The scaling of rain attenuation models has been developed in several parts of the world. Since the climatic parameters are different in different parts of the world, the scaling parameters are also limited for the best fit in a particular geographical area. However, scaling models are always needed for better applicability, whose performance can be “fine-tuned” by the local climatic parameters.
- attenuation measurement
- frequency scaling
- terrestrial link
- slant link
- received signal level
1. Introduction
Rain attenuation is a significant impairment in terrestrial and satellite communications wave propagation, among other environmental disturbances [1][2][1,2]. Due to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the demand to transfer the data volume is increasing [3]. The millimeter-wave (mm-wave) frequency is a viable alternative for creating bandwidth to transfer the higher data volume [4]. However, at the same time, this mm-wave frequency is highly disturbed by rain attenuation for terrestrial or satellite communications applications [5]. As a result, accurate rain attenuation prediction requires consistent association with the link budget planning [6]. We are very familiar with rain attenuation in existing frequency bands, but there is still an opportunity to research millimeter-wave bands, although significant research has been performed. The frequency scaling technique enables precise rain attenuation prediction for another frequency band, at which the attenuation statistics is still unknown [7]. Besides, in adaptive fade mitigation measuring systems, real-time frequency attenuation scaling can be used [6]. Frequency scaling predicts attenuation values at a particular frequency using previously measured attenuation at a baseline frequency [8]. The baseline frequency attenuation is known from past investigations. The idea of frequency scaling can be expanded to other parameters of rain attenuation: polarization scaling, elevation angle scaling, and pathlength scaling, because the attenuation is a function of the pathlength, elevation angle, and frequency [9]. The polarization scaling enables us to estimate the attenuation for horizontal polarization from vertical polarization and vice versa [10]. Elevation angle scaling can help estimate the attenuation at an unknown elevation with the help of previously known attenuation at a particular elevation angle [11]. Likewise, the scaling approach of the route length may be used to assess the attenuation form of a particular microwave link with varied attenuation lengths for the link. Except for these four parameters, an additional 13 or more parameters were reported in [9]. Is it thus possible to scale rain attenuation for each of these parameters? Although the result appears intuitively reasonable, the scaling for other parameters has not yet been addressed.
Frequency attenuation scaling can be implemented with statistical scaling and instantaneous scaling techniques [12][13][12,13]. Instant frequency scaling is an attenuation of the reference frequency scaling to anticipate the attenuation in each unit period at the desired frequency [6]. Scaling of statistic frequencies allows link budgets to be determined for new systems with a fixed attenuation margin [14]. Traditional device design requires a margin to resolve the anticipated fading within a link budget. As deep fades occur several hours a year [15], cost compensation for greater transmission capacity, antenna size, or enhanced antenna capability may be acknowledged. An option to include the power margin is the use of adaptive processes such as adaptive power regulation and adaptive encoding [6]. The transmission power can be raised to compensate for the attenuation at the Earth station transmitter end. The adaptive link budget planning checks whether it is required to resolve fades, as long as the fade persisted [16]. In such a link budget plan, instantaneous scaling frequency is essential [13]. The attenuation values at the reference frequency can be employed to estimate the attenuation values at the target frequency. The significant contributions of this survey are: We developed a scaling rain attenuation technique taxonomy and then organized all the relevant literature according to the taxonomy; In this work, we developed a comparative study of the existing scaling techniques and a comparative study of these methods.
This paper’s remainder is structured as follows: Section 2 presents the taxonomy developed through different parameter-based attenuation scaling methods and different formulation basis techniques. Section 3 is associated with literary analysis and the classification of various scaling techniques of rain attenuation methods. Section 4 discusses and contrasts the state-of-the-art scaling methods, and Section 5 discusses micro-and millimeter links’ scaling research scopes and challenges. Finally, Section 6 lays forth the findings and recommendations of this survey.
2. Existing Scaling Techniques
This section discusses the details of the rain attenuation scaling techniques as per the developed taxonomy in the earlier section.
