Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Hualou Long and Version 2 by Vivi Li.
Land use transition refers to the changes in land use morphologies, including dominant morphology and recessive morphology, of a certain region over a certain period of time driven by socio-economic change and innovation, and it usually corresponds to the transformation of the socio-economic development stage. The dominant morphology refers to the land use structure with features such as the quantity and spatial pattern of land use types. While the recessive morphology includes the land use features in the aspects of quality, property rights, management mode, input, output and function.
- land use transition
- land use morphology
- land system science
- literature review
- CiteSpace
- progress and prospects
1. Introduction
Land is the spatial carrier of anthropogenic activities, the most basic production factor of socio-economic development, and the most fundamental survival resource for urban and rural residents. Since the end of the 20th century, increasing intensive land use activities have become an important factor affecting global sustainable growth. On the one hand, over-exploitation and uncontrolled utilization of land resources in areas with higher natural suitability has brought huge challenges to regional sustainability. On the other hand, farmland abandonment in marginal areas has brought about a greater threat to food security [1][2][3][1,2,3]. A series of problems such as increased pressure on agricultural land, soil pollution and decreased biodiversity caused by high-intensity land use have brought about many difficulties to the development, management and sustainable use of land resources, and also attracted wide attention [4]. Land use faces the challenge of how to address the relations between meeting human needs and maintaining the long-term ability of the biosphere to provide goods and services [5].
At present, the world is experiencing major changes, which are intertwined with epidemic such as the COVID-19. Climate change poses severe threats to human survival [6]. As the leading sources of greenhouse gas emissions, land use transition (LUT) has greatly challenged the functions of ecosystems, thus having an important impact on climate change [7]. How to take effective measures to deal with resource exhaustion and the impact of human activities on the environment, ensure food security and further understand the feedback relationship between the natural environment and human society, has become an important issue that needs to be solved urgently [8]. LUT research helps to provide comprehensive information for decision-makers in land use planning and environmental management, and has important practical significance for coordinating regional social, economic and ecological development goals. In recent years, the research projects and related papers concerning LUT have shown a rapid growth trend, but the comprehensive and systematic bibliometric analysis is still insufficient. Scholars’ focus on LUT research is constantly changing and adjusting.
2. Statistical Analysis of Literatures Concerning LUT Research
2.1. An Overview of LUT Research
The number and trends of published literatures concerning LUT research from 1987 to 2020 were analyzed (Figure 1). We found that the number of literatures in this field has shown a fluctuating upward trend, and the number of published papers showed a rapid upward trend after 2013. According to the number of annual publications, the research on LUT can be roughly divided into two stages: (1) Slow growth stage (1987–2006). Research on LUT has been developed from scratch, and some developed countries have begun to devote themselves to related research on forest transition. (2) Rapid development stage (2007–present). Research on LUT has gradually received attention, the number of papers related to the subject of LUT has increased rapidly, and scholars have carried out a series of researches from different disciplines and perspectives with a variety of methods and technical means.
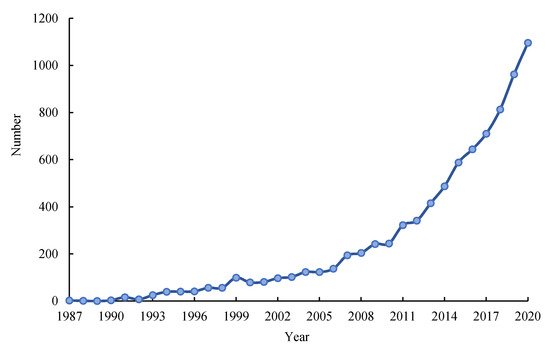

Figure 1. Number of literatures concerning LUT research from 1987 to 2020.
