Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation. Upregulation of the IGF1R pathway constitutes a common paradigm shared with other receptor tyrosine kinases such as EGFR, HER2, and MET in different cancer types, including colon cancer. The main IGF1R signaling pathways are PI3K-AKT and MAPK-MEK. However, different processes, such as post-translational modification (SUMOylation), epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and microenvironment complexity, can also contribute to intrinsic and acquired resistance.
- insulin-like growth factor receptor
- metastatic colorectal cancer
1. Insulin and the IGF Pathway
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) are closely related ligands that interact with the insulin receptor (INSR) and IGF1 receptor (IGF1R) family of receptors. Insulin is considered to be a metabolic hormone activating INSR, whereas IGF1 is generally considered to be a growth factor activating IGF1R. IGF1R is a homodimeric, type II receptor tyrosine kinase comprising two extracellular α subunits and two β subunits. The extracellular α subunits are required for IGF1, IGF2, and insulin ligand binding, whereas the two β subunits contain an extracellular portion, transmembrane region, and intracellular tyrosine kinase catalytic domain and ATP-binding site. IGF1R is closely related to INSR, with sequence similarity varying from 41% to 84%, depending on the domain. The interaction of the ligands with IGF1R, INSR, or hybrid receptors activates numerous downstream pathways within the cell. Ligand-activated IGF1R first binds to intracellular adaptor proteins, predominantly insulin receptor substrates (IRS1–6) and Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein 1 (SHC). Subsequent phosphorylation of these proteins induces the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways [1][2][3]. In addition, IGF1R signals different nuclear transcription factors that contribute, through signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins [4], to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell survival via upregulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL [5], and adaptive metabolic reprogramming via promotion of glycolysis and glutamine consumption through MYC activation [6].
The bioavailability of IGF ligands is abnormally high in many cancers, and IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and IGFBP proteases are important for regulating ligand bioavailability [7]. Whereas IGF1R mutations have not been described in tumors, IGF1R mutations have been described as rare causes of intrauterine and postnatal growth disorders [8][9]. Polymorphisms in genes encoding either IGF1 or IGFBPs contribute to up- or downregulation of IGF1R function [10]. Upregulation of IGF1R and/or INSR constitutes a common paradigm mediating tumor resistance [11][12] in different cancer types and is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, squamous cell lung cancer, and prostate cancer [13][14][15].
2. Mechanism of Resistance Related to the IGF1R Pathway
2.1. IGF1R Resistance Due to Other Tyrosine Kinase Receptors and Metalloproteinases
IGF1R interacts with tumor suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes. Disturbances in components in the p53/MDM2 network may upregulate IGF1R and confer cancer cells with a growth advantage [16][17][18]. Compensatory signaling mediated by IGF2 through the INRS can contribute to resistance to IGF1R compounds [19]. IGFBP proteins are tightly regulated by serine proteases and matrix metalloproteinases, particularly matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7) [20][21][22][23], which is associated with poor prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) [24][25]. MMP7 can indirectly contribute to IGFBP degradation [26] and IGF1R-related chemoresistance through AKT-dependent [27] and -independent pathways [28].
Other relevant aspects related to IGF1R signaling involve interactions with other oncogenic tyrosine kinase receptors and mutations in downstream pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and RAS/MAPK [29]. Crosstalk between IGF1R and other RTKs, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), epidermal growth factor 2 receptor (HER2), VEGFR2, PDGFR, MET, and ALK, results in reciprocal compensatory mechanisms that limit the response or mediate acquired resistance to IGF1R therapies [30]. One example of this IGF1R-EGFR crosstalk has been recently described in acquired osimertinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer [31].
2.2. IGF1R, SUMOylation, and Other Post-Translational Procesess
SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) proteins are proteins of approximately 12 kDa in size with a structure similar to ubiquitin [32] that belong to a broader family of eukaryote-specific peptidic post-translational modifiers called ubiquitin-like (Ubl) proteins. SUMOs are present mainly in three isoforms in mammalian cells (SUMO-1 to -3; herein, collectively called SUMO), of which SUMO-1 is the most extensively studied, plus two other paralogs (SUMO-4 and -5) [33]. SUMOylation is mainly observed in nuclear and perinuclear proteins. SUMOylation can occur on both isolated proteins and those in supramolecular complexes where its molecular effects are often more difficult to decipher [34]. SUMOylation is a transitory and dynamic process in which SUMO proteins attach to lysine residues on targeted proteins. Only a small fraction of the targeted substrate is modified at any given time. Therefore, SUMO proteins are necessary to initiate a certain activity but not to maintain it [35].
There is functional crosstalk between the conjugation of SUMO to a substrate and other post-translational modifiers, mainly, ubiquitylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation. The interaction between ubiquitylation and SUMOylation is complex and SUMO and ubiquitin are often conjugated to the same substrate, lysine, acting antagonistically or sequentially [36]. Another post-translational modification that was recently identified as a SUMO regulator is acetylation. Acetylation of Ubc9 at residue K65 regulates the SUMOylation of some substrates [37]. There is also a complex interaction between SUMOylation and phosphorylation [38]. Phosphorylation of SUMO substrates can positively or negatively regulate their modification by SUMO, depending on the protein. On the other hand, SUMO can also regulate the phosphorylation system through the SUMOylation of kinases and phosphatases. SUMO proteins control cellular signaling networks and regulate, among others, DNA repair, differentiation, apoptosis, nuclear transport, and EMT differentiation [39][40][41][42][43].
Phosphorylation of IGF1R and its subsequent nuclear translocation has been reported to be mediated by SUMOylation [44]. IGF1R exhibits a different function when phosphorylated in the nucleus because it acts as a transcription regulator (instead of a tyrosine kinase receptor) and its nuclear location is associated with poor prognosis [45]. RANBP2 and PIAS3, the main SUMO E3 ligases, have been implicated in IGF1R nuclear accumulation [46][47]. In the nucleus, pIGF1R has AKT/MEK-independent properties, such as cyclin D1 and axin2 activation [48][49]. Interestingly, treatment of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, but not naïve cells, with IGF1R inhibitors (either ganitumab, a monoclonal antibody, or AEV-541, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor) promoted IGF1R nuclear internalization and PIAS3 inhibition decreased cytoplasm–nuclear IGF1R trafficking [47].
2.3. IGF1R and EMT
EMT is a well-known mechanism of intrinsic [50][51] and acquired [52] chemoresistance. IGF1R signaling was recently implicated in EMT induction/maintenance through STAT3/NANOG/Slug [53] but also, importantly, was found to contribute to acquired chemoresistance [54][55]. Although IGF1R and EMT markers have been shown to be upregulated in drug-tolerant cells, the exact mechanism of resistance remains unknown. In addition, IGF-alternative mechanisms of EMT induction include NF-KB activation [56], WNT/β-catenin [57], and TGFβ/SMAD activation [58], extensively reviewed by Li et al. [59]. Therefore, because other alternatives that are at least partially IGF1R-independent promote EMT, combinations of EMT inhibitors with IGF1R inhibitors are more likely to be effective in CRC.
