Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 3 by Jason Zhu and Version 2 by Jason Zhu.
Chemerin belongs to the adipokines—proteins secreted by white adipose tissue. It plays an important role in angiogenesis and metabolism and its levels correlate with inflammation severity in many clinical states.
- chemerin
- inflammatory bowel disease
- anti-TNF
1. Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic immune disease, with two main subtypes: Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). In recent years, the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease is rising very rapidly [1].
Adipokines are hormones secreted by white adipose tissue (WAT) [2]. One of these is chemerin, which has a pro- and also anti-inflammatory function, which was first identified in 1997 in keratinocyte and fibroblast cultures [3]. It is synthesized as an inactive prochemerin, which is converted into its active form by serine proteases. Chemerin is secreted in large amounts not only in WAT, but also in the skin, colon, and lungs [4][5]. It binds to three types of receptors: ChemR23, GPR-1, and CCRL2 [6].
High serum levels of chemerin have been found in systemic lupus erythematosus [7], diabetes mellitus [8], asthma [9], esophageal, gastric [10], and colorectal cancer [11]; it correlates with the severity of inflammation in many immune-related diseases—for example in systemic sclerosis or psoriasis [12][13]. It stimulates macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin (IL) 6. A study has shown an increase in the expression of ChemR23 receptors in endothelial cells caused by pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL 1β, IL-6, and TNF [14].
Most reports point to the pro-inflammatory role of chemerin, but some data show its anti-inflammatory effects. Chemerin reduces neutrophil transepithelial migration, and CHEmR23 activation enhances apical neutrophil clearance [15]. It was also observed that its activation by a chemerin isoform (chemerin 15) in peritoneal macrophages inhibited the production of inflammatory mediators in response to IFN-γ and LPS. Therefore, chemerin may also contribute to acute inflammation suppression or termination [16].
Until now, circulating chemerin in IBD patients was only rarely evaluated and showed inconsistent results [17][18][19][20]. It has been noticed that the clinical condition of patients negatively correlates with body mass index (BMI), which may be due to reduced consumption and absorption of nutrients, as well as increased energy expenditure caused by the disease [21].
Activation of ChemR23 causes the migration of dendritic cells (DCs) to inflammation sites and stimulates phagocytosis [22]. An increased number of these cells in biopsy specimens from patients with active IBD has been observed, which may point to a possible local pro-inflammatory role of chemerin [23]. In another study, it has been shown that the expression, secretion, and processing of chemerin in the cecum and colon are positively associated with the severity of inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. [24]. A breakthrough in the treatment of IBD was the introduction of biological agents mainly based on anti-TNF antibodies, such as infliximab (IFX) or adalimumab (ADA), which are highly efficacious in severe cases [25][26]. These drugs are used in a variety of inflammatory conditions, such as various types of arthritis, hidradenitis suppurativa and psoriasis [27][28]. In rheumatoid arthritis patients, a significant decrease in serum chemerin was observed following anti-TNF therapy [29]. Up to now, no similar studies have been performed in IBD.
2. Results
Patient characteristics are presented in Table 1.Table 1.
General characteristics of the study participants and the results of serum chemerin concentrations.
| Parameters | IBD Group | HC (n = 42) |
p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 77) |
Exacerbation (n = 48) |
Remission (n = 29) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (IQR) |
35 (29–41) |
35 (30–41) |
36 (26–41) |
31 (25–44) |
1 0.557 2 0.468 3 0.350 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| N women (%) | 39 (50.6) |
24 (50.0) |
15 (51.7) |
19 (45.2) |
1 0.527 2 0.955 3 0.583 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2; IQR) |
23.2 (20.2–256) |
No (n = 51)23.2 (20.6–26.1) |
23.2 (19.7–25.2) |
24.0 | 351.5 (±229.3–424.2)
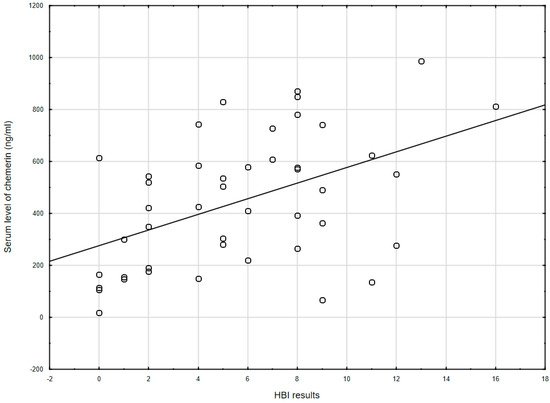 Figure 1. The correlation between chemerin concentration and the Harvey–Bradshaw index results (r = 0.478, p = 0.001) in CD patients. HBI: Harvey–Bradshaw index.