According to data from Web of Science, by the end of 2020, the top three countries with the number of publications on LUT research are USA (2982), China (1496) and Germany (844), followed by UK, Australia, Canada, Netherlands, France, Spain and Italy (Table 1). Research on LUT has attracted widespread attention in various fields. Statistical analysis shows that research results related to LUT have been published in more than 1600 SCI/SSCI indexed journals, covering multiple disciplines and fields such as geography, environmental science, ecology, sociology, economics and urban planning. The top 10 journals with publication volume are: Land Use Policy, Sustainability, Remote Sensing of Environment, Remote Sensing, Science of the Total Environment, Land, Plos One, Applied Geography, Landscape and Urban Planning and Environmental Research Letters (Figure 2).
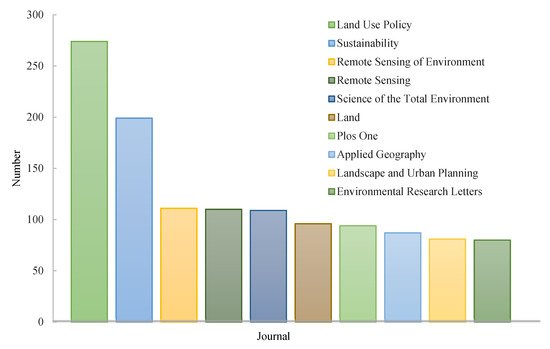

Figure 2. The top 10 journals with publication number concerning LUT during 1987–2020.
Table 1. Major countries publishing articles concerning LUT.
| Rank | Country | Number of Articles | Centrality a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 2982 | 0.32 |
| 2 | China | 1496 | 0.03 |
| 3 | Germany | 844 | 0.19 |
| 4 | UK | 727 | 0.14 |
| 5 | Australia | 563 | 0.16 |
| 6 | Canada | 515 | 0.17 |
| 7 | Netherlands | 454 | 0.1 |
| 8 | France | 435 | 0.14 |
| 9 | Spain | 358 | 0.08 |
| 10 | Italy | 350 | 0.05 |
Note: a Centrality is an indicator to measure the importance of nodes in the network [9][10]. The larger the value of centrality is, the more the number of publications cooperated with other countries.
2.2. Evolving Research Hot Topics
2.2.1. Analysis of Keywords and Hot Topics Distribution
CiteSpace provides three visualizations methods: cluster view, timeline view and timezone view. Among them, the timeline view focuses on delineating the relationship between clusters and the historical span of literature in a certain cluster. Based on CiteSpace, the keywords and hot topics related to LUT research since 2000 (few literatures on LUT previous to this) were analyzed. CiteSpace provides two indicators, modularity Q (Q) and weighted mean silhouette (S), based on the network structure and the definition of clustering. It can be used as a basis for us to judge the effect of atlas rendering. Generally speaking, Q value is generally within the interval of (0, 1), and Q > 0.3 means that the community structure divided is significant. Weighted mean silhouette means the homogeneity of the cluster. The higher the value is, the more consistent the members in the cluster will be. S > 0.7, means that the clustering is efficient and compelling [10][9]. The result showed the modularity Q and weighted mean silhouette of the cluster analysis are 0.6333 and 0.7154, respectively, indicating that the model clustering results are scientific and reasonable. Finally, the timeline map of LUT research from 2000 to 2020 was obtained (Figure 3). Related research hot topics can be roughly divided into 11 categories, i.e., LUT, land change, rural development, fallow management, circulation, shifting cultivation, change detection, habitat, land-use change, rural poverty alleviation and grassland traditional management. There are 10 keywords with a frequency of more than 30, i.e., dynamics, impact, China, deforestation, pattern, forest transition, cover change, urbanization, land use and model. Through the analysis of high-frequency words, it is found that the keywords of LUT research cover a wide range, and there are obvious differences in the research focus and hot topics at different stages. In general, it can be divided into the following three stages:
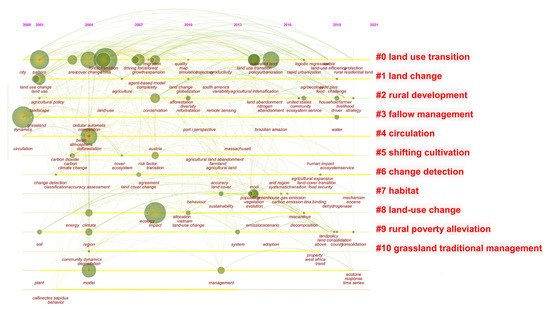

Figure 3. Timeline map of LUT research.
