Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Beatrix Zheng and Version 1 by Irene Peral-Sanchez.
The societal burden of non-communicable disease is closely linked with environmental exposures and lifestyle behaviours, including the adherence to a poor maternal diet from the earliest preimplantation period of the life course onwards. Epigenetic variations caused by a compromised maternal nutritional status can affect embryonic development and offspring health later in life.
- DOHaD
- maternal diet
- epigenetics
- embryo
- preimplantation period
- ART
1. Introduction
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), neurological disorders, obesity, and some cancers, are on the rise, leading to around 34 million deaths worldwide per annum [1]. The significant increase in NCDs is closely linked to environmental exposures and lifestyle behaviours. It is also clear that exposure to these different largely modifiable conditions (i.e., poor diet, stress, and chemicals) from the preimplantation period onwards is important in the origin of these diseases [2]. The relationship between exposure to the maternal environment and the development and health of the foetus is captured in the developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD) hypothesis [3].
The research in DOHaD, which has increased substantially from the 1990s, has shown that the maternal environment during pregnancy can affect programming during development and increase the risk of offspring developing long-term diseases [3,4][3][4]. Professor David Barker was one of the pioneer researchers to demonstrate the DOHaD phenomenon in his epidemiological studies in 1989, linking perinatal weight and the subsequent growth trajectory with health and disease risk in later life [5,6][5][6]. Since the development of the DOHaD hypothesis, many authors have linked birth weight with the development of NCDs. Initially, only low birth weight was related; however, some studies found that this relationship was U-shaped, indicating that high birth weight can also relate to the risk of developing pathologies associated with metabolic syndrome [7]. The maternal environment is one of the most studied conditions that can influence offspring phenotype. The maternal environment comprises both extrinsic and intrinsic factors. Extrinsic factors act from the outside and are related to the environmental conditions (pollution, exposure to chemicals, etc.), but intrinsic factors act from within an individual and are directly dependent on the mother’s condition (eating behaviours, metabolism, lifestyle, etc.). Despite the importance of human studies, animal studies provide an advantage in that environmental exposures can be controlled (extrinsic factors) and maternal and subject confounders can be reduced (intrinsic factors) [8]. These studies have demonstrated that the origin of NCDs can be attributable to the maternal and gestational environment, laying the foundation for DOHaD. These studies have further progressed to reveal that an array of environmental factors experienced during pregnancy, including toxins, stress, diet, and lifestyle, contribute to physiological and metabolic development, impacting foetal growth and offspring phenotype and health.
DOHaD research in nutritional studies has now found links between the quality of maternal diet during pregnancy and its possible contribution to changes in the genome expression of the offspring in utero. These changes act to coordinate the physiological, metabolic and growth characteristics, and are mediated through epigenetic mechanisms [9,10][9][10]. Epigenetic changes refer to different molecular states that affect the regulation of gene expression by changing the structural organisation of the DNA, but without changing the sequence [11]. Epigenetic changes during foetal development can depend on microenvironmental variations. Thus, environmental factors, such as maternal diet, during early pregnancy can affect maternal metabolism, which can also impact offspring development [12,13][12][13]. The main epigenetic changes include DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the expression of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Whilst the association between the in utero environment and offspring health has been widely described over the years, the underlying molecular processes influencing the epigenome are generally unknown. The study of epigenetic changes that occur during pregnancy is not limited to natural conditions, but may also operate in clinical settings, such as ART. The next goal in DOHaD research will be to understand the molecular details linking the maternal and clinical environment to the epigenome, and the subsequent biological steps that lead to the onset of disease risk in later life [14].
2. ART and Epigenetic Modifications
ART includes a range of techniques, such as superovulation, sperm capacitation, intrauterine insemination (IUI), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in vitro fertilization (IVF) and culture, cryopreservation, and embryo transfer for infertility treatment in humans and the production of transgenic farm animals [144,145][15][16]. ART treatment can interfere with epigenetic changes, particularly DNA methylation [146][17], starting from the preimplantation period in humans and animals [147[18][19],148], affecting early embryogenesis and offspring health [149,150,151][20][21][22]. The procedures implemented during ART treatment, such as ovarian stimulation using hormones, the in vitro maturation of oocytes and preimplantation embryos, and the use of ICSI and embryo cryopreservation, expose the embryo to environmental conditions that differ from those in spontaneous fertilization and embryogenesis, and which may alter the normal epigenetic mechanisms [149,152][20][23].
