exact mechanism of the increase in CXCL1 expression depends on the type of p53 mutation. DNA-contact p53 mutants (for example R248Q and R273H) bind directly to the CXCL1 promoter [75]. Some of the single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) of p53 may increase the ability of p53 with the aforementioned mutation to attach to the CXCL1 promoter. An example of this is the P72R SNP polymorphism of p53 (rs1042522) [75]. The R72 p53 mutant has a higher binding capacity to the CXCL1 promoter than the P72 p53 mutant. DNA-contact p53 mutants also increase NF-κB activation, which increases the expression of genes dependent on this transcription factor, including CXCL1 [69].
Another type of mutation is the Zn2+ region conformational p53 mutant. Examples of such p53 mutants are R175H and H179R, which attach directly to the CXCL1 promoter, and thus increase CXCL1 expression [74]. It appears that p53 with this type of mutation also increases CXCL1 expression by increasing H-Ras activity [69]. This effect is related to the interaction of mutant p53 with B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2). Significantly, NF-κB is not required in the induction of CXCL1 expression by Zn2+ region conformational p53 mutants [74].
The last type of mutation is the L3 loop conformational p53 mutant [69]. An example of such a mutation is G245S p53. Although this type of p53 mutation increases CXCL1 expression, the effect is much smaller than when p53 expression is significantly reduced [69]. This is likely due to the reduced effect of p53 with such a mutation, relative to wild-type (WT) p53.
Another protein that attaches near the CXCL1 gene is p63, a transcription factor from the p53 transcription factor family [76][77][76,77]. Both proteins (p53 and p63) induce the expression of different genes, but can also cooperate in the expression of the same genes. p63 attaches to the −3 kb region of the upstream transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, thus increasing its expression [77]. This transcription factor may also cooperate with NF-κB in increasing CXCL1 expression. The significance of p63 in CXCL1 expression was found in tumors, particularly in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells.
3.2.3. CXCL1 Expression and Hypoxia
The promoter of murine KC, a paralog for human CXCL1, contains five hypoxia response element (HRE) sequences at loci −1309 bp, −433 bp, −313 bp, −302 bp and −289 bp [78]. The expression of this gene is induced by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2, as shown by studies in mouse epithelial cells [79] and murine chondrocytes [78]. HIF-1 also increases KC expression in murine myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) [80]. CXCL1 expression may depend indirectly on HIF-1; for example, in human aortic endothelial cells and mouse aortic endothelial cells, HIF-1 increases miR-19a expression [81], which indirectly increases the expression of CXCL1. Based on d“https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene; atabaccesse, the researchersd date: 15 November 2021”, we identified seven sequences thought to be an HRE, i.e., 5′-A/GCGTG-3′ and complementary ones in the region up to the −2 kbp upstream transcription start site of the human CXCL1 gene [82][83][82,83]. HRE is the binding site of HIF-1 and HIF-2, transcription factors activated by hypoxia. Therefore, it seems theoretically possible that hypoxia increases CXCL1 expression—this was already shown by a study involving hepatocellular carcinoma cells [84]. Nevertheless, this effect may depend on the particular research model, as hypoxia did not affect CXCL1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells [85].
3.2.4. Other Mechanisms That Alter CXCL1 Promoter Activity
In addition to the effects on CXCL1 expression of the aforementioned factor binding sites near the transcription start site, there are also regulatory sequences located at various distances from the CXCL1 gene.
CXCL1 expression is increased in an AP-1-dependent manner, as shown by experiments using IL-17 [41] and TNF-α [86][87][86,87].
The transcription factors responsible for the induction of CXCL1 expression by TNF-α also include early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) [50], which binds directly to the CXCL1 promoter at two loci: −367 bp and −134 bp. This process is significant in cancer, particularly in esophageal cancer, where Erg-1 is frequently overexpressed [88].
Studies on breast cancer cells showed that a breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) complex with GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) reduced CXCL1 expression [89]. Nevertheless, further studies are required to determine whether this effect is direct or indirect.
