Deregulation of the
TAL1 oncogene is a feature of T-ALL that typically exhibits a late cortical thymocyte immunophenotype (CD4
+, CD8
+, CD3
+) and comprises approximately 40% of T-ALL
[27][28][135,136]. This T-ALL subtype includes
TAL1 and
TAL2 rearranged cases and is further classified into two subgroups by expression profiles whose one expresses
PTCRA (pre-TCR) suggesting LCK activation that correlated with dasatinib sensitivity
[28][37][41][136,145,149]. During normal T-cell differentiation,
TAL1 expression is transcriptionally silenced along with T-cell lineage commitment to proceed appropriate
TCR rearrangements and differentiation
[25][133].
TAL1 overexpression is induced by several mechanisms: (1) chromosomal translocations with
TCRA/D; (2) sub-microscopic interstitial deletion (
STIL-TAL1); (3) disruption of insulated neighborhoods by losing CTCF binding sites
[42][150]; and (4) somatic indels in a noncoding intergenic regulatory element upstream of
TAL1 to generate aberrant MYB binding site (
MuTE)
[29][137]. The latter two mechanisms have benefited of NGS technologies for their identification. Dysregulated
TAL1 expression inhibits the function of E-protein dimers by forming TAL1-E-protein heterodimer
[43][151]. Furthermore, TAL1 forms the central node of the core regulatory circuit to coordinately regulate downstream target genes with several hematopoietic transcription factors including
GATA3,
RUNX1,
MYB, and the ETS family genes, which is active in normal hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) and progenitor cells
[44][45][152,153], and RUNX1 inhibition is reported to impair the growth of T-ALL but not normal hematopoietic cells
[46][154]. However, although TAL1 functions as a master transcription factor related to T-cell differentiation and leukemogenesis of T-ALL, only 30% of transgenic mice develop T-ALL after a latent period, indicating that additional abnormalities are required for leukemogenesis
[47][155]. Expression of
Lmo2 accelerates the onset of leukemia in
Tal1 transgenic mice, and
LMO1/LMO2 are commonly expressed in human
TAL1-driven T-ALL
[48][49][156,157]. Other cooperative genes and noncoding RNAs in
TAL1-driven T-ALL include
ARID5B,
ARIEL, and
MYC, driving aberrant expression of
TAL1 [50][51][158,159]. In addition, PI3K-AKT pathway genes including
PTEN are frequently mutated in this subgroup
[27][28][135,136], which associates with glucocorticoid resistance and can be reversed by the inhibition of this pathway
[52][160]. Several cell cycle regulators including
CDK6 and
CCND3 are regulated by TAL1 complex
[44][152] and may be potential targets of therapeutic intervention
[53][161].
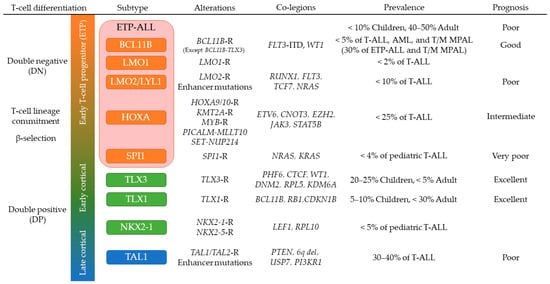
3.4. Early T-Cell Precursor (ETP) ALL and Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia
ETP-ALL is often referred to as a subtype of T-ALL as it exhibits an immunophenotype analogous to the earliest stages of T-cell development (cytoplasmic CD3
+, CD7
+; CD8
−, CD1a
−, CD5
weak), and with expression of myeloid and/or stem-cell markers
[36][54][144,162]. However, the genomic alterations and gene expression profile of ETP-ALL are more similar to a hematopoietic stem cell than a T cell precursor, suggesting that ETP-ALL could be included in a subgroup of immature acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage (ALAL), originating from a hematopoietic progenitor at a maturational stage prior to initiation of a definitive program of T cell differentiation. Consistent with this, recent studies have defined a subgroup of
BCL11B-deregulated ALAL, that includes one third of ETP-ALL and T/myeloid mixed phenotype acute leukemia (T/M MPAL) cases with a very distinct expression profile
[5].
BCL11B-deregulated ALAL is characterized by structural variations of the region containing
BCL11B at 14q32 including translocations and high-copy amplification generating a distal neo-enhancer, that each leads to aberrant expression of
BCL11B, in the case of the rearrangements by hijacking super-enhancers active in CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPCs)
[5][39][5,147].