2.1. Human Studies
DNA methylation, following ART, has been investigated at different stages of development. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in cord blood and placenta revealed differences in the methylation status between ART and spontaneous conceiving populations at certain CpG sites [153,154,155,156][24][25][26][27]. In ICSI-manipulated oocytes, this can include an abnormal methylation status at imprinted genes at differentially methylated region 1 (DMR1), H19 DMR, and PEG1 DMR [157][28]. Following ICSI treatment, day 3 embryos also showed aberrant methylation patterns at the same imprinted loci [158][29]. The aberrant methylation pattern of these DMRs is linked to imprinting disorders, such as Silver–Russell syndrome (SRS) and Beckwith–Weidemann syndrome (BWS) [159,160,161,162,163][30][31][32][33][34]. All the BWS patients conceived via ART had DNA methylation errors at H19/Igf2 IG DMR and/or KCNQ10T1:TSS DMR, and the DNA methylation error rates were significantly higher when compared to the spontaneously conceived BWS patients (100% versus 43.6% DNA methylation error rates, respectively) [151][22]. Interestingly, the DNA methylation levels of H19/Igf2 DMR and KCNQ10T1 DMR were significantly lower in the placentas of IVF/ICSI patients compared to the spontaneously conceived patients [164][35]. However, no differences in DNA methylation levels were reported between IVF and the spontaneous controls at individual CpG sites and entire DMRs of KvDMR1 in cord blood and placental villi, as well as PEG10 in placental villi [165][36]. These findings suggest that certain epigenetic variations in ART-conceived embryos may resolve throughout development, whereas others do not, and might associate with offspring outcomes. To further support this hypothesis, a positive correlation was observed between the DNA methylation of ERVFRD-1 and placental weight, as well as ERVFRD-1 and SNURF with birth weight, whereas the epigenetic variations at birth, as a consequence of ART, were largely resolved by adulthood [164,166][35][37]. Moreover, the epigenetic changes at certain genes and the transmission to offspring might be tissue-specific [164,165][35][36]; for example, the differences in methylation levels between ART and spontaneous conceptions for the H19/Igf2 and KCNQ1OT1 DMRs observed in the placenta were absent in the cord blood [164][35].
2.2. Animal Studies
Animal studies provide more insight into the prenatal period to help understand the origin and flow of epigenetic changes. The profiling of DNA methylation levels in mouse embryonic cells, blastocysts, the placenta, and the foetus displayed differences between ART and the controls [152,167,168,169][23][38][39][40]. Similarly to humans, some epigenetic alterations at certain genes among the ART population arise during the periconception and preimplantation period, and can be maintained throughout pregnancy. Aberrant methylation patterns at certain CpG sites of the Igf2/H19 imprinting control region (ICR) are observed in the IVF mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), placenta, foetal brain, and liver tissues of certain mouse strains [170,171][41][42]. Differences in methylation status at the H19 ICR were also reported in ART blastocysts, embryos, aorta, and placental tissues [149,172][20][43]. Nevertheless, the presence of alterations might also differ among the crossed strains [150,171,173][21][42][44]. A reduction in methylation for KvDMR1 and KCNQ1OT1 was observed in the ART placentas compared to the controls, whereas no difference was observed in the foetal brain and liver tissues [150,152,171,172][21][23][42][43]. Other examples are the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N (Snrpn), PEG1 and PEG3 ICRs that showed an altered methylation status in certain tissues, whereas no difference was observed in others [150,171,172,174][21][42][43][45]. Altogether, these alterations can be correlated to the aberrant expression levels of the relative genes, blastocyst maturity, and foetal development, and the imprinting disorders observed among ART offspring [149,152][20][23]. Moreover, the alterations in the methylation levels of SCAP/SCREPF1-2 in the lungs and the promoter of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene in the aortic and vascular tissue implicate the role of epigenetic alterations as a basis for the cardiovascular and respiratory dysfunction observed among ART-conceived offspring [167,174,175,176][38][45][46][47].
