Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Catherine Yang and Version 1 by Valeria Costantino.
Porifera, commonly referred to as marine sponges, are acknowledged as major producers of marine natural products (MNPs). Sponges of the genus Phorbas have attracted much attention over the years. They are widespread in all continents, and several structurally unique bioactive compounds have been identified from this species.
- marine sponges
- marine natural products (MNPs)
- bioctivity
1. Introduction
Biodiversity of marine organisms that reflects on their rich chemical diversity is an important source of novel drug-lead skeletons. Sponges, among other organisms, are one of the main sources of novel skeletons as well as of lead compounds [1,2][1][2], promising remedies in drug discovery [3,4][3][4] and biotechnological applications. Even if the origin of sponge-derived compounds is still under debate, a growing body of evidence suggests that many marine natural products (MNPs) are produced by microorganisms associated with the sponge [5,6][5][6]. In fact, multicellular organisms, such as sponges, are now defined as “holobionts”, i.e., an association between the host and its microorganism community. Therefore, studies performed on sponge organic extracts are actually categorized as studies on holobiont organic extracts [7]. One of the most common classes of sponge-symbionts is cyanobacteria, known as the real producer of some classes of secondary metabolites, specially cyanotoxins [8,9,10][8][9][10].
Chemical diversity coming from marine sponges may still drive drug discovery research [11,12,13][11][12][13]. The genus Phorbas is a suitable example to illustrate this point. Phorbas-derived natural products discovered so far include compounds belonging to four main classes: alkaloids, macrolides, steroids, and terpenoids. Many of them possess unique structures that might play an important role in biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications.
The genus Phorbas belongs to the class Demospongiae, order Poecilosclerida, family Hymedesmiidae [14], and is the most representative among the 10 accepted genera, which also includes Hamigera, Acanthancora, and Hemimycale [15,16,17,18][15][16][17][18]. Phorbas stands out not only in the number of isolated MNPs, but also in the large number of bioactive compounds, mainly displaying cytotoxic activity [19]. These sponges are widespread and are present on all continents, including Antarctica (Figure 1) [20].
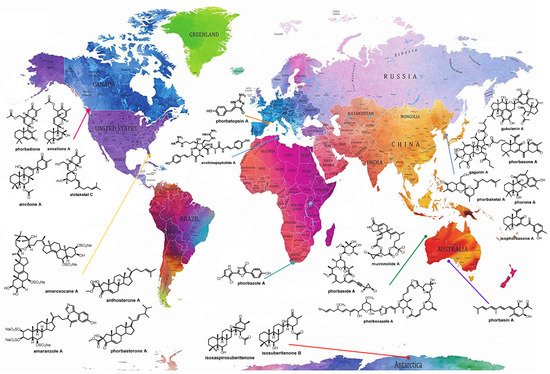
Figure 1. Global distribution of sponges of the genus Phorbas and their bioactive metabolites, allowing visualization of the wide distribution of sponges of this genus across all continents, even in the presence of different biotic and abiotic factors. Many metabolites of the same class are found in species collected from different locations. Original world map image source: https://www.amazon.it/Stylish-Living-Mappamondo-Planisfero-Decorazione/dp/B07N1NNPD8 (accessed on 25 February 2021).
2. Bioactivity of Compounds Isolated from Sponges of the Genus Phorbas
The oceans are places on the Earth containing a wide spectrum of natural resources. The advent of new technologies allowed for profound study of marine biochemical diversity and the discovery of new bioactive marine natural products (MNPs). The complex habitats and exposure to extreme conditions of light, temperature, pH, salinity, and other external factors induce marine organisms to produce a wide variety of specific and potent active substances that cannot be found elsewhere [79][21]. The genus Phorbas, as well as several other sponges found in the aquatic environment, is a rich source of bioactive natural products such as alkaloids, terpenes, macrolides, steroids, and peptides.
Among the bioactivities described for compounds identified from the genus Phorbas, the cytotoxic activity (Table 1) stands out. However, other bioactivities (Table 2) have been reported. Bioactivity evaluation of pure compounds is often hampered by the low quantity that can be obtained from the natural source. Indeed, some compounds have been evaluated for their pharmacological properties only after being obtained on a larger scale by chemical synthesis.
Table 1. List of MNPs isolated from Phorbas sp. having antiproliferative activity.
| Name | Class | Species | Cell Lines | Dose/Concentration | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Zarzissine | Alkaloid | Phorbas | tenacior | P-388 |
kidney carcinoma; h breast carcinoma; i ovarian cancer; j gastric cancer.
Table 2. List of MNPs originated from Phorbas with biological activities.