Other transcription factors also attach to the CXCL1 promoter. In particular, the activation of transcription factor 2 (ATF2) and acute myeloid leukemia 1 (AML1) is responsible for the increase in CXCL1 transcription by IL-17, which attaches to the CXCL1 promoter [41].
At locus −277 bp, upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, a binding site for myeloid ecotropic viral integration site 1 (MEIS1) was identified [90]. MEIS1 is a transcription factor that is overexpressed in cancer cells, particularly in ovarian cancer, increasing the expression of many chemokines including CCL18, CCL4, CXCL7, and indirectly increasing the expression of CXCL1, as the identified binding site of this transcription factor appears to be non-functional.
At −375 bp upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, a binding site for the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) was identified [91]. This is a transcription factor important for melanocyte differentiation. It also undergoes overexpression in melanoma. Therefore, the increase in CXCL1 expression in melanoma depends partly on MITF.
The −551 bp to −517 bp region upstream of the transcription start site region of the KC gene contains a binding site for Y-box protein-1 (YB-1) [92]. KC expression is induced upon the binding of this protein; this process is relevant in a murine bile duct ligation model, where the expression of KC increases in the liver in a YB-1-dependent manner. However, further studies are required to confirm the role of YB-1 in humans.
The −984 bp to −301 bp region, upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene, contains a binding site for Snail, a transcription factor crucial for epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) [93][94][93,94], a process important in cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis. After EMT, the tumor cell begins to migrate. The increased expression of CXCL1 in this cell plays an important role in migration [95] and metastasis formation [64][96][64,96] by stimulating the tumor cell to migrate, and causing the supporting adhesion of the tumor cell to target tissues, as well as in the recruitment of different cells in metastasis.
Further from the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene at the locus −2 kbp, a Hey-like (HeyL) binding site is located [97][98][97,98]. This factor belongs to Notch signaling, which is overexpressed in many cancers, such as in breast cancer. Because CXCL1 is an angiogenic chemokine [12][13][13,14], Notch signaling in cancer increases CXCL1 expression, and thus causes angiogenesis.
Some proteins regulating the expression of CXCL1 can be bound very far from the CXCL1 gene. In particular, avian v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (MAF)F binds to three sites, precisely at the −15 kpb, −12.5 kpb and −7.5 kbp upstream of the transcription start site of CXCL1 gene [99]. MAFF increases CXCL1 expression in human term myometrium [99][100][99,100]. However, to date, the function of CXCL1 during labor is unknown. The mechanism of induction of CXCL1 expression in human term myometrium is not related to inflammatory factors, which means that CXCL1 expression is induced by a specific transcription factor independent of inflammatory responses [99]. This shows that CXCL1 is not only a mediator of inflammatory responses but may also have its own physiological functions unrelated to inflammation.
Histone methylation is another important means of regulating CXCL1 expression. A −2.0 to −1.5 kbp fragment upstream of the transcription start site of the CXCL1 gene undergoes histone H3 Lys36 trimethylation (H3K36me3) by histone H3 lysine 36 methyltransferase SET-domain-containing 2 (SETD2) [101]. This leads to a reduction in CXCL1 expression. This process is important because, in cancers such as breast cancer [102], glioblastoma multiforme [103], hepatocellular carcinoma [104] and lung adenocarcinoma [101] the SETD2 gene is either mutated or there is a decreased expression of the product of this gene. However, in castration-resistant prostate cancer, SETD2 is an oncogene that supports tumor growth [105]. The precise regulation of CXCL1 expression by SETD2 is not known. As this enzyme modifies a fragment very far from the CXCL1 gene, it is possible that it alters the ability to bind some proteins that are important for the regulation of gene expression (Table 1).
Table 1.