Whether these epigenetic changes are due to the underlying subfertility or to the ART treatment in humans warrants further investigation, yet similar datasets from animal models suggest that the effect of ART cannot be ignored; for example, ART was associated with alterations in DNA methylation in embryos at H19 and PEG 1 DMRs in both human and animal models [158,172][29][43]. In placentas, an alteration in the KCNQ1OT1 methylation status was associated with ART in human and animal models [164[35][42],171], whereas the outcomes on KvDMR1 and PEG10 ICR were inconsistent between humans and animals [150,165][21][36]. Besides, differences in methylation patterns have also been reported between different ART procedures [149,152[20][23][35][39],164,168], which emphasizes the effect of ART manipulation on the epigenetic profile and subsequent disease risk
3. Diet and ART Outcomes
In the sub-fertile population, diet has been related to fertility [177,178][48][49] and implicated in the intermediate ART outcomes, such as fertilization rate [179][50] and embryo yield [180][51], as well as clinical outcomes, including, importantly, pregnancy [181][52] and live birth rates [179][50]. Adherence to a healthy dietary pattern increased the number of mature oocytes [181,182][52][53]. Higher fertility and implantation rates were associated with the Iranian traditional medicine (ITM)-based diet and “pro-fertility” diet, respectively [181,183][52][54]. Increased embryo yield was observed with higher adherence towards the Mediterranean and ITM-based diets [180,181][51][52]. The chance of pregnancy was also improved with increased adherence to the “pro-fertility”, Mediterranean and ITM-based diets [181,183,184,185][52][54][55][56]. Furthermore, Twigt et al. reported an association between the chance of ongoing pregnancy and higher preconception dietary risk scores [186][57]. Besides, the rate of live birth was also improved by healthy dietary behaviours in women [179,183,187][50][54][58]. In contrast, unhealthy dietary behaviour was linked to a lower mature oocyte count, embryo quality, pregnancy chance, and live birth rate in human and mouse models [182,188,189][53][59][60]. Moreover, Li et al. investigated the effect of antioxidant intake, and showed improvements in the oocyte yield and live birth rate, which were dependent on the source and type of antioxidant [190][61].
A diet–epigenetic–ART connection might, in part, explain the ART outcomes observed, yet studies investigating this connection are limited [172,191][43][62]; for example, a healthy and balanced maternal diet could, through correcting the epigenetic alterations caused by ART, modify the corresponding outcomes [172,192][43][63]. On the other hand, an unbalanced diet (i.e., HFD diets) may pose epigenetic alterations that might not be observed otherwise [193][64]. A suggested mechanism behind this connection can be related to the effect of diet on the molecular interactions and biomarker levels within the body, which can induce epigenetic alterations; for example, improved pregnancy and live birth rates were associated with folate intake, which was also observed with adherence to the Mediterranean diet, which showed an association with the folate and vitamin B6 levels [179,184,185][50][55][56]. Subsequently, Rahimi et al. showed that DNA methylation defects induced by ART were partially restored with moderate folic acid supplementation in a mouse embryo and placenta [172][43]. In terms of phenotypic changes, moderate folic acid supplementation reduced the number of embryos with developmental delays, associated with ART treatment [172][43], which can further affect the disease risk in offspring [194,195][65][66].
4. Conclusions
Maternal diet could induce metabolic and physiological changes in offspring through epigenetic modifications. The altered epigenetic regulation of genes is associated with increased predisposition to disease later in life. Despite the advances in sequencing, there are still many mechanisms that need to be studied to understand the exact contributions of developmentally induced epigenetic markers and their effect on the risk of disease development. Understanding the relationship between maternal diet during pregnancy, epigenetic markers, and disease development may allow the discovery of therapeutic targets for the prevention and treatment of NCDs.
