Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Ariadni Spyroglou and Version 2 by Lindsay Dong.
Primary aldosteronism, mainly caused by aldosterone producing adenomas or bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, is the most common cause of endocrine hypertension. Information on the role of transcriptomics, epigenetics and metabolomics in the pathophysiology of this disease is summarized herein.
- primary aldosteronism
- transcriptomics
- epigenetics
- metabolomics
1. Introduction
Primary aldosteronism (PA) is the most common cause of endocrine hypertension, with a prevalence of approximately 10% in hypertensive subjects [1][2][1,2]. In addition to hypertension and occasionally hypokalemia, aldosterone excess significantly increases cardiovascular risk, stressing the need for better understanding of its pathophysiology for the optimization of treatment strategies [3]. There are two main clinical presentations of PA: aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma (APA), and bilateral adrenal hyperplasia (BAH), whereas the clinical picture can rarely be attributed to an adrenocortical carcinoma [1]. Recently, both somatic and germline mutations have been identified as causative for the development of APAs; these also affect the clinical phenotype of the disease.
The most frequent genetic alteration in APAs, with a female predominance and a prevalence of 40–50% (and even higher in Asian populations), is a Potassium Inwardly Rectifying Channel Subfamily J Member 5 (KCNJ5) mutation which causes depolarization of the membrane of zona glomerulosa (ZG) cells, opening the voltage gated Ca2+ channels and increasing Ca2+ influx [4][5][6][7][4,5,6,7]. Acting in a similar way, identified mutations in the ATPase Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Transporting 3 (ATP2B3) and the Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 D (CACNA1D) genes act by increasing the intracellular Ca2+ and stimulating Cytochrome P450 Family 11 Subfamily B Member 2 (aldosterone synthase-CYP11B2) expression and subsequent aldosterone synthesis [8][9][8,9]. Mutations in the ATPase Na+/K+ Transporting Subunit Alpha 1 (ATP1A1) gene induce cellular acidification due to H+ leakage, but the exact mechanism resulting in autonomous aldosterone secretion has not been elucidated yet [8][10][8,10]. β-catenin 1 (CTNNB1) mutations, identified in a small proportion of APAs, cause constitutive activation of β-catenin and are considered to directly promote CYP11B2 synthesis [11]. More recently, co-existence of CTNNB1 with G Protein Subunit Alpha Q (GNAQ)/G Protein Subunit Alpha 11 (GNA11) mutations was documented in 59% of APAs [12]. Rarely, Protein Kinase cAMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha (PRKACA), sporadic Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 H (CACNA1H) and Chloride Voltage-Gated Channel 2 (CLCN2) mutations have also been identified in sporadic APAs [13][14][15][13,14,15].
In addition to the rather common somatic mutations responsible for sporadic PA cases, four rare familial forms of the disease associated with early-onset hypertension have been identified. In short, familial hyperaldosteronism type I is attributed to a hybrid Cytochrome P450 Family 11 Subfamily B Member 1 (CYP11B1)/CYP11B2 gene inherited as an autosomal dominant characteristic where aldosterone synthesis is adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)- and not angiotensin II-dependent [16]. Familial hyperaldosteronism type II is caused by a CLCN2 mutation in chloride channels, clinically expressed as early-onset hypertension along with hypokalemia and was initially described in a population of PA individuals under the age of ten [17]. KCNJ5 germline mutations are the genetic basis of familial hyperaldosteronism type III [4][18][4,18], whereas CACNA1H mutations result in a gain of function of the Ca2+ voltage gained channel, leading to familial hyperaldosteronism type IV [19][20][19,20].
However, the already complex genetic landscape of PA provides a trigger for the further understanding of the pathophysiology of this common endocrine form of hypertension caused by adrenal tumours and/or cancer. Gene expression profiling along with epigenetic and metabolomic studies can elucidate the mechanisms and signaling pathways which have a role in the pathogenesis of PA, enabling the identification of subgroups of PA with distinct clinical, histological, and molecular profiles.
