Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Marino B. Arnao and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
Melatonin, a multifunctional molecule that is present in all living organisms studied, is synthesized in plant cells in several intercellular organelles including in the chloroplasts and in mitochondria.
- carbohydrates
- melatonin
- phytomelatonin
- primary metabolism
- starch
- sucrose
1. Introduction
Plants obtain their energy and resources via an autotrophic means. All their organic molecules are synthesized from inorganic elements such as CO2 and primarily from diverse compounds including nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus, among others. In addition to their rich secondary metabolism, plants produce a multitude of primary metabolites including carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids. The group of carbohydrates of plant origin comprises a wide range of simple sugars such as mono- and disaccharides, sugar alcohols, and polymers such as starch and cellulose [1][2][1,2].
2. Biosynthesis of Melatonin in Plants
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a tryptophan-derived compound discovered in plants in 1995 [3][4][5][6,7,8]. Melatonin is a highly studied biomolecule due to its known role in mammals as a regulating hormone of sleep-wake cycles, and other functions in endogenous rhythms, mood, metabolism, and immunological responses [6][7][9,10]. In addition, it has been investigated as to its therapeutic efficacy in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinsonism, cancer, diabetes, and SARS-CoV-2 [8][9][10][11][12][13][14][11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
Melatonin biosynthesis in plants originates with the amino acid tryptophan, which is endogenously synthesized in plant cells in the chorismate pathway. Five enzymes are involved in the conversion of tryptophan to melatonin; these are tryptophan decarboxylase (TDC), tryptamine 5-hydroxylase (T5H), serotonin N-acetyltransferase (SNAT), acetylserotonin methyltransferase (ASMT), and caffeic-O-methyltransferase (COMT) [15][16][18,19]. These enzymes catalyze the conversion of the indolic compounds tryptophan, tryptamine, serotonin, 5-methoxytryptamine, and N-acetylserotonin to melatonin, as illustrated in the biosynthetic pathway shown in Figure 1. However, this primary melatonin biosynthetic pathway may present alternatives such as serotonin biosynthesis through 5-hydroxytryptophan, although this possibility seems specific to animals since the responsible enzyme (tryptophan hydroxylase) has not been detected in plants. In addition, a conversion of N-acetylserotonin to serotonin by the enzyme N-acetylserotonin deacetylase has been described [15][17][18,20]. With respect to the subcellular localization, several studies in arabidopsis and rice plants indicated that the involved enzymes act in the cytoplasm (TDC, ASMT and COMT), endoplasmic reticulum (T5H), and chloroplasts (SNAT) [18][21]. In addition, the participation of mitochondria has been described, through arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferases (AANAT) and hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferases (HIOMT), observing that, when the melatonin pathway is artificially blocked in chloroplasts, melatonin biosynthesis shifts to the mitochondria to maintain melatonin generation [18][19][21,22]. Generally, stressors induce melatonin biosynthesis in plants through the upregulation of diverse biosynthesis isozyme transcripts, increasing endogenous melatonin production [20][23].
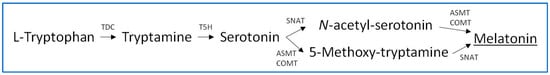

Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of melatonin in plants.
3. Roles of Melatonin in Plants
Melatonin is a pleiotropic molecule in plants. Melatonin has many beneficial actions, generally improving physiological responses such as seed germination and growth, photosynthesis (pigment content, photorespiration, stomatal conductance and water economy), seed and fruit yield, osmoregulation, and the regulation of the different metabolic pathways (carbohydrates, lipids, nitrogen compounds, sulphur, and phosphorus cycles) [21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. With respect to secondary metabolism, melatonin induces the biosynthesis of simple phenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and several terpenoids [32][33][34][35][35,36,37,38]. Melatonin promotes rooting processes [36][37][38][39][40][39,40,41,42,43] and also delays leaf senescence [41][42][43][44][45][46][44,45,46,47,48,49]. In postharvest fruit, it regulates ethylene and lycopene content, as well as general ripening metabolism and induces parthenocarpy during fruiting [47][48][49][50,51,52]. It also preserves cut flowers [50][51][53,54]. In pathogen infections, melatonin slows damage, stimulating systemic acquired resistance (SAR) and contributes to crop health [52][55]. Due to this high number of actions, melatonin has been referred to as a plant master regulator [53][54][56,57], mainly due to its role as a plant hormone regulator, with a substantial influence on auxin, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, ethylene, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, and brassinosteroids [55][56][58,59].