There is now great interest in understanding the environmental basis affecting epigenetic modifications that may be the origin of diseases in offspring. In humans, we have mentioned examples of epidemiological and ART-associated studies that could be used to understand the origins of some diseases or syndromes. However, animal studies are more flexible and controlled, as defined conditions can provide us with more information on the environmental effect during embryonic development and the outcome of the offspring in a shorter time, and, interestingly, we found that in both the natural condition and ART, maternal diet influences the offspring outcomes (Figure 1).
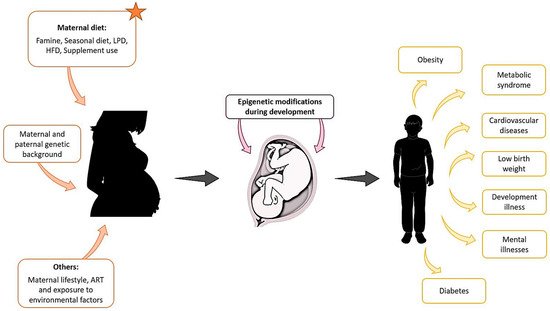
Figure 1. Maternal exposure to environmental factors, diet changes, genetic background, and other parameters such as lifestyle, can affect the development of the foetus from the first stages of pregnancy and compromise the health of the offspring later in life.
References
- Stanaway, J.D.; Afshin, A.; Gakidou, E.; Lim, S.S.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 84 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994.
- Bateson, P. Fetal experience and good adult design. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 928–934.
- Barker, D.J.P. The origins of the developmental origins theory. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 412–417.
- Lin, Y.-J. Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents born premature and small-for-gestational age: A scenario of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD). Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 109–110.
- Barker, D.; Osmond, C.; Winter, P.; Margetts, B.; Simmonds, S. Weight in Infancy and Death from Ischaemic Heart Disease. Lancet 1989, 334, 577–580.
- Limesand, S.W.; Thornburg, K.L.; Harding, J.E. 30th anniversary for the developmental origins of endocrinology. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 242, E1–E4.
- Blackmore, H.L.; Ozanne, S.E. Maternal diet-induced obesity and offspring cardiovascular health. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 338–347.
- Bianco-Miotto, T.; Craig, J.M.; Gasser, Y.P.; Van Dijk, S.J.; Ozanne, S.E. Epigenetics and DOHaD: From basics to birth and beyond. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 513–519.
- Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Sánchez-Agurto, A.; Lamperti, L.; Martorell, M. Epigenetics, Maternal Diet and Metabolic Programming. Open Biol. J. 2019, 7, 45–51.
- Masuyama, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Effects of a High-Fat Diet Exposure in Utero on the Metabolic Syndrome-Like Phenomenon in Mouse Offspring through Epigenetic Changes in Adipocytokine Gene Expression. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2823–2830.
- Yamada, L.; Chong, S. Epigenetic studies in Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: Pitfalls and key considerations for study design and interpretation. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 30–43.
- Slater-Jefferies, J.L.; Lillycrop, K.A.; Townsend, P.A.; Torrens, C.; Hoile, S.P.; Hanson, M.A.; Burdge, G.C. Feeding a protein-restricted diet during pregnancy induces altered epigenetic regulation of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-α in the heart of the offspring. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2011, 2, 250–255.
- Watkins, A.J.; Lucas, E.S.; Wilkins, A.; Cagampang, F.R.A.; Fleming, T.P. Maternal Periconceptional and Gestational Low Protein Diet Affects Mouse Offspring Growth, Cardiovascular and Adipose Phenotype at 1 Year of Age. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28745.
- Lillycrop, K.; Burdge, G.C. Maternal diet as a modifier of offspring epigenetics. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2015, 6, 88–95.
- Bonakdar, E.; Edriss, M.A.; Bakhtari, A.; Jafarpour, F.; Asgari, V.; Hosseini, S.M.; Boroujeni, N.S.; Hajian, M.; Rahmani, H.R.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. A physiological, rather than a superovulated, post-implantation environment can attenuate the compromising effect of assisted reproductive techniques on gene expression in developing mice embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 191–206.
- Farquhar, C.; Marjoribanks, J. Assisted reproductive technology: An overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD010537.
- Mani, S.; Ghosh, J.; Coutifaris, C.; Sapienza, C.; Mainigi, M. Epigenetic changes and assisted reproductive technologies. Epigenetics 2020, 15, 12–25.
