Mastocytosis is a heterogeneous group of rare diseases defined by abnormal accumulation of clonal mast cells (MC) in the skin, bone marrow and/or other visceral organs.
- Bibliography
1. IDefintroductition
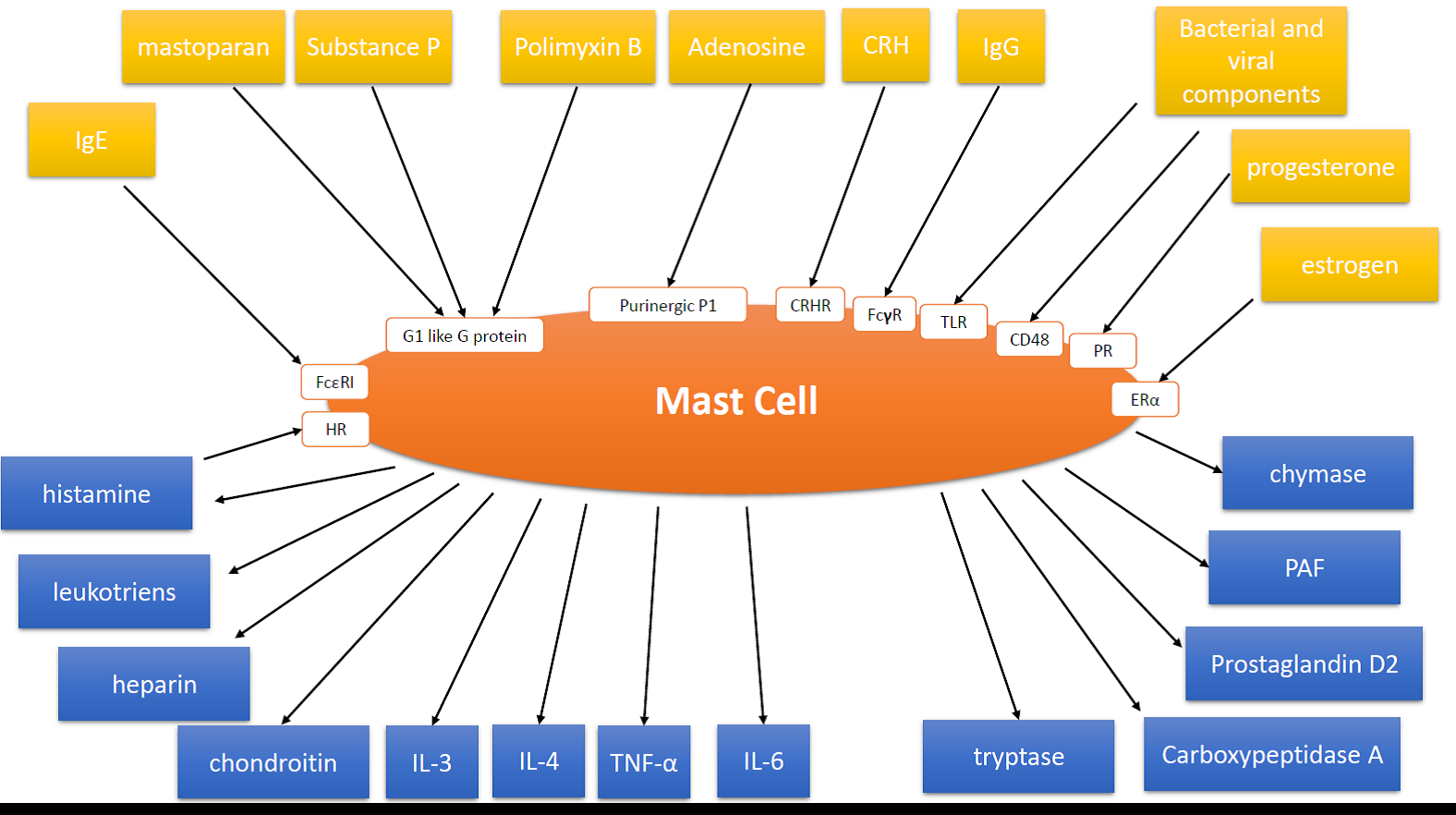
Mast cells (MC) are healthy, bone marrow derived cells in the body, usually found in the skin and other tissues. MC are multifunctional cells regulating both innate and adaptative immune system. MC participate in detection of harmful pathogens like viruses, bacteria, parasites and toxins, play the role in wound healing, cancer and tumor progression. Inappropriate, recurrent mast cell activation (MCA) and secretion MC-derived mediators plays an essential role in many human diseases: allergy, asthma, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, anaphylaxis, atopic dermatitis, mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS). [5]. [34] MC have a role in the early steps of the body’s coordination of healing responses to an injury. [6][33][34].[6, 33, 34] MC granules within the mast cells contain histamine and other chemicals (figure 1) :
- histamine
- leukotriene C4
- prostaglandin D2
- carboxypeptidase
- heparin
- cathepsin G-like protease
- tryptase
- tumour necrosis factor-A
- chymase
- interleukin-3, 4, 6, 8
- others
When a mast cell is activated, these chemicals are released into the surrounding skin. Mast cell chemicals are mediators of inflammation, and cause the blood vessels to leak, resulting in localised itching, swelling, redness and sometimes