Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Vincenzo Russo and Version 3 by Vicky Zhou.
Process intensification (PI) is defined as an innovative principle applied in chemical reaction engineering and process design. The first definitions were given in 2000, when the pioneering work of Stankiewicz and Moulijn began this means of novel enthusiastic definition of chemical processes, which can bring significant benefits in terms of process and efficiency, higher quality of products, lower capital and operating expenses, less waste, and improved process safety. Starting from that moment, several roadmaps, books, and scientific papers were published in the field, focused on PI in the chemical industry.
- process intensification
- chemical reaction engineering
- micro and milli reactors
- static mixers
- unconventional heating and mixing systems
- alternative fluids
1. Overview of Strategies for PI
Efficiency in terms of atoms, mass and energy, along with process profitability, mainly depend on the selection of a proper chemical transformation, a suitable catalyst, and a favorable reactor type. More active and long-term stable catalysts are one route for significant improvement. For a synthesis with an already optimized catalyst, the productivity and selectivity of the process can be remarkably affected by the choice of the reactor type and operating conditions, because thermodynamic equilibrium as well as reaction kinetic properties are fixed in this case. Although the reactor typically represents only 5% to 15% of the capital and operating costs of the plant, it mainly dictates the number of up- and downstream process units, and therefore the costs and efficiency of the whole process [1][2][16,17]. For improvements in reactor technology, chemical reaction engineers have focused on the integration of multiple unit operations in one apparatus, enhanced transport properties, and alternative process fluids and energy sources [3][14].
-
Maximize the effectiveness of intramolecular and intermolecular events (example: dynamically changing conditions to attain kinetic regimes with higher conversion and selectivity).
-
Provide all molecules the same process experience (example: plug flow reaction with uniform, gradientless heating).
-
Optimize driving forces at all scales and maximize the specific surface areas to which they apply (example: increase transfer surface area through microchannel designs).
-
Maximize synergistic effects from partial processes (example: multifunctional reactors).
The principles and the main concepts are accepted worldwide, and are today considered common practice and theory. The four principles above lead to practical application. Changing the structure of a conventional reactor means focusing both on the catalyst and on the reactor’s shape and dimension. The synergy between chemical reaction and separation unit leads to the design of more compact and cheaper plants, reducing the amount of equipment and thus simplifying the control systems of the chemical plant. The pursuit of novel energy sources leads to more efficient mixing and heating systems, allowing for optimal heat and mass transfer properties. Alternative time use and optimization can be reached by implementing dynamic operations or using alterative fluids that enhance the global conversion of a reaction network.
A summary of the main idea, including the four principles and their means of application, is shown in Figure 1.
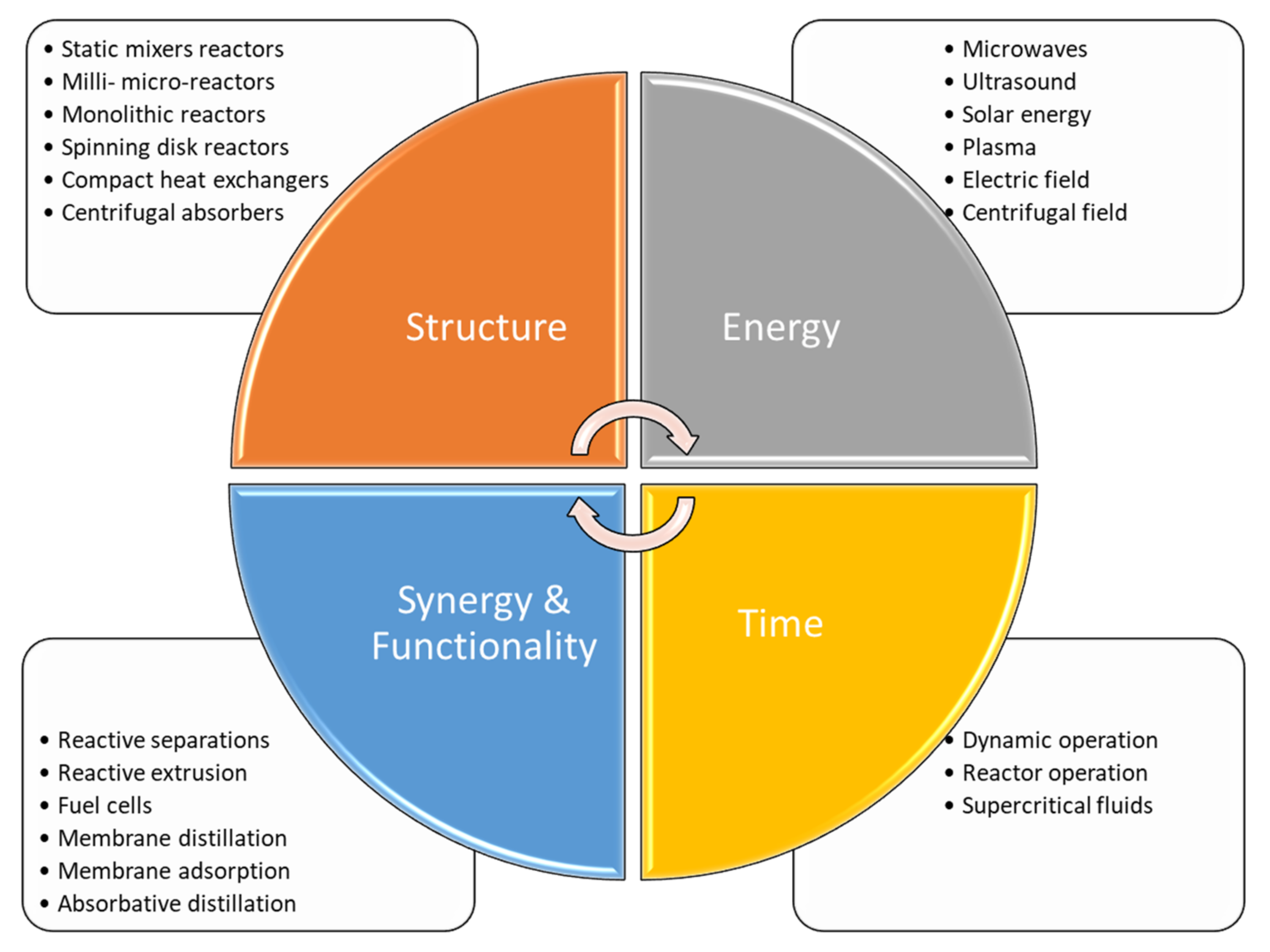
Figure 2. Scival Analysis trends obtained using Process Intensification as keyword.