2. Transcriptomics, Epigenetics, and Metabolomics
2.1. Transcriptomics
Gene expression profiles of APAs have increasingly been applied to shed light on the pathophysiology of PA. Either by microarray or serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE), the gene expression profile of APAs is routinely compared to that of adjacent adrenal glands or normal adrenal glands. Thus, an interplay between PA and a variety of signaling pathways can be documented. Among other factors, upon PA a differential expression of several molecules was observed, from classical enzymes involved in steroidogenesis, nuclear receptor transcription factors, ion channels, molecules involved in calcium signaling, and G-coupled proteins to molecules responsible for cell energy, mitochondrial function, protein binding, transcription factors, and oncogenes (Table 1 and Figure 12).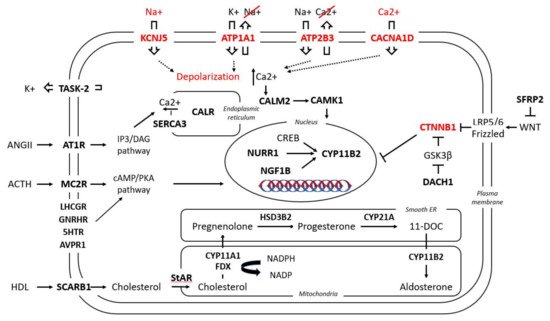
Figure 1. Simplified presentation of the main pathways involved in aldosterone regulation under physiological conditions and in APAs. In bold are the molecules involved in these pathways which have been found to be up-/down-regulated in APAs; in red are the five known mutant genes responsible for APAs and their aberrant cellular function. For nomenclature, the name of the respective genes and proteins have been used; for their respective abbreviations, see Table 1.
Table 1. Transcriptome-identified genes up- (↑) or downregulated (↓) in the following conditions: (a) in APAs versus normal adrenal tissue or other adrenal adenomas; (b) in two different subgroups of APAs: ZF-like (in some studies defined as carrying KCNJ5 mutations) versus ZG-like (in some studies defined as either WT or as carrying the ATP1A1, ATP2B3, CACNA1D or CTNNB1 mutations).
| Genes | Description | Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Steroidogenic enzymes | ||
| CYP11B2 | Cytochrome P450 Family 11 Subfamily B Member 2 | ↑(a), ↔ ↑(b) |
| CYP11B1 | Cytochrome P450 Family 11 Subfamily B Member 1 | ↑(b) |
| CYP21A2 | Cytochrome P450 Family 21 Subfamily A Member 2 | ↑(a) |
| HSD3B2 | Hydroxy-Delta-5-Steroid Dehydrogenase, 3 Beta- And Steroid Delta-Isomerase 2 | ↑(a) |
| CYP17A1 | Cytochrome P450 Family 17 Subfamily A Member 1 | ↓ (a), ↑(b) * |
| CYP11A1 | Cytochrome P450 Family 11 Subfamily A Member 1 | ↑(a) |
| AKR1C3 | Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member C3 | ↓(a) |
| Nuclear receptors/transcription factors | ||
| NR4A2 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 2 (NURR1) | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| NR4A1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 1 (NGF1B) | ↑(a) |
| NR0B1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 0 Group B Member 1 (DAX1) | ↑(a) * |
| NR5A1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 5 Group A Member 1 (Steroidogenic factor 1 _ SF1) | ↑(a) |
| NR1B1 | Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha (RARα) | ↓(a) |
| Plasma membrane receptor | ||
| SCARB1 | Scavenger Receptor Class B Member 1 (CD36) | ↑(a) |
| Ion channels | ||
| KCNK1 | Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 1 (TWIK-1) | ↓(b) |
| KCNK5 | Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 5 (TASK-2) | ↓(a) |
| SLC24A3 | Solute Carrier Family 24 Member 3 (sodium calcium exchanger) | ↓(b) |
| ANO4 | Anoctamin 4 (calcium dependent chloride channel) | ↓(a) |