2.4. IGF1R and the Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment includes cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and vascular and immune cells. CAFs and myeloid cells contribute to STAT3 activation in cancer cells through IL-6, CCL2, TGFB, and CCL5 release, and promote regulatory T-cell (Treg) expansion [60]. Preclinical data concerning the combination of IGF1R and STAT3 inhibitors, but not IGF1R inhibition alone, showed a reduction in tumor burden through CAF and myeloid cell depletion [60][61]. Interestingly, anti-IGF1R therapies (cixutumumab) or radiotherapy can promote an immune-suppressive microenvironment due to IGF2- [61] or CAF-dependent IGF1 release from cancer cells [62]. In this latter work, radiotherapy-activated CAFs promoted the survival of CRC cells through metabolic reprogramming (favoring increased glycolysis and glutamine consumption). Therefore, this seminal paper indicates that paracrine IGF/IGF1R signaling contributes to metabolic reprogramming (induction of lactate and glutamine consumption) [63][64][65], a well-known mechanism in the immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment, due to M2 polarization [66] and Treg selection [67].
3. IGF1R Pathway: Lessons to Learn for Adequate Drug Development in RAS Wild-Type mCRC Patients
3.1. IGF1R in the Clinical Scenario
Several studies have evaluated the activity of the IGF1R receptor or its ligands (either IGF1 or IGF2) or IGFBPs as a surrogate marker of chemotherapy or anti-EGFR or anti-IGF1R resistance (see Table 1). Although the activity of the receptor (IGF1R phosphorylation) would be a solid biomarker, the similarity of IGF1R with INSR complicates the application of this approach in clinical practice. A pIGF1R antibody (anti-pY1316, a COOH-terminal antibody provided by Dr. Rubini) was used by our group to address IGF1R activation. Curiously, nuclear pIGF1R staining (which occurs in less than 10% of patients), but no other more common patterns of staining (such as cytoplasmic or membrane-associated), is correlated with chemotherapy and targeted therapy resistance [68].
Table 1. IGF1R pathway biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer.
| Author | Study Design | Treatment Arms | LB/N | Biomarker Methodology | Biomarker | Conclusion |
|---|
[93][94]. This aspect is important because 30–35% of included patients basally had RAS or BRAF mutations that are related to intrinsic EGFR resistance [94]. Therefore, we propose that new agents or re-challenge strategies in patients progressing to anti-EGFR include only patients with liquid biopsy determination of the RAS and BRAF genotype. In ongoing EGFR re-challenge studies or those with new compounds (anti-HER2 and anti-MET), liquid biopsy is not mandatory to exclude RAS/BRAF patients. We believe that this limitation can compromise the efficacy of new drugs.
3.3.2. Prospective Trials with New Strategies or New Compounds (HER2 Inhibitors, MET Inhibitors, and Re-Challenge with EGFR Inhibitors [Cetuximab or Panitumumab])
The IGF axis has been proposed as a target for anticancer therapies. Antibody, tyrosine kinase, and ligand inhibitors of the IGF receptor have been studied. In phase I trials, these antibodies seem to be well-tolerated; the most common toxicity is hyperglycemia [95]. Early-phase trials in the last lines of treatment showed promising results, mainly a stable response, but the results were negative in later-phase trials. The efficacy of anti-IGF1R and Sym004 was hugely disappointing, with nearly null activity with anti-IGF1R compounds (ganitumab, figitumumab, and dalotuzumab) and less than a 15% response rate with Sym004 [71][74][93][94]. One of the major limitations in these studies is the absence of targeted biomarker selection. This is a potentially important issue to address with new strategies (re-challenge with EGFR compounds [96]) or new agents (HER2 and MET inhibitors). Re-challenge strategies lack a suitable biomarker for patient selection, but only patients with HER2+++ overexpression (with DS8201) or patients with MET amplification should probably be included with new agents. The importance of biomarker selection has been highlighted by the low activity of MET inhibitors without biomarker selection [97][98].
A second important area concerns the trial design itself. Although objective responses have been reported with re-challenge anti-EGFR strategies involving cetuximab and irinotecan, the overall response rate is less than 15% [96]. It is important to note that, in this trial, it is unclear if the efficacy was due to irinotecan, cetuximab, or their combination. Regardless, the benefit in the subgroup of patients without RAS/BRAF mutation seems very modest (median progression-free survival (PFS), 4.1 months). We speculate that the efficacy of new strategies (e.g., re-challenge with anti-EGFR) or new compounds would probably not deserve further phase III trial development if monotherapy activity is below 30%, which is the expected response rate in the CHRONOS trial. In randomized clinical trials with standard-of-care schedules in second-line therapies (e.g., FOLFIRI in the BEYOND trial) or third-line therapies (regorafenib or TAS-102 in the PULSE trial, TAS-102 in the VELO trial, or regorafenib or investigator choice in the FIRE-4 trial), significant differences in PFS or overall survival (OS) should be calculated based on ESMO-MCBS expectations.
Five clinical trials have reported HER2 inhibitor activity in pretreated double wild-type RAS and BRAF mutation (2WT) mCRC patients with HER2 overexpression or amplification [99][100][101][102][103] (Table 2). Four phase II trials have evaluated combinations of trastuzumab with lapatinib [99], trastuzumab plus pertuzumab (100,101), or trastuzumab/T-DM1 plus pertuzumab [102]. Response rates ranged from 9% to 35% with a modest median PFS of 4 months. The only reported phase II study with trastuzumab-deruxtecan (DS-8201a), DESTINY-CRC 001, showed a promising 45% BOR and median survival of 7 months [103]. DS-8201a is a HER2-targeting antibody–drug conjugate, structurally composed of a human anti-human HER2 antibody, an enzymatically cleavable peptide linker, and a topoisomerase I inhibitor (DX-8951). The results of the DESTINY-CRC 001 are in accordance with preclinical data showing that DS-8201a has improved antitumor efficacy compared with T-DM1 [104]. In view of these results, the development of DS-8201a in HER2-positive mCRC patients has been prioritized. The DESTINY-CRC03 clinical trial will compare DS-8201a vs. standard of care in second-line 2WT CRC patients with HER2+++ overexpression.
