Candida albicans is a major fungal pathogen of humans, accounting for 15% of nosocomial infections with an estimated attributable mortality of 47%. C. albicans is usually a benign member of the human microbiome in healthy people.
- polymorphism
- hyphal morphogenesis
- hyphal activation
- signal transduction pathways
- cell cycle regulation
1. Introduction
Candida albicans is a commensal fungus that is usually a benign member of the microflora in the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary tract, mouth, and skin of most healthy individuals [1][2][3][4][1,2,3,4]. C. albicans is also an opportunistic fungal pathogen responsible for infections ranging from mild superficial infections to life-threatening candidemia [5]. The use of modern medical therapies such as broad-spectrum antibiotics, cancer chemotherapy, and solid organ transplant has led to an increase in the population vulnerable to invasive candidiasis [6][7][6,7]. C. albicans is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections; in the intensive care unit (ICU), candidemia may represent up to 15% of nosocomial infections with an estimated attributable mortality of 47% [7][8][9][10][11][7,8,9,10,11].
C. albicans displays a wide range of virulence factors and fitness attributes, including its capacity for rapid evolution of resistance to commonly used antifungals (e.g., azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins) and its ability to form biofilms on medical devices, contributing to its success as a pathogen. One striking feature that allows C. albicans to cross the commensal-to-pathogen boundary is its ability to switch reversibly between two morphological forms, namely unicellular budding yeast, or filamentous form (hyphae and pseudohyphae), in response to various environmental cues that reflect the host environment [12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
Yeast, hyphal, and pseudohyphal forms of C. albicans are all present in tissues of human patients and animals with systemic invasive candidiasis [20][21][20,21]. Yeast cells exhibit a round-to-oval cell morphology that arises from budding and nuclear division [22]. In contrast, hyphae consist of tubular cells that remain firmly attached following cytokinesis without a constriction at the site of septation. Pseudohyphae share features resembling both yeasts and hyphae, which are branched chains of elongated yeast cells with constrictions at the septum. Both yeast and hyphal forms have crucial and complementary roles important for infection [23]. For instance, the yeast form is required for adhesion to endothelial cells and dissemination into the bloodstream, while the hyphal form is required for tissue penetration during the early stages of infection and yielding resistance towards phagocytosis [24][25][26][27][28][29][24,25,26,27,28,29]. Hyphae-specific virulence factors such as adhesins (Hwp1, Als3, Als10, Fav2, and Pga55), host tissue degrading proteases (Sap4, Sap5, and Sap6), and cytolytic peptide toxin (Ece1), aggrandize the host cell damage during infection [22][30][22,30].
2. Negative Regulators of Hyphal Morphogenesis
C. albicans morphogenesis is negatively regulated by the transcriptional repressors Tup1, Nrg1, and Rfg1 [31][32][33][156,157,158]. Tup1 is a global transcriptional repressor, and its inactivation leads to constitutive filamentous growth and derepression of hyphal-specific genes [34][31][35][130,156,159]. Nrg1 and Rfg1 are well characterized DNA-binding proteins, which regulate different subsets of hyphal-specific genes by recruiting co-repressor Tup1. A DNA microarray analysis revealed significant up-regulation of 61 genes in response to serum and 37 °C [36][160]. Approximately half of these genes are found to be repressed by the transcription factors Tup1, Nrg1, and Rfg1, suggesting their importance in repressing hyphal morphogenesis. C. albicans cells that lack these repressors develop into pseudohyphae with the expression of hyphal-specific genes [37][161]. Surprisingly, only nrg1Δ/Δ mutants form hyphae in response to serum. In addition, nrg1Δ/Δ mutants appear to display stronger hyphal phenotypes than rfg1Δ/Δ mutants, suggesting its predominant role in the negative regulation of hyphal growth [38][162].