blistering. This reaction is normal in insect bites and is thought to be a protective mechanism. For example, a mosquito injects saliva when it bites. The saliva triggers mast cell activation to a varying degree, depending on the individual's hypersensitivity to the saliva. The unpleasant itch soon persuades the person to try to avoid getting bitten again.
Figure 1. Mast Cell and its triggering factors, their corresponding receptors (if those are present), activation pathways and degranulation products. (IgE – immunoglobulin E, IgG – immunoglobulin G, ACTH – Adrenocorticotropic hormone, CRH – corticotropin-releasing hormone, Rab3A – Ras-related protein, HR – histamine receptor, FcεRI – receptor for immunoglobulin E, FcγR – receptor for immunoglobulin G, CRHR – corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor, TLR – Toll like receptor, PR – progesterone receptor, ERα – estrogen receptor α, KIT – Tyrosine kinase receptor, IL-6R – receptor specific for interleukin 6, Lyn – Tyrosine-protein kinase, Syk – spleen tyrosine kinase, PLCγ1 – 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma 1, RAS – small GTPase class protein, ERK – extracellular signal-regulated kinase, JAK – Janus kinase, STAT – signal transducer and activator of transcription, IL-6 – interleukin 6, PAF – Platelet Activating Factor, TNF-α – Tumor necrosis factor α, IL-3 – Interleukin 3, IL-4 – Interleukin 4, PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, DAG, diacylglycerol,IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate).