Table 2. New strategies in 2WT mCRC patients after anti-EGFR progression.
| Author | Design(n) | Treatment arms | LLB at Entry * | Biomarker Driven **/Targeted Therapy BiBiomarker Driven **/Targeted Therapyomarker Selection | BOR% | PFS (m) | mOS (m) | ESMO-MCBS: ESMO-Magnitude Clinical Benefit Scale | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winder et al. [10] | Retrospective/prospective | Cetuximab | No/130 | ||||||||||||
| Montagut et al. [94] | II-R (254) | Sym004-12 mg/kg vs. Sym004-9 mg/kg vs. Investigator choice | No | Polymorphisms | IGF1 (rs2946834-AA) | Increased efficacy | |||||||||
| No | 14.1 | 9.6 | 2.9 | - - - |
11.9 8.9 8.4 |
1 | Codony-Servat et al. [47] | Retrospective/prospective | CHT+/−mAb | No/470 | IHC | High pIGF1R (nuclear) | Decreased efficacy | ||
| Cremolini et al. [96] | II (28) | Irinotecan-Cetuximab | No | No | 14 | 4.1 ** | - | NA | Fuchs et al. [69] | Retrospective/prospective | CHT | Yes/527 | ELISA | High IGFBP3 and IGF1 | Improved OS |
| Rimassa et al. [97] | II (41) | Tivantinib-Cetuximab | No | No | 9.8 | 2.6 | - | García-Albéniz et al. [70] | Retrospective | CHT | Yes/41 | ELISA | IGF1 increment | Improved OS | |
| Van Cutsem et al. [71] | Retrospective/prospective | Ganitumab-Panitumumab vs Panitumumab | Yes/94 | ELISA | High IGFBP1 and IGFBP2 | Improved OS | |||||||||
| Guercio et al. [72] | Prospective | CHT+mAb | Yes/1084 | ELISA | High IGFBP3 and IGFBP7 | Improved OS | |||||||||
| Scartozzi et al. [73] | Retrospective | I-Cetuximab | No/112 | IHC | Low IGF1 | Increased efficacy | |||||||||
| Sclafani et al. [74] | Retrospective/prospective | Dalotozumab-Cetuximab-I vs Cetuximab-I | No/344 | IHC | High IGF1 | Decreased OS | |||||||||
| Huang et al. [75] | Retrospective | Cetuximab | No/70 | RNA expression | High IGF1R | Increased efficacy |
CHT, chemotherapy; LB, liquid biopsy; N, number of patients included; I, irinotecan; IHC, immunohistochemistry; mAb, monoclonal antibody; pIGF1R, phosphorylated IGF1R.
Our group and others have evaluated potential IGF biomarkers based on liquid biopsy (ligands (IGF or IGFBP) by ELISA) [69][70][71][72] or IGF, IGFBP, and/or IGF1R protein in paraffin-embedded tissues (immunohistochemistry [73][74]), DNA (polymorphisms [10]), or RNA expression [75]. Global interpretation is hampered by trial design (most results are derived from retrospective analysis that were not designed for this purpose), nonstandardized biomarker cut-offs, and the use of different techniques (ELISA, DNA polymorphisms, and RNA expression). However, we conclude that high levels of IGFBP could identify a subgroup of mCRC patients with better prognosis [72]. It remains unclear whether any of these markers would predict the efficacy of IGF1R or EGFR inhibitors.
3.2. Liquid Biopsy in RAS Wild-Type Anti-EGFR Pretreated Patients to Select Optimal Patients for New Therapies. Mechanism of Resistance
The identification of biomarkers of the response to anti-EGFR therapy has proven to be promising. The monoclonal antibodies cetuximab and panitumumab, which neutralize the extracellular domain of EGFR, have demonstrated effectiveness, in terms of both a better response and improved survival when used as first-, second-, or third-line treatment regimens. Unfortunately, however, patients with mCRC who have mutant RAS (KRAS/NRAS; ~55%) or BRAF (V600E; ~5–10%) genes do not derive any therapeutic benefit from anti-EGFR drugs [76][77]. Although patients with wild-type (WT) RAS and BRAF (30–35% of mCRC patients) are sensitive to first-line chemotherapy plus anti-EGFR treatment (best overall response (BOR) range, 55–75%) [78][79][80], most of these patients develop resistance within the first 2 years. Primary inter- and intratumor heterogeneity and acquisition of secondary RAS and BRAF mutations during the course of such treatments are the major factors responsible for acquired resistance [81][82][83][84][85][86][87][88] (Figure 1). The recent gene expression-based molecular classification of consensus molecular subtypes (CMSs) has demonstrated the existence of phenotypic heterogeneity in CRC [89], highlighting the need for improved risk stratification and selection of patient populations before any specific treatment options are offered. Although the CMS classification in mCRC suggested prognostic significance, its clinical significance in terms of predicting the response to anti-EGFR therapy remains unclear [90][91][92]. Furthermore, given that genetic mutations can induce certain gene expression phenotypes in CRC, a comprehensive phenotypic exploration (including not only cancer epithelial cells, but also the tumor cell-type microenvironment) is critically required to establish biomarkers that can robustly predict the response to anti-EGFR therapies.
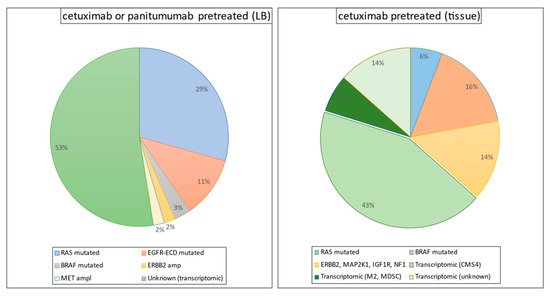
Figure 1. Mutation profile in biopsy and liquid biopsy (LB) samples from pretreated colorectal patients with KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF wild-type.
3.3. New Targeted Agents in Anti-EGFR Pretreated Patients with RAS Wild-Type mCRC
3.3.1. Selection of Optimal Patients with Liquid Biopsy (RAS and BRAF)
CRC patients included in clinical trials of anti-IGF1R compounds and Sym004 (a mixture of two monoclonal antibodies—futuximab and modotuximab—that binds epitopes in the EGFR extracellular domain) were not selected based on RAS/BRAF WT in liquid biopsy [8][71]
| NA | ||||||||
| Delord et al. | ||||||||
| [98] | I-II (13) | Capmatinib-Cetuximab | No | No | 0 | - | - | NA |
| Sartore-Bianchi et al. [99] | II (27) | Trastuzumab-Lapatinib | No | Yes/HER2 (+++) | 26 | 5.1 | - | NA |
| Nakamura et al. [100] | II (18) | Trastuzumab-Pertuzumab | Yes | Yes/HER2 (amplification) | 35 | 4 | - | NA |
| Gupta et al. [101] | II (28) | Trastuzumab-Pertuzumab | No | Yes/HER2 (+++) | 25 | 4.2 | - | NA |
| Sartore-Bianchi et al. [102] | II (31) | TDM1-Pertuzumab | No | Yes/HER2 (+++) | 9.7 | 4.1 | - | NA |
| Siena et al. [103] | II (53) | Trastuzumab-Deruxtecan | No | Yes/HER2 (+++) | 43.4 | 6.9 | - | NA |
| CHRONOS * | II (129) | Panitumumab | Yes | No | - | - | - | - |
| BEYOND * | II-R (85) | FOLFIRI-Panitumumab vs FOLFIRI | Yes | No | - | - | - | - |
| VELO * | II-R (112) | TAS-102-Panitumumab vs TAS-102 | No | No | - | - | - | - |
| PULSE * | II-R (106) | Panitumumab vs Regorafenib or TAS-102 | Yes | No | - | - | - | - |
| FIRE-4 * | III (230) | Irinotecan-Cetuximab vs Regorafenib or Investigator choice | No | No | - | - | - | - |
| PERSPECTIVE * | II (48) | Tepotinib-Cetuximab | Yes | Yes/MET (amplification) | - | - | - | - |
2WT, double wild-type for RAS and BRAF mutations; N, number; LB, liquid biopsy; BOR, best overall response; mPFS, median progression-free survival in months; mOS, median overall survival in months; ESMO-MCBS, ESMO-Magnitude Clinical Benefit Scale; NA, not applicable. * Prospective studies without available results. ** Patients without mutations in liquid biopsy. (+++) Amplification 3 crosses.