Melatonin displays a relevant role in the stress responses. Similar to what occurs in animal cells, melatonin acts as an excellent scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) in plants. This antioxidant capacity has been extensively studied [57][58][59][60,61,62]. The data show that melatonin acts as a direct antioxidant, neutralizing several ROS/RNS and other radical species harmful to the cell, and also acts as an activator of the antioxidant response, upregulating various transcription factors that trigger the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutases, catalases, peroxidases, and those involved in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle, among others [19][60][22,63]. Via these means, melatonin acts as a master regulator of the responses of the redox, hormonal, and osmoregulatory systems [53][55][56][61][56,58,59,64]. In summary, as can be seen in Figure 2, through the redox and hormonal network, melatonin regulates photosynthesis, primary and secondary metabolism, and pathogenic response to increase abiotic/biotic tolerance and, as a result, crop yield. One of the most interesting aspects is the ability of melatonin to regulate the carbohydrate metabolism and its relationship with the osmoregulatory response, which is a key in stressful situations of plants.
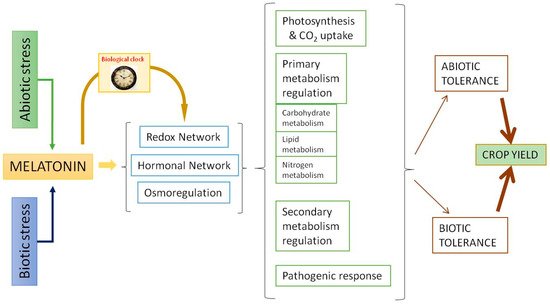

Figure 2.
Melatonin actions as a response to abiotic and biotic stressors.
4. Effect of Melatonin in Simple Carbohydrates, Starch, and Polyalcohols
The term phytomelatonin refers to melatonin of plant origin as opposed to the animal hormone, but they have the identical chemical structure. The first studies on the role of phytomelatonin in plants appeared at the end of the last century and the beginning of the present one [62][65]. Table 1 summarizes the results of studies on melatonin and carbohydrates in plants. Based on these data, the initial report related to melatonin and carbohydrates in plants is an in vitro study in cherry rootstock. In this study, exogenous melatonin added to the culture media induced plant growth and rooting in shoot tip explants; in addition, an elevation in endogenous levels of total soluble sugars in 9-week-old plants, both in leaves and roots, and in chlorophylls, carotenoids, and proline level were also observed. These findings indicate an improvement in plant primary carbon metabolism, with a melatonin-concentration dependent response [28][31]. Also in apple trees, melatonin treatment of leaves produced an increase in the levels of monosaccharides, sucrose, starch, and sorbitol as well as an improvement in the photosynthetic rate and a reduction in foliar senescence and autophagy [29][32]. Other studies were focused on improving the plants’ tolerance to certain stresses. Thus, melatonin treatments enhanced saline tolerance in soybean [30][33], tomato [63][66], and bermudagrass plants [64][67] (see Table 1), accompanied by an activation of carbohydrate metabolism and, in some cases, lipid and ASC-GSH metabolism as well [65][68]. There are many studies on the promotional effect of fruit development after the application of melatonin in leaves and/or roots. One of the first was carried out in tomato plants, where melatonin applications induced photosynthetic processes with a higher yield in biomass and a greater number of fruits which were of greater caliber and exhibited optimal ripening [66][69]. In pear trees, 100 µM melatonin treatments induced higher total sugars and starch levels and better fruit sizes which were of high quality [67][70]. In addition, postharvest melatonin treatments in various fruits gave rise to higher quality fruits with an increased content of sugars, starch, organic acids, and pigments, as had been demonstrated in tomato [68][71] and banana [69][72], and other fruits such as peach, strawberry, pear, plum, and litchi [24][50][27,53]. In one comprehensive study, melatonin treatments induce innate immunity in Arabidopsis with the accumulation of various sugars and glycerol, as well as increasing disease resistance against Pseudomonas syringe [70][73]. In general, plants treated with melatonin exhibit increases in the levels of simple sugars, sucrose, starch, and some polyalcohols.
Table 1.
