Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most common of rare hereditary diseases in Caucasians, and it is estimated to affect 75,000 patients globally. CF is a complex disease due to the multiplicity of mutations found in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene causing the CFTR protein to become dysfunctional. Although CFTR is the main chloride channel in the lungs, others could, e.g., anoctamin-1 (ANO1 or TMEM16A), compensate for the deficiency of CFTR.
- cystic fibrosis
- anoctamin-1
- calcium-activated chloride channel
- CFTR-independent therapy
1. Introduction
2. Anoctamin-1
3. ANO1 in Cystic Fibrosis
3.1. Overview
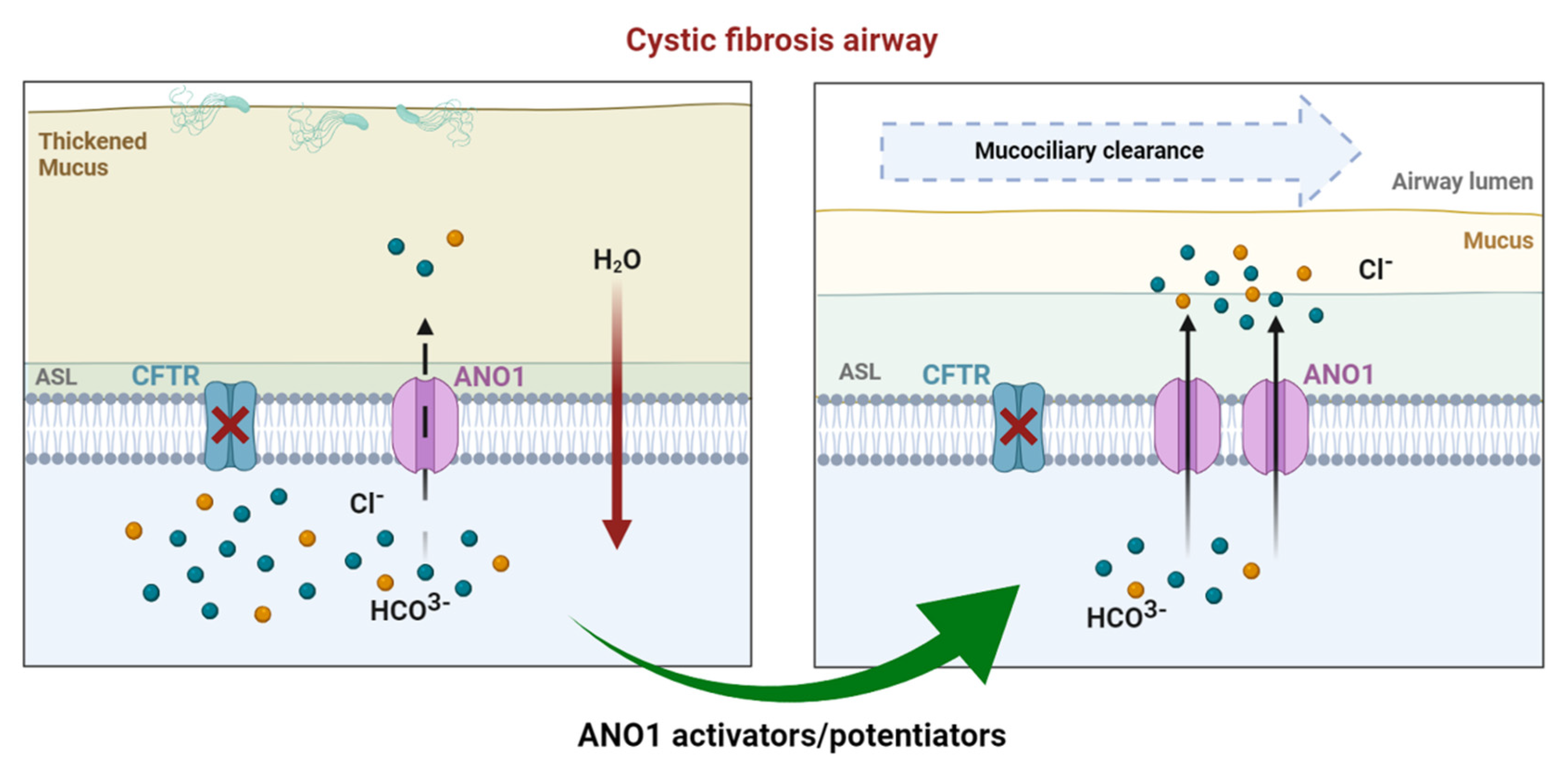
3.2. Drug Approaches Targeting ANO1 in Cystic Fibrosis
Inhibitors | Specificity | Assay | References | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ANI9 | Not specific | In vitro | ||||||||||
CCinh-A01 | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo |
[86] |
[26] |
||||||||
DIDS | Not specific | In vitro |
[87] |
[27] |
||||||||
Diphenylamine-2-carboxylate (DPC), 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino) benzoic acid | Not specific | In vitro |
[88] |
[28] |
||||||||
Flufenamic acid | Not specific | In vitro | ||||||||||
Niclosamide | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo |
[91] |
[31] |
||||||||
Niflumic acid | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo |
[92] |
[32] |
||||||||
Plumbagin | Not specific | In vitro |
[93] |
[33] |
||||||||
Quercetin | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo, clinical trial (phase II) | ||||||||||
Tannic acid | Not specific | In vitro |
[97] |
[37] |
||||||||
T16ainh-A01 | Specific | In vitro |
[86] |
[26] |
||||||||
Activators | ||||||||||||
Denufosol (INS37217) | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo, clinical trial (phase III failed) | ||||||||||
Duramycine (MOLI1901) | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo, clinical trial (phase II failed) |
[100] |
[45] |
||||||||
Eact | Not specific | In vitro |
[86] |
[26] |
||||||||
ETD002 (or ETX001) | Specific | In vitro, in vivo, clinical trial (phase I) |
[101] |
[46] |
||||||||
Interleukin 4 | Not specific | In vitro |
[14] |
|||||||||
Resveratrol | Not specific | In vitro, in vivo, clinical trial | ||||||||||
TSB ANO1 | Specific | In vitro, in vivo, preclinical |
[83] |
[50] |
References
- Cutting, G.R. Cystic fibrosis genetics: From molecular understanding to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 45–56.
- Lopes-Pacheco, M. CFTR Modulators: The Changing Face of Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1662.