Though Tup1 is found to act independently of the cAMP-PKA and MAPK pathways to regulate morphogenesis, it seems to play a crucial role in the farnesol response pathway [39][35][90,159]. Farnesol, an endogenous QSM, is produced when the cell densities of C. albicans are high. While farnesol can block the yeast-to-hyphae transition, it cannot block the elongation of pre-existing filaments [40][41][42][163,164,165]. Morphological and transcriptional studies, which investigated the possible functional overlap between farnesol and hyphal transcriptional repressors, have demonstrated the direct involvement of Tup1 in the farnesol-mediated inhibition of filamentous growth [39][90]. tup1Δ/Δ and nrg1Δ/Δ mutants display elevated levels of farnesol and are constitutively filamentous even in the presence of exogenous farnesol. In the presence of farnesol, TUP1 levels increase, but NRG1 and RFG1 levels are unaffected [39][90]. Further targeted studies on the farnesol-mediated inhibition pathway have unraveled its dedicated mechanistic control of filamentous growth [43][166]. Upon inoculation of cells into fresh medium, where farnesol inhibition is relieved, the transcriptional repressor Cup9 is constantly degraded by the N-end rule E3 ubiquitin ligase Ubr1, allowing the expression of kinase Sok1 and subsequent degradation of Nrg1. In contrast, the presence of farnesol inhibits the degradation of Cup9, thereby repressing Sok1 expression, which in turn blocks the degradation of Nrg1 and hyphal development [43][166].
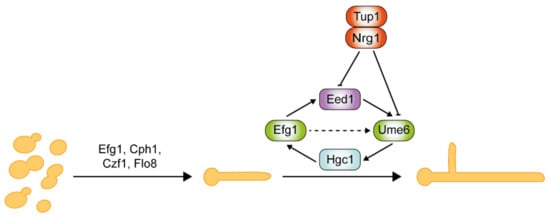
Critical regulators of hyphal initiation and the activation of hypha-associated genes, such as Efg1, Cph1, Czf1, and Flo8, are shown in Figure 14 . Thereafter, a second regulatory network is required for the hyphal elongation process and long-term maintenance of hyphal growth through Hgc1, Eed1, and Ume6, which are negatively regulated by Tup1 and Nrg1 [44][45][46][47][144,167,168,169]. Eed1 was first identified in oral tissue infections from patients suffering from oral disease, and its associated regulatory network was explored through comprehensive transcriptomics analysis [45][167]. Eed1 is positively regulated by Efg1 as the overexpression of EED1 partially rescues the hyphal defects in efg1Δ/Δ mutants. EED1 expression is significantly up-regulated in the continuously filamentous nrg1Δ/Δ and tup1Δ/Δ mutants under non-hyphae-inducing conditions [45][167]. In contrast, under hyphae-inducing conditions, EED1 levels were slightly decreased in nrg1Δ/Δ and tup1Δ/Δ mutants, but elevated 10-fold in wild-type cells. Collectively, this suggests that EED1 is repressed by both Nrg1 and Tup1 in wild-type C. albicans. Ume6 acts downstream of Eed1 as the overexpression of UME6 restored the hyphal elongation defect observed in eed1Δ/Δ mutants [45][167]. UME6 expression levels were significantly down-regulated in eed1Δ/Δ mutants [45][167]. HGC1 expression is detected within 5 min of hyphal induction, whereas UME6 expression is only detected after 15 min upon induction [48][170]. This suggests that a Ume6-independent mechanism initially induces HGC1. Nrg1 and Tup1 negatively regulate both Ume6 and Hgc1 [37][47][161,169]. Ume6 can also be induced as a result of relief of transcriptional repression by the Nrg1-Tup1 complex.
The stability of hyphae-specific transcription factor Ume6 is governed by two parallel pathways in response to O2 and CO2 concentrations [49][50][171,172]. Ofd1 negatively regulates the stability of Ume6 by E3 ubiquitin ligase Ubr1 under hypoxia conditions. ofd1Δ/Δ and ubr1Δ/Δ mutants can maintain hyphal elongation in atmospheric O2 and 5% CO2 [49][50][171,172]. However, deletion of UBR1 does not block Ume6 degradation in atmospheric CO2, suggesting the involvement of additional E3 ubiquitin ligase in response to CO2 [50][172]. Recently, it was discovered that CO2, an inducer of filamentous growth, also plays a critical role in the sustenance of hyphal growth in response to high CO2 (5%) [50][172]. In the CO2 signaling of sustained hyphal growth, a type 2C protein phosphatase (PP2C) Ptc2 and a cyclin-dependent kinase Ssn3 were identified to be the major positive and negative regulators, respectively [50][172]. High CO2 induces Ptc2-mediated dephosphorylation of Ssn3. Consequently, the hypophosphorylated Ssn3 fails to phosphorylate Ume6 at the S437 residue. This prevents subsequent ubiquitination of Ume6 by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF Grr1, resulting in stabilization of Ume6 for the sustenance of hyphal growth.