Proteins that bind to the
CXCL1
gene promoter, leading to a change in its expression.
| Name of the Factor | BINDING SITE | Effect on Expression | Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p50:p65 NF-κB | −78 bp to −66bp | ↑ | High basal NF-κB activity in cancer conditions; high basal CXCL1 expression in tumors. Activated in inflammation |
[33][34][35][36][33,34,35,36] |
| p50:p50 NF-κB | ? | ↓ | Prevention of chronic liver disease | [49] |
| HMGA1 | From −74 bp to −73 bp | ↑ | Essential in the full activation of the CXCL1 promoter by NF-κB | [34] |
| CDP | from −93 bp to −78 bp | ↓ | Reduction in CXCL1 expression by disruption of NF-κB function | [50][52][53][50,52,53] |
| PARP1 | from −93 bp to −78 bp | ↓ | PARP1 binding in the inactive state. Inhibition of NF-κB binding to the CXCL1 promoter | [55][55[56],56] |
| CUX1 | −94 bp to −84 bp | ↑ | Enhancement of CXCL1 expression by the joint action of IL-17 and TNF-α | [51] |
| Sp1 | −129 bp to −119 bp | ↑ | Significant in basal CXCL1 expression and in upregulation of CXCL1 expression by IL-17 or TNF-α | [34][50][34,50] |
| STAT1 | −154 bp | ↓ | Reduction in CXCL1 expression by IFN-γ through disruption of Sp1 function | [57] |
| STAT1/STAT4 | ? | ↑ | Enhancement of CXCL1 expression by IL-35 | [58] |
| HIF-1 and HIF-2 | ? | (↑) | Increased expression of CXCL1 in hypoxia. No precise studies on the direct effect | [84] |
| MEIS1 | −277 bp | (↑) | Sequence identified as potential binding site but non-functional. Factor influence indirect. Relevant in cancer, particularly in ovarian cancer | [90] |
| Erg-1 | −367 bp and −134 bp | ↑ | Important in cancer, especially in esophageal cancer | [88] |
| MITF | −375 bp | ↑ | Important in cancer, especially in melanoma cancer | [91] |
| Snail | from −984 bp to −301 bp | ↑ | Increased CXCL1 expression during EMT, important in cancer during metastasis formation | [94] |
| SMAD4 | −1247 bp and −560 bp |
(↓) | Sequences identified as potential binding sites but non-functional. Theoretically, when TGF-β action is reduced, the effect of SMAD4 is abolished, and thus CXCL1 expression increases | [61] |
| SETD2 | from −2.0 to −1.5 kbp | ↓ | This is the enzyme that causes histone methylation. The exact mechanisms of how epigenetic changes in this region affect CXCL1 expression are not known | [101] |
| HeyL | −2 kbp | ↑ | Notch signaling element. Relevant for cancer | [97][98][97,98] |
| Mutated p53 | ? | ↑ | Relevant in cancers with TP53 gene mutation | [74][75][74,75] |
| p63 | −3 kb | ↑ | Relevant in cancer, especially in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells | [77] |
| MAFF | −15 kpb, −12.5 kpb and −7.5 kbp |
↑ | Induction of CXCL1 expression in human term myometrium, immediately before birth. The exact functions of CXCL1 in labor are unknown | [99] |
3.3. Regulation during Transcription
The induction of signaling pathways and attachment of all transcription factors to the promoter of the CXCL1 gene is followed by transcription. RNA polymerase II (Pol II) begins to transcribe the CXCL1 mRNA fragment with a length of approximately 50 nucleotides [106]. Then, transcription elongation requires the phosphorylation on Ser2 of Pol II by positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb). Hairy and Enhancer of Split-1 (Hes1) prevent this phosphorylation, and therefore inhibit CXCL1 transcription [106]. This regulation occurs particularly in macrophages treated with pro-inflammatory agents such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [107].
