Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Jonas Jutzi and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Histone methylation tightly regulates chromatin accessibility, transcription, proliferation, and cell differentiation, and its perturbation contributes to oncogenic reprogramming of cells. In particular, many myeloid malignancies show evidence of epigenetic dysregulation.
- KDM
- Jumonji C (JmjC) domain
- histone demethylation
- leukemia
- myelodysplastic syndrome
1. Introduction
Non-genetic chromatin alterations play a significant role in disease development, maintenance, and relapse of myeloid malignancies. Among epigenetic modifying enzymes, histone demethylases have gained special attention in recent years for their involvement in myeloid malignancies. Histone lysine demethylases (KDMs) are subdivided into two subclasses, FAD-dependent and Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing (JMJD) demethylases (Figure 1). Although there are only two FAD-dependent demethylases, KDM1A and KDM1B, JMJD demethylases comprise a larger group of more than twenty proteins [1][2][3][1,2,3]. Based on the evolution of their JmjC domain and the occurrence of additional domains, JMJD demethylases are subdivided into numbered subgroups (KDM2–7). Most KDMs are attributed to demethylate methylated lysines of histone 3 or 4, as well as of non-histone proteins, thereby activating or repressing transcription. KDM1A has been studied extensively, culminating in the development of inhibitors currently in clinical trials for patients with leukemia [2]. The JmjC domain containing KDMs, which require Fe(II) and a-ketoglutarate (a-KG) as cofactors, however, have been less intensely studied and their substrate specificity varies greatly [3][4][5][3,4,5]. Our lack of knowledge regarding the function of these KDMs in benign hematopoiesis makes understanding their role in malignancies even harder. Moreover, the exact contribution of individual KDMs in either a tumor-suppressive or tumor-promoting manner, is dependent on the specific disease-context.
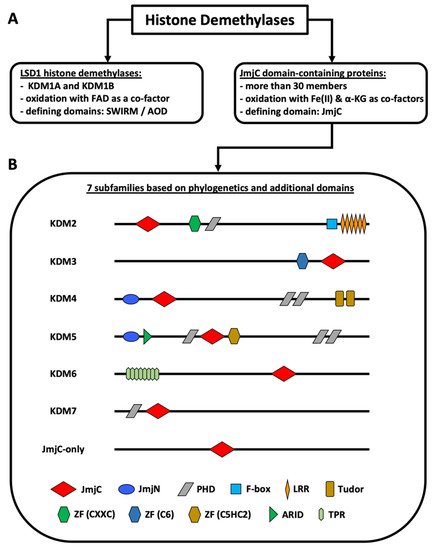
Figure 1. Classification of histone demethylases. (A) Types of histone demethylases. (B) Subfamilies of JmjC domain-containing proteins. The KDM2–7 subfamilies are known histone demethylases. The JmjC-only subfamily contains demethylases, hydroxylases, and proteins with unknown functions. KDM4D+E lack the PHD and the Tudor domains. KDM5C+D only possess one C-terminal PHD domain. KDM6B lacks the TPR domains. The figure is based on Klose et al. [1], Chen et al. [6], Franci et al. [7], Markolovic et al. [8], and Chang et al. [9]. Abbreviations: αKG (alpha-ketoglutarate), AOD (amino oxidase domain), ARID (AT-rich interaction domain) domain, FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), JmjC (Jumonji C) domain, JmjN (Jumonji N) domain, LRR (leucine-rich repeat) domain, PHD (plant homeodomain) domain, TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat domain), ZF (zinc finger) domain.
2. The KDM2 Family
The KDM2 subfamily of the Jumonji domain-containing histone demethylases encompasses two members, KDM2A and KDM2B. As reviewed by Markolovic et al., both enzymes possess catalytic activity towards mono- and di-methylated lysine residues [8]. H3K36 is the known main histone target of KDM2 demethylases [8]. In myeloid malignancies both enzymes have been shown to demethylate H3K36me2 [10][11][12][10,11,12].
2.1. KDM2A
Cumulating evidence indicates a tumor-suppressor role for this histone demethylase in myeloid leukemias (Figure 2) [10][13][14][10,13,14]. KDM2A is required for the maintenance of heterochromatin, as its deletion delocalizes HP1 from chromatin, impairs centromeric integrity and, thereby, increases genomic instability [14]. Fittingly, Inoue et al. observed KDM2A downregulation in the bone marrow (BM) of mice with benzene-induced acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) compared to control BM (Table 1) [13]. Functional evidence provided by Zhu et al. showed that KDM2A reduces expression of Hoxa9 and other MLL target genes in MLL-AF10 mice, resulting in increased differentiation [10]. MLL is a H3K4 histone methyltransferase and MLL gene rearrangements are common chromosomal abnormalities associated with acute leukemias [15]. Mechanistically, KDM2A reversed H3K36me2 methylation, a mark written by the histone methyltransferase ASH1L to facilitate binding of MLL and its associated oncoprotein LEDGF (Table 1) [10]. KDM2A activity thus counteracts MLL-driven leukemogenesis, underlining an anti-leukemic role for KDM2A in myeloid leukemias.