MET inhibitors (capmatinib and tivantinib) have been tested in combination with cetuximab in two phase II studies [97][98]. Globally, in nonselected patients, the activity is very modest with a BOR < 10% and a less than 3-month median PFS. An unplanned subanalysis with tivantinib suggested that MET-amplified patients would be more sensitive to MET inhibition. Due to this subanalysis, a prospective clinical trial has recently begun recruiting mCRC patients with MET amplification (PERSPECTIVE). Although this trial will include only mCRC patients with MET amplification, other well-known resistance mechanisms such as EMT (which increases not only hepatocyte growth factor, but also other alternative EMT-driven biomarkers) would also contribute to tepotinib-cetuximab resistance [105].
3.3.3. EGFR and Trastuzumab-Acquired Resistance
In addition to genetic mutations, a comprehensive profiling of gene expression patterns and their application in tissue and plasma samples might not only allow identification of superior predictive biomarkers for anti-EGFR therapy, but also further understanding of potential new strategies (such as re-challenge with anti-EGFR) or the addition of new agents. Indeed, less than 30% of patients that progress to chemotherapy plus anti-EGFR compounds can currently be explained by genetic resistance mechanisms and detected by ctDNA analysis. A transcriptomic resistance mechanism to cetuximab has recently been described, emphasizing the importance of the immune microenvironment in anti-EGFR resistance [88]. Cetuximab and panitumumab exert at least part of their activity through Fc-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), although this mechanism of resistance has largely been unexplored. ADCC activity is hampered by M2 microenvironment polarization [106][107] or antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) loss mediated by dendritic cells [108] and, therefore, deciphering immune microenvironment changes could potentially improve current anti-EGFR efficacy.
Trastuzumab activity in preclinical models has recently been associated with ADCP mediated by macrophages but not with ADCC through natural killer cells or neutrophils, complement cellular cytotoxicity (CDC), or T-cell adaptive immunity [109]. CD47 overexpression in cancer cells (a “do not eat me” receptor) has been inversely associated with trastuzumab efficacy. DS-8201a, also in a preclinical CRC mouse model, upregulates CD86, dendritic cells, and CD8 T-cells and PD-L1 and MHC-I in tumor cells, which emphasizes the importance of not only ADCP, but also adaptive immunity in drug activity. It seems that its crucial effect on immune activation is specifically due to the effect of deruxtecan [110]. Despite these preclinical data with trastuzumab and DS8201a, only 45% of patients clinically responded to DS8201a and less than 30% to trastuzumab plus lapatinib or pertuzumab. In addition, most initial responders (>90% of cases) progress in the first year. Therefore, understanding of how metabolic reprogramming can impair ADCP function or how chronic therapeutic antibody-mediated ADCP stimulation can influence acquired mechanisms of trastuzumab or DS8201a resistance would be valuable. Autophagy, a metabolic reprogramming process increased in highly hypoxic nutrient-deprived tumors such as pancreatic adenocarcinomas [111], has recently been shown to increase immune suppression [112][113]. It is further unclear how autophagy suppresses the immune system, although Yamamoto et al. suggest that autophagy increases immunosuppression through reduced MCH-I expression [112]. Other authors indicate that autophagy can decrease TNFα-dependent cell death by immune CD8+ T-cells [113]. We are tempted to speculate that continuous ADCP stimulation (either by cancer-mediated autophagy metabolic reprogramming or antibody-mediated stimuli) induces LAP-dependent M2 polarization [114] and PD-L1 and IDO-1 expression [115] (see Figure 2).
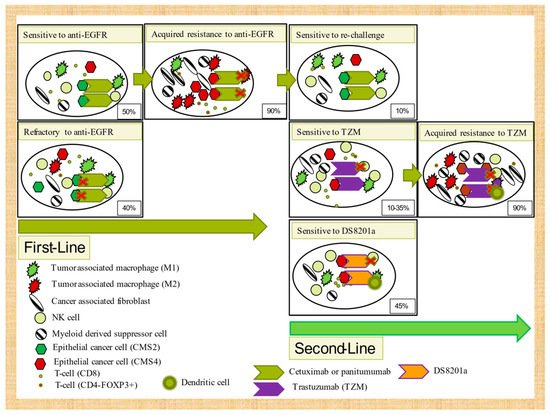
Figure 2. Tumor microenvironment mechanisms of intrinsic and acquired resistance to targeted therapies in 2WT RAS/BRAF colorectal cancer.
References
- Gallagher, E.J.; Leroith, D. Hyperinsulinaemia in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 629–644.
- Li, J.; Choi, E.; Yu, H.; Bai, X. Structural basis of the activation of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11.
- Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.-I. 40 years of IGF1: IGF1 receptor signaling pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T69–T86.
- Himpe, E.; Kooijman, R. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction and the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway. BioFactors 2009, 35, 76–81.
- Sekharam, M.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Dan, H.C.; Boulware, D.; Cheng, J.Q.; Coppola, D. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Enhances Invasion and Induces Resistance to Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells through the Akt/Bcl-XL Pathway. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7708–7716.
- Werner, H. Tumor suppressors govern insulin-like growth factor signaling pathways: Implications in metabolism and cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2703–2714.
- Xu, Y.; Kong, G.K.-W.; Menting, J.G.; Margetts, M.B.; Delaine, C.A.; Jenkin, L.M.; Kiselyov, V.V.; De Meyts, P.; Forbes, B.E.; Lawrence, M.C. How ligand binds to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13.
- Abuzzahab, M.J.; Schneider, A.; Goddard, A.; Grigorescu, F.; Lautier, C.; Keller, E.; Kiess, W.; Klammt, J.; Kratzsch, J.; Osgood, D.; et al. IGF-I Receptor Mutations Resulting in Intrauterine and Postnatal Growth Retardation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2211–2222.
- Solomon-Zemler, R.; Basel-Vanagaite, L.; Steier, D.; Yakar, S.; Mel, E.; Phillip, M.; Bazak, L.; Bercovich, D.; Werner, H.; De Vries, L. A novel heterozygous IGF-1 receptor mutation associated with hypoglycemia. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 395–403.
- Winder, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Ning, Y.; Bohanes, P.; Gerger, A.; Wilson, P.M.; Pohl, A.; Mauro, D.J.; Langer, C.; et al. Germline Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in the IGF1 Pathway Predict Efficacy of Cetuximab in Wild-type KRAS mCRC Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5591–5602.
- Forest, A.; Amatulli, M.; Ludwig, D.L.; Damoci, C.B.; Wang, Y.; Burns, C.A.; Donoho, G.P.; Zanella, N.; Fiebig, H.H.; Prewett, M.C.; et al. Intrinsic Resistance to Cixutumumab Is Conferred by Distinct Isoforms of the Insulin Receptor. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1615–1626.