| Compound | Class | Species | Biological Activity | Dose/Concentration | Reference | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | IC | 50 | 12 µg/mL | [ | 37] | [22] | |||||||||||||||
| Anchinopeptolide A | Alkaloid | P. tenacior | Displacement of specific ligands from their biochemical receptors | 5 µg/mL-average inhibition values roughly 35–40% in all receptor binding | [ | 21,22] | [37][38] | KB | b | IC | 50 | 5 µg/mL | ||||||||||
| 2 | Anchinopeptolide B | Alkaloid | P. tenacior | Displacement of specific ligands from their biochemical receptors | 5 µg/mL-71% human B2 bradykinin receptor; 80% neuropeptide Y receptor | [21, | [37 | 22] | ][38] | |||||||||||||
| 3 | Anchinopeptolide C | Alkaloid | P. tenacior | NSCLC-N6 | c | IC | 50 | 10 µg/mL | ||||||||||||||
| Displacement of specific ligands from their biochemical receptors | 5 µg/mL-62% somatostatin receptor; 52% human B2 bradykinin receptor; 57% neuropeptide Y receptor | [ | 21 | , | 22 | ] | [37][38] | 17 | Phorboxazole A | |||||||||||||
| 4 | Macrolide | Anchinopeptolide D | Phorbas | sp. | AlkaloidHCT-116 | d | P. tenacior | GI | 50 | 4.36 × 10 | Displacement of specific ligands from their biochemical receptors | −10 | M | 5 µg/mL-77% somatostatin receptor | [24] | [23] | ||||||
| [ | 21 | , | 22 | ] | [ | 37][38] | HT29 | d | GI | 50 | 3.31 × 10 | −10 | M | |||||||||
| 19 | Muironolide A | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 96.5 μg/mL | [40] | [24] | |||||||||||
| 20 | Phorbaside A | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 30.0 μM | [44] | [25] | |||||||||||
| 22 | Phorbaside C | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 2 μM | [44] | [25] | |||||||||||
| 23 | Phorbaside D | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 61.9 μM | [44] | [25] | |||||||||||
| 24 | Phorbaside E | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 10.2 μM | [44] | [25] | |||||||||||
| 29 | Phorbasterone A | Steroid | Phorbas | amaranthus | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 1–3 µg/mL | [48,73] | [26][27] | |||||||||||
| 30 | Phorbasterone B | Steroid | Phorbas | amaranthus | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 1–3 µg/mL | [48,73] | [26][27] | |||||||||||
| 31–32 | Phorbasterone C | Steroid | Phorbas | amaranthus | HCT-116 | |||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Zarzissine | Alkaloid | P. topsenti | Antimicrobial | Paper disk agar-(100 µg, purified product) 12,10, and 11 mm | [37] | [22] | |||||||||||||||
| 14 | p | -Hydroxybenzaldehyde | Alkaloid | P. topsenti | Antimicrobial | Paper disk agar-(100 µg, purified product) 8,7, and 7 mm | [37] | [22] | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | Phorbatopsin A | Alkaloid | P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.88 ± 0.28 | [26] | [39] | |||||||||||||
| 15 | Phorbatopsin B | Alkaloid | P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.50 ± 0.08 | [26] | [39] | |||||||||||||
| 16 | Phorbatopsin C | Alkaloid | P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.21 ± 0.02 | [26] | [39] | |||||||||||||
| 17 | Phorboxazole A | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | Antifungal | Agar disk diffusion assay- | C. albicans | : 12 mm (1 µg) and 9 mm (0.1 µg); | Saccharomyces carlsbergensis | : 1, 20 mm (1 µg), and 13 mm (0.1 µg) | [24] | [23] | ||||||||||
| 18 | Phorboxazole B | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | Antifungal | Agar disk diffusion assay-C. albicans: 11 mm (1 µg) and 8 mm (0.1 µ g); | Saccharomyces carlsbergensis | : 1, 16 mm (1 µg), and 10 mm (0.1 µg) | [24] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| 19 | Muironolide A | Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | Antifungal | MIC 16 μg/mL | [40] | [24] | d | IC | 50 | 1–3 µg/mL | [48 | |||||||||
| 22 | , | 73 | Phorbaside C | ] | [ | 26][27] | ||||||||||||||||
| Macrolide | Phorbas | sp. | Macrophage infectivity potentiator (Mip) | Binding affinity of 75 with Chlamydia pneumoniae | [ | 88] | [40] | 33–34 | Phorbasterone D | Steroid | Phorbas | amaranthus | HCT-116 | d | IC | |||||||
| 37 | Amaroxocane A | Steroid | 50 | P.amaranthus | 1–3 µg/mL | Anti-predatory activity | [48, | Little feeding deterrence (8/10 pellets eaten) | 73] | [26][27] | ||||||||||||
| [ | 50 | ] | [ | 41 | ] | 45 | Phorbaketal A | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | A549 | c | IC | 50 | 11–12 µg mL | −1 | [52 | |||||
| 38 | , | 54 | ] | [ | 28 | ][ | Amaroxocane B29] | |||||||||||||||
| Steroid | P. amaranthus. | Anti-predatory activity | Significant deterrent activity (3/10 pellets eaten) | [ | 50 | ] | [41] | HT-29 | d | IC | 50 | 11–12 µg mL | −1 | |||||||||
| 45 | Phorbaketal A | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Osteogenic differentiation Anti-inflammatory |
Phorbaketal A stimulates TAZ-mediated osteoblast differentiation through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (1–10 µg/mL) Dose dependent inhibition of LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and the transcriptional activity NF-κB (2.5, 5, and 10 μM) and adipocyte differentiation through transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (1–10 µg/mL) |
[84] [82,83] | [42] [43][44] |
HepG2 | e | IC | 50 | 11–12 µg mL | −1 | ||||||||
| 60 | Alotaketal A | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | cAMP signaling activation | cAMP cell signaling pathway-EC | 50 | of 18 nM | [55] | [45] | 46 | Phorbaketal B | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | A549 | c | IC | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | [52,54] | [28][29] |
| 61 | Alotaketal B | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | cAMP signaling activation | cAMP cell signaling pathway-EC | 50 | of 240 nM | [55] | [45] | HT-29 | d | IC | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | |||||||