| CACNA1A | Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 A | ↑(a) |
| CACNA1C | Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 C | ↑(a) |
| CACNA1E | Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 E | ↑(a) |
| Calcium signaling | ||
| CALM2 | Calmodulin 2 | ↑(a) |
| CALR | Calreticulin | ↑(a) |
| CAMK1 | Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase I | ↑(b) |
| CAMK2B | Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase II Beta | ↓(b) |
| CALN1 | Calneuron 1 | ↑(a) |
| ATP2A3 | ATPase Sarcoplasmic/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Transporting 3 (SERCA3) | ↑(a) |
| CLGN | Calmegin | ↑(a) |
| PCP4 | Purkinje Cell Protein 4 | ↑(a) |
| VSNL1 | Visinin Like 1 | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| GSTA1 | Glutathione S-Transferase Alpha 1 | ↓(a), ↓(b) |
| G-protein coupled receptors | ||
| LHCGR | Luteinizing Hormone/Choriogonadotropin Receptor | ↑(a) ** |
| GNRHR | Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor | ↑(a) |
| HTR2A | 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2A | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| HTR4 | 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 4 | ↑(a) |
| AGTR1 | Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 (AT1R) | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| PTGER1 | Prostaglandin E Receptor 1 | ↑(a) |
| GRM3 | Glutamate Metabotropic Receptor 3 | ↑(a) |
| EDNRB | Endothelin Receptor Type B | ↑(a) |
| MC2R | Melanocortin 2 Receptor | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| AVPR1A | Arginin Vasopressin Receptor 1A | ↓(a) |
| PTGFR | Prostaglandin F Receptor | ↓(a) |
| GPER1 | G-Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 | ↑(a) |
| Energy | ||
| FDX1 | Adrenodoxin | ↑(a) |
| POR | Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase | ↑(a) |
| CYB5 | Cytochrome B5 Type A | ↑(a) |
| ATAD3C | ATPase Family AAA Domain Containing 3C | ↑(a) |
| ACSS3 | Acyl-CoA Synthetase Short Chain Family Member 3 | ↑(b) |
| - | Genes related to lipid metabolism, glycolysis, and antioxidant systems | ↑(a) |
| Protein binding | ||
| NEFM | Neurofilament Medium Chain | ↓(b) |
| NPNT | Nephronectin | ↓(b) |
| MRAP | Melanocortin 2 Receptor Accessory Protein | ↑(a), ↑(b) |
| PROM1 | Prominin 1 | ↑(a) |
| SFRP2 | Secreted Frizzled Related Protein 2 | ↓(a) |
| Cell growth/cell death | ||
| COPS5 | COP9 Signalosome Subunit 5 (JAB1) | ↑(a) |
| MYC | MYC Proto-Oncogene, BHLH Transcription Factor | ↑(a) |
| IGFBP2 | Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 | ↑(a) |
| CCN3 | Cellular Communication Network Factor 3 (IGFBP9 or NOV) | ↑(a) |
| TDGF1 | Teratocarcinoma-Derived Growth Factor 1 | ↑(a) |
| BID | BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist | ↓(b) ** |
| BIRC2 | Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 2 | ↓(b) ** |
| BIRC3 | Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 3 | ↓(b) ** |
| Immune response | ||
| - | Genes related to inflammatory response, interferon-γ response, and IL-6, JAK/STAT3 signaling | ↓(a) |
| DNA binding/RNA polymerase | ||
| GATA6 | GATA Binding Protein 6 | ↑(a) |
| PRRX1 | Paired Related Homeobox 1 | ↑(a) |
| DACH1 | Dachshund Family Transcription Factor 1 | ↓(a) |
| BEX1 | Brain-Expressed X-Linked 1 | ↑ (a), ↓(b) |
* Ambiguous results, please see text for details. ** Higher expression in CTNNB1 tumors.