- Wright, K.; Brown, L.; Brown, G.; Casson, P.; Brown, S. Microarray assessment of methylation in individual mouse blastocyst stage embryos shows that in vitro culture may have widespread genomic effects. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 2576–2585.
- Santos, F.; Hyslop, L.; Stojkovic, P.; Leary, C.; Murdoch, A.; Reik, W.; Stojkovic, M.; Herbert, M.; Dean, W. Evaluation of epigenetic marks in human embryos derived from IVF and ICSI. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2387–2395.
- Fauque, P.; Jouannet, P.; Lesaffre, C.; Ripoche, M.-A.; Dandolo, L.; Vaiman, D.; Jammes, H. Assisted Reproductive Technology affects developmental kinetics, H19 Imprinting Control Region methylation and H19 gene expression in individual mouse embryos. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 116.
- Li, B.; Chen, S.; Tang, N.; Xiao, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, F.; Huang, X.; Sun, F.; Wang, X. Assisted Reproduction Causes Reduced Fetal Growth Associated with Downregulation of Paternally Expressed Imprinted Genes That Enhance Fetal Growth in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 45.
- Hattori, H.; Hiura, H.; Kitamura, A.; Miyauchi, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Takahashi, S.; Okae, H.; Kyono, K.; Kagami, M.; Ogata, T.; et al. Association of four imprinting disorders and ART. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 21.
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wen, L.; Lei, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Changes in DNA methylation and imprinting disorders in E9.5 mouse fetuses and placentas derived from vitrified eight-cell embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 404–415.
- Melamed, N.; Choufani, S.; Wilkins-Haug, L.E.; Koren, G.; Weksberg, R. Comparison of genome-wide and gene-specific DNA methylation between ART and naturally conceived pregnancies. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 474–483.
- Chi, F.; Zhao, M.; Li, K.; Lin, A.-Q.; Li, Y.; Teng, X. DNA methylation status of imprinted H19 and KvDMR1 genes in human placentas after conception using assisted reproductive technology. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 854.
- Tobi, E.W.; Almqvist, C.; Hedman, A.; Andolf, E.; Holte, J.; Olofsson, J.I.; Wramsby, H.; Wramsby, M.; Pershagen, G.; Heijmans, B.T.; et al. DNA methylation differences at birth after conception through ART. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 36, 248–259.
- Song, S.; Ghosh, J.; Mainigi, M.; Turan, N.; Weinerman, R.; Truongcao, M.; Coutifaris, C.; Sapienza, C. DNA methylation differences between in vitro- and in vivo-conceived children are associated with ART procedures rather than infertility. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 1–10.
- Shi, X.; Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Aberrant DNA methylation of imprinted loci in human in vitro matured oocytes after long agonist stimulation. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 167, 64–68.
- Shi, X.; Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Abnormal DNA Methylation of Imprinted Loci in Human Preimplantation Embryos. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 978–983.
- Binder, G.; Begemann, M.; Eggermann, T.; Kannenberg, K. Silver–Russell syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 153–160.
- Cocchi, G.; Marsico, C.; Cosentino, A.; Spadoni, C.; Rocca, A.; De Crescenzo, A.; Riccio, A. Silver-Russell syndrome due to paternal H19/IGF2 hypomethylation in a twin girl born after in vitro fertilization. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2013, 161, 2652–2655.
- Krzyzewska, I.; Alders, M.; Maas, S.M.; Bliek, J.; Venema, A.; Henneman, P.; Rezwan, F.I.; Lip, K.V.D.; Mul, A.N.; Mackay, D.J.; et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome patients without molecular confirmation after routine diagnostics. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 53.
- Pandita, A.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, G.; Panghal, A. Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome with IC2 (KvDMR1) hypomethylation defect: A novel mutation. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017.
- Elalaoui, S.; Garin, I.; Sefiani, A.; De Nanclares, G.P. Maternal Hypomethylation of KvDMR in a Monozygotic Male Twin Pair Discordant for Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. Mol. Syndr. 2014, 5, 41–46.