- Li, H.; Salomon, J.J.; Sheppard, D.N.; Mall, M.A.; Galietta, L.J. Bypassing CFTR dysfunction in cystic fibrosis with alternative pathways for anion transport. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 34, 91–97.
- Mall, M.A.; Galietta, L.J. Targeting ion channels in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2015, 1, 561–570.
- Moore, P.J.; Tarran, R. The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) as a therapeutic target for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 687–701.
- Balazs, A.; Mall, M.A. Mucus obstruction and inflammation in early cystic fibrosis lung disease: Emerging role of the IL-1 signaling pathway. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54 (Suppl. 3), S5–S12.
- Cross, N.L. Initiation of the activation potential by an increase in intracellular calcium in eggs of the frog, Rana pipiens. Dev. Biol. 1981, 85, 380–384.
- Miledi, R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1982, 215, 491–497.
- Frings, S.D.; Reuter, B.; Kleene, S.J. Neuronal Ca2+-activated Cl-channels—Homing in on an elusive channel species. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 60, 247–289.
- Leblanc, N.; Ledoux, J.; Saleh, S.; Sanguinetti, A.; Angermann, J.; O’Driscoll, K.; Britton, F.; Perrino, B.A.; Greenwood, I.A. Regulation of calcium-activated chloride channels in smooth muscle cells: A complex picture is emerging. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 83, 541–556.
- Kidd, J.F.; Thorn, P. Intracellular Ca2+ and Cl-channel activation in secretory cells. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 493–513.
- Kunzelmann, K.; Tian, Y.; Martins, J.R.; Faria, D.; Kongsuphol, P.; Ousingsawat, J.; Thevenod, F.; Roussa, E.; Rock, J.; Schreiber, R. Anoctamins. Pflug. Arch. 2011, 462, 195–208.
- Dibattista, M.; Amjad, A.; Maurya, D.K.; Sagheddu, C.; Montani, G.; Tirindelli, R.; Menini, A. Calcium-activated chloride channels in the apical region of mouse vomeronasal sensory neurons. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 3–15.
- Caputo, A.; Caci, E.; Ferrera, L.; Pedemonte, N.; Barsanti, C.; Sondo, E.; Pfeffer, U.; Ravazzolo, R.; Zegarra-Moran, O.; Galietta, L.J. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science 2008, 322, 590–594.
- Schroeder, B.C.; Cheng, T.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride channel subunit. Cell 2008, 134, 1019–1029.
- Yang, Y.D.; Cho, H.; Koo, J.Y.; Tak, M.H.; Cho, Y.; Shim, W.S.; Park, S.P.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Kim, B.M.; et al. TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature 2008, 455, 1210–1215.