2.2.1. Steroidogenic Enzymes
As the rate limiting step for aldosterone synthesis, CYP11B2 overexpression is present in a number of studies investigating gene expression profiles in APAs [14][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30][14,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Interestingly, several studies have observed heterogeneity in CYP11B2 expression in APAs, with one subgroup overexpressed and another group with either unchanged or even reduced CYP11B2 expression [23][31][32][33][47,55,56,57]. Several studies confirmed that CYP11B2 expression was significantly higher in tumors carrying ATP1A1, ATP2B3 or CACNA1D mutations than in tumors carrying KCNJ5 mutations [23][24][25][34][47,48,49,58]. Kitamoto et al. found increased CYP11B2 expression in ATP2B3 tumors but not in ATP1A1 tumors [35][59]. Another discrepancy in addition to this initial observation was described by Monticone et al., who documented increased CYP11B2 expression in APAs with KCNJ5 mutations [22][46]. In line with CYP11B2 expression, differential expression of CYP11B1, responsible for cortisol synthesis, has been recognized in several studies. As a common observation, two different CYP11B1 expression profiles were observed, with a subgroup of APAs presenting an overexpression of this steroidogenic enzyme and a second subgroup displaying very low expression [33][57]. Interestingly, CYP11B1 expression was inversely correlated with CYP11B2 expression. Thus, tumors carrying a KCNJ5 mutation presented overexpression of CYP11B1 and concomitant rather low CYP11B2 levels, whereas ATP1A1, ATP2B3 and CACNA1D mutant tumors had very low CYP11B1 expression along with significant CYP11B2 overexpression [36][37][25][35][22,37,49,59]. This pattern is suggestive of a particular biological behaviour of KCNJ5 tumors, which also appear to co-secrete cortisol [38][60]. Unlike this rather common finding, a large European multicenter study did not document any significant CYP11B1 expression differences among the different mutations of APAs [39][24]. Differential expression of Cytochrome P450 Family 21 Subfamily A Member 2 (CYP21A2), the enzyme catalyzing the conversion of progesterone to 11-deoxycorticosterone (a precursor of aldosterone synthesis), is also well documented in PA, with APAs displaying a significant overexpression of this enzyme [24][29][48,53]. A concomitant increased expression of Hydroxy-Delta-5-Steroid Dehydrogenase, 3 Beta- And Steroid Delta-Isomerase 2 (HSD3B2), the enzyme converting pregnenolone to progesterone, has been documented in the majority of APAs [40][24][35][41][21,48,59,61]. Interestingly, Cytochrome P450 Family 17 Subfamily A Member 1 (CYP17A1) expression in APAs has thus far, shown contradictory trends. In one study, CYP17A1, responsible for the hydroxylation of pregnenolone and progesterone, was downregulated in the majority of APAs compared to adjacent adrenal tissue.2.2.2. Nuclear Receptor Transcription Factors
Several nuclear receptors, acting mainly as transcription factors, have been acknowledged as being involved in aldosterone secretion regulation. In line with these findings, several studies have presented an increase of the Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 2 (NR4A2 or NURR1) and Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 1 (NR4A1 or NGF1B) transcription factors in APAs [11][36][24][11,22,48], particularly KCNJ5 mutant APAs correlated with a pronounced NURR1 increase [36][42][22,62]. Two further transcription factors play a role in both adrenal development and steroidogenesis, namely Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 5 Group A Member 1 (NR5A1 or steroidogenic factor-1, SF-1) and Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 0 Group B Member 1 (NR0B1 or dosage-sensitive sex reversal, DAX-1); both were found to be significantly increased in APAs [24][43][48,63].
2.2.3. Plasma Membrane Receptors
The single plasma membrane receptor identified so far with a role in APAs is the Scavenger Receptor Class B Member 1 (SCARB1), also known as CD36 antigen, responsible for the transport of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) into the ZG cells. In one study, the SCARB1 expression, important for the cholesterol supplies in the adrenocortical cells, was found significantly upregulated in APAs compared to the adjacent adrenal glands [29][53].
23.2.4. Ion Channels
Little data is available concerning the differential expression of ion channels in APAs. Concomitant to the expression pattern of CYP11B1 in APAs, and depending on their mutation status as described above, the Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 1 (KCNK1 or TWIK-1) potassium channel and the Solute Carrier Family 24 Member 3 (SLC24A3) sodium/calcium exchanger show significant negative correlation with CYP11B1 expression in APAs [40][21]. The Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 5 (KCNK5 or TASK2) channel is also consistently less expressed in APAs compared to normal adrenal cortex [44][65]. Recently, Anoctamin 4 (ANO4), a calcium dependent chloride channel, was found to be significantly downregulated in APAs compared to normal ZG, independent of their respective mutation status [45][66]. Expression data on L-type and T-type voltage dependent calcium channels has demonstrated high CACNA1H expression in both normal adrenal glands and APAs, while CACNA1A, CACNA1C and CACNA1E expression was significantly upregulated in APAs [20].