| 62 | Alotaketal C | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Latency-reversing agent (LRA) | HIV-1 provirus/GFP expression of J-Lat 9.2 cells-1 μM | [56, | [ | 57, | 46 | 78] | ][47][48] | HepG2 | e | IC | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | |||||
| 63 | Alotaketal D | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Latency-reversing agent (LRA) | HIV-1 provirus/GFP expression of J-Lat 9.2 cells-30 μM | [56,57,78] | [46][47][48] | 47 | Phorbaketal C | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | |||||||||
| 65 | Ansellone A | A549 | Sesterterpenoid | c | Phorbas | sp. | cAMP signaling activation Latency-reversing agent (LRA)cAMP activatorIC | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | cAMP cell signaling pathway-EC | [52,54] | [28][29] | ||||||||||
| 50 | of 14 µM | HIV-1 provirus/GFP expression of J-Lat 9.2 cells-30 μM | [ | 57 | ,62] | [47][49] | HT-29 | d | IC | |||||||||||||
| 66 | Ansellone B | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | Inhibition of inducible NOS (iNOS) | |||||||||||||||
| RAW 264.7 LPS-activated mouse macrophage cells-IC | 50 | = f 4.5 μM, | [ | 66 | ] | [50] | HepG2 | e | IC | 50 | 12–460 µg/mL | |||||||||||
| 73 | Anvilone A | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Latency-reversing agent (LRAs) | HIV-1 provirus/GFP expression of J-Lat 9.2 cells-30 μM | [57] | HT-29 | d | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | ||||||||||
| ] | [ | 51 | ] | 50 | Phorbaketal N | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | PANC-1 | f | IC | 50 | 11.4 µM | [53] | [30] | |||||||
| A498 | g | IC | 50 | 18.7 µM | ||||||||||||||||||
| [ | 47 | ] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | Phorbasone A | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Osteogenic properties | Calcium deposition effect at a concentration of 0.5 μg/mL | [65 | |||||||||||||||
| 79 | Phorbasone A acetate | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Inhibition of inducible NOS (iNOS) | Inhibitory activity on NOS in RAW 264.7 LPS-activated mouse macrophage cells-IC | 50 | = 2.8 μM | [66] | [50] | ||||||||||||
| 83 | Oxaspirosuberitenone | Sesterterpenoids | P. areolatus | Antimicrobial | Activity against MRSA at the highest concentration tested (160 µM) | [67] | [31] | |||||||||||||||
| 94 | Phorbasin H | Diterpenoid | ACHN | g | LC | 50 | 24.4 µM | |||||||||||||||
| Phorbas | sp. | Antifungal | Suppression of the hyphal development of | C. albicans | (250 μg/mL) | [86] | [52] | 84 | Isosuberitenone B | Sesterterpenoid | Phorbas | areolatus | ||||||||||
| 93–95 | Phorbasins | A549 | c | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp.IC | 50 | 8.8 μM | [ | Antifungal | EtOH extract-growth inhibitory activity against the gram-positive bacteria | Staphylococcus aureus | and | Micrococcus luteus | –Concentration: N/A | 67] | [31] | |||||
| [ | 68 | , | 69 | ] | [ | 53][54] | HT-29 | |||||||||||||||
| 104 | Gagunin D | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | d | IC | 50 | 9.0 μM | ||||||||||||||
| Anti-melanogenic | IC | 50 | = 5.7 µg/mL; 10 µM on UVB irradiated human skin models demonstrated a considerable reduction melanin biosynthesis | [ | 87 | ] | [55] | HepG2 | e | IC | 50 | 7.4 μM | ||||||||||
| MCF-7 | h | IC | 50 | 8.8 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 85 | 19-episuberitenone B | Sesterterpenoid | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 101–117 | Gagunins | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | Isocitrate lyase (ICL) inhibition | LC | 50 | of 55–140 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | Phorbas | |||||||||||
| 125 | Astaxanthin | Carotenoid | P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.22 ± 0.02 | [26] | [39] | areolatus | A549 | c | ||||||||||
| 126 | Adonirubin | IC | 50 | 5.1 μM | [ | Carotenoid | 67] | [31] | ||||||||||||||
| P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.024 ± 0.001 | [ | 26] | [39 | HT-29 | d | IC | 50 | 6.4 μM | ||||||||||
| ] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 127 | Taurine | Sulfonic acid | P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 0.083 ± 0.013 | [26] | [39] | |||||||||||||
| 128 | Taurobetaine | Sulfonic acid | HepG2 | e | IC | 50 | 5.0 μM | |||||||||||||||
| P. topsenti | Antioxidant | ORAC | FL | 00.019 ± 0.002 | MCF-7 | h | IC | 50 | 5.1 μM | |||||||||||||
| 88 | Phorbasin B | Diterpene | Phorbas | sp. | A549 | c | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | [70] | [32] | |||||||||||
| HT-29 | d | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 89 | Phorbasin C | Diterpene | Phorbas | sp. | A549 | c | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | [70] | [32] | |||||||||||
| HT-29 | d | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 91 | Phorbasin E | Terpenyl-taurine | Phorbas | sp. | A549 | c | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | [70] | [32] | |||||||||||
| HT-29 | d | LG | 50 | 5–15 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101 | Gagunin A | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 50.1 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 102 | Gagunin B | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 10.4 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 103 | Gagunin C | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.71 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 104 | Gagunin D | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.13 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 105 | Gagunin E | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.03 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 106 | Gagunin F | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.11 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 107 | Gagunin G | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 2.0 µg/mL | [75] | [33] | |||||||||||