- Knowles, M.R.; Clarke, L.L.; Boucher, R.C. Activation by extracellular nucleotides of chloride secretion in the airway epithelia of patients with cystic fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 533–538.
- Frizzell, R.A.; Rechkemmer, G.; Shoemaker, R.L. Altered regulation of airway epithelial cell chloride channels in cystic fibrosis. Science 1986, 233, 558–560.
- Blouquit, S.; Regnier, A.; Dannhoffer, L.; Fermanian, C.; Naline, E.; Boucher, R.; Chinet, T. Ion and fluid transport properties of small airways in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 299–305.
- Benedetto, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Wanitchakool, P.; Zhang, Y.; Holtzman, M.J.; Amaral, M.; Rock, J.R.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Epithelial Chloride Transport by CFTR Requires TMEM16A. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12397.
- Benedetto, R.; Centeio, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Janda, M.; Kunzelmann, K. Transport properties in CFTR-/- knockout piglets suggest normal airway surface liquid pH and enhanced amiloride-sensitive Na(+) absorption. Pflugers Arch. 2020, 472, 1507–1519.
- Ruffin, M.; Voland, M.; Marie, S.; Bonora, M.; Blanchard, E.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Naline, E.; Puyo, P.; Le Rouzic, P.; Guillot, L.; et al. Anoctamin 1 dysregulation alters bronchial epithelial repair in cystic fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 2340–2351.
- Quinton, P.M. Role of epithelial HCO3(−) transport in mucin secretion: Lessons from cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C1222–C1233.
- Danahay, H.; Gosling, M. TMEM16A: An Alternative Approach to Restoring Airway Anion Secretion in Cystic Fibrosis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2386.
- Ramu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shin, H.G.; Lu, Z. Counteracting suppression of CFTR and voltage-gated K+ channels by a bacterial pathogenic factor with the natural product tannic acid. eLife 2014, 3, e03683.
- Genovese, M.; Borrelli, A.; Venturini, A.; Guidone, D.; Caci, E.; Viscido, G.; Gambardella, G.; di Bernardo, D.; Scudieri, P.; Galietta, L.J.V. TRPV4 and purinergic receptor signalling pathways are separately linked in airway epithelia to CFTR and TMEM16A chloride channels. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5859–5878.
- Gianotti, A.; Ferrera, L.; Philp, A.R.; Caci, E.; Zegarra-Moran, O.; Galietta, L.J.; Flores, C.A. Pharmacological analysis of epithelial chloride secretion mechanisms in adult murine airways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 781, 100–108.
- Danko, T.; Hargitai, D.; Pataki, A.; Hakim, H.; Molnar, M.; Zsembery, A. Extracellular alkalinization stimulates calcium-activated chloride conductance in cystic fibrosis human airway epithelial cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 27, 401–410.
- McCarty, N.A.; McDonough, S.; Cohen, B.N.; Riordan, J.R.; Davidson, N.; Lester, H.A. Voltage-dependent block of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- channel by two closely related arylaminobenzoates. J. Gen. Physiol. 1993, 102, 1–23.
- Reddy, M.M.; Quinton, P.M. Effect of anion transport blockers on CFTR in the human sweat duct. J. Membr Biol. 2002, 189, 15–25.
- Fischer, H.; Illek, B.; Sachs, L.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Widdicombe, J.H. CFTR and calcium-activated chloride channels in primary cultures of human airway gland cells of serous or mucous phenotype. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L585–L594.
- Cabrita, I.; Benedetto, R.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Niclosamide repurposed for the treatment of inflammatory airway disease. JCI Insight. 2019, 4, e128414.
- Scott-Ward, T.S.; Li, H.; Schmidt, A.; Cai, Z.; Sheppard, D.N. Direct block of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl(-) channel by niflumic acid. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2004, 21, 27–38.
- Yu, B.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Jin, L.; Xu, J.; Ma, T.; Yang, H. Plumbagin Prevents Secretory Diarrhea by Inhibiting CaCC and CFTR Channel Activities. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1181.
- Pyle, L.C.; Fulton, J.C.; Sloane, P.A.; Backer, K.; Mazur, M.; Prasain, J.; Barnes, S.; Clancy, J.P.; Rowe, S.M. Activation of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator by the Flavonoid Quercetin. Am. J. Respir Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 607–616.
- Zhang, S.; Smith, N.; Schuster, D.; Azbell, C.; Sorscher, E.J.; Rowe, S.M.; Woodworth, B.A. Quercetin increases cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-mediated chloride transport and ciliary beat frequency: Therapeutic implications for chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2011, 25, 307–312.