4. CXCL1 mRNA Stability as a Method to Regulate CXCL1 Expression
The production of a 1.1–1.2 kb-long transcript [7][8] is followed by the next step: the regulation of CXCL1 expression, associated with changes in the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [108]. CXCL1 mRNA is a transcript with a low half-life; if the cell is not influenced by any factors that increase its stability, then this transcript is degraded within 1 to 4 h [109][110][109,110]. The half-life of CXCL1 mRNA is estimated to be approximately 15 min [37]. After this time, from the ends of the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of CXCL1 mRNA, an approximately 130-nucleotide fragment is removed [109][110][109,110]. CXCL1 mRNA is transformed into a 0.9 kb transcript. However, there are many mechanisms, some of which increase and some of which decrease the half-life of CXCL1 mRNA. In particular, regions 6–23 and 632–651 on the 3′-UTR of CXCL1 mRNA are responsible for increasing the stability of the transcript. Region 562–581 on the 3′-UTR of CXCL1 mRNA is responsible for decreasing the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [111]. The AUUUA motifs on the 3′-UTR also act to reduce the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [42].
Various proteins that are activated by factors such as IL-1 [37][109][110][37,109,110], TNF-α [37] and IL-17 [43] are responsible for increasing CXCL1 mRNA stability. This effect depends on the cell type and tissue selected as the research model, as these factors can also increase CXCL1 transcription, e.g., depending on NF-κB activation [37][39][57][37,39,57]. Notably, in non-cancer cells, where there is no high basal NF-κB activation, transcriptional regulation plays a major role in regulating CXCL1 expression [37]. Additionally, no less important for CXCL1 mRNA stability are miRNAs, which cause the decay of this transcript [112][113][114][115][116][117][112,113,114,115,116,117]. All of the factors mentioned in this section lead to the degradation or improvement in the stability of CXCL1 mRNA. This alters the half-life of CXCL1 mRNA, and consequently, the number of these transcripts in the cytoplasm, at unchanged CXCL1 gene transcription levels.
4.1. Role of Cytokines in Regulating CXCL1 Expression by Altering mRNA Stability. The Mechanisms of IL-17-Induced Effects on CXCL1 Expression
CXCL1 mRNA decay is IL-17-sensitive. In unstimulated cells, splicing factor 2 (SF2)/alternative splicing factor (ASF) attaches to the 3′-UTR of CXCL1 mRNA, which reduces the stability of this transcript [118]. This factor attaches to CXCL1 mRNA sites other than tristetraprolin (TTP). The activation of the receptor for IL-17 leads to activation of Act1, TRAF2 and TRAF5. Act1 causes the phosphorylation of SF2/ASF via the inhibitor of NF-κB kinase ε (IKKε) [43] and forms the Act1-TRAF2-TRAF5-SF2/ASF complex [118][119][118,119]. In this complex, SF2/ASF is no longer bound to CXCL1 mRNA, which increases the stability of this transcript. At the same time, Act1 causes K63-linked polyubiquitination of the human antigen R (HuR) [108]. This process is dependent on Ubc13-Uev1A E2 complex. Therefore, modified HuR binds to the AU-rich element (ARE) on CXCL1 mRNA, causing its stabilization; HuR also promotes the translation of CXCL1.
Act1 can also cause the phosphorylation of decapping 1 (Dcp1) via TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) [43]. This inhibits the decapping of CXCL1 mRNA, and of other transcripts. On the 3′-UTR of CXCL1 mRNA, there is a fragment at locus 780–900 that forms a secondary structure with four stem loops. This is a “similar expression to fibroblast growth factor genes + IL-17R” (SEFIR)-binding element. Act1 binds directly to it, which increases the stability of the transcript in question by competing with SF2/ASF binding [43].
IL-17 increases CXCL1 mRNA stability, and thus CXCL1 expression. Nevertheless, IL-17 can also increase CXCL1 transcription, but this effect is not as significant as the change in CXCL1 mRNA stability and may also depend on the research model chosen [41]. An increase in CXCL1 transcription is associated with NF-κB activation by the IL-17R receptor [39][40][41][39,40,41]. Additionally, other transcription factors increase CXCL1 expression, including AP1, ATF2, AML1 and SP1 [41][57][41,57].