| 108 | Gagunin H | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 10.0 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 109 | Gagunin I | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 11.5 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 110 | Gagunin J | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 9.1 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 111 | Gagunin K | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 17.5 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 112 | Gagunin L | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 12.5 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 113 | Gagunin M | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.71 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 114 | Gagunin N | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | > 50 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 115 | Gagunin O | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 11.1 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 116 | Gagunin P | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 8.5 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 117 | Gagunin Q | Diterpenoid | Phorbas | sp. | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | > 50 µg/mL | [76] | [34] | |||||||||||
| 118 | Gukulenin A | tetraterpenoid | Phorbas | gukulensis | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 62 nM | [30] | [35] | |||||||||||
| FaDu | b | IC | 50 | 57 nM | ||||||||||||||||||
| SN12C | g | IC | 50 | 92 nM | ||||||||||||||||||
| MKN45 | j | IC | 50 | 0.13 nM | ||||||||||||||||||
| TOVG-21G | i | IC | 50 | 0.04 μM | [80] | [36] | ||||||||||||||||
| [ | 26 | ] | [ | 39 | ] | OVCAR-3 | i | IC | 50 | 0.13 μM | ||||||||||||
| A2780 | i | IC | 50 | 0.03 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| SKOV3 | i | IC | 50 | 0.36 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 119 | Gukulenin B | tetraterpenoid | Phorbas | gukulensis | HCT-116 | d | IC | 50 | 0.55 μM | [30] | [35] | |||||||||||
| A2780 | i | |||||||||||||||||||||
| FaDu | b | IC | 50 | 0.63 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| SN12C | g | IC | 50 | 0.61 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| MKN45 | j | IC | 50 | 0.72 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| 123 | Gukulenin F | Tetraterpenoid | Phorbas | gukulensis | K-562 | a | LC | 50 | 0.4 µM | [30] | [35] | |||||||||||
| FaDu | b | IC | 50 | 0.63 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| SN12C | g | IC | 50 | 0.61 μM | ||||||||||||||||||
| MKN45 | j | IC | 50 | 0.72 μM |
a leukemia; b pharynx carcinoma; c lung carcinoma; d colon carcinoma; e liver carcinoma; f pancreas carcinoma; g
2.1. Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Activity
The bioactivities of the metabolites isolated from sample of genus Phorbas mainly focus on the antiproliferative activity. For clarity and better reading purposes, data have been summarized in Table 1.
The alkaloid zarzissine (13) showed a potent cytotoxic activity against three cell lines: murine leukemia P-388, human nasopharyngeal carcinoma KB, and human lung carcinoma NSCLC-N6 [37][22].
Macrolides such as phorbasides A (20), C (22), D (23), and E (24) exert prominent cytotoxic effects against HCT-116 (human colon cancer cell line), demonstrated through in vitro assays. However, phorbaside B (21) showed no activity. These results suggest that the presence of the free hydroxyl group at C-2 of the sugar moiety may play a key role in maintaining bioactivity [44][25]. Muironolide A (19) and phorboxazole A (17) are two other representative macrolides that possess cytotoxic activity against colon tumor cells [40][24].
Among steroids, phorbasterones A–D (29–32) displayed moderate cytotoxicity toward HCT-116 cells [48][26]. More recently, the lipid fraction obtained from samples of P. amaranthus, likely enriched of sterols, was found to possess antiproliferative properties against HCT-116 cells [73][27].
The sesterterpenoids phorbaketals A–C (45–47) exhibited cytotoxic activity against human colorectal cancer HT-29, hepatoma cancer HepG2, and adenocarcinoma human alveolar basal epithelial cells lines A549, while phorbaketal N (50) was cytotoxic against human renal cancer cell lines A498 and ACHN and pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1. Phorbaketal N (50) showed a better activity than the positive control molecule, fluorouracil. Studies on 50 and derivatives may be a path in the search for new treatments for pancreatic cancer [52,53][28][30]. Phorbaketal H–I (55–56), isolated from the sponge Monanchora sp., showed weak cytotoxicity against the human renal A498 cancer cell line. Considering structure−activity relationships, a ketone group at C-5 of ring A of phorbaketals is much more favorable than a hydroxy group for activity, and the hydroperoxy group in the side chain is harmful to the cytotoxicity [54][29].
The compound phorbin A (59), isolated from Monanchora sp., a possible precursor of several sesterterpenoids isolated for Phorbas, also showed moderate activity against renal human cancer cell lines ACHN and A498, and potent cytotoxicity against human pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1 and MIA-paca, similar to or better than the positive control, 5-fluorouracil [54][29].
In addition, the sesterterpenoids isosuberitenone B (84) and 19-suberitenone B (85) unveiled significant grow-inhibitory effects against A549, HepG2, HT-29, and MCF-7 tumor cell lines. In the same study, compounds suberitenone B (82), oxaspirosuberitenone (83), and isooxaspirosuberitenone (86) showed moderate activity against these same cell lines. These sesterterpenoids isolated from P. areolatus were also tested against Mia-Paca-2 (pancreatic cancer cell line), but showed no activity [67][31].