FLT3 activating mutations were found in 80% of
BCL11B-deregulated ALAL, and concurrent expression of
BCL11B and
FLT3-ITD on HSPC exhibited synergistic effects on activating T-cell directed differentiation to express cytoplasmic CD3 while blocking myeloid differentiation
[5]. Other genomic features of ETP-ALL include a subgroup of aberrant expression of
PU.1 (
SPI1 fusions),
HOXA genes (rearrangements of
HOXA genes,
KMT2A rearrangements,
PICALM-MLLT10,
SET-NUP214) and mutations of multiple cellular pathways (Ras signaling, JAK-STAT signaling, and epigenetic regulators) and transcription factors related to T-cell development
[27][28][55][135,136,163]. Especially, T-ALL with
SPI1 fusions represents unique expression profiles with high relapse rate
[5][28][5,136]. Again, several of these genomic mutations were shared with T/M MPAL, including biallelic
WT1 alterations, mutations of hematopoietic transcription factors (
ETV6,
RUNX1,
CEBPA) and activating mutations of signaling pathways (JAK-STAT,
FLT3, Ras)
[56][55][92,163], supporting that they are similar entities in the spectrum of immature leukemias and both might have sensitivity to FLT3 and/or JAK inhibition
[57][164].
3.5. NOTCH1 Activating Mutations in T-ALL
NOTCH1 encodes a highly conserved ligand-dependent transcription factor. The NOTCH1 signaling pathway plays an important role in the commitment of T-cell lineage specification and for further T-cell development
[25][58][133,165]. In T-ALL,
NOTCH1 activating mutations are found in more than 70% of cases and is considered an oncogene involved in leukemogenesis
[27][28][135,136]. Aberrant activation of NOTCH1 pathway in T-ALL is mostly induced by (1) ligand-independent activation (somatic mutations, indels and large deletions that disrupt the negative regulatory region), or (2) impairment of the proteasomal degradation of intracellular domain of NOTCH1 (truncation of the PEST domain,
NOTCH1 mutations in 3′ untranslated region, and
FBXW7 mutations)
[59][60][61][62][63][64][166,167,168,169,170,171]. These two types of
NOTCH1 activating mutations have synergistic effects and more than 20% of T-ALL cases harbor both types of alterations
[59][166]. However, most
NOTCH1 activating mutations found in human T-ALL are considered as a weak tumor initiator event. Co-existence of both types of
NOTCH1 mutations in hematopoietic progenitors tends to induce a transient preleukemic CD4
+/CD8
+ double positive cells and takes 10 to 15 weeks to fully transform into T-ALL, suggesting that they are alone incompletely leukemogenic
[65][66][67][172,173,174]. In addition, more than 40% of T-ALL cases harbor subclonal
NOTCH1 activating mutations and their heterogeneity at diagnosis was reported by several studies
[27][28][68][135,136,175]. Furthermore,
NOTCH1 activating mutations are considered to be acquired as a late secondary event in leukemogenesis
[31][68][69][139,175,176].
A key target of NOTCH1 is the
MYC oncogene that shares several overlapping target genes with NOTCH1 to promote cell proliferation and dysregulate anabolic pathways in T-ALL
[67][70][71][174,177,178]. NOTCH1 controls T-cell-specific distal enhancer of
MYC (“NMe”), resulting in the NOTCH1-MYC regulatory circuit
[67][70][71][174,177,178]. In addition, pre-TCR signaling also correlates with NOTCH signaling, leading to LCK signaling and robust cell growth at DN3 stage in the T-cell development, which can be targetable by dasatinib
[41][72][149,179].
Due to the high prevalence and importance of
NOTCH1 activating mutations in T-ALL, targeted therapy on NOTCH1 pathway has been a major interest. This includes γ-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), ADAM inhibitors, SERCA inhibitors, and monoclonal antibodies
[73][180]. Among them, GSIs, that block the activation process of NOTCH receptors by inhibiting proteolytic cleavage, have been tested in preclinical and Phase 1 studies
[74][75][181,182]. However, the usage of GSIs in T-ALL is still in a developing phase due to gastrointestinal toxicity and insufficient antitumor responses that mostly induce transient growth arrest rather than cell death
[76][77][183,184]. To overcome these problems, combination with other agents have been explored including glucocorticoids that showed synergistic effects by reversing glucocorticoid resistance
[78][185]. Inhibition of mTORC1 signaling and PKCδ signaling are also promising combination strategies to restore GSIs sensitivity in resistant cells
[79][80][186,187].