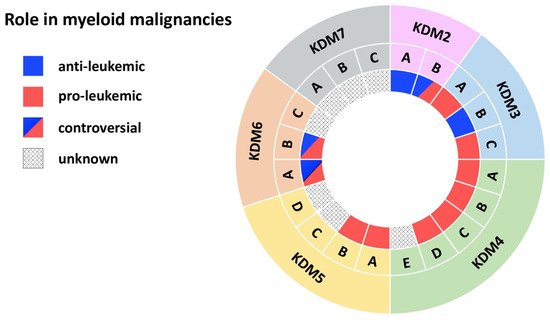

Figure 2. JmjC domain-containing histone demethylases in myeloid malignancies. The outer ring names the KDM subfamily, while the middle ring specifies members of each subfamily. The inner ring indicates the role in myeloid malignancies: blue (anti-leukemic), red (pro-leukemic), blue and red (controversial role), black dots (unknown role).
Table 1.
Involvement of JmjC domain-containing histone demethylases in myeloid malignancies.
| Demethylase | Disease | Model | Effect | Mechanism | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDM2A | AML | MLL-AF10-induced leukemia in mice | anti-leukemic | KDM2A antagonizes oncogenic LEDGF/ASH1L | [10] | ||||
| AML | Chemically induced leukemia | KDM2A is downregulated in benzene-induced AML cells | [13] | ||||||
| KDM2B | AML | AML patient cells; MLL-AF9 transduced CD34+ cells; mouse xg models | pro-leukemic | KDM2B as part of the PRC1.1 complex regulates LDHA/PKM independent of H3K27me | 3 | [16] | |||
| AML | Tg mouse model with Kdm2b overexpression | KDM2B induces leukemia by increasing expression of Nsg2 and OXPHOS genes | [17] | ||||||
| AML | AML cell lines; AML CD34 | + | primary cells | KDM2B promotes cell cycle progression by reducing the tumor suppressor p15 | [11] | ||||
| AML | AML patient cells; | Hoxa9/Meis1-induced leukemia | KDM2B promotes leukemic transformation by reducing the tumor suppressor p15 | [12] | |||||
| MDS | Primary MDS cells, MDS cell lines | anti-leukemic | KDM2B suppresses EZH2 through miRNA let-7b expression | [18] | |||||
| AML | KrasG12D mice | KDM2B interacts with PRC1/2, increases Irf+Stat, downregulates Hoxa10+Smarca4/Brg1 | [19] | ||||||
| KDM3A | AML | Primary AML patient cells | pro-leukemic | KDM3A is recruited by Oct1 to the CDX2 promoter to remove repressive H3K9me2 | [20] | ||||
| KDM3B | APL | NB4 APL cell line | anti-leukemic | KDM3B kd enhances proliferation, blocks differentiation, inhibits degradation of PML/RARα | [21] | ||||
| AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines | KDM3B is downregulated in AML/MDS and overexpression represses colony formation | [22] | ||||||
| AML | AML cell lines | Expression of KDM2B reduces leukemic growth | [23] | ||||||
| KDM3C | AML | AML cell lines | pro-leukemic | KDM3C modulators selectively inhibit the growth of leukemic stem cells | [24] | ||||
| Ph+ MPN | K562 and MEG-01 cell lines | KDM3C kd impairs proliferation, viability, and sensitivity towards chemotherapy | [25] | ||||||
| Ph- MPN | Jak2V617F mice | Loss of Kdm3c is dispensable for disease initiation | [26] | ||||||
| AML | AML; MLL cell lines | The Kdm3c inhibitor JDI-16 induces apoptosis and differentiation | [27] | ||||||
| AML | Mouse MLL-AF9 leukemia cells | Loss of Kdm3c activity increases apoptosis+differentiation via RAS/MAPK, JAK-STAT, IL3 | [28] | ||||||
| AML | HOXA9/MEIS1 bone marrow transplantation model | Kdm3c upregulates key glycolytic and oxidative genes independent of its enzymatic activity | [29] | ||||||
| Ph-MPN | Primary MPN cells; NFE2 overexpressing mice; MPN cell lines | KDM3C and NFE2 form a positive feedback loop | [30] | ||||||
| AML | MLL-AF9 and HOXA9 leukemia mice | KDM3C interacts with HOXA9 and supports a HOXA9-controlled gene-expression program | [31] | ||||||
| AML | AML cell lines | KDM3C is recruited by RUNX1–RUNX1T1 to maintain low H3K9me2 at its target genes | [32] | ||||||
| AML | MLL-AF9 Tx mouse models; AML cell lines | Depletion of Kdm3c increases apoptosis of leukemic cells | [33] | ||||||
| KDM4A-C | AML | MLL-AF9 mouse model and cell lines | pro-leukemic | Combined KDM4 demethylase activity promotes survival of leukemic cells and increases expression of Il3ra | [34] | ||||