- Hopkins, B.D.; Pauli, C.; Du, X.; Wang, D.G.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Amadiume, S.C.; Goncalves, M.D.; Hodakoski, C.; Lundquist, M.R.; et al. Suppression of insulin feedback enhances the efficacy of PI3K inhibitors. Nature 2018, 560, 499–503.
- Ahearn, T.U.; Peisch, S.; Pettersson, A.; Ebot, E.M.; Zhou, C.K.; Graff, R.E.; Sinnott, J.A.; Fazli, L.; Judson, G.L.; Bismar, T.A.; et al. Expression of IGF/insulin receptor in prostate cancer tissue and progression to lethal disease. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1431–1437.
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, W.; Streicher, K.; Morehouse, C.; Brohawn, P.; Ge, X.; Dong, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhu, G.; Gu, Y.; et al. Increased IR-A/IR-B ratio in non-small cell lung cancers associates with lower epithelial-mesenchymal transition signature and longer survival in squamous cell lung carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 131.
- Law, J.H.; Habibi, G.; Hu, K.; Masoudi, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Stratford, A.L.; Park, E.; Gee, J.M.; Finlay, P.; Jones, H.E.; et al. Phosphorylated Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I/Insulin Receptor Is Present in All Breast Cancer Subtypes and Is Related to Poor Survival. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10238–10246.
- Werner, H.; Karnieli, E.; Rauscher, F.J.; Leroith, D. Wild-type and mutant p53 differentially regulate transcription of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8318–8323.
- Girnita, L.; Girnita, A.; Brodin, B.; Xie, Y.; Nilsson, G.; Dricu, A.; Lundeberg, J.; Wejde, J.; Bartolazzi, A.; Wiman, K.G.; et al. Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor I receptor in malignant cells expressing aberrant p53: Functional impact. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5278–5283.
- Girnita, L.; Girnita, A.; Larsson, O. Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8247–8252.
- Garofalo, C.; Mancarella, C.; Grilli, A.; Manara, M.C.; Astolfi, A.; Marino, M.T.; Conte, A.; Sigismund, S.; Carè, A.; Belfiore, A.; et al. Identification of Common and Distinctive Mechanisms of Resistance to Different Anti-IGF-IR Agents in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1603–1616.
- Adachi, Y.; Li, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Min, Y.; Piao, W.; Wang, Y.; Imsumran, A.; Li, H.; Arimura, Y.; Lee, C.-T.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor blockade reduces the invasiveness of gastrointestinal cancers via blocking production of matrilysin. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1305–1313.
- Miyamoto, S.; Yano, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Ishii, G.; Hasebe, T.; Endoh, Y.; Kodama, K.; Goya, M.; Chiba, T.; Ochiai, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 facilitates insulin-like growth factor bioavailability through its proteinase activity on insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 665–671.
- Nakamura, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Maeda, H.; Ishii, G.; Hasebe, T.; Chiba, T.; Asaka, M.; Ochiai, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 degrades all insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and facilitates insulin-like growth factor bioavailability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 1011–1016.
- Miyamoto, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yano, K.; Ishii, G.; Hasebe, T.; Endoh, Y.; Sangai, T.; Maeda, H.; Shi-Chuang, Z.; Chiba, T.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 triggers the matricrine action of insulin-like growth factor-II via proteinase activity on insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 in the extracellular matrix. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 685–691.
- Adachi, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Itoh, F.; Hinoda, Y.; Okada, Y.; Imai, K. Contribution of matrilysin (MMP-7) to the metastatic pathway of human colorectal cancers. Gut 1999, 45, 252–258.
- Maurel, J.; Nadal, C.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Gallego, R.; Carcereny, E.; Almendro, V.; Mármol, M.; Gallardo, E.; Augé, J.M.; Longarón, R.; et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels identifies poor prognosis advanced colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1066–1071.
- Gallego, R.; Codony-Servat, J.; García-Albéniz, X.; Carcereny, E.; Longarón, R.; Oliveras, A.; Tosca, M.; Augé, J.M.; Gascón, P.; Maurel, J. Serum IGF-I, IGFBP-3, and matrix metalloproteinase-7 levels and acquired chemo-resistance in advanced colorectal cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 311–317.
- Jenkins, P.J.; Khalaf, S.; Ogunkolade, W.; McCarthy, K.; David, T.; Hands, R.E.; Davies, D.; Bustin, S.A. Differential expression of IGF-binding protein-3 in normal and malignant colon and its influence on apoptosis. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 891–901.
- Williams, A.C.; Smartt, H.; H-Zadeh, A.M.; Macfarlane, M.; Paraskeva, C.; Collard, T.J. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human colorectal carcinoma cells through inhibition of NF-κB. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 137–145.
- Cao, L.; Yu, Y.; Darko, I.; Currier, D.; Mayeenuddin, L.H.; Wan, X.; Khanna, C.; Helman, L.J. Addiction to Elevated Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor and Initial Modulation of the AKT Pathway Define the Responsiveness of Rhabdomyosarcoma to the Targeting Antibody. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8039–8048.
- Simpson, A.; Petnga, W.; Macaulay, V.M.; Weyer-Czernilofsky, U.; Bogenrieder, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Pathway Targeting in Cancer: Role of the IGF Axis and Opportunities for Future Combination Studies. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 571–597.
- Wang, R.; Yamada, T.; Kita, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, K.; Terashima, M.; Ishimura, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; et al. Transient IGF-1R inhibition combined with osimertinib eradicates AXL-low expressing EGFR mutated lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–14.
- Kotamarthi, H.C.; Sharma, R.; Ainavarapu, S.R.K. Single-Molecule Studies on PolySUMO Proteins Reveal Their Mechanical Flexibility. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2273–2281.
- Chang, H.-M.; Yeh, E.T.H. SUMO: From Bench to Bedside. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 1599–1619.
- Boulanger, M.; Chakraborty, M.; Tempé, D.; Piechaczyk, M.; Bossis, G. SUMO and Transcriptional Regulation: The Lessons of Large-Scale Proteomic, Modifomic and Genomic Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 828.
- Geiss-Friedlander, R.; Melchior, F. Concepts in sumoylation: A decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 947–956.
- Denuc, A.; Marfany, G. SUMO and ubiquitin paths converge. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 34–39.
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Kuo, H.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Naik, M.T.; Liao, P.H.; Ho, C.C.; Huang, T.C.; Jeng, J.C.; Hsu, P.H.; Tsai, M.D.; et al. Ubc9 acetylation modulates distinct SUMO target modification and hypoxia response. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 791–804.
- Wilkinson, K.A.; Henley, J.M. Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation. Biochem. J. 2010, 428, 133–145.
- Wasik, U.; Filipek, A. Non-nuclear function of sumoylated proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2878–2885.
- Bogachek, M.V.; De Andrade, J.P.; Weigel, R.J. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through SUMOylation of transcription factors. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 11–15.
- Du, L.; Li, Y.-J.; Fakih, M.; Wiatrek, R.L.; Duldulao, M.; Chen, Z.; Chu, P.; Garcia-Aguilar, R.L.W.M.D.Z.C.J.; Chen, Y. Role of SUMO activating enzyme in cancer stem cell maintenance and self-renewal. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11.