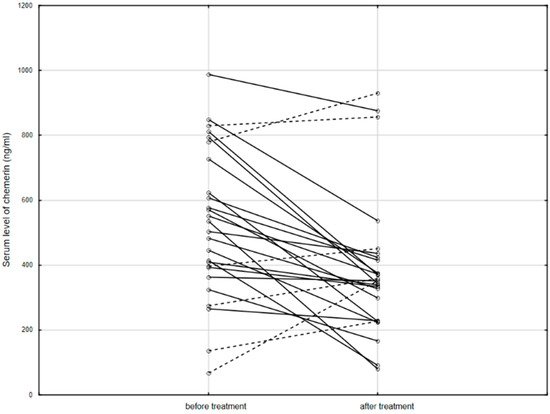 Figure 2. The serum level of chemerin in patients before and after anti-TNF therapy. Solid line: decreased concentration; dashed line: increased concentration.
Table 2. Relationship between the selected clinical parameters and the concentration of chemerin in the IBD patients’ blood serum.
3. ConclusionsIn conclusion, chemerin positively correlated with the clinical severity of IBD, and its level decreased after anti-TNF treatment. As shown in the present study, as well as in others, chemerin may be an indicator of clinical activity of IBD—CD in particular—as well as being useful in anti-TNF treatment monitoring. It would be useful to further compare the clinical value of chemerin with other known markers of IBD severity—in particular, with calprotectin. Additionally, future research should focus on the molecular basis of the relationship between chemerin levels and responses to anti-TNF therapy. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Dahlhamer, J.M.; Zammitti, E.P.; Ward, B.W.; Wheaton, A.G.; Croft, J.B. Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Among Adults Aged ≥18 Years—United States, 2015. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 1166–1169.
- Chudek, J.; Adamczak, M.; Nieszporek, T.; Wiecek, A. The Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ—A Nephrologists’ Perspective. Obes. Kidney 2006, 151, 70–90.
- Nagpal, S.; Patel, S.; Jacobe, H.; DiSepio, D.; Ghosn, C.; Malhotra, M.; Teng, M.; Duvic, M.; Chandraratna, R.A. Tazarotene-induced Gene 2 (TIG2), a Novel Retinoid-Responsive Gene in Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 109, 91–95.
- Zabel, B.A.; Silverio, A.M.; Butcher, E.C. Chemokine-Like Receptor 1 Expression and Chemerin-Directed Chemotaxis Distinguish Plasmacytoid from Myeloid Dendritic Cells in Human Blood. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 244–251.
- Mariani, F.; Roncucci, L. Chemerin/chemR23 axis in inflammation onset and resolution. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 85–95.
- Wittamer, V.; Franssen, J.-D.; Vulcano, M.; Mirjolet, J.-F.; Le Poul, E.; Migeotte, I.; Brézillon, S.; Tyldesley, R.; Blanpain, C.; Detheux, M.; et al. Specific Recruitment of Antigen-presenting Cells by Chemerin, a Novel Processed Ligand from Human Inflammatory Fluids. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 977–985.
- Li, H.-M.; Zhang, T.-P.; Leng, R.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Li, X.-M.; Liu, H.-R.; Ye, D.; Pan, H.-F. Emerging role of adipokines in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 820–830.
- Motawi, T.M.; Mahdy, S.G.; El-Sawalhi, M.M.; Ali, E.N.; El-Telbany, R.F.A. Serum levels of chemerin, apelin, vaspin, and omentin-1 in obese type 2 diabetic Egyptian patients with coronary artery stenosis. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 38–44.
- Zhou, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, Q.; Jin, M.; Jiang, E. Relationship of circulating chemerin and omentin levels with Th17 and Th9 cell immune responses in patients with asthma. J. Asthma 2017, 55, 579–587.
- Wang, C.; Wu, W.K.; Liu, X.; To, K.-F.; Chen, G.G.; Yu, J.; Ng, E.K. Increased serum chemerin level promotes cellular invasiveness in gastric cancer: A clinical and experimental study. Peptides 2014, 51, 131–138.
- Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, N.-K.; Chu, S.-H.; Lee, D.-C.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, J.-W.; Jeon, J.Y. Serum chemerin levels are independently associated with quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176929.
