Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Hena khatoon and Version 2 by Yvaine Wei.
Lawesson’s reagent (LR) is a well-known classic example of a compound with unique construction and unusual chemical behavior, with a wide range of applications in synthetic organic chemistry. Its main functions were rounded for the thionation of various carbonyl groups in the early days. Now its use can help the chemistry community to understand innovative ideas. These include constructing biologically valuable heterocycles, coupling reactions, and the thionation of natural compounds.
- Lawesson’s reagent
- organic synthesis
- thio analogs
1. Introduction
Two essential reagents, namely phosphorus pentasulfide (P4S10) and Lawesson’s reagent (LR) (Figure 1), are the most widely used agents for such a transformation. However, as the most commonly used reagent since the beginning of the 20th century, LR has gained the upper hand with essential applications in synthetic organic chemistry [1][2][3][4][5][6][1,2,3,4,5,6].
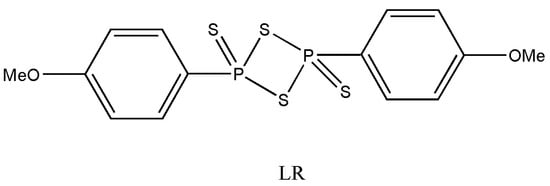
Figure 1. 2,4-bis(p-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dithiadiphosphetane-2,4-disulfide or Lawesson’s reagent (LR).
The main advantage of LR over P4S10 is its lesser requirement and shorter reaction time, primarily if reactions are carried out using microwave irradiation techniques. In addition, the high yields, convenient handling, availability, and soft thionation reactions are also unique LR benefits.
Lawesson’s reagents were first systematically studied by Lawesson and co-workers in 1978, mainly for carbonyl groups’ transition to thiocarbonyls [7][8][9][7,8,9]. LR is commercially available and widely used in organic synthesis. However, it has been reviewed that LR becomes unstable above 110 °C and decomposes or polymerizes slowly [10].
LR is also widely used to form organothiophosphorus compounds, a subclass of organophosphorus compounds with many applications in the pesticide industry, medical fields, and oil additives. Furthermore, these compounds have been identified as anticancer, antiviral, cardioprotective therapeutics, and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors in medicinal chemistry [11][16].
2. Synthesis of Some Biologically Essential Thioketones
Ketones can be easily converted by O/S exchange using Lawesson’s reagent (LR), which forms comparatively stable aromatic thioketones; therefore, it has been studied extensively for the past three decades. Additionally, the versatility of aromatic thioketones has been explored extensively as building blocks for complex sulfur-containing compounds. Ferrocenyl-functionalized compounds have found a key place in materials chemistry, medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, and polymer sciences, but little is known about ferrocenyl-substituted thioketones despite their wide variety of applications. A series of ferrocenyl hetaryl ketones was prepared by G. Mloston et al. [12][18] by consequent thionation to provide thioketones (5). For the conversion of ferrocenyl hetar, phenyl ketone (4) was formulated by its reaction with LR in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 65 °C. The impure product was purified via column chromatography in a 75–85% yield (Scheme 12).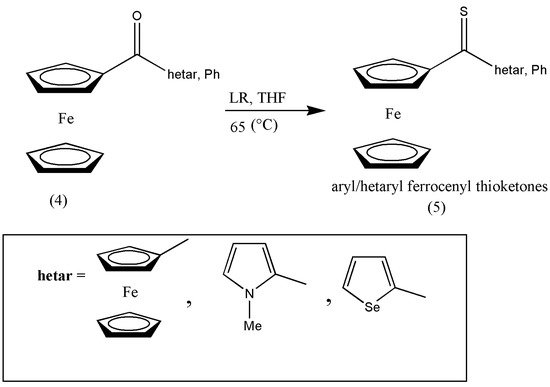
Scheme 12. Synthesis of aryl/hetaryl ferrocenyl thioketones (5) via conventional methods.
The ferrocenyl and hetaryl thioketones are considered building blocks in the organic chemistry of sulfur. Two methods are formulated in the synthesis process via conventional and microwave-assisted techniques. First, the traditional practices are progressed in boiling THF or toluene, with low to high yields and prolonged reaction times of 1 to 2 h [12][13][18,19], which is overcome by applying microwave irradiation. The synthesized ferrocenyl thioketones are unique substrates to prepare the hitherto unknown ferrocenyl-substituted thiiranes and disparately substituted alkenes with diazo compounds [12][18].