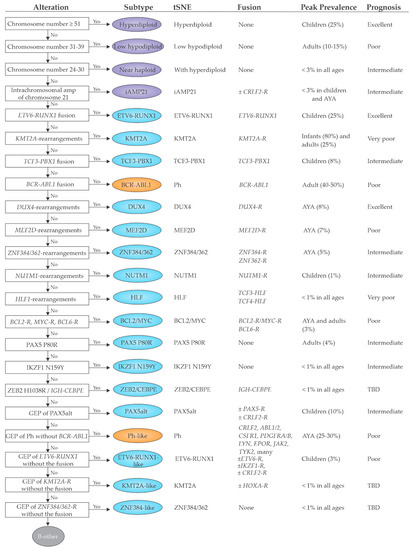
4. Implications for Diagnosis
The revolution in genomic characterization of ALL has created important opportunities and challenges for the clinical implementation of sequencing-based approaches for diagnosis and management of ALL (
Table 1). This is particularly true for B-ALL, where many of the recently identified subtypes are associated with prognosis (even in the context of MRD-based risk-adapted therapy)
[22][21][82,83] and where molecular characterization is needed to identify patients suitable for targeted therapy (an exemplar being Ph-like ALL). This is currently less compelling for T-ALL where identification of founding lesions driving T-ALL subtypes are of biological and mechanistic interest but are not typically used to risk stratify or guide therapy, exceptions possibly being kinase inhibition for JAK-STAT alterations and
ABL1 rearrangements, identification of alterations in Ras,
PTEN,
NOTCH1 and/or
FBXW7 that have been found to be associated with outcome in some studies
[81][188], and LCK dependence for dasatinib therapy
[41][149]. The challenge is clinical implementation of appropriately comprehensive diagnostic approaches to identify all key genomic features. Despite the mutationally sparse genome of ALL, there is striking diversity of the nature of underlying driver alterations, including sequence mutations, DNA copy number alterations, and structural variations, many of which may involve the non-coding genome. Accurate subtyping is also challenged by the inability of conventional cytogenetic and targeted molecular approaches to identify several types of driver (e.g.,
DUX4-rearrangement) and the importance of identifying phenocopies (e.g.,
ETV6-RUNX1-like, and Ph-like ALL). Thus, moving forward, optimal clinical diagnostics require genomic approaches. The choice of approach in part rests on how clinical information will be used. If comprehensive subtyping and identification of all potentially clinically relevant genomic alterations is desirable, a combination of DNA and RNA-based technologies is required. For example, the combination of WGS and WTS enables the identification of sequence mutations, DNA copy number alterations, aneuploidy and structural variants (from WGS) together with identification of fusion chimeras, mutant allele expression, and gene expression profiling (from WTS). The use of one or both approaches is becoming increasingly widely used, and at St Jude Children’s Research Hospital, three platform sequencing (WGS, WTS and exome sequencing) is clinical standard of care, informs clinical decision making in ALL
[40][148], and retrieves more actionable clinical information than any single platform alone
[82][189]. WGS is offered using a paired non-tumor sample to aid identification of somatic variants and provides the opportunity to return clinically relevant germline findings. Moreover, this comprehensive approach enables a more streamlined workflow
[83][84][85][190,191,192], provided the demands of analysis and interpretation can be met.
Table 1. Clinical implementation of high-throughput sequencing.
|
| Platform |
|
| Capability |
|
| Cost |
|
| Detectable |
| Subtypes |
|
| Difficult |
| Subtypes |
|
|
| WTS |
| (RNAseq) |
|
| Fusion chimeras |
| Gene expression profiling |
| Mutant allele expression |
| Alternative splicing analysis |
| (BCR/TCR rearrangements) |
| (Sequence mutations) |
| (Copy number analysis) |
|
| Moderate |
|
| B-ALL |
| ETV6-RUNX1; KMT2A; TCF3-PBX1; BCR-ABL1; DUX4; MEF2D; ZNF384/362 |
| NUTM1; HLF; BCL2/MYC; PAX5alt; ZEB2/CEBPE; |
| -like subtypes |
|
| B-ALL |
| Aneuploidies |
|
|
| T-ALL |
| HOXA ( KMT2A-R, PICALM-MLLT10, SET-NUP214); SPI1; NKX2-1; TAL1 (STIL-TAL1) |
|
| T-ALL |
| BCL11B; TLX1/3; LMO1/2; HOXA (others); TAL1 (others); T-other |
|
|
| WGS |
|
| Sequence mutations |
| Structural variants |
| Copy number analysis |
| (BCR/TCR rearrangements) |
| (GWAS) |
|
| High |
|
| B-ALL |
| Aneuploidies; ETV6-RUNX1; KMT2A; TCF3-PBX1; BCR-ABL1; DUX4; MEF2D; ZNF384/362; NUTM1; HLF; BCL2/MYC; PAX5 P80R; IKZF1 N159Y; ZEB2/CEBPE; Sequence and structural alterations in Ph-like ALL |
|
| B-ALL |
| -like subtypes; |
| Part of PAX5alt |
|
|
| T-ALL |
| BCL11B; TLX1/3; LMO1/2; HOXA; |
| SPI1; NKX2-1; TAL1 |
|
| T-ALL |
| T-other |
|
|
| WES |
|
| Sequence mutations (coding) |
| Structural variants (coding) |
| Copy number analysis |
|
| Moderate |
|
| B-ALL |
| (Aneuploidies) |
| PAX5 P80R |
| IKZF1 N159Y |
| Sequence mutations in Ph-like ALL (e.g., JAK1/2/3, Ras) |
|
| Most of other B-ALL and T-ALL subtypes |
|
|
| Targeted sequencing |
| (DNA and/or RNA) |
|
| Fusion chimeras (targeted) |
| Gene expression (targeted) |
| Sequence mutations (targeted) |
| Structural variants (targeted) |
| (Copy number analysis) |
|
| Low |
|
| Targeted alterations |
|
| Non-targeted |
| alterations |
|
The parenthesis in “Capability” indicates analyses in development. Abbreviations: WTS: whole transcriptome sequencing; BCR: B-cell receptor; TCR: T-cell receptor; WGS: whole genome sequencing; GWAS: genome wide association study; WES: whole exome sequencing; -R: rearranged.