Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Qinghua Wei and Version 2 by Jason Zhu.
The route to achieve self-healing of hydrogels is by noncovalent or reversible dynamic covalent bonding in polymeric materials, and enhancing the conductivity of hydrogels by the addition of conductive fillers, conductive polymers or conductive ions.
- Hydrogel
- Self-Healing
- Noncovalent Interactions
1. Introductions
In recent years, breakthroughs have been made in research on hydrogels, but most hydrogels still have poor mechanical strength and are susceptible to damage (accidental fracture, etc.), leading to some microscopic or macroscopic cracks [1][2][79,80]. As these cracks are further extended, the structure of the hydrogel network is destroyed, its mechanical properties are significantly reduced and its original function is lost, resulting in a waste of resources. To reduce environmental pollution and save resources, it is necessary to study self-healing materials that can prolong life cycles via the autonomous repair of damage [3][81]. The self-healing ability allows the hydrogel to recover from the damage it has sustained, thus maintaining its main properties and functions, and finally extending the service lifetimes of the materials [4][5][6][82,83,84]. The self-healing properties of polymeric materials can be divided into extrinsic and intrinsic self-healing, depending on whether the self-healing component is inserted into the polymer or the original component in the polymer matrix. Extrinsic self-healing materials can heal by encapsulating the components that enable healing, such as monomers, that are dispersed in matrix materials in the form of capsules, and the components inside the capsules are released upon damage. This method has difficulty achieving repeated self-healing. In the second category of intrinsic self-healing materials, healing is achieved through noncovalent or reversible dynamic covalent bonds in polymeric materials. When a hydrogel is subjected to external forces, the covalent or noncovalent bonds in the gel will break, forming a fracture surface. By re-contacting the fracture surface, the polymer chain segments interpenetrate and re-establish the dynamic cross-linking sites in the damaged area to repair the network structure of the hydrogel and restore its original mechanical properties and function to a certain extent.
2. Noncovalent Interactions
Noncovalently cross-linked hydrogels have been developed to assemble self-healing hydrogels using various mechanisms, including hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, host–guest interactions and metal coordination leading to dynamic and reversible networks. When the hydrogels are subjected to an external force, the noncovalent interaction in the network will dissociate and associate, and the hydrogel will have hysteresis in the process of deformation and recovery, dispersing the energy [7][98]. Thus, the hydrogels exhibit reproducible features and a fascinating self-healing ability. However, these hydrogels have stimuli responses and are less mechanically robust structures.
2.1. Hydrophobic Associations
Hydrophobic associated hydrogels are physically cross-linked hydrogels formed by hydrophobic interactions [8][85]. The preparation of hydrophobic association hydrogels generally adopts the micellar polymerization method [9][99]. Micelle polymerization is formed by introducing the hydrophobic segment into the hydrophilic polymer segment for copolymerization, and the hydrophobic segment serves as the dynamic cross-linking point of the hydrogel. When the hydrogel is stretched, these physically cross-linked points could dynamically dissociate/associate to reorganize the polymer chains, distributing the applied stress uniformly over the entire network. Meanwhile, physically cross-linked points dissipate the energy by a large hysteresis [10][86]. In micellar polymerization, hydrophilic segments, hydrophobic segments and surfactants are required [11][12][87,88]. Tuncaboylu et al. [13][100] reported a hydrophobic interaction self-healing hydrogel. Using stearyl methacrylate as the hydrophobic monomer and n-alkyl(meth)acrylate as the physical cross-linking agent, copolymerization in wormlike sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)/NaCl aqueous solutions was performed to prepare the hydrogel. Additionally, the effects of the length of the alkyl side chain of the hydrophobe and the surfactant concentration on the properties of the self-healing gel are discussed.
To enhance the mechanical properties of hydrogels, self-healing hydrogels are usually designed by combining hydrophobic association effects with other physical interactions [14][101]. A composite hydrogel was prepared by incorporating grape seed-extracted polymer (GSP) into an acrylamide, methacrylate stearate matrix [15][102]. As the side chains of GSP contain carboxyl groups, ammonia groups, hydroxyl groups and alkyl groups, these groups tend to form dynamic noncovalent bonds (hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions and hydrophobic association) in the hydrogel, which could dissipate energy efficiently. The hydrophobic association existing in the system can self-heal after being broken, which gives the hydrogel excellent mechanical properties and self-healing properties.