Putative anticancer lead compounds with a diterpenoid backbone were a) phorbasin B–C (88–89) and the terpenyl-taurine phorbasin E (91), tested in a colon cancer model (HCT-116 cell line) [70][32] and b) gagunins A–Q (101–117) in K-562 cells (leukemia cell line) [75][33]. Among the latter, gagunins A and B (101–102) turned out to be the less active compounds. The authors suggest that the presence of a bulky group at C-11 of the five-membered ring negatively affects bioactivity, as compounds 107 and 108 are far less active than their congeners featuring either an acetoxyl group or hydrogen at the same position [75][33]. However, a synthetic gagunin A-derivative, in which the substituent groups placed on the three rings were replaced by hydroxyl groups, lacks activity [75][33].
The tetraterpenoid gukulenin B (119) exhibited significant cytotoxicity against human pharynx cell carcinoma line FaDu, gastric carcinoma cell MKN45, colon carcinoma cell line HCT-116, and renal carcinoma cell SN12C, and gukulenins C−F (120–123) showed potent cytotoxicity against K-562 and A549 cells [30][35]. Interestingly, gukulenin F (123) exhibited cytotoxicity against K-562 that was 17-fold more potent than doxorubicin, a positive control [30][35]. Moreover, gukulenin A (118) was shown to be a promising antitumor agent that (a) inhibited tumor growth in an ovarian cancer xenograft mouse model without any considerable adverse effect on their body weights, and (b) markedly reduced cell viability through apoptosis induction via the activation of caspases in four ovarian cancer cell lines. The cytotoxic activity of gukulenin A (118) is more potent than the positive control, cisplatin, in all ovarian cancer cells tested. This is the first report of an in vivo activity among compounds isolated from Phorbas [80][36].
2.2. Other Biological Activities
Secondary metabolites isolated from sponges of the genus Phorbas displayed a large array of biological activities other than cytotoxicity (Table 2).
Anchinopeptolides B–D (2–4), peptide alkaloids from P. tenacior, exhibited high efficacy in displacing specific ligands from their relevant receptors: human B2 bradykinin, which has a high correlation with inflammation mediators by causing vasodilation, increasing vascular permeability, and stimulating the synthesis of prostaglandins; neuropeptide Y, which is involved in physiological and homeostatic processes such as vasoconstriction and growth of fat tissue; and somatostatin receptors, which belong to the G protein class and have a wide expression pattern in both normal tissues and solid tumors [22,72,73][38][56][27]. On the other hand, anchinopeptolide A (1) was found to have weaker bioactivity in these binding assays [21][37]. The alkaloids zarzissine (13) and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (14) showed slight antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (gram-positive bacterium) and C. albicans and C. tropicalis (yeasts) [37][22].
The crude extract of Phorbas topsenti was reported to have high antioxidant activity in oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) assay, thereby leading to the isolation of phorbatopsins A–C (14–16), i.e., the compounds responsible for the observed radical scavenging activity. The antioxidant capacity of the isolated compounds was also evaluated with ORAC assay, measuring the loss of fluorescence of fluorescein in the presence of the oxidative species AAPH [2,2′-azobis(2-amidino-propane) dihydrochloride] and compared with Trolox®, used as the positive control. Phorbatopsin A (14) was the most active substance, with an ORAC value comparable to Trolox®. These data clearly indicate the importance of the C5–C6 double bond in compound 14 in improving the antioxidant properties of the phorbatopsin scaffold [26][39].
Macrolides phorboxazoles A–B (17–18) exhibited antifungal activity in the agar disc diffusion inhibition assay against Candida albicans and Saccharomyces carlsbergensis [24][23]. Another example is the macrolide muironolide A (19), which was reported to have antifungal activity against strains of Cryptococcus neoformans [81][57].
The genus Phorbas is also a source of other bioactive compounds, such the steroids amaroxocanes A–B (37–38), which were isolated and tested for chemical defense of the Caribbean coral reef sponge Phorbas amaranthus from fish predators. Amaroxocane B (38) showed significant deterrent activity (3/10 pellets eaten), while amaroxocane A (37) elicited little feeding deterrence (8/10 pellets eaten) against a common reef predator, namely the bluehead wrasse. This study suggests that structural differences in the heterocycle moiety or the degree of sulfation may be responsible for differential anti-predatory activity [50][41].
Phorbaketal A (45), which also showed cytotoxic activity, can promote osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells, which exhibited increased levels of differentiation markers such as osteocalcin, Dlx5, ALP, Runx2, and TAZ after drug exposure. This compound showed potential for bone reformation processes and new anabolic therapeutics in bone diseases. Moreover, as inhibiting mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into adipocytes through a transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif, compound 45 may be a promising lead in designing novel drugs to treat obesity. In addition, this compound showed a promising dose dependent inhibition of inflammatory mediators via down-regulation of the NF-κB pathway and up-regulation of the HO-1 pathway [82,83,84][43][44][42]. The sesterterpenoids phorbasones A–B (76–77) promote calcium deposition in mensenchymal C3H10T1/2 cells, thus inducing osteoblast differentiation. The authors concluded that phorbasone A (76) showed a distinct calcium deposition effect as compared to phorbasone B (77). Particularly, gene expression analysis of osteoblast differentiation markers revealed that compound 76 increases Runx2 (a Runt protein), ALP (alkaline phosphatase), OSX (osterix), PTH (parathyroid hormone), and PTHrP (PTHrelated peptide) mRNA [65][51]. Another study reported on the potent inhibitory activity on nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW 264.7 LPS-activated mouse macrophage cells by phorbasone A acetate (79). This result indicated that effective suppression of NO production is a valuable strategy for the discovery of anti-inflammatory compounds [65][51].