2. Process Intensification: Potentials and Guidelines
In this paragraph, the potential of the PI strategies described in the previous section will be described and discussed. Moreover, some guidelines are provided to help the researchers choose between the different available options for intensification of a given chemical process. In Table 1, the main benefits and drawbacks of the different PI strategies are reported, together with some common application areas. This table may be of interest for a reader who is starting his or her scientific journey in the field of PI.Table 1. Main benefits and drawbacks of different PI strategies and potential application areas.
| PI Strategy | Pros | Cons | Application | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Miniaturisation and structurisation |
| ||
The main benefits were already discussed in the previous paragraph; thus, it may be worthwhile here to underline some important drawbacks of these operations.
Miniaturized and structured systems seem to be the best alternative in PI, as they allow to work in ideal conditions in terms of fluid dynamics, allowing achievement of high selectivity and low chemical risks and reducing operation volumes. Therefore, operation is difficult to scale at industrial level, as numbering up is an expensive procedure due to the high price of a single reactor. Moreover, there is an elevated blocking risk as microchannels can be blocked by even small traces of microparticles contained in the reactant vessels.
Static mixers are easy to be set up, as the operation consists of packing a standard pipe. Therefore, even if good mixing can be achieved the reactor volume can decrease dramatically, leading long pipes to achieve the reasonable residence times needed for operation.
Multifunctional reactors are very efficient when selectivity problems are the main issue in the process; however, their operation can be expensive and sophisticated in terms of process control. Membranes are usually expensive, and must be maintained and replaced frequently overall when the reaction leads to heavy byproducts. A simulated moving bed needs a sophisticated control logic to control the switch between the feed and withdrawal positions.
MW, US and Plasma are very good options when thermal control is an issue; therefore, the equipment is expensive and characterized by an intrinsic risk, i.e., exposure to irradiation, which requires additional attention to the management of the chemical plant.
Dynamic operations are useful to optimize product selectivity; however, complex process control is required to ensure reproducibility; thus, phase composition may vary at the reactor outlet from test to test, which must be avoided during the operation of the industrial plant.
Alternative fluids are well-suited to replace standard solvents, and ensure high mixing of reactant and products as well as their subsequent separation. Therefore, these liquids are often very expensive, and their recovery and relayed purification is a major issue.
A second question to be answered is how to choose between the different PI strategies. In Table 2, the most frequently encountered process limitations and the suitability of different PI strategies are reported. This table can be considered a conceptual map where the reader should detect the correct PI strategy once the limitations of the chemical process of interest are defined.
Table 2. Commonly-encountered process limitations and suitability of different PI strategies.
| PI Strategy | Limitations by | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Kinetics | Internal Mass Transfer | External Mass Transfer | Product Selectivity | Process Complexity | Thermal Control | Mixing | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment | Miniaturisation and structurisation |
|
|
X |
|
X |
| ||||||||||||||||
| X | X | X | X | Integrated mixing elements |
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Integrated mixing elements | X |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| X | X | X | X | Multifunctional reactors |
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Multifuctional reactors | X | X | Energy | Microwave |
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Energy |
|
|
|
Microwave |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| X | X | Ultrasound |
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Ultrasound |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| X | X | Plasma |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Plasma |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| X | X | X | Operation | Dynamic/transient operation |
|
| |||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dynamic/transient operation | X |
|
|
|
X | X | Alternate fluids |
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| Alternate fluids | ||||
| X | X | X |
35. Conclusions
There is no a single choice, nor a simple choice, to intensify a chemical process. The PI strategy must be tailored to the chemical and physical application by investing time, passion, and energy in trying to find the best solution to achieve the PI goal. Possible alternatives, routes, and strategies are numerous, and new technologies will definitely emerge along with the need to reducing energy and loss of resources. Herein have summarized the main definitions and the strategies for PI in an attempt to provide order to the enormous literature published on this topic to date.