(1) Slow growth stage (2000–2007): This stage focuses on forest transition and land use change caused by large-scale deforestation due to population growth and agricultural expansion, as well as the impact of LUT on climate change, landscape, ecosystem, grassland management and agriculture policy.
(2) Fluctuant rising stage (2008–2012): At this stage, research on LUT has gradually attracted attention. The research focuses on land use change under the context of globalization, and the impact of farmland abandonment, grassland degradation and other factors on land use management and sustainable regional development.
(3) Rapid development stage (2013–present): Related research pays more attention to LUT and its resources and environmental effects in the process of globalization and rapid urbanization. Measuring methods and models of LUT have been explored extensively. At this stage, land abandonment and farmers’ livelihood changes brought about by farmland and rural housing land transition have arisen the attention on the issues of ecosystem service changes.
2.2.2. Burst Words Analysis
The keywords emergence degree can be used to explore the words with high frequency changes in a certain period of time from a large number of subject words, thereby reflecting the change of research hot topics during that period. Burst words represent the phenomenon that the keywords to be investigated transition in a short period of time. Burst words can detect words with a high frequency change rate in a certain period of time from a large number of subject words by investigating word frequency, emphasizing sudden change. Burst terms detection in CiteSpace was used to detect the emergent keywords in the LUT research from 2000 to 2020, and 25 emergent words were detected (Table 2). It can be seen from Table 2 that at different stages, there are obvious differences in research focus and hot topics areas. Before 2010, there were relatively few research on LUT, mostly focusing on the impact of grassland degradation and deforestation on ecosystems, as well as the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of LUT and simulation studies. After 2010, the direction of LUT research has become more diverse, the frequency of hot topics has increased and more attentions have been paid to the research on complex issues caused by LUT. From 2010 to 2017, research topics such as land-change, transition-matrix, management, land-cover change and land-use change received more attentions. From 2017 to 2020, relevant research pays more attention to the impact of urbanization expansion and globalization on LUT. Among them, the spatio-temporal evolution of land-use change process, driving factors and its impacts on regional sustainability have become hot topics.
Table 2. Top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts during 2000–2020.
| Keywords | Year | Strength a | Begin | End | 2000–2020 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vegetation | 2000 | 14.51 | 2000 | 2007 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| evolution | 2000 | 7.01 | 2000 | 2007 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| simulation | 2000 | 15.47 | 2000 | 2011 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| record | 2000 | 9.2 | 2000 | 2014 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| ecosystem | 2000 | 11.03 | 2002 | 2010 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| fire | 2000 | 8.45 | 2002 | 2011 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| pasture | 2000 | 7.41 | 2004 | 2011 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| grassland | 2000 | 8.67 | 2005 | 2009 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| deforestation | 2000 | 7.32 | 2007 | 2008 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| forest transition | 2000 | 7.17 | 2008 | 2013 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| land-change | 2000 | 15.71 | 2010 | 2010 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| transition-matrix | 2000 | 3.22 | 2010 | 2010 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| management | 2000 | 3.3 | 2012 | 2018 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| carbon stock | 2000 | 7.42 | 2014 | 2017 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| land cover change | 2000 | 3.44 | 2015 | 2016 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| land-use change | 2000 | 3.35 | 2015 | 2017 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| expansion | 2000 | 3.62 | 2017 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃ |
| sustainable development | 2000 | 9.74 | 2018 | 2019 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂ |
| land use transition | 2000 | 4.11 | 2018 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ |
| life cycle assessment | 2000 | 7.05 | 2018 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ |
| urbanization | 2000 | 6.39 | 2018 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ |
| ecosystem service | 2000 | 11.36 | 2019 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
| renewable energy | 2000 | 9.2 | 2019 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
| politics | 2000 | 7.51 | 2019 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
| consolidation | 2000 | 7.45 | 2019 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
Note: a Strength is an indicator to measure the degree of a burst event. The larger the value is, the more active the keyword is in the research field. b The red line indicates the year with active burst words, and the green line indicates the year with inactive burst words.