2.2.5. Calcium Signaling
As one of the main pathways promoting physiological aldosterone secretion upon angiotensin II or potassium stimulation is calcium signaling, it is not a surprise that several molecules of the calcium signaling pathway are differentially regulated in APAs. Assié et al. documented an increased expression of Calmodulin 2 (CALM2), Calreticulin (CALR) and ATPase Sarcoplasmic/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Transporting 3 (ATP2A3, or calcium adenosine triphosphatase 3, SERCA3) in APAs compared to the adjacent normal adrenal tissue [29][53]. Interestingly, in line with the already described heterogeneity of CYP11B2 expression in two subgroups of APAs, one APA subgroup presents overexpression of Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase I (CAMK1) in parallel with CYP11B2 overexpression and Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase II Beta (CAMK2B) underexpression, while another group presents the opposite profile [33][57]. Calneuron 1 (CALN1), localized in the endoplasmatic reticulum, binds calcium ions and positively correlates with the increased CYP11B2 expression in APAs in comparison to non-functioning adrenal adenomas [46][67]. The endoplasmatic reticulum carrier Calmegin (CLGN) is also upregulated in APAs compared to non-functioning adenomas, with a clear positive correlation with CYP11B2 expression [47][48][41,68]. Purkinje Cell Protein 4 (PCP4), a molecule modulating calcium binding by calmodulin, has been found to be significantly increased in APAs compared to the adjacent adrenal glands [27][51]. F
2.2.6. G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
Several genes encoding G-protein coupled receptors have been identified as differentially expressed in APAs, whereas a clear interrelation between GPCRs and physiological aldosterone secretion is acknowledged for the Melanocortin 2 Receptor (MC2R) and the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor (5-HTR-4). In several studies, Luteinizing Hormone/Choriogonadotropin Receptor (LHCGR), Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor (GNRHR), 5-HTRs 2A and 4, Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 (AGTR1 or AT1R), Glutamate Metabotropic Receptor 3 (GRM3), Endothelin Receptor Type B (EDNRB), MC2R, and Prostaglandin E Receptor 1 (PTGER1), among others, were all found to be significantly upregulated in APAs [26][49][50][51][50,70,71,72].
2.2.7. Energy
The cytochrome P450 steroidogenic enzymes require electrons to exert their catalytic activity on cholesterol during the various steps involved in the formation of aldosterone precursors. In accordance with this need, the expression of energy-providing enzymes such as Adrenodoxin (FDX1), Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase (POR), Cytochrome B5 (CYB5) have been found to be significantly upregulated in APAs compared to the adjacent ZG or normal adrenal glands [27][29][32][51,53,56]. ATPase Family AAA Domain Containing 3C (ATAD3C), a mitochondrial membrane bound ATPase, showed the highest increase in APAs in one study [32][56], whereas Acyl-CoA Synthetase Short Chain Family Member 3 (ACSS3), a gene with acetate-CoA ligase activity, was the top gene upregulated in KCNJ5 mutant APAs in comparison to wild types in another study [42][62].
2.2.8. Protein Binding
Neurofilament Medium (NEFM), which encodes a neurofilament subunit, was significantly upregulated in wild-type APAs for KCNJ5 mutations (ZG-like APAs) compared to APAs carrying KCNJ5 mutations (ZF-like APAs). Silencing of NEFM leads to a significant increase of aldosterone secretion in human adrenocortical cell cultures (H295R), suggesting a role of NEFM in the physiological negative regulation of aldosterone production [42][52][62,76].
Nephronectin (NPNT) is a secreted matrix protein with a role in calcium ion binding as well as in integrin binding. NPNT was found to be highly overexpressed in APAs with a ZG-like structure carrying ATP1A1, ATP2B3 and CTNNB1 mutations. NPNT production is regulated by the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and may upregulate aldosterone production [23][53][47,77].
PROM1 encodes a transmembrane protein with actinin- and cadherin-binding properties, which also binds cholesterol on the plasma membrane. Prominin 1 (PROM1) was found significantly upregulated in APAs when compared to normal adrenal glands [32][56].
A well-acknowledged mechanism for the development of PA is the constitutive activation of the wnt/β-catenin pathway. In accordance with this, Secreted Frizzled Related Protein 2 (SFRP2), a WNT inhibitor, was significantly downregulated in APAs compared to normal adrenal glands or non-functioning adrenal adenomas [11].
2.2.9. Cell Growth/Cell Death
In a SAGE study, although APAs are considered benign tumors, several oncogenes were identified as upregulated in comparison to normal adrenal glands, among others Jun-binding protein (JAB1), avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (v-MYC), IGF-binding protein-2 (IGFBP2), teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor (TDGF1), and nephroblastoma overexpressed gene (NOV). Although v-MYC, IGFBP2 and NOV overexpression was not confirmed by in situ hybridization, no clear conclusions can be made on the mechanisms of tumorigenesis in APAs [29][53]. The Teratocarcinoma-Derived Growth Factor 1 (TDGF1) upregulation in APAs has, however, been confirmed in another microarray study [54][78]. The apoptosis inhibitors BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist (BID) and Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 2 (BIRC2) and 3 (BIRC3) were also found overexpressed in a subgroup of APAs harboring CTNNB1 mutations [25][49].