| KDM4A | AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines; mouse xg models | pro-leukemic | Loss of KDM4A induces apoptosis and downregulates pro-leukemic gene expression | [35] | ||||
| APL | NB4 APL and other cancer cell lines | KDM4A inhibitors increase H3K9/H3K36 methylation and kill malignant cells | [36] | ||||||
| KDM4B | AML | MLL-AF9 transduced CD34+ cells; Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines | pro-leukemic | KDM4B supports proliferation through upregulation of S100A8/9 and loss of KDM4B reduces growth of leukemic cells | [37] | ||||
| KDM4C | AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines; mouse xg models | pro-leukemic | KDM4C regulates miR-328-3p/CCND2 through MALAT1 resulting in Ara-C resistance | [38] | ||||
| AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines; mouse xg models | KDM4C upregulates ALKBH5 resulting in increased AXL mRNA stability | [39] | ||||||
| AML | Leukemic cells with MLL fusions and MOZ-TIF2; mouse xg models | KDM4C regulates target genes of MLL fusions/MOZ-TIF2 via H3K9me | 3 | demethylation | [40] | ||||
| AML | AML cell lines | KDM4C mediates oncogenic activity of PRL-3 by reducing H3K9me | 3 | at the Leo1 promoter | [41] | ||||
| KDM4D | AML | AML cell lines | pro-leukemic | KDM4D promotes proliferation in AML cells and activates expression of MCL-1 through H3K9me | 3 | demethylation | [42] | ||
| KDM5A | AML | Mouse NUP98 fusion-induced leukemia | pro-leukemic | NUP98-KDM5A (PHD finger) fusions induces differentiation arrest and leukemia | [43] | ||||
| CML | K562 cells | KDM5A kd in CML-BP stimulates leukemia cell differentiation and inhibits cell proliferation | [44] | ||||||
| CML | K562 cells, primary patient samples | miR-181d downregulates KDM5A which inhibits NF-κB subunit, p65 | [45] | ||||||
| KDM5B | AML/CML | CD34+ cells, AML and CML cell lines | pro-leukemic | KDM5B is highly expressed AML/CML cells, kd reduced leukemia colony-forming abilities | [46] | ||||
| AML | Mouse MLL-AF9/10 leukemia cells, MLLr patient samples | KDM5B negatively regulates leukemogenesis | [47] | ||||||
| AML | Clinical data | KDM5B expression predict survival | [48] | ||||||
| AML | Mouse | KDM5B is required for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal | [49][50] | [49,50] | |||||
| KDM5C | AML | Primary AML patient cells (M5) | unknown | KDM5C is overexpressed in pediatric AML (M5) | [51] | ||||
| AML | Primary AML patient cells | KDM5C is mutated and enriched in chemotherapy-resistant pediatric leukemia | [52] | ||||||
| KDM6A | CMML | KDM6A ko mice | anti-leukemic | Loss of KDM6A causes an CMML-like disease | [53] | ||||
| MDS | KDM6A ko mice | Loss of KDM6A causes myelodysplasia | [54] | ||||||
| AML | KDM6A ko mice, AML cell lines | KDM6A ko causes COMPASS complex malfunctioning with upregulation of ETS signaling | [55] | ||||||
| AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines | Loss of KDM6A confers cytarabine resistance through ENT1 downregulation | [56] | ||||||
| CML | Primary CML patient cells; CML cell lines | pro-leukemic | KDM6A promotes imatinib-resistance through upregulation of TRKA | [57] | |||||
| AML/CML | AML and CML cell lines | KDM6A depletion reduces | Runx1 | , | Mll1 | and | Scl | expression and impairs proliferation | [58] |
| AML | Primary AML patient cells; AML cell lines | KDM6A promotes cancer cell survival via upregulation of DOCK5/8 | [59] | ||||||
| KDM6B | MDS | Primary MDS patient CD34+ cells | pro-leukemic | Inhibition of KDM6B resulted in an increase in erythroid colonies in MDS | [60] | ||||
| AML | Clinical data | KDM6B is overexpressed in AML and correlates with a. poor survival | [61] | ||||||
| MDS/CMML | Tg KDM6B overexpression in mice | KDM6B overexpression showed features of MDS in mice | [62] | ||||||