2.2.3. Analysis of Institutional Cooperation Network
The institutional cooperation network map can show us how the various institutions are connected, as well as the contribution of each institution in the field of LUT research, which helps us identify researchers and institutions that deserve attention. Through analyzing the major research institutions and cooperation networks of LUT research, we found that LUT research has received extensive attentions in 88 countries and 420 research institutions all over the world (Figure 4). Universities and scientific research institutes have relatively close ties and cooperation. There are 47 institutions with more than 40 articles. The Chinese Academy of Sciences occupies a central position in the cooperation network in the field of LUT research, with University of Maryland, Beijing Normal University, University of Wisconsin, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Colorado State University, Humboldt University, University of Copenhagen and Peking University, as the linkage of the network. In addition, Wageningen University, Michigan State University, University of Amsterdam, Arizona State University, Columbia University, Stanford University, Yale University and other research institutes have also published more fruitful works.
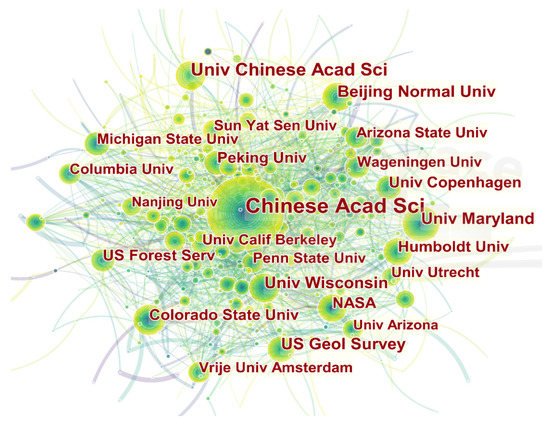

Figure 4. Institutional cooperation network map of LUT research.
3. Key Fields and Hot Topics of LUT Research
3.1. Theories and Hypothesis of LUT
Due to population growth, the global demand for food has accelerated the transformation of natural ecosystems into agricultural land. However, in some developed countries with diversified livelihood strategies, forest coverage has also increased. The latter trend is referred to as the forest transition, which is defined as the transition from net deforestation to net forest coverage increase [11]. In the early 1990s, Mather pioneered the forest transition hypothesis [12][13][12,13]. In 1995, Grainger proposed the concept of LUT from the perspective of land use morphology changes in forestry countries. He assumed that most forestry countries have to go through some stages of development: continuous deforestation and increased forest land until a new balance is reached between the forestry and agricultural sectors [14][15][14,15]. Forested land can even increase again due to self-regeneration and artificial afforestation. This turning point is what Mather calls forest transition, that is, at this point, the national forestry cover stops decreasing and starts to increase. In 2005, Foley constructed a stage model of LUT, suggesting that land may undergo five stages of transformation from natural ecosystems such as forests to territorial reclamation, subsistence agriculture and smallholder management, gradual intensification and intensive use [5]. Due to differences in the historical, social, economic conditions and ecological environment of different regions, the speed and stage of LUT are also different, and they are subject to socio-economic levels and national policies.