3. Mechanisms of Hyphal Morphogenesis
The nucleus migrates out from the mother cell to the septin band within the developing hyphae, and the first nuclear division occurs in this subapical compartment [51][184]. One daughter nucleus migrates back to the mother cell, while the other nucleus migrates to the apical compartment. After mitosis, the protein phosphatase Cdc14, which regulates mitotic exit, localizes to the septum in yeast cells and dephosphorylates the Mob2-Cbk1 complex, allowing the transcription factor Ace2 to translocate to the nucleus and activate the transcription of genes involved in cell separation [52][185]. However, in hyphal cells, Cdc14 does not localize to the septum, and Mob2-Cbk1 remains at the hyphal tip [52][185]; thus, cytokinesis does not result in cell separation or the formation of a constriction between cells as observed in yeast or pseudohyphae, respectively. The septin ring splits into two rings with the formation of the primary septum dividing the hyphal compartments. Both rings are maintained in hyphal cells, unlike in yeast and pseudohyphal cells, where the septin rings are dissembled after cytokinesis. However, in sep7Δ/Δ mutants, Cdc14 can localize to the hyphal septum, activating the Ace2-dependent cell separation program, resulting in hyphal cell separation [53][186]. The subapical compartment of the hyphae is vacuolated and remains in the G1 phase.
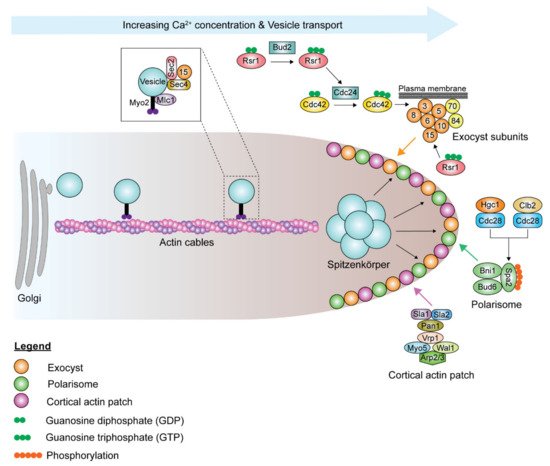
Although the polarisome and exocyst complexes also localize to the hyphal tip, polarized growth in hyphae is driven by a Spitzenkörper, a vesicle-rich structure responsible for hyphal growth directionality, which is present during all stages of the cell cycle, including septation [54][193]. Spa2, Bni1, and Bud6 coordinate the functions of the Spitzenkörper and the polarisome complex at the hyphal tip [55][54][191,193]. During hyphal growth, the post-Golgi secretory vesicles travel along actin cables to the Spitzenkörper, which acts as a vesicle supply center and is maintained at a fixed distance from the hyphal tip ( Figure 25 ). The vesicle-associated proteins Sec4, Sec2, and Mlc1 are localized to the Spitzenkörper during hyphal growth [55][56][191,194]. At the Spitzenkörper, the secretory vesicles are loaded onto actin cables nucleated by the polarisome and transported to the plasma membrane, where they dock with the exocyst. Actin cables are essential in hyphal growth, as their disruption inhibits hyphal formation [54][193]. Loss of BNI1 does not affect bud emergence, as germ tube formation can be initiated in bni1Δ/Δ mutants. However, the germ tubes are wider in diameter, and bni1Δ/Δ mutants cannot maintain polarized cell growth [57][195]. Deletion of SPA2 leads to polarity and hyphal growth defects [58][196]. spa2Δ/Δ mutants display random budding with multiple surface protrusions. Similar to the bni1Δ/Δ mutants, spa2Δ/Δ mutants can form germ tubes. However, unlike in bni1Δ/Δ mutants, hyphal growth can be maintained in the spa2Δ/Δ mutants, albeit in the form of severely swollen and curvy hyphae. Actin depolymerizing drugs, cytochalasin A and latrunculin A, disrupt the actin cytoskeleton, thus inhibiting hyphal growth and also suppressing the expression of hyphal-specific genes [59][60][61][143,197,198]. Chlorpropham, a drug affecting actin microfilament organization, inhibits hyphal growth [62][199].