- Rabellino, A.; Andreani, C.; Scaglioni, P.P. The Role of PIAS SUMO E3-Ligases in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1542–1547.
- Seeler, J.-S.; Dejean, A. SUMO and the robustness of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 184–197.
- Sehat, B.; Tofigh, A.; Lin, Y.; Trocmé, E.; Liljedahl, U.; Lagergren, J.; Larsson, O. SUMOylation Mediates the Nuclear Translocation and Signaling of the IGF-1 Receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra10.
- Aleksic, T.; Chitnis, M.M.; Perestenko, O.V.; Gao, S.; Thomas, P.H.; Turner, G.D.; Protheroe, A.S.; Howarth, M.; Macaulay, V.M. Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor Translocates to the Nucleus of Human Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6412–6419.
- Packham, S.; Warsito, D.; Lin, Y.; Sadi, S.; Karlsson, R.; Sehat, B.; Larsson, O. Nuclear translocation of IGF-1R via p150Glued and an importin-β/RanBP2-dependent pathway in cancer cells. Oncogene 2014, 34, 2227–2238.
- Codony-Servat, C.; Codony-Servat, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Molina, M.A.; Chaib, I.; Ramirez, J.L.; Gil, M.D.L.L.; Solca, F.; Bivona, T.G.; Rosell, R. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47305–47316.
- Warsito, D.; Sjöström, S.; Andersson, S.; Larsson, O.; Sehat, B. Nuclear IGF1R is a transcriptional co-activator of LEF1/TCF. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 244–250.
- Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; Waraky, A.; Haglund, F.; Agarwal, P.; Jernberg-Wiklund, H.; Warsito, D.; Larsson, O. SUMO-modified insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) increases cell cycle progression and cell proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2722–2730.
- Lin, L.; Liu, A.; Peng, Z.; Lin, H.-J.; Li, P.-K.; Li, C.; Lin, J. STAT3 Is Necessary for Proliferation and Survival in Colon Cancer–Initiating Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7226–7237.
- Xiong, H.; Hong, J.; Du, W.; Lin, Y.-W.; Ren, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Su, W.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; et al. Roles of STAT3 and ZEB1 Proteins in E-cadherin Down-regulation and Human Colorectal Cancer Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 5819–5832.
- Yang, A.D.; Fan, F.; Camp, E.R.; Van Buren, G.; Liu, W.; Somcio, R.; Gray, M.J.; Cheng, H.; Hoff, P.M.; Ellis, L.M. Chronic Oxaliplatin Resistance Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12 (14 Pt 1), 4147–4153.
- Yao, C.; Su, L.; Shan, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bian, X.; Shao, J.; et al. IGF/STAT3/NANOG/Slug Signaling Axis Simultaneously Controls Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 820–831.
- Dallas, N.A.; Xia, L.; Fan, F.; Gray, M.J.; Gaur, P.; Van Buren, G.; Samuel, S.; Kim, M.P.; Lim, S.J.; Ellis, L.M. Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer Cells, the Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype, and Increased Sensitivity to Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor Inhibition. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1951–1957.
- Sharma, S.V.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, B.; Quinlan, M.P.; Takahashi, F.; Maheswaran, S.; McDermott, U.; Azizian, N.; Zou, L.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A Chromatin-Mediated Reversible Drug-Tolerant State in Cancer Cell Subpopulations. Cell 2010, 141, 69–80.
- Li, C.-W.; Xia, W.; Huo, L.; Lim, S.-O.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Chao, C.-H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yang, N.-K.; Ding, Q.; et al. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TNF-α Requires NF-κB–Mediated Transcriptional Upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1290–1300.
- Grasso, C.S.; Giannakis, M.; Wells, D.K.; Hamada, T.; Mu, X.J.; Quist, M.; Nowak, J.A.; Nishihara, R.; Qian, Z.R.; Inamura, K.; et al. Genetic Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 730–749.
- Goswami, M.T.; Reka, A.K.; Kurapati, H.; Kaza, V.; Chen, J.; Standiford, T.J.; Keshamouni, V.G. Regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity by TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1888–1898.
- Li, H.; Batth, I.S.; Qu, X.; Xu, L.; Song, N.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. IGF-IR signaling in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and targeting IGF-IR therapy: Overview and new insights. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–15.
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Flashner-Abramson, E.; Shalapour, S.; Zhong, Z.; Taniguchi, K.; Levitzki, A.; Karin, M. Targeting colorectal cancer via its microenvironment by inhibiting IGF-1 receptor-insulin receptor substrate and STAT3 signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2634–2644.
- Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Boo, H.-J.; Hwang, S.-J.; Hong, S.; Lee, S.-C.; Park, Y.-J.; Chung, T.-M.; Youn, H.; Lee, S.M.; et al. STAT3-mediated IGF-2 secretion in the tumour microenvironment elicits innate resistance to anti-IGF-1R antibody. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–15.
- Tommelein, J.; De Vlieghere, E.; Verset, L.; Melsens, E.; Leenders, J.; Descamps, B.; Debucquoy, A.; Vanhove, C.; Pauwels, P.; Gespach, C.P.; et al. Radiotherapy-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Tumor Progression through Paracrine IGF1R Activation. Cancer Res. 2017, 78, 659–670.
- Apicella, M.; Giannoni, E.; Fiore, S.; Ferrari, K.J.; Fernández-Pérez, D.; Isella, C.; Granchi, C.; Minutolo, F.; Sottile, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; et al. Increased Lactate Secretion by Cancer Cells Sustains Non-cell-autonomous Adaptive Resistance to MET and EGFR Targeted Therapies. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 848–865.e6.
- Kim, B.G.; Sung, J.S.; Jang, Y.; Cha, Y.J.; Kang, S.; Han, H.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, N.H. Compression-induced expression of glycolysis genes in CAFs correlates with EMT and angiogenesis gene expression in breast cancer. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–15.
- Pedrosa, L.; Esposito, F.; Thomson, T.M.; Maurel, J. The Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1172.
- Colegio, O.R.; Chu, N.-Q.; Szabo, A.L.; Chu, T.; Rhebergen, A.M.; Jairam, V.; Cyrus, N.; Brokowski, C.E.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Phillips, G.M.; et al. Functional polarization of tumour-associated macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature 2014, 513, 559–563.
- Angelin, A.; Gil-De-Gómez, L.; Dahiya, S.; Jiao, J.; Guo, L.; Levine, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Quinn, W.J.; Kopinski, P.K.; Wang, L.; et al. Foxp3 Reprograms T Cell Metabolism to Function in Low-Glucose, High-Lactate Environments. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1282–1293.e7.
- Rubini, M.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Carturan, S.; Yumet, G.; Catalano, E.; Shan, S.; Huang, Z.; Criscuolo, M.; Pifferi, M.; Baserga, R. Characterization of an Antibody That Can Detect an Activated IGF-I Receptor in Human Cancers. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 251, 22–32.