Yang et al. [16][103] proposed a polyacrylamide (PAM)/cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) hydrogel by in situ polymerization. CNFs dispersants uniformly disperse the MWCNTs in the hydrogel and strengthen the mechanical properties of the hydrogel by hydrophobic interactions and electrostatic repulsion. The prepared hydrogel had conductivity, an electromagnetic shielding function and self-healing properties. The hydrogel could be bent 1000 times without breaking after self-healing. The hydrogel could completely self-heal in approximately 7 days, with a healing efficiency of 77.2%.
2.2. Hydrogen Bond
Hydrogen bonding, as a type of physical interaction, is formed by the short-range supramolecular interaction between an electron-deficient hydrogen atom and an electron-rich species [17][18][89,104]. The hydrogen bond can be broken by heating. It can also be regenerated at a certain temperature. This reversible effect enables the material to achieve self-healing effects [19][90]. Due to the inherent weakness of hydrogen bonding, hydrogen bonding can be susceptible to competition with the surrounding water molecules, potentially weakening the mechanical properties of hydrogels.
Improvement in the mechanical properties of hydrogels can be achieved by designing the network structure of the hydrogel, such as a double-network hydrogel. A double-network hydrogel with poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) (PAM-co-PAA) as the first network and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as the second network was prepared [20][105]. The first network was formed by free radical copolymerization, and the second network was created by freezing and thawing a large number of hydrogen bonds as cross-linking points. The mechanical properties and self-healing properties of the hydrogel were improved by these hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds can also be derived from the interaction of C=O and N-H, in addition to the hydroxyl groups.
In addition, hydrogen bonding is often combined with other cross-linking interactions to produce self-healing hydrogels with excellent mechanical strength. The self-healing hydrogel was also prepared by carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) in a paste with water and acidified with a citric acid solution [21][106]. The self-healing effect was the best when the hydrogel was soaked in citric acid at a concentration of 8 mol/L. When the hydrogel was cut in half and re-contacted, the uncross-linked CMC built new hydrogen bonds with hydrogen ions, thereby restoring the damaged area of the hydrogel. The self-healing efficiency reached 81%, and the compressive strength reached 2.3 MPa. Hydrogen bonds can also work with other chemical bonds to improve the mechanical properties of the hydrogel. Wang et al. [22][107] added acrylic acid and methylene bisacrylamide to a mixed solution of cellulose and PVA, and a double-network hydrogel was obtained by UV-induced polymerization. The cutting hydrogel contacted for 16 h, and the cracks disappeared completely and could be bent, at room temperature. This double-network structure improved the mechanical properties of the hydrogel. In addition, the self-healing properties of the hydrogel were also improved by forming hydrogen bonds and metal coordination bonds.
In addition, the introduction of 2-uridine 4-pyrimidinone (UPy) in the preparation of hydrogels has enabled excellent self-healing properties. UPy has been widely used as a multi-hydrogen bonding motif in supramolecular chemistry due to its higher intermolecular bonding strength than single hydrogen bonds. For example, the UPy group was used as a cross-linking point with a PANI/PSS network to form a self-healing conductive hydrogel [23][108]. The hydrogel completely self-heals within 30 s after damage due to the multiple hydrogen bonds generated by UPy. Furthermore, the combined effect of multiple hydrogen bonds and metal–ligand coordination not only enables the hydrogel to achieve rapid self-healing, but also improves the mechanical properties of the hydrogel (the tensile strength of the self-healed hydrogel reached 7.9 MPa). This hydrogel also has excellent self-healing properties. The damaged hydrogels can recover 91% of their initial properties within 1 h [24][109].
2.3. Host–Guest Interaction
The host–guest interaction is a type of noncovalent interaction formed by the physical insertion of the guest’s moiety into the host moiety [25][91]. Generally, host molecules include cyclodextrins (CDs), pillar[n]arenes, crown ethers, calix[n]arenes, cucurbiturils and adamantane. The commonly used guest molecules include ferrocene, azobenzene, cholic acid and N-vinylimidazole derivatives.