| AML | Kdm6b ko (VAVCre, MxCre, ERT2-Cre) | Loss of Kdm6b reduced HSCs and attenuates MLL-AF9-induced AML | [63] | ||||||
| AML | AML cell lines | KDM6B kd reduced the proliferation and increased chemo-sensitivity | [64] | ||||||
| AML | HL-60; primary patient samples; PML-RARα-, AML1-ETO9a, or MLL-AF9 tg mice | anti-leukemic | KDM6B exerts anti-AML effect by directly modulating H3K4 and H3K27 | [65] |
AML (acute myeloid leukemia), APL (acute promyelocytic leukemia), BP (blast phase), CMML (chronic myelomonocytic leukemia), CML (chronic myeloid leukemia), HSC (hematopoietic stem cell), kd (knockdown), ko (knockout), MDS (myelodysplastic syndrome), MPN (myeloproliferative neoplasms), tg (transgenic), xg (xenograft).
2.2. KDM2B
Two complementary studies suggested an oncogenic role for KDM2B in myeloid leukemia (Figure 2) [11][12][11,12]. KDM2B demethylates H3K36me2 at the promoter of the tumor suppressor p15 (Ink4b), leading to decreased expression. p15 (lnk4b) silencing leads to cell-cycle progression in both AML cell lines and in CD34+ primary AML cells [11] and supports AML transformation by Hoxa9/Meis1 in mice (Table 1) [12]. Moreover, transgenic (tg) mice overexpressing KDM2B develop myeloid and B cell leukemias through a KDM2B-mediated increase in Nsg2 and OXPHOS expression [17]. These mice show impaired HSC differentiation and dysregulation of metabolic processes. Nsg2 impairs HSC differentiation, while upregulation of OXPHOS genes provides a metabolic proliferative advantage for tg Kdm2b hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) [17]. As a member of the non-canonical polycomb repressive complex 1.1 (PRC1.1) KDM2B also contributes to metabolic dysregulation. PRC1.1 controls the expression of genes essential for leukemogenesis, for example pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase, and is required for the viability of MLL-AF9 driven murine leukemias, as well as of primary patient AML cells (Table 1) [16]. These data thus suggest an oncogenic role for KDM2B.
Contradictory findings, however, support a tumor-suppressor role for KDM2B in myeloid malignancies (Figure 2). Karoopongse et al. showed that low expression of KDM2B, seen in primary MDS cells, allows upregulation of let-7b, a microRNA that targets EZH2 mRNA for degradation. Vice versa, KDM2B overexpression rescues EZH2 expression in MDS cell lines by suppressing let-7b [18]. EZH2 functions as a tumor suppressor [66][67][66,67], clinically apparent by the poor prognosis of patients with AML/MDS with reduced EZH2 activity [68][69][68,69]. Andricovich et al. likewise described an association between low expression of KDM2B and reduced survival of AML patients [19][70][71][19,70,71]. Moreover, this finding was confirmed in a Vav1-Cre KrasG12D-driven AML mouse model. Mice displayed shortened survival upon loss of Kdm2b, while overexpression significantly extended survival of KrasG12D-induced AML [19]. Mechanistically, loss of Kdm2b resulted in cell-cycle activation and reduced interferon signaling. Overexpression led to the activation of transcriptional programs linked to interferon signaling (Irf3, Irf5, Irf7, Stat1, Stat2) and inhibition of the PRC2 antagonists Hox10 and Smarca4/Brg1 (Table 1) [19]. In myeloid disorders, the PRC2 complex is associated with tumor suppressive activity [72][73][72,73]. In several model systems KDM2B acts as a tumor suppressor, by preventing degradation of a second tumor-suppressor, by inhibiting tumor-suppressor antagonists, or by reducing cell activation. In conclusion, the role of KDM2B in myeloid malignancies appears to be strongly context dependent. Future studies exploring any potential therapeutic targeting of KDM2B will need to consider that KDM2B either acts as an oncogene or a tumor suppressor depending on the specific genetic background.