Citing the requirement for hetaryl and ferrocenyl-functionalized thioketones in diverse synthetic applications such as synthesizing heterodienes via thia-Diels–Alder reactions and as reactive dipolarophiles in the [3+2]-cycloaddition with diazo compounds prompted Fałdyga et al. [14][20] to elaborate on efficient and practical methods for their synthesis.
The thioketones can be prepared via conventional and microwave irradiation (MW) methods, but the conventional techniques required prolonged reaction times of 1 to 2 h, and in some instances, the yield was not satisfactory. Therefore, MW techniques were explored to improve hitherto applied protocol.
Reactions were performed in toluene solution with LR and substituted ketones (6) placed in a reaction tube and irradiated for 2 min using 150 W of power. Further purification of the obtained compound (7) was achieved via flash chromatography using the eluents petroleum ether and dichloromethane (8:2) (Scheme 23) [14][20].
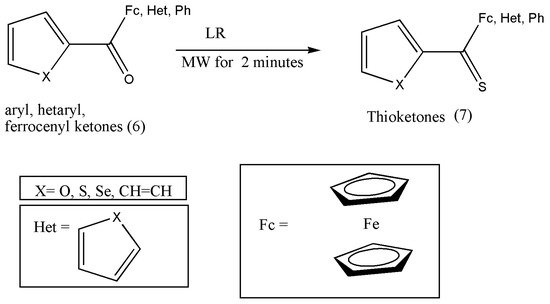

Scheme 23. Microwave-assisted synthesis of thioketones (7).
The synthesis of more diverse thioketones such as thiofluorenones should be explored and experimented with due to their importance in cycloaddition chemistry.
The most common approach employed for the synthesis of thioketones using LR involves reactants and a suitable solvent. The conventional methods usually demand an excess of LR and a longer reaction time of 2–25 h at higher temperatures in the presence of dry solvents. Notable work has been done to provide a high-yield synthetic pathway to transform ketones and other carbonyl compounds into their thio analogs [15][21] to avoid dry solvents and excess LRs.
Jasmine and jasmone analog odor fragrances are indispensable in the perfume industry. The conversion of jasmone to its thio analogs makes an exciting group of compounds, with profound possibilities, as S fragrant compounds have been widely registered. The significance of fragranced jasmone prompted Pawelczyk et al. [16][22] to synthesize thio analogs of jasmones under solvent-free conditions. Consequently, it has also been found that replacing conventional methods with microwave solvent-free methods for the thionation of jasmone heterocyclic analogs to thio analogs have been observed in quite a bit of research literature due to its high-yielding, environmentally friendly, and economical procedures [15][17][18][21,23,24].
These new jasmine analogs were centered on five-membered heterocyclic ketones containing one or two heteroatoms, for example, oxazolidione, pyrrolidinone, thiazolidinone, and Z-jasmone. The reactions progressed in microwave conditions to reduce time to just a few minutes compared to conventional methods (Scheme 34).
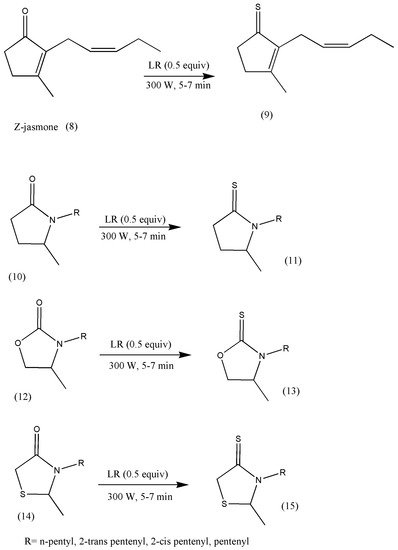

Scheme 34. Synthetic pathways to prepare fragrant thioketones (9, 11, 13, 15).