Among the frequently used host molecules, CD has lipophilic inner cavities and hydrophilic outer surfaces, enabling high-affinity interactions with specific hydrophobic guest moieties. Specifically, as the most important member of the CD family, β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) is most widely produced and possesses a cavity that matches the size of numerous guest molecules and can be easily crystallized, separated and purified. Furthermore, β-CD inclusion complexes can enhance the resistance of the encapsulated guest molecules to various environments, such as acidic and alkaline media, light and heat [26][27][28][110,111,112]. A self-healing hydrogel was synthesized by the host–guest interaction between the hydrophobic isopropyl group of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and β-CD [26][110]. The isopropyl group in NIPAM serves as the guest component and β-CD serves as the host component to form a host–guest complex. Hydrogels have a variety of hydrogen bonds and host–guest interactions. Extensive comparative experiments have shown that the host–guest interaction is the principal factor influencing the self-healing of hydrogels. The hydrogel, cut into two pieces, is capable of rapid self-healing at room temperature. The self-healing ability of the hydrogel was measured by its weight-bearing capacity before and after healing. For example, the original hydrogel (before cutting) could bear 200 g and after healing it could bear 55 g. Therefore, the self-healing efficiency is approximately 28%. Adamantane, as the guest molecule, can form a stable inclusion complex with the β-CD cavity and has a high binding constant with the β-CD cavity compared with other guest molecules. Rodell et al. [29][113] used methacrylate to modify hyaluronic acid and further used it as the main chain of β-cyclodextrin/amantadine (β-CD/Ad) to prepare a double network hydrogel with self-healing properties. The cross-linking point of the first network was formed by the host and guest interaction, and the second network was a methacrylate network. Not only were the mechanical properties greatly improved, but self-healing could also be completed in an instant. The experimental results show that the cut hydrogel fragments heal quickly within about 1 s. However, hydrogels synthesized by chemical processes take a long time and produce toxic byproducts that are unsuitable for biological applications. Therefore, a nonchemical grafting method to prepare hydrogels was proposed [30][114]. In this hydrogel, the amphiphilic substance N,N-dimethyl-1-adamantane (DM-AD) was used as a cross-linking agent, and CMC and poly β-cyclodextrin (β-CDP) were used as the polysaccharide skeleton. One end of DM-AD is the adamantly group, which is wrapped by β-CDP through host–guest interactions. The nitrogen atom at the other end combines with protons to form a quaternary ammonium compound and is electrically attracted to the carboxyl anion. To verify the self-healing ability of the hydrogel, two identical hydrogels were stained with different colors and cut from the middle of hydrogel. Take two different colored hydrogel cut surfaces into contact with each other. After much time (more than 0.5 h), the hydrogel was completely healed, and there was no obvious sign of fracture on the fracture surface of the hydrogel. In addition, stretching the ends of the hydrogel again, the hydrogel did not fracture.
In summary, by changing the host and guest monomers and polymers, different synthetic methods can be utilized to design and prepare host–guest complexes according to the different applications. Self-healing hydrogels containing reversible host–guest interactions exhibit some advantages, such as a repeatable healing process without any external energy, long storage time and high healing rate. Self-healing based on host–guest interactions is still a wide field for research due to the diversity of guest molecules and their reversible nature.
2.4. Metal Coordination
Metal coordination is a supramolecular structure that introduces metal ions and organic ligands into the matrix. Metal coordination interactions have a wide selection of metal ions (Fe3+, Zn2+ and Cu2+) and ligands (-COOH, -NH2 and -OH), which can respond quickly to external stimulation. Meanwhile, their coordination strength and applicability cover a large range of natural and synthetic polymers, thus metal coordination interactions are widely used in the synthesis of self-healing materials.