In macrophages [120], keratinocytes [36] and fibroblasts [121], tristetraprolin (TTP) is responsible for reducing the stability of KC mRNA, as shown by experiments on mouse cells. TTP binds to AREs and, more specifically, to AUUUA motifs on the 3′-UTR of KC mRNA. This leads to a recruitment of the deadenylases, and consequently, to a decay of KC mRNA. However, activated p38 MAPK by LPS can activate the MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) [122]. This kinase phosphorylates TTP, which does not affect the binding of TTP to mRNA but prevents the recruitment of deadenylases by this factor and prevents the decay of KC mRNA [123]. However, research on human cells showed that TTP does not affect the stability of CXCL1 mRNA [42].
4.2. The Role of miRNAs in the Regulation of CXCL1 Expression
To date, many miRNAs have been found to be involved in reducing CXCL1 expression. In particular, many of them have important roles in cancer due to the pro-tumorigenic properties of CXCL1 (Figure 2) [4][114][124][125][5,114,124,125]. The development of cancer is associated with a decrease in the expression of miRNAs regulating CXCL1 expression in the tumor, and consequently, is associated with an increase in the expression of this chemokine. In ovarian cancer, renal cancer [112] and hepatocellular carcinoma [114], there is a downregulation of the miR-200 family [112]; in ovarian cancer there is a downregulation of miR-27b-5p [116]; and in gastric cancer, there is a downregulation of miR-204 [115]. Other examples include miR-302e in colorectal cancer [117] and miR-141 in non-small cell lung cancer [113].
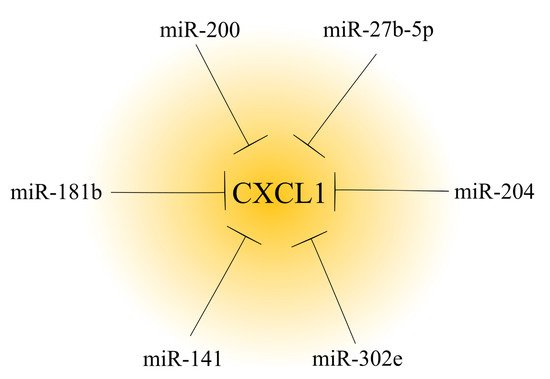

Figure 2. Effect of microRNAs on CXCL1 expression in a tumor. In cancer tumors, CXCL1 expression is regulated by microRNAs. Based on the available literature, six different microRNAs that decrease CXCL1 expression have been identified to date.
A change in miRNA expression may also account for the effects of some anticancer substances. An example of this is the increased expression of miR-181b in breast cancer cells by curcumin [126]. This miRNA directly decreases CXCL1 expression, which is one of the anticancer mechanisms of curcumin.
It is also possible that miRNAs affect signaling pathways that increase the expression of chemokines, which would mean that such miRNAs indirectly decrease CXCL1 expression. An example of this is miR-155 in tumor-infiltrating MDSCs [80]. This miRNA decreases HIF-1 levels, and thus the expression of genes dependent on the transcription factor HIF-1, such as CXCL1.
CXCL1 expression can also be indirectly increased by miRNAs. Examples of this are miR-155, miR-193b and miR-210 [127]. These miRNAs are secreted in extracellular vesicles by cancer cells, and then increase CXCL1 expression in fibroblasts. This mechanism was demonstrated in gastric cancer [127].
It is not only in cancers that the regulation of CXCL1 expression by miRNAs occurs. During cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury, there is a downregulation of miR-429 in brain microvascular endothelial cells [128] and miR-532-5p in brain tissues [129]. At least for miR-532-5p, this was shown to be related to the promoter of this miRNA: hypermethylation. Both miRNAs directly reduce the expression of CXCL1. Therefore, when the levels of these miRNAs are decreased, there is an increase in CXCL1 expression, which leads to brain tissue damage during cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury.
Additionally, studies of extracellular vesicles from murine, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells showed that they contain miR-150-5p [130]. This miRNA reduces the expression of KC. This chemokine is important in the development of hepatic fibrosis. Therefore, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells may inhibit the development of hepatic fibrosis.
Another miRNA that reduces CXCL1 expression is miR-7641 [131]. The expression of this miRNA occurs in human embryonic stem cells and decreases during endothelial cell biogenesis. This increases the expression of CXCL1, a chemokine also important in angiogenesis.