Human activities have modified the natural environment considerably. As the population grows, growing demand for food makes more land is needed to expand food production, which intensifies land-use and land-cover changes (LUCC) [16][17][18][16,17,18]. To gain better understanding of land-use and land-cover changes and of the physical and human driving forces behind these processes, LUCC project was cosponsored [19]. LUT is one of the manifestations of LUCC, and is also an important research content of GLP. Scholars have carried out research on the conceptual connotation, theoretical models, measurement methods, driving mechanism and environmental effects of LUT [20][21][22][23][24][20,21,22,23,24]. Long theorized land use transitions by developing and expanding the concept and connotations of land use morphology as dominant morphology and recessive morphology [23]. The dominant morphology refers to the land use structure of a certain region over a certain period of time, with features such as the quantity (area and proportion) and spatial pattern of land use types. While the recessive morphology includes the land use features in the aspects of quality (nutrient, pollution and degradation), property rights (state-owed and collective-owed), management mode (individual, joint-stock system and transfer and large-scale management), input (capital, technology and labor), output (yield, output value and input-output ratio) and function (production, living, ecology and culture). Accordingly, the concept of LUT was further developed as the changes in land use morphologies, including dominant morphology and recessive morphology, of a certain region over a certain period of time driven by socio-economic change and innovation, and it usually corresponds to the transformation of the socio-economic development stage [23][25][23,25]. Long put forward the theoretical model of regional land use transitions, i.e., as the socio-economic development, the competition/trade-off between different land use types presents a decreasing trend, and finally achieves a stable equilibria [25][26][25,26].
Based on the special socio-economic, socio-ecological and physical conditions, some scholars probed the research theoretical framework and hypotheses of LUT [27][28][29][30][31][32][27,28,29,30,31,32]. Qu and Long (2018), based on existing researches and the Environmental Kuznets Curve, put forward a theoretical hypothesis of the interactive mechanism among the land use transitions, the economic effect, the environmental effect and the land use management. Finding that there was a one-way Granger causality from urban construction land use transitions to economic development and environmental pollution, respectively, and no significant Granger causality was found from land use management to economic development or environmental pollution [33]. Some scholars supported that LUT refers to any change in land use systems from one state to another one, land use change is non-linear and different parts of the world are in different transition stages, depending on their history, social and economic conditions and ecological context [32][34][32,34].
3.2. Measuring LUT
The selection of land use morphology indicators and the measurement of its transition process are the premise and basis for analyzing the characteristics of LUT. The extension of land use morphology brings about opportunities and challenges as the qualitative aspect of land use transitions is reflected by the changes of recessive land use morphology, which is difficult to be measured or represented [35][36][35,36]. The research on the dominant morphology of land use is an important prerequisite for the recessive morphology research. The dominant and recessive morphologies are coupled to construct the characterization index of LUT, and various methods are used to quantify LUT. Comprehensive measurement helps to explore the characteristics and regularities of LUT from multiple perspectives and levels. Accordingly, Long put forward three innovative integrated approaches to study land use transitions: one is the multidisciplinary research framework for recessive LUT which involves disciplines including geography, management, economics and sociology [23]; another is the horizontal comparison research method with space to exchange for time [25]; the other is the transect research method based on the key gradient factor of regional socio-economic development [37]. Tsai used interactive LUT agent-based model by endogenizing the interactions of socio-ecological feedbacks and socio-economic factors in a generalizable model to simulate changes in land use caused by farmers’ decision-making behaviors, and the recursive effects of land use changes on farmers’ decision-making behaviors, and explored the conditions for forest transition in different scenarios [38]. Some scholars have used land satellite images and GIS to explore the trajectory of long-term series of forest cover changes, reveal the main driving paths of forest transition, and analyze the impact of forest transition on ecosystem products and services [39][40][41][39,40,41].
Through literature review, it is found that since the end of the 20th century, related research has shifted from focusing on single-dimensional LUT to multi-dimensional one [42][43][44][42,43,44]. At present, scholars are conducting research on the measurement, simulation, spatial differentiation characteristics and influence factors of LUT based on remote sensing data, national statistics data and survey data [45][46][47][48][49][45,46,47,48,49]. The measurement methods include classification and regression tree (CART) models, interactive land use transition agent-based model (ILUTABM), global land-use model (GLM), system of environmental-economic accounting (SEEA), center of gravity model, cold/hot spots analysis and other methods [22][50][51][52][53][54][55][56][57][58][22,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58] (Table 3). At the same time, methods such as structural analysis, questionnaire interviews and the spatial econometric model have also been gradually applied to related researches. Abundant data sources and multiple models provide a variety of ideas for the measurement of LUT, and also provide scientific support for the research of LUT caused by socio-ecological feedback under the background of globalization. However, current researches focus on the measurement of the dominant morphology transformation of land use, while the measurement of the recessive morphology transformation of land use and its impact on “social-economic-ecological” still need to be further explored.