Lee et al. [31] modified CNTs with mussel adhesion protein to improve their compatibility with polymer materials and enabled CNTs to be uniformly dispersed in the solution. Then, FeLee et al. [115] modified CNTs with mussel adhesion protein to improve their compatibility with polymer materials and enabled CNTs to be uniformly dispersed in the solution. Then, Fe3+ was added to the solution to form a reversible metal coordination with the carboxyl group, which acted as the physical cross-linking point of the system. However, when the hydrogel is damaged, the metal coordination interaction between the carboxyl group and the Fe3+ ion at the affected area can be re-established to form a new physical cross-linking point to achieve fast self-healing. In fact, the healing time directly affects the performance of the sensor. Therefore, many researchers have focused on how to shorten the healing time of hydrogels by some methods, such as a self-healing conductive hydrogel that introduces Zn2+ and 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine (tpy) ligand into a polypyrrole (PPy) matrix with good conductivity by sol–hydrogel conversion [32]. Its excellent conductivity could reach 12 S m and 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine (tpy) ligand into a polypyrrole (PPy) matrix with good conductivity by sol–hydrogel conversion [92]. Its excellent conductivity could reach 12 S m−1. The coordination of Zn2+ could connect the separated PPy chains to reform the supramolecular structure and achieve the self-healing of the material after the hydrogel was broken. Self-healing could completely restore its original conductivity at room temperature in 1 min.
In addition to using the method of chemical cross-linking to prepare this type of hydrogel, the approach of physical cross-linking cannot be ignored. Hussain et al. [33] added FeIn addition to using the method of chemical cross-linking to prepare this type of hydrogel, the approach of physical cross-linking cannot be ignored. Hussain et al. [116] added Fe3+ as the cross-linking agent to the physical cross-linking network formed by hydroxyethyl cellulose and PAA. The metal–ligand effectively dispersed energy and improved the mechanical properties of the self-healing hydrogel. In enhancing the mechanical properties of hydrogels, double metal coordination bonds are also used to prepare hydrogels. Shao et al. [34] proposed a physically cross-linked CNF composite hydrogel by a one-pot strategy. Self-healing was achieved by double metal coordination bonds (iron ions and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized CNFs and carboxylate ions on PAA) and hydrogen bonds (PAA and CNF molecular chains). Fe as the cross-linking agent to the physical cross-linking network formed by hydroxyethyl cellulose and PAA. The metal–ligand effectively dispersed energy and improved the mechanical properties of the self-healing hydrogel. In enhancing the mechanical properties of hydrogels, double metal coordination bonds are also used to prepare hydrogels. Shao et al. [117] proposed a physically cross-linked CNF composite hydrogel by a one-pot strategy. Self-healing was achieved by double metal coordination bonds (iron ions and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized CNFs and carboxylate ions on PAA) and hydrogen bonds (PAA and CNF molecular chains). Fe3+ and CNFs were used as the cross-linking agents to improve the mechanical properties, such as excellent fracture strength (1.37 MPa), fracture elongation (1803%) and fast self-healing (95.7% recovery ratio within 1 h). Tannic acid (TA) was coated on the surface of nanocrystals (CNCs) by static electricity, and AA polymerization was carried out in situ by free radicals in TA@CNC solution [35]. Aluminum ions were then introduced to form a variety of coordination bonds, as shown in and CNFs were used as the cross-linking agents to improve the mechanical properties, such as excellent fracture strength (1.37 MPa), fracture elongation (1803%) and fast self-healing (95.7% recovery ratio within 1 h). Tannic acid (TA) was coated on the surface of nanocrystals (CNCs) by static electricity, and AA polymerization was carried out in situ by free radicals in TA@CNC solution [118]. Aluminum ions were then introduced to form a variety of coordination bonds, as shown in Figure 2d. A nanocellulose-reinforced hydrogel material with a dynamic cross-linking structure and excellent self-healing properties was prepared. The hydrogel could directly adhere to human skin and be used as a wearable electronic sensor to detect large deformations (wrist swings) and weak physiological signals (pulse beats).
3. Dynamic Covalent Bonds
Repeated self-healing of hydrogels is also possible by forming reversible dynamic covalent bonds in the hydrogel network. Because the bonding strength of dynamic covalent bonds is higher than that of noncovalent bonds, these hydrogels possess good mechanical strength. In addition, these hydrogels also have some other excellent properties, such as pH sensitivity, redox sensitivity and temperature sensitivity. Currently, some dynamic covalent bonds have been successfully utilized to prepare self-healing hydrogels, containing Schiff base linkages, disulfide bonds, boronic/boronate ester bonds and Diels–Alder (DA) reactions. Such covalent links are formed by reversible couplings, and hydrogels are formed via the association equilibrium between rupture and reformation.