2. Classification of mastocytosis
Mastocytosis can be divided in WHO classification into 7 variants: cutaneous mastocytosis (CM), indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM), smoldering SM (SSM), SM with an associated hematological neoplasm (SM‐AHN), aggressive SM (ASM), MC leukemia (MCL), and MC sarcoma (MCS). The diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis (SM) is based on WHO criteria, including the basal serum tryptase level, histopathological and immunophenotypic (CD2/CD25) features of MCs and somatic KIT mutations in codon 816. [1].[1]
The majority of children are suffering from CM and have a favorable prognosis with spontaneous regression in puberty period. In contrast, in adults, mastocytosis usually presents as SM, and sometimes progresses to an aggressive disease. The background of spontaneous regression of the disease in pubertal period observed in some children remains unclear. [2][3][4][5][6][7][8].[2-8]
In most patients with SM, somatic mutations in the KIT gene are found, the most prevalent in SM being D816V (rs121913507, D[GAC] > V [GTC]). The protein product of KIT (KIT=CD117) gene is a transmembrane receptor for stem cell factor (SCF), a major regulator of MC differentiation and survival. The KIT D816V mutation results in SCF‐independent differentiationof MCs. KIT D816V mutation is detected in more than 80% of all adults with SM. In contrast in children with CM, this mutation is less frequent (35%) and other mutations, located in gene regions encoding the external cellular domain of KIT ((Del419, F522C, ITD502–503, K509I, M541L, L852L), are more commonly found childhood patients (18%). Furthermore, it was found that 48% of children had the wild type WT sequence at codon 816 [7][9][10].[7,9,10,26]
3. Diagnosis
3.1. Cutaneous mastocytosis
Cutaneous mastocytosis (CM) is usually diagnosed by its clinical appearance and positive Darier sign. However, a skin biopsy may be helpful for confirmation of clinical diagnosis. [5][31][32].[5, 31, 32]
There different form of CM:
- Solitary mastocytoma
- Maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis
- Diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis
- Telangiectatic cutaneous mastocytosis (telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans)
- Plaque-type mastocytoma
- Solitary and multiple nodular mastocytomas
3.2. Systemic mastocytosis
3.2.1. Major criteria
- Multiple areas of dense infiltrate of mast cells in the bone marrow or other extracutaneous organs, confirmed by special stains on histology, such as mast cell tryptase (> 15 mast cell aggregating)
3.2.2. Minor criteria
- In mast cell infiltrates in the bone marrow or other extracutaneous organs, >25% of mast cells are spindle-shaped or otherwise atypical OR in bone marrow smears > 25% of mast cells are spindle-shaped or otherwise atypical
- Activating point mutation of the stem cell factor, c-KIT in codon 816 is present in extracutaneous organs using PCR-based technology
- Mast cells in extracutaneous organs found using CD117 co-express either CD2 or CD25, or both, as determined by flow cytometry
- Serum tryptase is persistently > 20ng/ml (this is not relevant in patients that have SM-AHNMD)
To set the diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis, ether one major + one minor criterium or 3 minor criteria has to be fulfilled [1][2][3][4][1-4].
Systemic mastocytosis occurs more commonly in adults than children (it is extremely rare in children).
3.3. Indolent systemic mastocytosis
Indolent systemic mastocytosis is the most common and least serious presentation of systemic mastocytosis in adults – it is characterised by a low mast cell burden (<30%), the presence of mediator-related symptoms such as flushing and diarrhoea, and skin involvement (usually maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis, see above).
3.4. Genetic background of mastocytosis
Studies of genetic background performed so far in CM and SM focused on gene polymorphisms of cytokines and their receptors (IL-13, IL-6, IL6R, IL-31, IL4R, VEGFA), TLRs and variants of the KIT gene have shown that some cytokine or cytokine receptor gene polymorphisms may be associated with the presence of SM and/or CM [11][12][13][14][15][16].[11-16] Other studies performed in ISM found associations of SM disease with SNPs in RAB27A, ETS1, ITGB1, MLL3, and ITGAV genes [17].[17]
In advanced SM, additional to D816V recurrent somatic mutations involving genes encoding factors regulating splicing, signaling transmission and epigenetic processes have recently been described [17][18][19][20][21].[17-21] The most frequently mutated genes are TET-2, DNMT3A, SRSF2, ASXL1, and RUNX. increase D816V oncogenic potential [18][19][20][21][22].[18-22]
In general mastocytosis is not a genetic disease, a germline mutations of KIT gene in children with mastocytosis were rare, occurring in different gene regions [15][16][17][15-17], and is estimated in 4% (34/916)) of published cases and 9% of twins [26]. [26]Many of these changes are polymorphic . In familial cases is inherited in autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. [26][27][28][31][32]. [26-28, 31,32]
4. Clinical symptoms
When mast cells degranulate, the substances that are released can cause a number of symptoms that can vary over time and can range in intensity from mild to severe. Because mast cells play a role in allergic reactions, the symptoms of mastocytosis often are similar to the symptoms of an allergic reaction. [1][2][3][4][5][6][31][32].[1-6, 31, 32]They may include (table 1):
- Fatigue
- Skin lesions (urticaria pigmentosa, itching, and dermatographic urticaria,
- "Darier's Sign", a reaction to stroking or scratching of urticaria lesions.