Table 3. Characterization and measurement methods of LUT.
| Data a | Methods | Object/Research Question | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote sensing data | Classification and regression tree (CART) models | Land use transitions in unsustainable arid agro-ecosystems | Romo et al., 2014 [41]; Bonilla-Moheno and Aide, 2020 [50] |
| Cellular automata models | Rules relate LUCC variables to the observed historical changes | Roodposhti et al., 2019 [51] | |
| Land-use transfer matrix | Regional land use type conversion | Liu and Long, 2016 [22]; Quintero-Gallego et al., 2018 [52] | |
| Interactive land use transition agent-based model (ILUTABM) |
Simulates the land use changes resulting from farmers’ decision | Tsai et al., 2019 [56] | |
| Statistics data | Global land-use model (GLM); earth system models (ESMs) | Harmonization of land-use scenarios | Hurtt et al., 2020, 2011 [47][57][47,57] |
| Transect research method | Rural housing land transition | Long et al., 2007 [37] | |
| Land use change (LUC) models, Dyna-CLUE model | Assessment Land use change modelling accuracy | Lü et al., 2020 [54] | |
| System of environmental-economic accounting (SEEA) | Land cover account | Wentland et al., 2020 [48]; Weber, 2007 [49] | |
| Survey data | Ethnographic fieldwork | How customary land tenure systems mediate transformations of land use and livelihoods | Rignall and Kusunose, 2018 [58] |
| Decoupling index model and balance index model | Coupling relationship of land use transition between cultivated land and rural residential land in China | Qu et al., 2019 [55] |
Note: a Measuring LUT is highly depended on the data sources, which is an important criterion and perspective for the classification of the techniques of measuring LUT. Therefore, we divided the measurement methods of LUT into three types based on data sources, i.e., remote sensing data, statistics data and survey data.
3.3. The Impacts of LUT on “Social-Economic-Ecological” System
3.3.1. Impacts of LUT on Social Development
LUT is the result of the interaction between natural environmental conditions and socio-economic factors. Influential factors of LUT include endogenous socio-ecological forces and exogenous socio-economic factors [32]. On the one hand, various land use issues are related to the rapid urban-rural transformation development, which has significant impacts on land use policies [59][60][61][59,60,61]. On the other hand, socio-economic system and policies, especially those that related to land resources management, are important external factors that play a vital role in shaping land use morphology [62][63][62,63].
Considering the regions that LUT takes place, it can be divided into two counterparts-urban area and rural area. Urban LUT is a process of the expansion of construction land and reduction of cultivated land and forestland in the process of urbanization. Farmland transition and rural housing land transition are two crucial contents of rural LUT [64][65][66][64,65,66]. Against the context of globalization, marketization and urbanization, the growing foreign direct investment and tertiary industry accelerates the expansion of urban construction land, which encroaches on vast farmland and drives the changes of household livelihood and population flow, and, finally, induces the alteration of land use structure [67][68][67,68]. In view of rural regions, the variation of regional land use morphology is tightly associated with rural transformation development, and at the same time, is constrained by system vicissitude and national strategy [58][69][58,69]. The strategy to alleviate the pressure on land resources in some areas is to move production activities from one area to another [70], and it is not a sustainable way. Therefore, some scholars proposed sustainable land management scheme to assess the risk of land consolidation and agricultural development, reconcile environmental and agricultural policies, and to solve the problems of grassland abandonment and low land use efficiency [71][72][71,72].