- Fuchs, C.S.; Goldberg, R.M.; Sargent, D.J.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Wolpin, B.M.; Green, E.M.; Pitot, H.C.; Pollak, M. Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factors, Insulin-like Binding Protein-3, and Outcome in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results from Intergroup Trial N9741. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 8263–8269.
- Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Gallego, R. Prognostic Role of Plasma Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) and IGF-Binding Protein 3 in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5288.
- Van Cutsem, E.; Eng, C.; Nowara, E.; Świeboda-Sadlej, A.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Mitchell, E.; Davidenko, I.; Stephenson, J.; Elez, E.; Prenen, H.; et al. Randomized Phase Ib/II Trial of Rilotumumab or Ganitumab with Panitumumab versus Panitumumab Alone in Patients with Wild-type KRAS Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4240–4250.
- Guercio, B.J.; Zhang, S.; Ou, F.-S.; Venook, A.P.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Lenz, H.-J.; Innocenti, F.; Pollak, M.N.; Nixon, A.B.; Mullen, B.C.; et al. IGF-Binding Proteins, Adiponectin, and Survival in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results From CALGB (Alliance)/SWOG 80405. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021, 5, pkaa074.
- Scartozzi, M.; Mandolesi, A.; Giampieri, R.; Pierantoni, C.; Loupakis, F.; Zaniboni, A.; Galizia, E.; Giustini, L.; Silva, R.R.; Bisonni, R.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 expression correlates with clinical outcome in K-RAS wild type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab and irinotecan. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1941–1947.
- Sclafani, F.; Kim, T.Y.; Cunningham, D.; Kim, T.W.; Tabernero, J.; Schmoll, H.J.; Roh, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, Y.S.; Guren, T.K.; et al. A Randomized Phase II/III Study of Dalotuzumab in Combination With Cetuximab and Irinotecan in Chemorefractory, KRASWild-Type, Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv258.
- Huang, F.; Xu, L.-A.; Khambata-Ford, S. Correlation between Gene Expression of IGF-1R Pathway Markers and Cetuximab Benefit in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1156–1166.
- Lièvre, A.; Bachet, J.-B.; Le Corre, D.; Boige, V.; Landi, B.; Emile, J.-F.; Côté, J.-F.; Tomasic, G.; Penna, C.; Ducreux, M.; et al. KRAS Mutation Status Is Predictive of Response to Cetuximab Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3992–3995.
- Van Brummelen, E.M.J.; De Boer, A.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. BRAF Mutations as Predictive Biomarker for Response to Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies. Oncologist 2017, 22, 864–872.
- Douillard, J.-Y.; Oliner, K.S.; Siena, S.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Panitumumab–FOLFOX4 Treatment and RAS Mutations in Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1023–1034.
- Van Cutsem, E.; Lenz, H.-J.; Köhne, C.-H.; Heinemann, V.; Tejpar, S.; Melezínek, I.; Beier, F.; Stroh, C.; Rougier, P.; Van Krieken, J.H.; et al. Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, and Irinotecan Plus Cetuximab Treatment and RAS Mutations in Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 692–700.
- Morano, F.; Corallo, S.; Lonardi, S.; Raimondi, A.; Cremolini, C.; Rimassa, L.; Murialdo, R.; Zaniboni, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Tomasello, G.; et al. Negative Hyperselection of Patients with RAS and BRAF Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Who Received Panitumumab-Based Maintenance Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3099–3110.
- Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Buscarino, M.; Corti, G.; Cassingena, A.; Crisafulli, G.; Ponzetti, A.; Cremolini, C.; Amatu, A.; Lauricella, C.; et al. Clonal evolution and resistance to EGFR blockade in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 795–801.
- Arena, S.; Bellosillo, B.; Siravegna, G.; Martínez, A.; Cañadas, I.; Lazzari, L.; Ferruz, N.; Russo, M.; Misale, S.; González, I.; et al. Emergence of Multiple EGFR Extracellular Mutations during Cetuximab Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2157–2166.
- Pietrantonio, F.; Vernieri, C.; Siravegna, G.; Mennitto, A.; Berenato, R.; Perrone, F.; Gloghini, A.; Tamborini, E.; Lonardi, S.; Morano, F.; et al. Heterogeneity of Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 23, 2414–2422.
- Siena, S.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Karthaus, M.; Smith, D.; Tabernero, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Guan, X.; Boedigheimer, M.; Ang, A.; et al. Dynamic molecular analysis and clinical correlates of tumor evolution within a phase II trial of panitumumab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 119–126.
- Kim, T.W.; Peeters, M.; Thomas, A.L.; Gibbs, P.; Hool, K.; Zhang, J.; Ang, A.L.; Bach, B.A.; Price, T. Impact of Emergent Circulating Tumor DNA RAS Mutation in Panitumumab-Treated Chemoresistant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5602–5609.
- Khan, K.H.; Cunningham, D.; Werner, B.; Vlachogiannis, G.; Spiteri, I.; Heide, T.; Mateos, J.F.; Vatsiou, A.; Lampis, A.; Damavandi, M.D.; et al. Longitudinal Liquid Biopsy and Mathematical Modeling of Clonal Evolution Forecast Time to Treatment Failure in the PROSPECT-C Phase II Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1270–1285.
- Maurel, J.; Alonso, V.; Escudero, P.; Fernández-Martos, C.; Salud, A.; Méndez, M.; Gallego, J.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Martín-Richard, M.; Fernández-Plana, J.; et al. Clinical Impact of Circulating Tumor RAS and BRAF Mutation Dynamics in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With First-Line Chemotherapy Plus Anti–Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapy. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–16.
- Woolston, A.; Khan, K.; Spain, G.; Barber, L.J.; Griffiths, B.; Gonzalez-Exposito, R.; Hornsteiner, L.; Punta, M.; Patil, Y.; Newey, A.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Determinants of Therapy Resistance and Immune Landscape Evolution during Anti-EGFR Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 35–50.e9.
- Dienstmann, R.; Vermeulen, L.; Guinney, J.; Kopetz, S.; Tejpar, S.; Tabernero, J. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 79–92.
- Trinh, A.; Trumpi, K.; Melo, F.D.S.E.; Wang, X.; De Jong, J.H.; Fessler, E.; Kuppen, P.J.; Reimers, M.S.; Swets, M.; Koopman, M.; et al. Practical and Robust Identification of Molecular Subtypes in Colorectal Cancer by Immunohistochemistry. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 387–398.
- Lenz, H.-J.; Ou, F.-S.; Venook, A.P.; Hochster, H.S.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Goldberg, R.M.; Mayer, R.J.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Blanke, C.D.; Zemla, T.; et al. Impact of Consensus Molecular Subtype on Survival in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results From CALGB/SWOG 80405 (Alliance). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1876–1885.
- Stintzing, S.; Wirapati, P.; Lenz, H.-J.; Neureiter, D.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Kaiser, F.; Al-Batran, S.; Heintges, T.; et al. Consensus molecular subgroups (CMS) of colorectal cancer (CRC) and first-line efficacy of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab in the FIRE3 (AIO KRK-0306) trial. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1796–1803.
- Becerra, C.R.; Salazar, R.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Thomas, A.L.; Vázquez-Mazón, F.J.; Cassidy, J.; Maughan, T.; Castillo, M.G.; Iveson, T.; Yin, N.; et al. Figitumumab in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with standard therapies: A nonrandomized, open-label, phase II trial. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 695–702.