Among sesterterpenoids, suberitenones A and B, oxaspirosuberitenone, isosuberitenone B, 19-episuberitenone B, and isooxaspirosuberitenone (81–86), isolated from Phorbas areolatus (non-polar fraction), were tested against gram positive (methicillin resistant and methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, and MSSA) and gram negative (Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae) bacteria. This study reported oxaspirosuberitenone (83) as a significant antimicrobial compound against MRSA at the highest concentration tested [67,85][31][58].
Ansellone A (65) can activate cAMP signaling in HEK293 cells, derived from human embryonic kidney cells grown in a tissue culture, which is a very important technique for the development of treatments for several diseases such as heart failure, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. cAMP signaling activation by ansellone A (65) was comparable to that of forskolin, a natural product used for the treatment of cancer, obesity, and allergies [56][46]. The latency reversal activity (LRA) of 65, which has the function of reactivating the virus production in infected cells and producing an immune response or cell death, was also reported and determined by quantification of the changes in intracellular GFP expression in microplate [64][59]. The sesterterpenoid ansellone B (66) was reported as a potent inhibitor on nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 LPS-activated mouse macrophage cells [59][60].
Alotaketals A and B (60–61) have also been reported for the activation of the cAMP cell signaling pathway. In addition, the compounds alotaketal C (62) and D (63) and anvilone A (74) were reported to activate the latent proviral HIV-1 gene expression. Notably, alotaketal C (62) was more potent and gave a stronger effect than the control compound prostratin at the same concentration, while alotaketal D (63) and anvilone A (74) elicited similar responses as prostratin [52,54,77,78][28][29][61][48]. The diterpen phorbasin H (94) was reported as an inhibitor of the yeast-to-hypha transition in Candida albicans. Growth experiments suggested that this compound does not inhibit yeast cell growth but inhibits filamentous growth in C. albicans, which means that the phorbasin H (94) induces a change in C. albicans morphology [86][52]. Another study reported the ethanolic extract rich in phorbasins (87–89) from the Phorbas sp. could exert growth inhibitory activity against gram positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus luteus. It was not possible to test pure compounds due to the low amount available and their instability [31,68][62][53].
One study concerning the cosmetic use of gagunin D (104) identified this compound as a potential anti-melanogenic agent. Gagunin D (104) inhibited the synthesis of melanin in both mouse melan-a cells and a reconstructed human skin model. Suppression of tyrosinase expression and increased rate of tyrosinase degradation as well as inhibition of its enzymatic activity are putative mechanisms underlying the anti-melanogenic activity exhibited by gagunin D (104). These studies highlight the potential use of gagunin D (104) for skin lightening cosmetic formulations [87][55].
The summary of these biological activities reported for compounds isolated from extracts of the genus Phorbas sp. are found in Table 2.
References
- Esposito, G.; Della Sala, G.; Teta, R.; Caso, A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Pawlik, J.R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Polyketide-Peptides from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia conulosa: Structure elucidation on microgram scale. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 2871–2875.
- Britstein, M.; Devescovi, G.; Handley, K.M.; Malik, A.; Haber, M.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Costantino, V.; Burgsdorf, I.; Gilbert, J.A.; et al. A new N-Acyl homoserine lactone synthase in an uncultured symbiont of the red sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1274–1285.
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223.
- Varijakzhan, D.; Loh, J.Y.; Yap, W.S.; Yusoff, K.; Seboussi, R.; Lim, S.H.E.; Lai, K.S.; Chong, C.M. Bioactive compounds from marine sponges: Fundamentals and applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 246.
- Thomas, T.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Lurgi, M.; Björk, J.R.; Easson, C.; Astudillo-García, C.; Olson, J.B.; Erwin, P.M.; López-Legentil, S.; Luter, H.; et al. Diversity, structure and convergent evolution of the global sponge microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11870.
- Della Sala, G.; Hochmuth, T.; Costantino, V.; Teta, R.; Gerwick, W.; Gerwick, L.; Piel, J.; Mangoni, A. Polyketide genes in the marine sponge Plakortis simplex: A new group of mono-modular type I polyketide synthases from sponge symbionts. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 809–818.
- Pita, L.; Rix, L.; Slaby, B.M.; Franke, A.; Hentschel, U. The sponge holobiont in a changing ocean: From microbes to ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 46.
- Lemloh, M.-L.; Fromont, J.; Brümmer, F.; Usher, K.M. Diversity and abundance of photosynthetic sponges in temperate Western Australia. BMC Ecol. 2009, 9, 4.
- Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Marrone, R.; De Sterlich, C.; Casazza, M.; Anastasio, A.; Lega, M.; Costantino, V. A fast detection strategy for Cyanobacterial blooms and associated cyanotoxins (FDSCC) reveals the occurrence of lyngbyatoxin A in Campania (South Italy). Chemosphere 2019, 225, 342–351.
- Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Esposito, G.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Scarpato, S.; Casazza, M.; Anastasio, A.; Lega, M.; Costantino, V. Monitoring cyanobacterial blooms during the COVID-19 pandemic in Campania, Italy: The case of lake avernus. Toxins 2021, 13, 471.
- Teta, R.; Irollo, E.; Della Sala, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Smenamides A and B, chlorinated peptide/polyketide hybrids containing a dolapyrrolidinone unit from the Caribbean sponge Smenospongia aurea. Evaluation of their role as leads in antitumor drug research. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4451–4463.
- Caso, A.; Esposito, G.; Della Sala, G.; Pawlik, J.R.; Teta, R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Fast detection of two smenamide family members using molecular networking. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 618.