- Choux, C.; Binquet, C.; Carmignac, V.; Bruno, C.; Chapusot, C.; Barberet, J.; LaMotte, M.; Sagot, P.; Bourc’His, D.; Fauque, P. The epigenetic control of transposable elements and imprinted genes in newborns is affected by the mode of conception: ART versus spontaneous conception without underlying infertility. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 331–340.
- Vincent, R.N.; Gooding, L.D.; Louie, K.; Wong, E.C.; Ma, S. Altered DNA methylation and expression of PLAGL1 in cord blood from assisted reproductive technology pregnancies compared with natural conceptions. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 739–748.
- Novakovic, B.; Lewis, S.; Halliday, J.; Kennedy, J.; Burgner, D.P.; Czajko, A.; Kim, B.; Sexton-Oates, A.; Juonala, M.; Hammarberg, K.; et al. Assisted reproductive technologies are associated with limited epigenetic variation at birth that largely resolves by adulthood. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12.
- Rexhaj, E.; Pireva, A.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Allemann, Y.; Cerny, D.; Dessen, P.; Sartori, C.; Scherrer, U.; Rimoldi, S.F. Prevention of vascular dysfunction and arterial hypertension in mice generated by assisted reproductive technologies by addition of melatonin to culture media. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1151–H1156.
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Guan, Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Yu, M.; Yang, X. Effects of superovulation, in vitro fertilization, and oocyte in vitro maturation on imprinted gene Grb10 in mouse blastocysts. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 298, 1219–1227.
- Bakhtari, A.; Rahmani, H.-R.; Bonakdar, E.; Jafarpour, F.; Asgari, V.; Hosseini, S.-M.; Hajian, M.; Edriss, M.-A.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.-H. The interfering effects of superovulation and vitrification upon some important epigenetic biomarkers in mouse blastocyst. Cryobiology 2014, 69, 419–427.
- Li, T.; Vu, T.H.; Ulaner, G.A.; Littman, E.; Ling, J.-Q.; Chen, H.-L.; Hu, J.-F.; Behr, B.; Giudice, L.; Hoffman, A.R. IVF results in de novo DNA methylation and histone methylation at an Igf2-H19 imprinting epigenetic switch. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 11, 631–640.
- De Waal, E.; Vrooman, L.A.; Fischer, E.; Ord, T.; Mainigi, M.; Coutifaris, C.; Schultz, R.M.; Bartolomei, M.S. The cumulative effect of assisted reproduction procedures on placental development and epigenetic perturbations in a mouse model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6975–6985.
- Rahimi, S.; Martel, J.; Karahan, G.; Angle, C.; Behan, N.A.; Chan, D.; Macfarlane, A.J.; Trasler, J.M. Moderate maternal folic acid supplementation ameliorates adverse embryonic and epigenetic outcomes associated with assisted reproduction in a mouse model. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 34, 851–862.
- Chen, S.; Sun, F.-Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, N.; Zhu, B.; Li, B. Assisted reproduction causes placental maldevelopment and dysfunction linked to reduced fetal weight in mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10596.
- Rexhaj, E.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Rimoldi, S.F.; Fuster, D.G.; Anderegg, M.; Somm, E.; Bouillet, E.; Allemann, Y.; Sartori, C.; Scherrer, U. Mice generated by in vitro fertilization exhibit vascular dysfunction and shortened life span. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 5052–5060.
- Valenzuela-Alcaraz, B.; Crispi, F.; Bijnens, B.; Cruz-Lemini, M.; Creus, M.; Sitges, M.; Bartrons, J.; Civico, S.; Balasch, J.; Gratacós, E. Assisted Reproductive Technologies Are Associated with Cardiovascular Remodeling in Utero That Persists Postnatally. Circulation 2013, 128, 1442–1450.
- Le, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Hu, M.; Jin, F.; Lou, H. Long-Term Disturbed Expression and DNA Methylation of SCAP/SREBP Signaling in the Mouse Lung From Assisted Reproductive Technologies. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 566168.
- Panth, N.; Gavarkovs, A.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The Influence of Diet on Fertility and the Implications for Public Health Nutrition in the United States. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 211.