3.1. Schiff Base Linkage
Schiff base linkage [36][37][93,94] is derived from the condensation of carbonyl groups with amines and used as one of the driving forces for self-healing hydrogels. The Schiff base reaction (imine, acylhydrazone bonds) is mediated by the nucleophilic attack of the N atom of the amino group on the electrophilic carbon atom of the aldehyde/ketone, which takes place in an aqueous solution under physiological conditions and generates nontoxic products, ensuring good biocompatibility for Schiff base reaction-based hydrogels. In addition, it has a high chemical reaction selectivity and rapid reaction speed. Once the Schiff base linkages in the network structure are disrupted, the amino or hydrazide groups on the fracture surface rapidly react with the aldehyde groups in contact and form imine or acylhydrazone bonds again, thus reconfiguring the hydrogel matrix for self-repair. It is worth noting that the Schiff base is only stable in an alkaline or neutral environment.
In recent years, polysaccharides (such as chitosan, hyaluronic acid, sodium alginate, cellulose and dextran) have become ideal matrix materials to prepare self-healing hydrogels with acylhydrazone bonds. This is mainly because their backbones carry a large number of functional groups that can participate in the Schiff base reaction either in a direct way (such as the primary amine groups of chitosan) or after being modified into aldehyde and amine groups. Among them, chitosan is a nontoxic, biodegradable and biocompatible polysaccharide that can only be soluble in acidic aqueous solutions. Therefore, researchers have enhanced chitosan’s water solubility by chemical modifications or conjugations with a specific ligand, making it suitable for the conditions of Schiff base reactions.
Zhang et al. [38] used a large amount of -NHZhang et al. [119] used a large amount of -NH2 on chitosan (CS) to condense with benzaldehyde groups on dibenzaldehyde-terminated telechelic PEG to form imine bonds. The study found that this could quickly form a hydrogel within 60 s after contacting CS with telechelic PEG at 20 °C. The self-healing experiment showed that the incision on the hydrogel gradually decreased over time and could be completely healed within 15 min, after the hydrogel broke. The broken hydrogels could self-heal by the dynamic properties of Schiff base linkage. To obtain the self-healing hydrogels with high performances, a self-healing hydrogel formed of oxidized sodium alginate (OSA) and acrylamide (AM) monomer by schiff base reaction was prepared [37]. on chitosan (CS) to condense with benzaldehyde groups on dibenzaldehyde-terminated telechelic PEG to form imine bonds. The study found that this could quickly form a hydrogel within 60 s after contacting CS with telechelic PEG at 20 °C. The self-healing experiment showed that the incision on the hydrogel gradually decreased over time and could be completely healed within 15 min, after the hydrogel broke. The broken hydrogels could self-heal by the dynamic properties of Schiff base linkage. To obtain the self-healing hydrogels with high performances, a self-healing hydrogel formed of oxidized sodium alginate (OSA) and acrylamide (AM) monomer by schiff base reaction was prepared [94]. Figure 1a shows the process of the self-healing hydrogel. The different colored hydrogels were cut into two semicircular hydrogels. Then, the separated semicircular hydrogel was contacted for a period of time, and the fractured surfaces joined together and healed. After self-healing, the hydrogel still retained excellent mechanical and conductivity properties. Yang et al. [39] used modified carboxyethyl cellulose with dibenzaldehyde-terminated PEG under the catalysis of 4-amino-DL-phenylalanine to form a self-healing hydrogel. The prepared hydrogel not only had better self-healing ability but also had dual responsiveness to pH and redox agents. This is because the acylhydrazone bond is more sensitive to pH and the disulfide bond is more sensitive to redox agents. As mentioned in previous studies, the imine and acylhydrazone bonds in Schiff base reaction-founded self-healing hydrogels can be formed under mild conditions and not only allow facile preparation of hydrogels without any stimulation, but also bestow the self-healing ability. Therefore, Schiff base reaction-founded hydrogels prepared through some modification strategies and methods will promote the development and effective application of hydrogels.a shows the process of the self-healing hydrogel. The different colored hydrogels were cut into two semicircular hydrogels. Then, the separated semicircular hydrogel was contacted for a period of time, and the fractured surfaces joined together and healed. After self-healing, the hydrogel still retained excellent mechanical and conductivity properties. Yang et al. [120] used modified carboxyethyl cellulose with dibenzaldehyde-terminated PEG under the catalysis of 4-amino-DL-phenylalanine to form a self-healing hydrogel. The prepared hydrogel not only had better self-healing ability but also had dual responsiveness to pH and redox agents. This is because the acylhydrazone bond is more sensitive to pH and the disulfide bond is more sensitive to redox agents. As mentioned in previous studies, the imine and acylhydrazone bonds in Schiff base reaction-founded self-healing hydrogels can be formed under mild conditions and not only allow facile preparation of hydrogels without any stimulation, but also bestow the self-healing ability. Therefore, Schiff base reaction-founded hydrogels prepared through some modification strategies and methods will promote the development and effective application of hydrogels.