If θ 1 and θ 2 are elevation angles and A ( θ 1), A ( θ 2) are the attenuations due to rain attenuation, then for a settled operating frequency, the attenuation scales with the elevation angle, which can be analytically written as (7) A ( θ 1) sin θ 1= A ( θ 2) sin θ 2 The implementation of ( 7) can be performed through various means such as power-law-based techniques, cosecant-rule-based techniques, and synthetic time-series-based techniques. All these different implementation techniques are briefly explained below: I. Power-law-based technique: Elevation angle scaling is defined as the ratio of rain attenuation at the zenith and the slant paths ( θ from 1∘ to 89∘ ) in [11]. The following simple formulation presents a competent model as the scaling factor S F ( θ ) : (8) S F ( θ ) = 1.741 θ − 0.6015 + 0.8931 It was shown in [11] that this method can predict slant link attenuation at a satisfactory level of accuracy from 5∘ ≤ θ ≤ 90∘ . According to the CCIR model [17][23], it is noteworthy that the elevation angle scaling is defined for θ > 10∘ ; II. Cosecant-rule-based technique [11]: The scaling factor ( S F [P ,θ ] ) is defined as the proportion of the attenuation across θ and the one anticipated from the zenith path using the simple cosecant law: (9) S F ( P ,θ ) = M M A d B ( P ,θ ) / csc ( θ ) A d B ( P ,90∘ ) The scaling factor S F can be calculated as the approximated fourth-order polynomial as: (10) S F ( p ,θ ) = α 1( θ ) P 3+ α 2 ( θ ) P 2+ α 3( θ ) P + α 4( θ ) where α 1,α 2,α 3, and α 4 are the coefficients of ( 10); III. Time-series-based technique: There is a strong impact of the elevation angle on the design of telecommunication facilities, particularly the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. At a low elevation angle for the LEO satellite, if a single rain cell intercepts the propagated signal from the Earth station antenna, it is possible to scale the elevation angle with the rainy time series generation technique [18][24] as per ( 11). (11) F = [( h r − h a ) ( h r ,1− h a ,1) ] · [sin ( θ 1) sin ( θ 2) ] · ( f 2f 1) 1.72 where the subscripts “1” and “2” are used for the base (reference) measured and operating (target) datasets. Here, the rain height and the antenna height are, respectively, h r ( km ) and h a ( km ), and both are with reference to the sea level, θ is the elevation angle, and f is the frequency in GHz. However, if multiple rain cells exist, it is impossible to scale the attenuation, and ( 11) will not be valid. It is assumed that by picking a collection of episodes from the ITALSAT database and scaling it to the factor indicated in ( 11), it is possible to recreate rain reduction statistics at a different frequency, height, and elevation for any other location. This technique needs several data processing steps, and among these steps, the most important things to check are: the original elevation angle needs to be mapped (e.g., from 37. 7∘ to 107∘ ); 20 terms are then expanded to result in a database to investigate whether there exist multiple rain cells (as in the case of multiple rain cells, the assumption made by ( 11) will not be valid). In [19][25], the effect of rain attenuation on the elevation angle was assessed using the synthetic storm approach to create rain attenuation time series. The study showed that if the elevation angle decreases to 20∘ , the impact of rain attenuation increases significantly, and at higher elevation angles (i.e., 40∘ to 80∘ ), the influence of rain attenuation is negligible. Such results are closely related to the value of the effective pathlength. These preliminary results suggest that using a prediction model for low elevation angle application systems such as the LEO satellite should consider the significant impact of rain attenuation, particularly in the heavy rain region.
The advantage of rain attenuation would have happened if the transmission of different frequencies had gone through the same storm. It is helpful to determine the amount of rain attenuation that will occur at a given frequency. For example, it is helpful to have experimental scale data available at one frequency to predict the device output at another frequency. The application of frequency scaling can be beneficial in determining predicted attenuation in a dual-frequency use of satellite communication or even in predicting attenuation at different frequencies [8][20][8,26].