- Montagut, C.; Argilés, G.; Ciardiello, F.; Poulsen, T.T.; Dienstmann, R.; Kragh, M.; Kopetz, S.; Lindsted, T.; Ding, C.; Vidal, J.; et al. Efficacy of Sym004 in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer With Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy and Molecularly Selected by Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e175245.
- Gualberto, A.; Pollak, M. Emerging role of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in oncology: Early clinical trial results and future directions. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3009–3021.
- Cremolini, C.; Rossini, D.; Dell’Aquila, E.; Lonardi, S.; Conca, E.; Del Re, M.; Busico, A.; Pietrantonio, F.; Danesi, R.; Aprile, G.; et al. Rechallenge for Patients with RAS and BRAF Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer With Acquired Resistance to First-line Cetuximab and Irinotecan: A Phase 2 Single-Arm Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 343–350.
- Rimassa, L.; Bozzarelli, S.; Pietrantonio, F.; Cordio, S.; Lonardi, S.; Toppo, L.; Zaniboni, A.; Bordonaro, R.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Tomasello, G.; et al. Phase II Study of Tivantinib and Cetuximab in Patients With KRAS Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer With Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors and Emergence of MET Overexpression: Lesson Learned for Future Trials With EGFR/MET Dual Inhibition. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2019, 18, 125–132.e2.
- Delord, J.-P.; Argilés, G.; Fayette, J.; Wirth, L.; Kasper, S.; Siena, S.; Mesia, R.; Berardi, R.; Cervantes, A.; Dekervel, J.; et al. A phase 1b study of the MET inhibitor capmatinib combined with cetuximab in patients with MET-positive colorectal cancer who had progressed following anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody treatment. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 1774–1783.
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Trusolino, L.; Martino, C.; Bencardino, K.; Lonardi, S.; Bergamo, F.; Zagonel, V.; Leone, F.; Depetris, I.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Dual-targeted therapy with trastuzumab and lapatinib in treatment-refractory, KRAS codon 12/13 wild-type, HER2-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (HERACLES): A proof-of-concept, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 738–746.
- Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, W.; Kato, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kato, K.; Iwasa, S.; Esaki, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Masuishi, T.; Nishina, T.; et al. TRIUMPH: Primary efficacy of a phase II trial of trastuzumab (T) and pertuzumab (P) in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with HER2 (ERBB2) amplification (amp) in tumour tissue or circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA): A GOZILA sub-study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v199–v200.
- Gupta, R.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Halabi, S.; Mangat, P.K.; D’Andre, S.D.; Meiri, E.; Shrestha, S.; Warren, S.L.; Ranasinghe, S.; Schilsky, R.L. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab (P+T) in patients (Pts) with colorectal cancer (CRC) with ERBB2 amplification or overexpression: Results from the TAPUR Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 4), 132.
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Lonardi, S.; Martino, C.; Fenocchio, E.; Tosi, F.; Ghezzi, S.; Leone, F.; Bergamo, F.; Zagonel, V.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Pertuzumab and trastuzumab emtansine in patients with HER2-amplified metastatic colorectal cancer: The phase II HERACLES-B trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000911.
- Siena, S.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Masuishi, T.; Loupakis, F.; Kawakami, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nishina, T.; Fakih, M.; Elez, E.; et al. A phase II, multicenter, open-label study of trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd; DS-8201) in patients (pts) with HER2-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): DESTINY-CRC01. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 15), 4000.
- Ogitani, Y.; Aida, T.; Hagihara, K.; Yamaguchi, J.; Ishii, C.; Harada, N.; Soma, M.; Okamoto, H.; Oitate, M.; Arakawa, S.; et al. DS-8201a, A Novel HER2-Targeting ADC with a Novel DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor, Demonstrates a Promising Antitumor Efficacy with Differentiation from T-DM1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5097–5108.
- Oliveres, H.; Pineda, E.; Maurel, J. MET inhibitors in cancer: Pitfalls and challenges. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 73–85.
- Pander, J.; Heusinkveld, M.; Van Der Straaten, T.; Jordanova, E.S.; Baak-Pablo, R.; Gelderblom, H.; Morreau, H.; Van Der Burg, S.H.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Van Hall, T. Activation of Tumor-Promoting Type 2 Macrophages by EGFR-Targeting Antibody Cetuximab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5668–5673.
- Rösner, T.; Kahle, S.; Montenegro, F.; Matlung, H.L.; Jansen, J.H.M.; Evers, M.; Beurskens, F.; Leusen, J.H.; Berg, T.K.V.D.; Valerius, T. Immune Effector Functions of Human IgG2 Antibodies against EGFR. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 75–88.
- Pozzi, C.; Cuomo, A.; Spadoni, I.; Magni, E.; Silvola, A.; Conte, A.; Sigismund, S.; Ravenda, P.S.; Bonaldi, T.; Zampino, M.G.; et al. The EGFR-specific antibody cetuximab combined with chemotherapy triggers immunogenic cell death. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 624–631.
- Tsao, L.-C.; Crosby, E.J.; Trotter, T.N.; Agarwal, P.; Hwang, B.-J.; Acharya, C.; Shuptrine, C.W.; Wang, T.; Wei, J.; Yang, X.; et al. CD47 blockade augmentation of trastuzumab antitumor efficacy dependent on antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e131882.
- Iwata, T.N.; Ishii, C.; Ishida, S.; Ogitani, Y.; Wada, T.; Agatsuma, T. A HER2-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate, Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (DS-8201a), Enhances Antitumor Immunity in a Mouse Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1494–1503.
- Yang, A.; Herter-Sprie, G.; Zhang, H.; Lin, E.Y.; Biancur, D.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Hai, J.; Yang, S.; Wong, K.-K.; et al. Autophagy Sustains Pancreatic Cancer Growth through Both Cell-Autonomous and Nonautonomous Mechanisms. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 276–287.
- Yamamoto, K.; Venida, A.; Yano, J.; Biancur, D.E.; Kakiuchi, M.; Gupta, S.; Sohn, A.S.W.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Lin, E.Y.; Parker, S.J.; et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I. Nature 2020, 581, 100–105.
- Zhu, X.G.; Chudnovskiy, A.; Baudrier, L.; Prizer, B.; Liu, Y.; Ostendorf, B.N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Arab, A.; Tavora, B.; Timson, R.; et al. Functional Genomics In Vivo Reveal Metabolic Dependencies of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 211–221.e6.
- Cunha, L.D.; Yang, M.; Carter, R.; Guy, C.; Harris, L.; Crawford, J.C.; Quarato, G.; Boada-Romero, E.; Kalkavan, H.; Johnson, M.D.; et al. LC3-Associated Phagocytosis in Myeloid Cells Promotes Tumor Immune Tolerance. Cell 2018, 175, 429–441.e16.
- Su, S.; Zhao, J.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Liu, Q.; Song, E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Overcomes ADCP-Induced Immunosuppression by Macrophages. Cell 2018, 175, 442–457.e23.