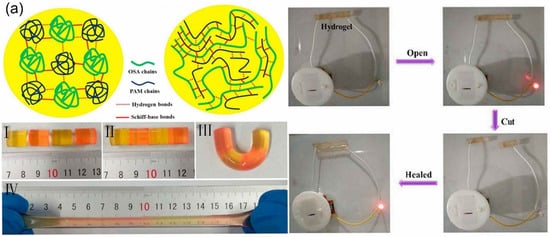
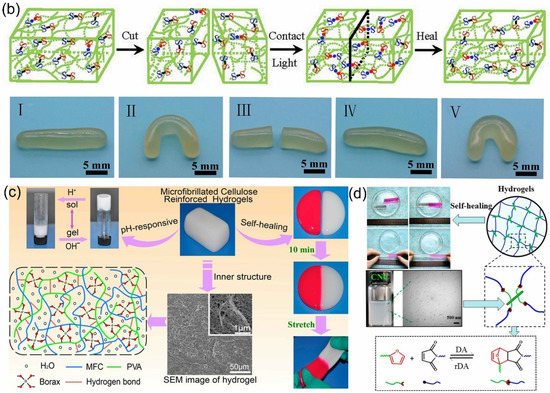
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of self-healing hydrogel and self-healing performance with (a) the Schiff base linkage, (b) the disulfide bond, (c) borate ester bond and (d) Diels–Alder (DA) reaction.
3.2. Disulfide Bond
The disulfide bond [40][121] is a dynamic covalent bond based on the thiol/disulfide dynamic exchange reaction, which is sensitive to many factors such as acid, alkali and ultraviolet light. Li et al. [41][122] proposed a photosensitive cellulose-based self-healing hydrogel by embedding thiuram disulfide bonds into hydrogels via the polyaddition method. The hydrogel could realize rapid self-healing within 2 min, and the cracks disappeared completely under visible light irradiation (Figure 1b). The reason is that the dithiocarbamate ester bonds in the CNC-containing hydrogel could be the result of homolytic cleavage under visible light and produce dormant dithiocarbamyl radical intermediates. When the fracture surfaces were in contact with each other, the dithiocarbamyl radicals broke and recombined on the re-contacted surfaces by exchange and transfer reactions, and the covalent S–S bond was reconstructed to realize the healing of the fracture surface. The self-healing efficiency reached 97%, and the hydrogel could be stretched 42.6 times of the original length. Usually, disulfide bonds are combined with other covalent or noncovalent bonds to enhance the mechanical properties and self-healing efficiency of hydrogels. Dang et al. [42][95] prepared a healable ionic hydrogel with acrylic acid (AA), choline chloride and ferric chloride through a simple, fast process. The self-healing properties are achieved due to the contribution from disulfide bonds, hydrogen bonds and coordination bonds in the hydrogel. Hydrogels can be used directly as wearable sensors to monitor human movement [43][123].