In the radio wave, polarization is the orientation of electric and magnetic fields. The polarization is the variety of radio waves that include vertical, horizontal, right-hand circular, and left-hand circular. Polarization scaling is helpful to anticipate the attenuation for the type of polarization for which attenuation is unknown in a given region at a particular frequency. The ITU-R model can forecast for vertical polarization attenuation because long-term attenuation statistics are available for horizontal polarization and vice versa for a particular link. Equations ( 38) and ( 39) are the mathematical formulas for determining the conversion of polarization as specified in [21][45]. (38) A V = 300A H ( 335+ A H ) ( d B ) (39) A H = 335A V ( 300− A V ) ( d B ) where A H and A V are the rain attenuations of the horizontal and vertical links, respectively. The scaling of polarization is essential for estimating the type of polarization for which attenuation is unknown at a specific frequency in climatic areas. The ITU-R model can forecast the vertical polarization attenuation since long-term attenuation data are available, with a frequency limit of 100 GHz, and it is expected to be valid in any region of the world, with an allowable link length up to 60 km. In circular polarization, the disadvantage of this model is that it cannot be used.
3. Comparison of Scaling Models
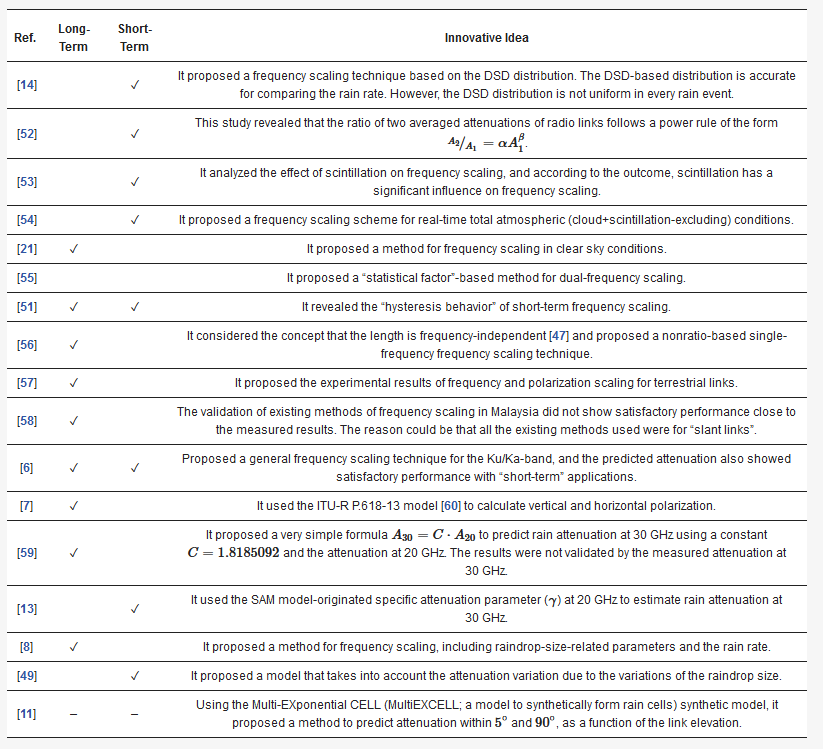
The scaling of rain attenuation models has been developed in several parts of the world. Since the climatic parameters are different in different parts of the world, the scaling parameters are also limited for the best fit in a particular geographical area. However, scaling models are always needed for better applicability, whose performance can be “fine-tuned” by the local climatic parameters. Among the climatic parameters, the rain rate is the frequently used parameter. However, in recent years, it has been validated that the DSD-based distribution gives more accurate results than the rainfall rate. However, the problem of the DSD-based model is that the rainfall distribution can change in different rain events. Furthermore, the availability of DSD-based measurement data is limited compared to rain-rate-based data. Among the developed models of scaling, the frequency-scaled models are the most common in the literature. Some scaling models consider only the ratio of frequencies, while other methods consider a more complicated one, including attenuation and frequency in the ratio-based scaling factor. Another critical feature of scaling techniques is the temporal domain perspective: “long-term” and “short-term” applicability. The “short-term” applicability is also called “instantaneous scaling [22][51]”. The “instantaneous scaling” techniques are sensitive to the variations of the same rain event due to the variations of the drop size distribution on the slant path [23][41]. In Table 1 and Table 2 , all the rain attenuation models’ innovative ideas, long or short applicability, reported frequency range and supported link are discussed.