- Chavarro, J.E.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C. Protein intake and ovulatory infertility. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, 210.e1–210.e7.
- Gaskins, A.J.; Afeiche, M.C.; Wright, D.L.; Toth, T.L.; Williams, P.L.; Gillman, M.W.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J. Dietary Folate and Reproductive Success among Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 124, 801–809.
- Sun, H.; Lin, Y.; Lin, D.; Zou, C.; Zou, X.; Fu, L.; Meng, F.; Qian, W. Mediterranean diet improves embryo yield in IVF: A prospective cohort study. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 73.
- Alibeigi, Z.; Jafari-Dehkordi, E.; Kheiri, S.; Nemati, M.; Mohammadi-Farsani, G.; Tansaz, M. Auswirkungen einer auf traditioneller Medizin basierenden Ernahrung und Lebensfuhrung auf die Infertilitatsbehandlung bei Frauen, die sich Masnahmen zur assistierten Reproduktion unterziehen: Eine randomisierte kontrollierte Studie. Complement. Med. Res. 2020, 27, 230–241.
- Jahangirifar, M.; Askari, G.; Taebi, M. Dietary Patterns and the Outcomes of Assisted Reproductive Techniques in Women with Primary Infertility: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 12, 316–323.
- Gaskins, A.J.; Nassan, F.L.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Arvizu, M.; Williams, P.L.; Keller, M.G.; Souter, I.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J.E. Dietary patterns and outcomes of assisted reproduction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 567.e1–567.e18.
- Karayiannis, D.; Kontogianni, M.; Mendorou, C.; Mastrominas, M.; Yiannakouris, N. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and IVF success rate among non-obese women attempting fertility. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 494–502.
- Vujkovic, M.; De Vries, J.H.; Lindemans, J.; Macklon, N.S.; Van Der Spek, P.J.; Steegers, E.A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P. The preconception Mediterranean dietary pattern in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment increases the chance of pregnancy. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 2096–2101.
- Twigt, J.M.; Bolhuis, M.E.C.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hammiche, F.; Van Inzen, W.G.; Laven, J.S.E.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. The preconception diet is associated with the chance of ongoing pregnancy in women undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2526–2531.
- Gaskins, A.J.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Williams, P.L.; Keller, M.G.; Toth, T.L.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J. Maternal whole grain intake and outcomes of in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 105, 1503–1510.e4.
- Machtinger, R.; Gaskins, A.; Mansur, A.; Adir, M.; Racowsky, C.; Baccarelli, A.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J. The association between preconception maternal caffeinated and non-caffeinated beverage intake on IVF outcomes. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 284.
- Sohrabi, M.; Roushandeh, A.M.; Alizadeh, Z.; Vahidinia, A.; Vahabian, M.; Hosseini, M. Effect of a high fat diet on ovary morphology, in vitro development, in vitro fertilisation rate and oocyte quality in mice. Singap. Med. J. 2015, 56, 573–579.
- Li, M.-C.; Nassan, F.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Williams, P.L.; Souter, I.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J. Intake of Antioxidants in Relation to Infertility Treatment Outcomes with Assisted Reproductive Technologies. Epidemiology 2019, 30, 427–434.
- Zhang, Y.; Kutateladze, T.G. Diet and the epigenome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3375.
- Yang, M.; Tao, J.; Wu, H.; Guan, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, S.-L.; He, C.; Ji, P.; Liu, J.; et al. Aanat Knockdown and Melatonin Supplementation in Embryo Development: Involvement of Mitochondrial Function and DNA Methylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 2050–2065.
- Andreas, E.; Reid, M.; Zhang, W.; Moley, K.H. The effect of maternal high-fat/high-sugar diet on offspring oocytes and early embryo development. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 25, 717–728.
- Cohen, E.; Wong, F.Y.; Horne, R.S.; Yiallourou, S. Intrauterine growth restriction: Impact on cardiovascular development and function throughout infancy. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 821–830.
- Jaddoe, V.W.V.; De Jonge, L.L.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Gaillard, R. First trimester fetal growth restriction and cardiovascular risk factors in school age children: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2014, 348, g14.
More