3.3. Boronic/Boronate Ester Bond
Boronic/boronate ester bonds are formed via a combination of boronic acid and 1,2- or 1,3-diols. These bonds can be formed or broken reversibly depending on the pH or aqueous media. Boronic acid can selectively bond to diols to form boronic esters or boronate esters; therefore, boronic acid can be applied in sensors as a component in drug delivery systems and self-healing materials [44][96].
In polymer networks containing boronic ester bonds, these bonds undergo facile bond exchange via associative or dissociative mechanisms. Lu et al. [45][124] designed a self-healing hydrogel with boronic ester bonds as the driving force. The process consisted of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid (AAPBA) and acrylamide (AM) chain copolymerization and covalently cross-linked with hydroxypropyl guar gum (HPG). The tensile strength increased as the AAPBA, HPG and AM increased. In the hydrogel, the phenylboronic acid groups in AAPBA combined with the 1,3-cishydroxyl moieties of HPG formed dynamic covalent phenylboronic (PBA)-diol ester bonds and endowed the hydrogel with good self-healing properties and tensile properties. The hydrogel (cut into two pieces) could be completely restored for 30 min at room temperature. It was found that the formation of PBA ester bonds was dependent on the pH value. In an acidic environment, AAPBA did not react with HPG, and the hydrogel had poor tensile stress. When the pH was higher than 8.2, stable boronic ester bonds were formed in the hydrogel.
In addition, boronate ester bonds are another dynamic covalent bond formed by free boronic acid and diol. In many studies, borax has been used as an alternative to boric acid, combining with diols to form dynamic B-O bonds, and dynamic B-O bonds are usually regarded as boronate esters. Because the borax can be hydrolyzed in water to form boric acid and borate ions, it has been widely used as a cross-linking agent in the preparation of PVA–borax hydrogels. Lu et al. [46][125] used the reversible dynamic boronate bond to mix with the microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) obtained by ball milling with borax, and then added a PVA solution to prepare a pH-responsive self-healing hydrogel. The hydrogel containing 3.0% MFC could be stretched 3000%, while the hydrogel without MFC was easily broken. This indicated that MFCs could improve the mechanical properties of the hydrogel. Then, the self-healing process of the two hydrogels was observed, as shown in Figure 1c. After 10 min, the broken hydrogel could be healed. Moreover, the hydrogel was sensitive to pH as it showed a repetitive sol–gel phase transition depending on the pH.
However, traditional self-healing hydrogels have long self-healing times. Modifying the components of the hydrogels could greatly shorten the self-healing time and increase the conductivity of the hydrogels [44][96]. In these hydrogels, dynamic boronate bonds were formed by PVA and benzoboric acid groups. The separated hydrogel was contacted for 15 s, and the fractured surfaces could join together and heal together.
3.4. Diels–Alder Reaction
The Diels–Alder (DA) reaction [47][126], also known as diene addition, is the reaction of conjugated diene and dienophile to generate substituted cyclohexene. The DA reaction, as one of the “click chemistry” reactions, plays an important role in the preparation of various functional hydrogels due to its high efficiency, high selectivity and lack of side reactions and byproducts [48][127]. Additionally, the DA reaction possesses atomic economy and generally requires no catalyst or initiator. Interestingly, the DA reaction is reversible under certain conditions (e.g., at elevated temperature or in organic solvents). Hence, the DA reaction has been used for the preparation of hydrogels. DA reaction-founded hydrogels can be healed by the reversible formation and breakage of covalent bonds upon heating. Specifically, in the damaged hydrogel, the Diels–Alder bonds break upon the application of heat, and the chains become elastic at high temperatures. The elastic chains move to the fracture site to reform the Diels–Alder bonds upon a decrease in temperature, and self-healing occurs as the network is reformed. Shao et al. [49][97] reported a tough, highly elastic and fast self-healing hydrogel with an interpenetrating network by the Diels–Alder click reaction. The synthesis process of self-healing hydrogels is shown in Figure 1d. The furan group at the crystal end of the modified CNFs and the maleimide at the end of the polyethylene glycol form a thermally reversible covalent bond. As a reinforcing agent and chemical cross-linking agent, CNFs can improve the mechanical properties of the hydrogels.