Table 1.
Comparison among the scaling of propagation links.
| Ref. | Location | Link | Atten. | DSD | Camp.Time | Freq. (GHz) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Italy | Satellite | ✓ | 06/2014– | 20/40 | ||
| [24] | [52] | Italy | Satellite | ✓ | 72/36 h | 11.6/17–17.8 | |
| [25] | [53] | Belgium | Satellite (Olympus) | ✓ | 7 mo. | 12.50/19.77–29.66 | |
| [26] | [54] | Italy | Satellite (ACTS, ITALSAT) | ✓ | – | 20.2/27.5 (ACTS); 39.6/49.5(ITALSAT) | |
| [27] | [21] | Worldwide | Satellite | ✓ | – | 10–100 | |
| [28] | [55] | Collected | Satellite | ✓ | – | 10-50 | |
| [22] | [51] | U.K. | Satellite | ✓ | 8–11 mo. | 12.5/20/30 | |
| [29] | [56] | Collected | Satellite/Terrestrial | ✓ | – | 13/19/30 | |
| [30] | [57] | Czech Rep. | Terrestrial | ✓ | 9 mo. | 58/93 | |
| [31] | [58] | Malaysia | Terrestrial | ✓ | 12 mo. | 23/26/38 | |
| [6] | USA | Satellite | ✓ | 12 mo. | 12/20/30 | ||
| [7] | India | Satellite | ✓ | 5 d | 20.2/30.5 | ||
| [32] | [59] | India | Satellite | ✓ | 2 y | 20/30 | |
| [13] | India | Satellite | ✓ | 20/30 | |||
| [8] | Italy | Satellite (ITALSAT) | ✓ | ✓ | 12 mo. | Ka/V bands (18.7/39.6/49.5) | |
| [33] | [49] | Italy | Satellite (ITALSAT) | 8 y | Ka/V (18.7/39.6/49.5) | ||
| [11] | Synthetic | Satellite | ✓ | – | 18.7/39.6 |
Table 2.
Comparison among the scaling of propagation links.
| Ref. | Long-Term | Short-Term | Innovative Idea |
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | ✓ | It proposed a frequency scaling technique based on the DSD distribution. The DSD-based distribution is accurate for comparing the rain rate. However, the DSD distribution is not uniform in every rain event. | |
| [52] | ✓ | This study revealed that the ratio of two averaged attenuations of radio links follows a power rule of the form A2A1/=αAβ1 |
| [53] | ✓ | It analyzed the effect of scintillation on frequency scaling, and according to the outcome, scintillation has a significant influence on frequency scaling. | |
| [54] | ✓ | It proposed a frequency scaling scheme for real-time total atmospheric (cloud+scintillation-excluding) conditions. | |
| [21] | ✓ | It proposed a method for frequency scaling in clear sky conditions. | |
| [55] | It proposed a “statistical factor”-based method for dual-frequency scaling. | ||
| [51] | ✓ | ✓ | It revealed the “hysteresis behavior” of short-term frequency scaling. |
| [56] | ✓ | It considered the concept that the length is frequency-independent [47] and proposed a nonratio-based single-frequency frequency scaling technique. | |
| [57] | ✓ | It proposed the experimental results of frequency and polarization scaling for terrestrial links. | |
| [58] | ✓ | The validation of existing methods of frequency scaling in Malaysia did not show satisfactory performance close to the measured results. The reason could be that all the existing methods used were for “slant links”. | |
| [6] | ✓ | ✓ | Proposed a general frequency scaling technique for the Ku/Ka-band, and the predicted attenuation also showed satisfactory performance with “short-term” applications. |
| [7] | ✓ | It used the ITU-R P.618-13 model [60] to calculate vertical and horizontal polarization. | |
| [59] | ✓ | It proposed a very simple formula A30=C⋅A20 |
C=1.8185092
| Ref. | Long-Term | Short-Term | Innovative Idea |
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | ✓ | It proposed a frequency scaling technique based on the DSD distribution. The DSD-based distribution is accurate for comparing the rain rate. However, the DSD distribution is not uniform in every rain event. | |
| [52] | ✓ | This study revealed that the ratio of two averaged attenuations of radio links follows a power rule of the form A2A1/=αAβ1 |
| [53] | ✓ | It analyzed the effect of scintillation on frequency scaling, and according to the outcome, scintillation has a significant influence on frequency scaling. | |
| [54] | ✓ | It proposed a frequency scaling scheme for real-time total atmospheric (cloud+scintillation-excluding) conditions. | |