3. The KDM3 Family
The KDM3 subfamily of the Jumonji domain-containing histone demethylases encompasses three members, KDM3A, KDM3B, and KDM3C. As reviewed by Markolovic et al., all members possess catalytic activity towards mono- and di-methylated lysine residues [8]. H3K9 is the known main histone target of KDM3 demethylases [8]. In myeloid malignancies, KDM3A has been shown to demethylate H3K9me2 [20], while KDM3B is associated with histone demethylase activity towards H3K9me1–2 [21][22][30][21,22,30]. The catalytic function of KDM3C in myeloid malignancies is controversial. Histone demethylase activity towards H3K9me1–3 [28][32][28,32] and H3K36me3 [28] has been observed, while other groups propose a non-enzymatic role in this context [29][31][29,31].
3.1. KDM3A
Jafek et al., demonstrate that KDM3A supports pro-leukemic processes in AML (Figure 2). Oct1 recruits KDM3A to the CDX2 promoter to remove the repressive H3K9me2 mark [20]. Overexpression of CDX2 is often observed in AML patients and is sufficient to induce leukemia in murine BM transplantation models [74][75][74,75]. To date, this is the only study describing a role for KDM3A in myeloid malignancies; further investigation is therefore required to corroborate the significance of KDM3A-mediated CDX2 overexpression in this context or to reveal additional pathophysiological roles for KDM3A.
3.2. KDM3B
KDM3B has been proposed to act as a tumor suppressor in myeloid disorders (Figure 2). Located on chromosome 5, an allele of KDM3B is lost upon 5q deletion, frequently observed in AML and MDS [23][76][23,76]. In AML cell lines harboring the 5q deletion, reintroduction of KDM3B represses clonogenic growth and colony formation) [22][23][22,23]. Moreover, in APL cell lines, KDM3B downregulation enhanced proliferation, impaired differentiation, and reduced ATRA-induced degradation of PML/RARα [21]. Mechanistically, KDM3B modulates H3K9me1–2 levels to maintain a compact chromatin status, thus, loss of KDM3B enhances chromatin accessibility [21][22][21,22]. Open chromatin allows PML/RARa access to ETS and bZIP transcription factor binding sites, among them the sites of SPI1/PU.1 and Jun-AP1 [21]. The SPI1/PU.1-mediated gene signature is essential for myeloid differentiation, and this is repressed upon PML/RARA binding [77][78][77,78]. Therapy with ATRA degrades PML/RARA. In APL cell lines, this process is accompanied by KDM3B upregulation, which enhances gene expression required for differentiation through its demethylase activity [21][22][21,22]. Taken together, KDM3B exerts anti-leukemic effects in AML, especially APL, and MDS by modulating chromatin accessibility through its enzymatic activity.
3.3. KDM3C
Research of the last decade revealed an oncogenic role for KDM3C in myeloid leukemias (Figure 2). Using an shRNA-mediated depletion screen Sroczynska et al. identified Kdm3c as one of the best candidate drug targets for leukemia therapy among 319 tested genes. In AML cell lines and in an MLL-AF9 mouse model, depletion of Kdm3c impaired growth and colony formation of leukemic cells by increasing apoptosis [33]. Further studies in the following years confirmed the finding by Sroczynska et al. and revealed catalytic and non-catalytic mechanisms through which KDM3C exerts its oncogenic potential.
Several groups have proposed that catalytic function of KDM3C is required for its pro-leukemic activity. In RUNX1-RUNX1T1-driven leukemia, KDM3C is directly recruited to its target genes by RUNX1-RUNX1T1. KDM3C-mediated demethylation of H3K9me2 at the promoters results in increased expression of its targets among them LMO2, ID1, EGR1, and CDKN1A. Vice versa, shRNA-mediated depletion of KDM3C reduced target gene expression and impaired proliferation and survival in AML cell lines [32]. Likewise, Izaguirre-Carbonell et al. showed that the catalytic JmjC-domain and the zinc finger domain of KDM3C are required for the survival of MLL-AF9 leukemia cells. Silencing of KDM3C promoted cell differentiation through upregulation of the IL3 receptor, followed by enhanced RAS/MAPK and JAK-STAT signaling) (Table 1) [28]. In this model, loss of KDM3C activity increased H3K36me3 levels while H3K91–3 methylation remained unaltered [28]. Despite reports showing non-enzymatic modes of action for KDM3C, these findings clearly show that KDM3C sustains leukemogenicity of AML cells through its enzymatic activity.