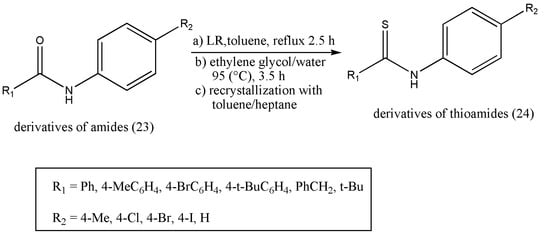
3. Synthesis of Biologically Active Thioamides
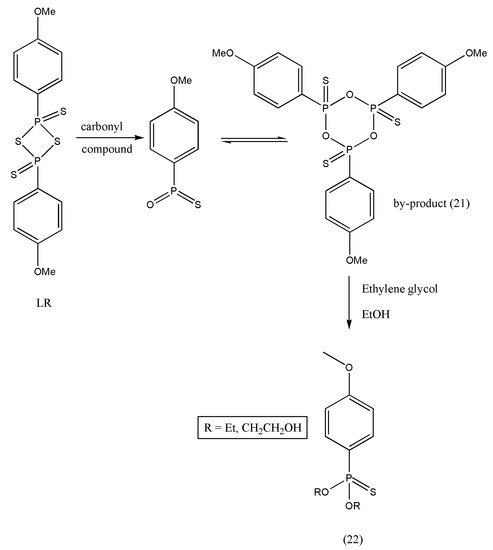
Thioamides were first prepared in the year 1815 by Gay-Lussak and later by Berzelius in 1843. The conversion of oxygen of amides to its thio analogs is the basis of thioamide formations. Even though they are structurally pretty similar to each other, there is a vast difference in the chemical properties of these two species. Thioamides are more polar than their respective amides, making them participate in more reactions. The chemical adaptability of thioamides makes them an excellent molecule for their extensive studies. The resourcefulness of thioamides makes them a good starting material to prepare thiazoles, amidenes, amidrazones, and many more [19][28]. The structural significance of thioamides has led researchers to investigate their biological properties [19][20][28,29]. Thioamides’ synthesis appeals to organic chemists because of their applications in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, electronic chemicals, and material science [21][22][23][24][25][26][30,31,32,33,34,35]. Moreover, the thio-substitution of the amide with LR is a simple, efficient, and straightforward reaction. However, the work-up procedure is constantly under criticism despite LR being a powerful, mild, and flexible thionating agent [27][28][36,37]. A six-membered ring structure (21) is formed as LR completes thio-substitution [29][38]. However, compound (21) polarity is similar to the desired products, and the purification of selected products becomes tedious and less efficient because of its good solubility; concerning this, LR is always limited to a small-scale preparation. An efficient work-up procedure decomposing by-products (21) of LR in ethylene glycol (Scheme 47) was formulated by Ke Wu et al. [30][39]. The freshly designed, column-free procedure avoided P-contained aqueous waste, and only organic effluents were released. The optimized approach was articulated to offer an opportunity to apply the LR for numerous thio-substituted reactions in scaling up preparations.
Scheme 47. Formation of six-membered by-product (21).
The exemplified reaction pathway of Scheme 5 8 demonstrates the reaction of amide derivatives (0.20 mol) (23) and LR (0.102 mol). An excess of ethylene glycol decomposed the by-product A.

Scheme 58. Synthesis of thioamides (24).
4. Synthesis of Biologically Active Thioesters and Thionolactones
Pyrrole-containing sulfur functionalities are scarce. Thioester-containing pyrroles are best known for their vital role as thioesterase-appended pyrroles in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites [31][32][46,47]. Literature review of pyrroles affixed with thionoesters is constricted to mono and di-pyrroles reacting with dithiocarbonates and methanolic solutions of thiophosgene [33][34][48,49]. With the knowledge of thioesters and to overcome the limitations, Groves et al. [35][50] synthesized thionoesters with 2-pyrrole carboxylate and Lawesson’s reagent at higher temperatures. A new class of pyrroles annulated with (1,3,2)-thiazaphospholidine unit were also reported (Scheme 612).
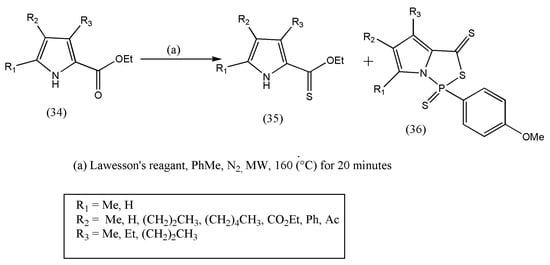

Scheme 612. Synthetic pathway to prepare thionoester (35) and (1,3,2)-thiazaphospholidine (36).
The synthetic work started with ethyl-2-pyrrole carboxylate, which is commercially available via Knorr-type condensation. Next, the microwave-assisted technique was applied instead of conventional methods, which endured long reaction times using LR.
The total material consumption (34) was accompanied by two new compounds (35, 36). The compounds were identified, and the desired product (35) was isolated with a 59% yield. Even though the (1,3,2)-thiazaphosphole functional group (N–P–S) is well defined, the authors could not find pyrrolic examples displaying this functionality [35][50]. On the other hand, the four-, five-, and six-membered cyclic thiazaphospholes were reported to be well defined. There is a possibility of adverse interactions between LR and 2-pyrrole carboxylates and the formation of dipyrins and their complexation products.