- Saurav, K.; Borbone, N.; Burgsdorf, I.; Teta, R.; Caso, A.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Esposito, G.; Britstein, M.; Steindler, L.; Costantino, V. Identification of quorum sensing activators and inhibitors in the marine sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 127.
- Elgoud Said, A.A.; Mahmoud, B.K.; Attia, E.Z.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Fouad, M.A. Bioactive natural products from marine sponges belonging to family Hymedesmiidae. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16179–16191.
- Woolly, E.F.; Singh, A.J.; Russell, E.R.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. Hamigerans R and S: Nitrogenous Diterpenoids from the New Zealand marine sponge Hamigera tarangaensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 387–393.
- Thacker, R.W.; Hill, A.L.; Hill, M.S.; Redmond, N.E.; Collins, A.G.; Morrow, C.C.; Spicer, L.; Carmack, C.A.; Zappe, M.E.; Pohlmann, D.; et al. Nearly complete 28S rRNA gene sequences confirm new hypotheses of sponge evolution. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, 373–387.
- Evcen, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Zengin, M.; Süer, S.; Rüzgar, M. New records of five sponge species (Porifera) for the Black Sea. Zootaxa 2016, 4103, 267–275.
- Huguenin, L.; Salani, S.; Lopes, M.F.; Albano, R.M.; Hajdu, E.; Esteves, E.L. Integrative taxonomy of hemimycale (hymedesmiidae: Poecilosclerida: Demospongiae) from southeastern Brazil, with the description of two new species. Zootaxa 2018, 4442, 137–152.
- Angulo-Preckler, C.; Cid, C.; Oliva, F.; Avila, C. Antifouling activity in some benthic Antarctic invertebrates by “in situ” experiments at Deception Island, Antarctica. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 105, 30–38.
- Koutsouveli, V.; Taboada, S.; Moles, J.; Cristobo, J.; Ríos, P.; Bertran, A.; Solà, J.; Avila, C.; Riesgo, A. Insights into the reproduction of some Antarctic dendroceratid, poecilosclerid, and haplosclerid demosponges. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e192267.
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Özogul, Y.; Regenstein, J.M. Marine bioactive compounds and their health benefits: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 446–465.
- Bouaicha, N.; Amade, P.; Fuel, D.; Roussakis, C. Zarzissine, a new cytotoxic guanidine alkaloid from the mediterranean sponge Anchinoe paupertas. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1455–1457.
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Phorboxazoles A and B: Potent cytostatic macrolides from marine sponge Phorbas Sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8126–8131.
- Dalisay, D.S.; Morinaka, B.I.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F. A tetrachloro polyketide hexahydro-1H-isoindolone, muironolide A, from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. natural products at the nanomole scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7552–7553.
- MacMillan, J.B.; Guang, X.Z.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F. Phorbasides A-E, cytotoxic chlorocyclopropane macrolide glycosides from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. CD determination of C-methyl sugar configurations. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 3699–3706.
- Masuno, M.N.; Pawlik, J.R.; Molinski, T.F. Phorbasterones A-D, Cytotoxic Nor-Ring A Steroids from the Sponge Phorbas amaranthus. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 731–733.
- Do Amaral, B.S.; da Silva, F.B.; Leme, G.M.; Schmitz, L.S.S.; Jimenez, P.C.; Martins, R.C.C.; Cass, Q.B.; Valverde, A.L. Integrated analytical workflow for chromatographic profiling and metabolite annotation of a cytotoxic Phorbas amaranthus extract. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1174, 122720.
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Sim, C.J.; Joung, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J. Phorbaketals A, B, and C, sesterterpenoids with a spiroketal of hydrobenzopyran moiety isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5590–5593.
- Wang, W.; Mun, B.; Lee, Y.; Reddy, M.V.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hahn, D.; Chin, J.; Ekins, M.; et al. Bioactive sesterterpenoids from a Korean sponge Monanchora sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 170–177.
- Lee, Y.; Wang, W.; Kim, H.; Giri, A.G.; Won, D.H.; Hahn, D.; Baek, K.R.; Lee, J.; Yang, I.; Choi, H.; et al. Phorbaketals L-N, cytotoxic sesterterpenoids isolated from the marine sponge of the genus Phorbas. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4095–4098.
- Solanki, H.; Angulo-Preckler, C.; Calabro, K.; Kaur, N.; Lasserre, P.; Cautain, B.; de la Cruz, M.; Reyes, F.; Avila, C.; Thomas, O.P. Suberitane sesterterpenoids from the Antarctic sponge Phorbas areolatus (Thiele, 1905). Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3353–3356.
- Zhang, H.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasins D-F: Diterpenyl-taurines from a Southern Australian marine sponge, Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1959–1962.
- Rho, J.R.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Shin, J. Gagunins, highly oxygenated diterpenoids from the sponge Phorbas sp. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 9585–9591.
- Kyoung, H.J.; Jeon, J.E.; Ryu, S.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Polyoxygenated diterpenes from the sponge Phorbas sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1701–1707.
- Jeon, J.E.; Liao, L.; Kim, H.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Cytotoxic diterpenoid pseudodimers from the Korean sponge Phorbas gukhulensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1679–1685.
- Ahn, J.H.; Woo, J.H.; Rho, J.R.; Choi, J.H. Anticancer activity of gukulenin a isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas gukhulensis in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 126.