Examples of studies on carbohydrates and melatonin.
| Plant | Melatonin Treatment (µM) | Compound Level vs. Un-Treated | Response vs. Un-Treated | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prunus avium x | Prunus cerasus | (in vitro) |
0.05–10 | ↑ total carbohydrates | ↑ rooting ↑ plant biomass |
[28] | [31] | |
| Malus hupehensis | tree |
100 | ↑ fructose, glucose, sucrose, starch ↑ sorbitol |
↑ photosynthesis ↓ senescence ↓ autophagy |
[29] | [32] | ||
| Tomato fruits | 1–500 | ↑ soluble sugars | ↑ fruit ripening and quality | [68] | [71] | |||
| Tomato plants | 100 | ↑ glucose, sucrose, inositol ↓ fructose, galactose |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant biomass ↑ fruit number and size |
[66] | [69] | |||
| 20–50 | ↑ soluble sugars ↑ ascorbate and GSH |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant growth ↑ NaCl tolerance |
[63] [71] | [66] [74] |
||||
| Soybean | 50 and 100 | ↑ carbohydrate metabolism, fatty acid biosynthesis, and ascorbate metabolism ↑ light reactions, Calvin cycle, carbohydrate, amino acid, fatty acid metabolism and Krebs cycle |
↑ germination, biomass ↑ photosynthesis ↑ cell division ↑ NaCl tolerance |
[30] | [33] | |||
| Bermudagrass | (Cynodon dactylon) | 4–100 | 54 metabolites, including amino acids, organic acids, sugars, and sugar alcohols ↑ photosyntesis, Calvin cycle and carbohydrate metabolism |
↑ NaCl tolerance ↑ cold tolerance ↑ drought tolerance |
[64] | [67] | ||
| 100 | ↑ arabinose, mannose, gluco-pyranose, maltose and turanose | ↑ cold tolerance ↑ photosynthesis |
[72] | [75] | ||||
| Maize | 10–100 | ↑ fructose, glucose, sucrose, starch and its biosynthesis genes | ↑ photosynthesis ↑ leaf and root growth |
[73] | [76] | |||
| 10–1000 | ↑ total soluble sugars ↑ nitrogen compounds ↑ expressions of genes involved in C- and N- metabolisms |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant growth |
[74] | [77] | ||||
| Banana fruits | 50–500 | ↑ total soluble sugars ↑ starch |
↑ fruit ripening and quality ↓ ethylene |
[69] | [72] | |||
| Vicia faba | 50 | ↑ soluble sugars ↑ ascorbate and GSH |
↑ As tolerance ↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant growth |
[65] | [68] | |||
| Brassica juncea | 10–50 | ↑ total soluble sugars ↑ reducing sugars |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant growth ↑ mineral nutrition |
[75] | [78] | |||
| Grape plants | 50–200 | ↑ fructose, sucrose, starch, reducing sugars ↑ sucrose biosynthesis genes |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ plant growth ↑ mineral nutrition |
[76] | [79] | |||
| Rice plants | 20 | ↑ fructose, sucrose, starch, reducing sugars ↑ sucrose biosynthesis genes |
↑ As tolerance ↑ Krebs cycle |
[77] | [80] | |||
| Pear tree | 100 | ↑ total soluble sugars ↑ sucrose, starch, reducing sugars, sorbitol ↑ sucrose synthase, invertases |
↑ photosynthesis ↑ fruit size and quality |
[67] | [70] | |||
| Malus domestica | (plants) |
1000 | ↑ fructose, glucose, sucrose, sorbitol ↓ fructokinase gene |
↑ melatonin-induced sugar accumulation ↑ growth inhibition |
[78] | [81] | ||
| Nicotiana tabacum | (in vitro) |
0.2 | ↑ starch ↑ PEPCK and α-amylase genes |
↑ sugar starved ↑ gluconeogenesis |
[79] | [82] | ||
| Chinese hickory (plants) | 100 | ↑ total soluble sugars, starch ↑ proline |
↑ drought tolerance ↑ photosynthesis, transpiration |
[80] | [83] | |||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | (Pseudomonas syringe infected) |
20 | ↑ fructose, glucose, melibose, sucrose, maltose, galatose, tagatofuranose and glycerol | ↑ bacterial innate immunity ↑ disease resistance |
[70] | [73] |
↑, Increased content or increased action; ↓, Decreased content or decreased action.