| [21] | ✓ | It proposed a method for frequency scaling in clear sky conditions. | |
| [55] | It proposed a “statistical factor”-based method for dual-frequency scaling. | ||
| [51] | ✓ | ✓ | It revealed the “hysteresis behavior” of short-term frequency scaling. |
| [56] | ✓ | It considered the concept that the length is frequency-independent [47] and proposed a nonratio-based single-frequency frequency scaling technique. | |
| [57] | ✓ | It proposed the experimental results of frequency and polarization scaling for terrestrial links. | |
| [58] | ✓ | The validation of existing methods of frequency scaling in Malaysia did not show satisfactory performance close to the measured results. The reason could be that all the existing methods used were for “slant links”. | |
| [6] | ✓ | ✓ | Proposed a general frequency scaling technique for the Ku/Ka-band, and the predicted attenuation also showed satisfactory performance with “short-term” applications. |
| [7] | ✓ | It used the ITU-R P.618-13 model [60] to calculate vertical and horizontal polarization. | |
| [59] | ✓ | It proposed a very simple formula A30=C⋅A20 |
C=1.8185092
Table 2. Comparison among the scaling of propagation links.
4. Research Scopes and Challenges
The primary challenge in scaling method studies is that long-term experiments are necessary. Besides considering the nonuniform distribution of rain, proper approximation techniques are required to be deployed that can represent the rain distribution along with the radio links. In addition, to develop a scaling method, depending on the scaling mechanism, it needs to record attenuation with varying different possible parameters. Long-term experimental data are required to enhance the scaling of rain attenuation further.
In [18][24], the SSA-based time series generation scaling techniques were proposed. An improved version of the SSA method was proposed in [34][61], which improved the performance over the conventional SSA technique. The characteristics can be retrieved from additional sources using this improved SSA approach, including a discriminating mechanism for distinguishing between stratiform and convective rain episodes. Consequently, there are research scopes to apply this improved version of the SSA technique for elevation scaling through rain attenuation time series.
It has been recently shown that rain attenuation is more effectively determined with the help of AI-based techniques [4]. Recently, in [35][62] an artificial neural network was used to determine the polarization and frequency scaling for terrestrial and slant links. Typically, long-term rain attenuation, rainfall rate, and other climatic or infrastructural-related parameters need to be studied for rain attenuation models. In recent years, it has been found that considering the microphysical phenomena of rainfall events can be helpful for accurate attenuation models for radio links [36][37][63,64]. Consequently, the rainfall rate and other related physical parameters can contribute to accurate attenuation prediction models. All these parameters can be helpful to develop rain attenuation scaling models for frequency, the elevation angle of the antenna, polarization, and pathlength scaling.
According to the study in [38][65], the liquid water content (LWC) can affect the attenuation over a wide frequency range up to 1000 GHz. It was shown that the attenuation due to the LWC is almost similar to the standard atmosphere condition, but within 1 GHz and 100 GHz, the attenuation due to the LWC is lower than the standard atmospheric condition. Consequently, in a particular region at a specific time, the LWC showed a more significant variation. To model the attenuation in such an area, it needs a separate procedure to calculate the attenuation due to the unusual LWC. It was mentioned in [9] that environmental visibility can affect the attenuation in terrestrial and slant links. Moreover, in [39][40][66,67], the perspective relationship was studied among the factors such as visibility, precipitation, and the presence of fog.