2.2.10. Immune Response
In a very recent study, microarray analysis of APAs compared to adjacent adrenal cortex identified differentially expressed genes in a series of immune-related pathways, including inflammatory response, interferon-γ response, and IL-6, JAK/STAT3 signaling. APAs presented, in general, significant downregulation of immune related genes, with several of these genes belonging to pathways related to cellular response to oxidative stress, suggesting that oxidative stress may elicit an immune response in the adjacent adrenal cortex. On the contrary, adrenocortical tumor cells appeared to possess mechanisms for counteracting metabolic stress through upregulation of antioxidant systems. APAs were documented to display a high proportion of tumor cells, suggesting that their particular transcriptome profile enables them to escape from immune surveillance [55][75].
2.2.11. DNA Binding/RNA Polymerase
GATA Binding Protein 6 (GATA6), a gene with role in cellular differentiation via activation of HSD3B in the remodeled subcapsular adrenocortical zone, has shown pronounced upregulation in APAs compared to normal adrenals [24][48]. Paired Related Homeobox 1 (PRRX1), a gene related to tumorigenesis encoding a transcription co-activator, was found to be significantly overexpressed in APAs in a microarray study [27][51]. Dachshund Family Transcription Factor 1 (DACH1), a modulator of gene expression and mediator of steroidogenic responses with a role in the wnt/β-catenin pathway, is highly expressed in the ZG and has been identified as a ZG marker and a negative regulator of aldosterone secretion. DACH1 expression was found to be downregulated in APAs in comparison to normal adrenal glands [32][56][56,81].
2.2. Epigenetics
The complex regulation of autonomous aldosterone secretion not only includes an altered transcriptional regulation, but also involves further mechanisms such as DNA methylation and the effects of microRNAs.
In general, APAs present hypomethylation of several genes, in part already recognized as presenting transcriptional alterations. The gene with the most frequently hypomethylated promotor is CYP11B2, aldosterone synthase. In detail, the CpG island in the promotor region of CYP11B2 has been found to be hypomethylated in APAs, but not in blood samples of the same patients [57][83]. Similarly, hypomethylation of CYP11B2 was not observed in the adjacent adrenal tissue [58][59][84,85]. Additionally, the hypomethylated region of CYP11B2 has not been proven to be induced by the KCNJ5 or ATP1A1 mutations [60][86]. CYP11B2 hypomethylation in APAs with parallel hypercortisolemia was unchanged; however, these tumors also presented CYP11B1 promoter hypomethylation, especially at two CpG sites near the Ad1/cAMP response element binding site [61][87]. Furthermore, lower methylation levels of CYP11B2 are documented in APAs compared to APMs, suggesting a role of demethylation in a possible APM to APA transition [59][85].
In addition to these hypomethylated genes, APAs present hypomethylation in other differentially expressed genes, as presented above. In particular, the G-coupled-protein receptors PCP4, HTR4, MC2R, PTGER1 showed hypomethylation in APAs [50][62][71,88]. PCP4, one of the genes highly expressed in APAs, presented as one of the most hypomethylated genes in APAs [62][88]. In a study applying integration of transcriptome and methylome analysis in APAs and the adjacent adrenal gland, 34 genes presented upregulation with parallel CpG hypomethylation. These include aldosterone-related genes (CYP11B2, MC2R and hemopexin (HPX)) as well as genes related to tumorigenesis (PRRX, member RAS oncogene family (RAB38), fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP), Glucosaminyl (N-Acetyl) Transferase 2 (I Blood Group) (GCNT2)) and to differentiation (Calmodulin-like Protein 3 (CALML3)) [58][84]. Inversely, hypermethylation of AVPR1 and Protein Kinase C alpha (PRKCA) has been observed in APAs in comparison to normal adrenal glands [57][83]. Thus, not only is CYP11B2 hypomethylated in APAs, but several molecules related to CYP11B2 expression present differential methylation levels as well.