3.3.2. Impacts of LUT on Economic Growth
LUT is motivated by socio-economic changes. Due to the extensive exchange of energy, material, and information flows between the internal and external urban-rural territorial system, the main bodies of land use are more sensitive to the economic and social responses. Decisions relating to economic development demand often directly or indirectly change the supply of land services, thereby triggering the transformation of land use structure and functions [63]. With the increase of population, in order to meet people’s various demands for land in production and living, productive land around the world has been extensively developed and converted [73]. Regarding competition for productive land, different scholars have different views, Malthusian believes that the stock of suitable land is finite, continuous development will lead to a shortage of productive land, which will have a negative impact on welfare. Ricardian reckoned that it becomes economically feasible to bring marginal land into use as prices of land-based commodities increase, but it comes at ever increasing economic, environmental and social costs. The economic impact of LUT is not directly proportional to the area loss, but is affected by the combined effects of soil capacity, dryland crop combination and local economic factors [74]. Due to the changes in socio-economic factors, such as the decline in soil quality, the increase in the opportunity cost of farming, the outmigration of rural labor, the adjustment of agricultural policies, and the reform of the land system, etc., land abandonment has become one of the important trends of global land use changes and it is crucial for agricultural production and landscape planning [1][52][75][1,52,75]. In response to the negative effects of LUT on rural economic development, Ojoyi pointed out that extra employment opportunities and livelihood support activities should be created to minimize dependence on natural resources [7]. Some scholars believe that through rural land use planning and advanced technologies, agglomerated economic production can be formed, which promotes the transition from the fragmented use of land under the subsistence agriculture model to the large-scale management under the intensive farm model, so as to reduce deforestation and relieve land pressure and improve land use efficiency [5][76][77][78][5,76,77,78].
Rural reform and development have always been the hot-spot issues of LUT, which function as the tool of regulating land use and promoting socio-economic development [33]. The internal driving force of LUT comes from the trade-offs and games between different stakeholders, which is manifested in the conflict of land use patterns. Driven by conflicts, the structure and function of land use are continuously adjusted to adapt to the new balance requirements, and, finally, LUT is realized through land services supply [4][79][4,79]. Farmland use is a complex process of rural agricultural economic reproduction and natural reproduction. The transition of cultivated land use has an important impact on the rural natural landscape and socio-economic development [53][80][53,80]. Especially in the context of ecological civilization construction and national food security, research on the mutual feedback mechanism of farmland transition and food security, and its impacts on farmers’ livelihoods, rural industrial development and rural transformation development have received widespread attention [24][81][24,81].
3.3.3. Impacts of LUT on Ecosystem Services
At present, research on LUT and its environmental effects is mainly implemented by using GIS techniques, ecosystem service value assessment, landscape pattern index and ecological environment index, at the scales of regional, drainage basin, provincial, prefecture-level city, county level and township level. In the process of socio-economic development, the impacts of LUT on eco-environment have become one of the research priorities of global change research. The corresponding research contents range from atmospheric composition to terrestrial ecosystem [82][83][84][82,83,84], which generally can be divided into three aspects: (1) the impacts of LUT on atmospheric environment, water environment, soil environment, vegetation and biodiversity; (2) the impacts on overall ecosystem service; (3) the landscape ecological pattern responses, and the coupling relations between land use structure and land use multifunctionality [85][86][87][85,86,87].
Land development is revenue-oriented, the increase in human activities and commercial space is mainly at the expense of forest-covered ecosystems, farmland and pasture [19][88][89][90][19,88,89,90]. How to deal with the trade-offs between the value derived from new land uses and the cost of lost ecosystem services has become a very important proposition. The rapid transformation and fragmentation of land cover may lead to a series of problems such as biodiversity loss, land degradation, water quality decline, insufficient food supply, extinction of wildlife and environmental degradation [91][92][93][94][95][91,92,93,94,95]. Faced with the trade-off between environmental protection and food security, some scholars have proposed ecological plans for cropland reforestation and urban green projects through the production of commodities with high income and price elasticity to alleviate the pressure on the ecological environment caused by over-development of land resources [86][96][86,96]. In order to alleviate the pressure on grassland areas caused by the transformation of grassland to cultivated land, the EU sets minimum standards for the protection of the ratio of permanent grassland to protect the ecological value of grassland [97].