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Olfactive intolerance
- Ear/nose/throat inflammation
- Anaphylaxis (shock from allergic or immune causes)
- Episodes of very low blood pressure (including shock) and faintness
- Bone or muscle pain
- Headache
- Depression
- Ocular discomfort
- Decreased bone density or increased bone density (osteoporosis or osteosclerosis)
- Increased stomach acid production causing peptic ulcers (increased stimulation of enterochromaffin cell and direct histamine stimulation on parietal cell)
- Malabsorption (due to inactivation of pancreatic enzymes by increased acid)[5]
- Hepatosplenomegaly
5. Treatment
In a majority of patients with mastocytosis, mediator-induced symptoms are recorded. These symptoms may be mild, severe or even life-threatening, especially when a concomitant IgE-dependent allergy is also present
The treatment for mastocytosis depends on the particular symptoms of each person. Treatment for symptoms that affect the skin include antihistamines and oral psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy. If the symptoms are not responsive to other treatment, a doctor may prescribe steroid creams, ointments, or solutions to be applied to the skin (topical corticosteroids treatment), imatinib, mast cells stabilisers ( Cromolyn sodium), kinase inhibitors (Midostaurin), epinephrine, and/or IgE-targeting antibodies are required to bring anaphylaxis (MCAS events) under control.
Proton pump inhibitors can be used to treat gastrointestinal symptoms and bone pain. Many specialists recommended that people with mastocytosis have injectable epinephrine that they can use in case of anaphylactic shock. Other recommendations include trying to avoid known triggers of symptoms of mastocytosis. [23][24][25][30][23-25, 30].
Table 1
| Clinical effects of mast cell mediators produced and released during MCA* | ||||||
| Symptomatology of MCA | Relevant involved mediators** | |||||
| Vascular instability, hypotension, | Histamine, LTC4, LTE4, PGD2, VEGF, | |||||
| tachycardia, syncopy, anaphylaxis* | PAF, TNF-alpha | |||||
| Enhanced vasopermeability, edema | Histamine, VEGF, LTC4, LTE4, PAF | |||||
| formation in various organs | ||||||
| Headache and nausea | Histamine | |||||
| Fever and chills*** | TNF-alpha | |||||
| Urticaria, pruritus, flushing | Histamine, VEGF | |||||
| Bronchoconstriction | Histamine, PGD2, LTC4, LTD4, PAF | |||||
| Mucus secretion | Histamine, Proteases, PGD2, LTC4 | |||||
| Nasal congestion, wheezing | Histamine | |||||
| Gastric hypersecretion | Histamine | |||||
| Abdominal pain and cramping | Histamine, LTC4, PAF | |||||
| Diarrhoea | Histamine | |||||
*Clinical symptoms recorded in patients with mastocytosis and MCAS. In patients with MCAS more than one symptom are typically recorded and in most patients, hypotension and signs of anaphylaxis are found. **Some of the clinically most relevant mast cell-derived mediators are listed. In patients with MCAS, histamine and arachidonic acid derivatives may play a central role. The impact of the other mast cell-derived mediators, like PAF, remains at present unknown. ***In about 1% of all patients with MCA, severe hypotension is associated with fever. Abbreviations: MCA, mast cell activation; MCAS, MCA syndrome; LT, leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor (=vascular permeability factor), PAF, platelet activating factor.
6. Epidemiology
Mastocytosis is described as a rare disease, but to our knowledge, the exact incidence and prevalence are not known. A diseaseis considered rare if it affects fewer than 200,000 people in the United States at any given time. An estimate of prevalence from a recent population-based study is approximately 1 case per 10,000 people. [6].[6]