- Nasal Potential Studies Utilizing Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator (CFTR) Modulators. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01348204 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Deterding, R.; Retsch-Bogart, G.; Milgram, L.; Gibson, R.; Daines, C.; Zeitlin, P.L.; Milla, C.; Marshall, B.; Lavange, L.; Engels, J.; et al. Safety and tolerability of denufosol tetrasodium inhalation solution, a novel P2Y2 receptor agonist: Results of a phase 1/phase 2 multicenter study in mild to moderate cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2005, 39, 339–348.
- Deterding, R.R.; Lavange, L.M.; Engels, J.M.; Mathews, D.W.; Coquillette, S.J.; Brody, A.S.; Millard, S.P.; Ramsey, B.W. Phase 2 randomized safety and efficacy trial of nebulized denufosol tetrasodium in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 362–369.
- Goss, C.H.; McKone, E.F.; Mathews, D.; Kerr, D.; Wanger, J.S.; Millard, S.P. Experience using centralized spirometry in the phase 2 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of denufosol in patients with mild to moderate cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 147–153.
- Kellerman, D.; Rossi Mospan, A.; Engels, J.; Schaberg, A.; Gorden, J.; Smiley, L. Denufosol: A review of studies with inhaled P2Y(2) agonists that led to Phase 3. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 21, 600–607.
- Moss, R.B. Pitfalls of drug development: Lessons learned from trials of denufosol in cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 676–680.
- Accurso, F.J.; Moss, R.B.; Wilmott, R.W.; Anbar, R.D.; Schaberg, A.E.; Durham, T.A.; Ramsey, B.W.; T.-I.S. Group. Denufosol tetrasodium in patients with cystic fibrosis and normal to mildly impaired lung function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 627–634.
- Ratjen, F.; Durham, T.; Navratil, T.; Schaberg, A.; Accurso, F.J.; Wainwright, C.; Barnes, M.; Moss, R.B.; T.-S.I. Group. Long term effects of denufosol tetrasodium in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 539–549.
- Lancovutide (Moli1901) Inhalation Solution Study in Adolescents and Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00671736 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Danahay, H.L.; Lilley, S.; Fox, R.; Charlton, H.; Sabater, J.; Button, B.; McCarthy, C.; Collingwood, S.P.; Gosling, M. TMEM16A Potentiation: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 946–954.
- Lu, B.D.; Corey, A.; Kelley, T.J. Resveratrol restores intracellular transport in cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. Cells 2020, 318, L1145–L1157.
- Non-pulmonary Contributors of Exercise Intolerance in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04166396 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Mechanisms for Vascular Dysfunction and Exercise Tolerance in CF. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02690064 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Sonneville, F.; Ruffin, M.; Coraux, C.; Rousselet, N.; Le Rouzic, P.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Corvol, H.; Tabary, O. MicroRNA-9 downregulates the ANO1 chloride channel and contributes to cystic fibrosis lung pathology. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 710.
- Benedetto, R.; Cabrita, I.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. TMEM16A is indispensable for basal mucus secretion in airways and intestine. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4502–4512.
- Centeio, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Cabrita, I.; Schreiber, R.; Talbi, K.; Benedetto, R.; Dousova, T.; Verbeken, E.K.; De Boeck, K.; Cohen, I.; et al. Mucus Release and Airway Constriction by TMEM16A May Worsen Pathology in Inflammatory Lung Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2888.
- Clarke, L.A.; Botelho, H.M.; Sousa, L.; Falcao, A.O.; Amaral, M.D. Transcriptome meta-analysis reveals common differential and global gene expression profiles in cystic fibrosis and other respiratory disorders and identifies CFTR regulators. Genomics 2015, 106, 268–277.
- Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Kudo, M.; Peters, C.J.; Woodruff, P.G.; Solberg, O.D.; Donne, M.L.; Huang, X.; et al. Calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A modulates mucin secretion and airway smooth muscle contraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16354–16359.
- Simoes, F.B.; Quaresma, M.C.; Clarke, L.A.; Silva, I.A.; Pankonien, I.; Railean, V.; Kmit, A.; Amaral, M.D. TMEM16A chloride channel does not drive mucus production. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201900462.
- Danahay, H.L.; Morris, D.G.; Gosling, M. Reply to Olschewski et al.: TMEM16A Potentiation: Possible Drawbacks. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 905–906.
- Olschewski, A.; Nagaraj, C.; Zabini, D.; Nagy, B.M.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Olschewski, H. TMEM16A Potentiation: Possible Drawbacks. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 904–905.