3.4. Drivers and Regulation of LUT
3.4.1. Research on the Driving Factors of LUT
In most cases, LUT is a random process [5]. Carrying out research on the driving factors of LUT will help scientifically regulate the quantity and quality of regional land resources, and is of great significance to regional land use planning, regional ecological environmental protection, mitigating global climate change and vegetation restoration strategies [7][98][99][7,98,99]. From the perspective of the land system, the driving factors of LUT can be divided into endogenous driving forces and external driving forces. The interaction and mutual influence of various factors have a comprehensive and complex impacts on urban-rural development and land use. On the one hand, with population growth, people’s demand for productive land and residential land has increased. Urban land and agricultural land have largely replaced other land, and were limited by the location [100][101][102][100,101,102]. On the other hand, with socio-economic development, global power has become the main determinant of LUT. Facing the pressure of population growth and extreme poverty, national markets and policies created opportunities and constraints for new land uses [103][104][105][103,104,105].
In general, LUT is the result of the combined effect of endogenous socio-ecological feedback and exogenous socio-economic factors [106]. The intense flows of information, capital, commodities and people generated by the increasing interactions in this globalized world greatly influence the land use patterns, which highlights the forces of the remote markets [107]. The driving forces of LUT are related and heterogeneous in different time and space dimensions, and are affected by many complex factors such as nature, politics, economy, and culture [50][108][50,108]. Natural factors include natural disasters, endowment discrepancy and climate change; socio-economic factors incorporates globalization, urbanization, marketization, demand for agricultural products, agricultural production activities and population growth; political factors consist of national policies, land consolidation and land resource management systems.
3.4.2. Research on Optimal Regulation of LUT
At present, the root cause of many issues arise from LUT is the contradiction between socio-economic advancement and environmental protection, which results from the fact that, in most cases, economic growth is at the expense of environmental sustainability [77]. How to deal with the relationship between the social and economic benefits and resources and environmental benefits is the key to optimal regulation of LUT. Through literature review, it is found that the optimization and regulation of LUT is mainly realized through engineering and technological means, and policy and system innovation. The main cause of LUT lies in the fact that rural land has been intensively occupied by urban construction land. In terms of the regulation of LUT, it is necessary to change the way in which the external system of the rural area affects the internal system, promoting the free flow of urban and rural elements [109][110][111][109,110,111]. Land use planning and land consolidation are important engineering techniques to optimize and control the LUT. Rural land use planning is a way to ensure the best use of land. By evaluating and balancing the trade-offs between different social, economic and environmental goals, it discusses how to adjust the land use structure through spatial planning, so as to achieve the optimal land use status and promote the transformation of land use from single-function oriented to multifunctional land use [112][113][114][115][112,113,114,115]. As a policy tool to optimize the structure of land use and improve the efficiency of land use, land consolidation has the dual attributes of engineering projects and policy measures [72][116][117][72,116,117].
In response to the problems induced by LUT, relevant management departments have formulated a series of policy interventions to promote the sustainable use of land resources. Such as America’s Endangered Species Act (ESA) and National Environmental Protection Act (NEPA), and land retirement programs and production subsidies, China’s “1.8 billion mu red line” and “Grain for Green Policy”, and Morocco’s Customary land tenure [29][30][31][29,30,31]. France has adopted environmental policies aimed at the conservation of natural habitats and wildlife, and Cameroon enacted national forest law, which provided the legal basis for the implementation of a land use zoning [8][75][118][119][8,75,118,119]. It is possible to design alternative land-use management strategies to fight desertification processes [70]. Customary land tenure is essential for regulating land use and farmers’ livelihoods and ensuring economic growth [69]. In addition, applications of dynamic land use classification have also been highly recognized. In order to facilitate the targeted implementation of land management strategy, some scholars divided territorial space into rural protection area, suburban coordination area, urban agglomeration area, restricted development area and conditional construction area, and propose corresponding management measures and policies according to the characteristics of each specific area to regulate land use activities and address the relationship between economic development and environmental protection [87][120][87,120].