Unlike APAs, ACCs present global hypomethylation when compared to normal and benign tissues. In comparison with benign samples, ACCs present differential methylation status of several CpG sites, including those associated with Insulin Like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2) and H19 Imprinted Maternally Expressed Transcript (H19), Tumor Protein P53 (TP53), and CTNNB1. Interestingly, hypermethylation in both ACCs and benign samples has been documented for genes involved in apoptosis and transcriptional and cell cycle control, in particular for Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A (CDKN2), ATA Binding Protein 4 (GATA4), Histone Deacetylase 10 (HDAC10), PYD And CARD Domain Containing (PYCARD), and Secretoglobin Family 3A Member 1 (SCGB3A1) [63][89].
Several microRNAs were identified in APAs as modulators of CYP11B2 expression and are responsible for the differential regulation of other aldosterone production relevant genes as well. Among others, miR-24 was significantly downregulated in APAs in comparison to normal adrenal glands [64][90], while its levels were found to be significantly lower in APAs with KCNJ5 mutations than in those without. In parallel, a significant negative correlation of this microRNA with the expression levels of its target gene, Glutamate Receptor interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), has been demonstrated, possibly posing this gene as a candidate factor for aldosterone autonomy [65][91].
2.3. Metabolomics
One of the oldest approaches to investigating metabolome differences in APAs began decades ago with the initial observation that a patient with APA had elevated C-18-oxygenated steroids [66][95]. Later studies confirmed the observation that patients with APAs had elevated 18-hydroxycortisol and 18-oxocortisol, while patients with BAH did not present this laboratory phenotype [67][96]. As a next step, the quantification of these two steroids in the adrenal veins of patients with PA undergoing adrenal vein sampling (AVS) took place and an elevated 18-oxocortisol/cortisol ratio was found, indicating the dominant site in the AVS and allowing differentiation of patients with APAs from patients with BAH [68][97]. In an attempt to develop a less invasive testing method, urinary 18-hydroxycortisol levels were used with sufficient diagnostic accuracy to distinguish APAs from BAHs [69][98]. Several metabolic adaptations have since been described in tumorigenesis, with tumor cells undergoing metabolic reprogramming in order to address increased metabolic demands and enhance progression. Characteristic examples include increased glucolysis in cancer cells (the Warburg effect) and the dysregulation of lipid oxidation with increased β-oxidation and subsequent increased NADPH (also critical for adrenal steroidogenesis) with enhancement of CYP11A1 and CYP11B2 activity, possibly leading to increased aldosterone synthesis [55][75].
The introduction of liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in the quantification of adrenal steroids confirmed the previous data, and additionally widened the spectrum of investigated steroids. In addition to the clear elevation of plasma 18-oxocortisol in APAs, increased levels of plasma cortisol, corticosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA-S were documented in patients with BAH [70][71][99,100]. The combination of peripheral venous steroid profiles with the imaging data from CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has improved the diagnostic accuracy of correct subtype classification of PA.
Distinct patterns of urinary metabolites were observed in another study, enabling the grouping and distinguishing of essential hypertensives from PA patients and of APA from BAH patients. The identified metabolites include pyrimidine nucleoside and precursors, purine nucleotides and catabolites, and
Targeted metabolomics of blood samples of patients with endocrine hypertension (PA, Cushing syndrome, pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma) and essential hypertension can distinguish between the two groups and has identified four metabolites as being common discriminators of the two disease groups, namely the long-chain acylcarnitines C18:1, C18:2, ornithine, and spermidine [72][107].
Finally, a proteomic and phosphoproteomic profiling of APAs in comparison to adjacent adrenal tissue demonstrated that increased steroidogenesis in APA positively correlates with the upregulation of the respective steroidogenic enzymes (CYP11B2, CYP21A1, HSD3B2) and their phosphorylation, without any increase in the mitochondrial enzymes providing the energy for the catalyzation of these reactions. Furthermore, the same study identified two distinct protein expression patterns, one common for KCNJ5 tumors and their adjacent adrenal tissue and another for wild-type APAs for KCNJ5 and their controls. This study also documented altered extracellular matrix composition in APAs and identified overexpression of Ras Homolog Family Member C (RHOC), an actin-organizing factor, in APAs along with deregulation of the mechanistic target of the rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in these tumors [73][109].