- Tekely, E.; Szostakiewicz-Grabek, B.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G. Serum levels of chemerin and pigment epithelium-derived factor in patients with psoriasis. Postępy Nauk Med. 2018, 31, 14–19.
- Sawicka, K.; Michalska-Jakubus, M.; Potembska, E.; Kowal, M.; Pietrzak, A.; Krasowska, D. Visfatin and chemerin levels correspond with inflammation and might reflect the bridge between metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2019, 36, 551–565.
- Kaur, J.; Adya, R.; Tan, B.K.; Chen, J.; Randeva, H.S. Identification of chemerin receptor (ChemR23) in human endothelial cells: Chemerin-induced endothelial angiogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1762–1768.
- Campbell, E.L.; Louis, N.A.; Tomassetti, S.E.; Canny, G.O.; Arita, M.; Serhan, C.N.; Colgan, S.P. Resolvin E1 promotes mucosal surface clearance of neutrophils: A new paradigm for inflammatory resolution. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 3162–3170.
- Cash, J.; Hart, R.; Russ, A.; Dixon, J.P.; Colledge, W.H.; Doran, J.; Hendrick, A.; Carlton, M.B.; Greaves, D.R. Synthetic chemerin-derived peptides suppress inflammation through ChemR23. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 767–775.
- Sochal, M.; Mosińska, P.; Fichna, J. Diagnostic value of chemerin in lower gastrointestinal diseases—A review. Peptides 2018, 108, 19–24.
- Weigert, J.; Obermeier, F.; Neumeier, M.; Wanninger, J.; Filarsky, M.; Bauer, S.; Aslanidis, C.; Rogler, G.; Ott, C.; Schäffler, A.; et al. Circulating levels of chemerin and adiponectin are higher in ulcerative colitis and chemerin is elevated in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 630–637.
- Terzoudis, S.; Malliaraki, N.; Damilakis, J.; Dimitriadou, D.A.; Zavos, C.; Koutroubakis, I.E. Chemerin, visfatin, and vaspin serum levels in relation to bone mineral density in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 814–819.
- Waluga, M.; Hartleb, M.; Boryczka, G.; Kukla, M.; Zwirska-Korczala, K. Serum adipokines in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6912–6917.
- Dong, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Pankaj, P.; Dai, N. Body Mass Index Is Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144872.
- Yoshimura, T.; Oppenheim, J.J. Chemokine-like receptor 1 (CMKLR1) and chemokine (C–C motif) receptor-like 2 (CCRL2); Two multifunctional receptors with unusual properties. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 674–684.
- Smrekar, N.; Drobne, D.; Smid, L.M.; Ferkolj, I.; Stabuc, B.; Ihan, A.; Kopitar, A.N. Dendritic cell profiles in the inflamed colonic mucosa predict the responses to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in inflammatory bowel disease. Radiol. Oncol. 2018, 52, 443–452.
- Dranse, H.J.; Rourke, J.L.; Stadnyk, A.W.; Sinal, C.J. Local chemerin levels are positively associated with DSS-induced colitis but constitutive loss of CMKLR1 does not protect against development of colitis. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12497.
- Sochal, M.; Krzywdzińska, M.; Gabryelska, A.; Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Małecka-Panas, E. Efficiency and safety of one-year anti-TNF-α treatment in Crohn’s disease: A Polish single-centre experience. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2020, 15, 156–160.
- Sochal, M.; Krzywdzińska, M.; Gabryelska, A.; Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Białasiewicz, P.; Małecka-Panas, E. A simple index to predict the efficiency of adalimumab treatment in Crohn’s disease with a limited duration of therapy. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020.
- Roberti, R.; Iannone, L.F.; Palleria, C.; De Sarro, C.; Spagnuolo, R.; Barbieri, M.A.; Vero, A.; Manti, A.; Pisana, V.; Fries, W.; et al. Safety profiles of biologic agents for inflammatory bowel diseases: A prospective pharmacovigilance study in Southern Italy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 1457–1463.
- Del Duca, E.; Morelli, P.; Bennardo, L.; Di Raimondo, C.; Nisticò, S.P. Cytokine Pathways and Investigational Target Therapies in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8436.
- Herenius, M.M.J.; Oliveira, A.S.F.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P.; Lebre, M.C. Anti-TNF Therapy Reduces Serum Levels of Chemerin in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A New Mechanism by Which Anti-TNF Might Reduce Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57802.
More