- Casapullo, A.; Finamore, E.; Minale, L.; Zollo, F. A dimeric peptide alkaloid of a completely new type, Anchinopeptolide A, from the marine sponge Anchinoe tenacior. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 6297–6300.
- Casapullo, A.; Minale, L.; Zollo, F.; Lavayre, J. Four new dimeric peptide alkaloids, anchinopeptolides B-D, and cycloanchinopeptolide C, congeners of anchinopeptolide A, from the mediterranean marine sponge Anchinoe tenacior. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1227–1233.
- Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, X.C.; Longeon, A.; Keryhuel, A.; Le, M.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Chau, V.M.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Antioxidant benzylidene 2-aminoimidazolones from the Mediterranean sponge Phorbas topsenti. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9256–9259.
- Vijayan, R.; Subbarao, N.; Manoharan, N. Discovery of marine sponge compound as promising inhibitor for Macrophage Infectivity Potentiator (Mip) protein against Chlamydia pneumoniae. Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinform. 2015, 5, 202–210.
- Morinaka, B.I.; Pawlik, J.R.; Molinski, T.F. Amaroxocanes A and B: Sulfated dimeric sterols defend the caribbean coral reef sponge Phorbas amaranthus from fish predators. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 259–264.
- Byun, M.R.; Kim, A.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Sung, M.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Hwang, B.S.; Rho, J.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. Phorbaketal A stimulates osteoblast differentiation through TAZ mediated Runx2 activation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1086–1092.
- Seo, Y.J.; Lee, K.T.; Rho, J.R.; Choi, J.H. Phorbaketal A, isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp., exerts its anti-inflammatory effects via NF-κB inhibition and heme oxygenase-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7005–7019.
- Byun, M.R.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, A.R.; Moon, S.A.; Sung, M.K.; Roh, J.-R.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.-H. Phorbaketal A inhibits adipogenic differentiation through the suppression of PPARγ-mediated gene transcription by TAZ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 181–187.
- Forestieri, R.; Merchant, C.E.; De Voogd, N.J.; Matainaho, T.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Alotaketals A and B, sesterterpenoids from the marine sponge hamigera species that activate the camp cell signaling pathway. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5166–5169.
- Daoust, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Williams, D.E.; Chavez, M.A.G.; Wang, Y.A.; Merchant, C.E.; Fontana, A.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Sesterterpenoids isolated from a northeastern pacific Phorbas sp. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 8267–8273.
- Wang, M.; Tietjen, I.; Chen, M.; Williams, D.E.; Daoust, J.; Brockman, M.A.; Andersen, R.J. Sesterterpenoids isolated from the Sponge Phorbas sp. activate latent HIV-1 provirus expression. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11324–11334.
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Duy Nguyen, D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2016, 34, 828–837.
- Daoust, J.; Fontana, A.; Merchant, C.E.; De Voogd, N.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Ansellone A, a sesterterpenoid isolated from the nudibranch cadlina luteromarginata and the sponge Phorbas sp., activates the cAMP signaling pathway. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3208–3211.
- Wang, W.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.G.; Mun, B.; Giri, A.G.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hahn, D.; Yang, I.; Chin, J.; et al. Phorone A and isophorbasone A, sesterterpenoids isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4486–4489.
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Joung, S.; Byun, M.R.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, H.Y. Phorbasones A and B, sesterterpenoids isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. and induction of osteoblast differentiation. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 884–887.
- Lee, S.H.; Jeon, J.E.; Ahn, C.H.; Chung, S.C.; Shin, J.; Oh, K.B. Inhibition of yeast-to-hypha transition in Candida albicans by phorbasin H isolated from Phorbas sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3141–3148.
- McNally, M.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasin B and C: Novel diterpenes from a Southern Australian marine sponge, Phorbas species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 645–647.
- Macklin, T.K.; Micalizio, G.C. Total synthesis and structure elucidation of (+)-phorbasin C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1392–1393.
- Lee, H.Y.; Jang, E.J.; Bae, S.Y.; Jeon, J.E.; Park, H.J.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.K. Anti-melanogenic activity of gagunin D, a highly oxygenated diterpenoid from the marine sponge Phorbas sp., via modulating tyrosinase expression and degradation. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 212.
- Takahashi, K.; Ogura, Y.; Kuse, M.; Takikawa, H. First synthesis and absolute configuration of phorbasin H, a diterpene carboxylic acid isolated from the sponge Phorbas gukulensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2198–2201.
- Xiao, Q.; Young, K.; Zakarian, A. Total synthesis and structural revision of (+)-Muironolide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5907–5910.
- Angulo-Preckler, C.; San Miguel, O.; García-Aljaro, C.; Avila, C. Antibacterial defenses and palatability of shallow-water Antarctic sponges. Hydrobiologia 2018, 806, 123–138.
- Yanagihara, M.; Murai, K.; Kishimoto, N.; Abe, T.; Misumi, S.; Arisawa, M. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of the potent HIV latency-reversing agent Ansellone A and its analogues. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 1720–1725.
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Tong, R. Unified asymmetric total syntheses of (−)-Alotaketals A-D and (−)-Phorbaketal A. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9224–9228.
- Tymann, D.; Bednarzick, U.; Iovkova-Berends, L.; Hiersemann, M. Progress toward the Total Synthesis of Gukulenin A: Photochemically Triggered Two-Carbon Ring Expansion Key to α-Tropolonic Ether Synthesis. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4072–4076.
- Vuong, D.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasin A: A novel diterpene from a southern Australian marine sponge, Phorbas species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1684–1685.
More