The extensive exocytosis, which occurs at the apical tip and allows for rapid cell wall and membrane deposition, is counterbalanced by endocytosis. Endocytosis is essential for hyphal growth. Suppression of endocytosis suppresses hyphal elongation, and inhibition of endocytosis blocks hyphal formation, while yeast proliferation is unimpeded in both situations. Actin patches form the sites of endocytosis, which is important for maintaining polarity through the endocytic recycling of polarity proteins [63][64][200,201]. Before budding or germ tube evagination, cortical actin patches cluster at the apical site [60][65][197,202]. Actin patches are highly dynamic, with a lifetime of 5–20 s [66][203]. As the bud continues to enlarge in yeast cells, the cortical actin patches are redistributed isotropically throughout the bud surface [65][202]. However, in hyphal cells, the cortical actin patches remain clustered at the hyphal tip throughout hyphal growth [65][202]. Endocytosis in C. albicans mainly occurs via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, and various genes involved in the process have been studied. Sla1 and Sla2 are actin cytoskeletal proteins involved in actin patch organization and dynamics, as well as actin cable polarization, and necessary for normal endocytosis [67][68][69][70][71][72][204,205,206,207,208,209]. Cortical actin patches formed in sla1Δ/Δ mutants are depolarized and less dynamic and form short filaments [69][73][206,210]. sla2Δ/Δ mutants cannot undergo hyphal and pseudohyphal growth as the localization and orientation of actin patches and cables are defective [67][68][204,205]. sla2Δ/Δ mutants grow slower and form enlarged cells, as Swe1, the morphogenesis checkpoint kinase, delays cell cycle progression. Swe1 phosphorylates the Clb2-Cdc28 complex in response to perturbations to the actin cytoskeleton, thus delaying the normal transition from polarized growth to isotropic bud growth and delaying nuclear division. Pan1 is a clathrin-mediated endocytosis scaffold protein that is essential for endocytosis [74][211]. Depletion of Pan1 leads to the formation of thick and swollen cells that have abnormal filamentation. The inhibitory protein kinase Akl1 interacts with Pan1 to repress endocytosis, suppressing hyphal elongation [75][212]. Deletion of AKL1 results in faster hyphal elongation rates and longer hyphae, while AKL1 overexpression reduces hyphal elongation rates. However, overexpression of PAN1 counteracts the effects of AKL1 overexpression.
The myosin type I protein Myo5, the Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASP) homolog WAL1, and the WASP-interacting protein Vpr1 form a complex similar to that in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [76][213]. The Vpr1-Wal1-Myo5 complex is required for the polarized distribution of cortical actin patches. The deletion of MYO5 leads to mislocalization of cortical actin patches, with the patches dispersed throughout the bud and the mother cell, resulting in excessive isotropic growth [77][214]. myo5Δ/Δ mutants are unable to endocytose and cannot form hyphae [77][214]. Deletion of WAL1 and VRP1 leads to defects in polarized growth [76][78][213,215]. wal1Δ/Δ mutants can initiate but cannot maintain hyphal growth. Instead, wal1Δ/Δ mutants form elongated, pseudohyphal cells under hyphae-inducing conditions. vpr1Δ/Δ mutants have a defect in hyphal formation that is slightly less severe than in wal1Δ/Δ mutants. Cortical actin patches are depolarized in both the mother cells and buds of vpr1Δ/Δ mutants. Myo5 and Wal1 activate the actin module Arp2/3 complex to initiate actin polymerization. Deleting ARP2 or ARP3 leads to an inability to form hyphae, although endocytosis is not abolished [71][72][208,209]. Deleting RVS161 and RVS167, which encode Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (BAR) domain proteins, results in defective actin patch polarization, with the rvs161Δ/Δ mutants displaying a more severe defect in endocytosis and morphogenesis than the rvs167Δ/Δ mutants [70][207].
4. CDKs, Cyclins, and Their Roles in Hyphal Morphogenesis
Maintenance of cell signaling is important for cell cycle progression and cell growth. The cell cycle-associated cyclins and CDKs tightly regulate the small GTPases and other components of polarized growth. C. albicans has three G1 cyclins (Ccn1, Cln3, and Hgc1) and two B-type mitotic cyclins (Clb2, Clb4), of which only Cln3 and Clb2 are essential. The essential CDK Cdc28 serves as the master regulator that controls cell cycle progression at G1/S and G2/M phases via specific cyclin interactions that dictate the timing of the phases. Levels of the G1 and B-type mitotic cyclins oscillate during the cell cycle, and a single cyclin-Cdc28 complex can regulate multiple events within each phase of the cell cycle. Cdc28 is usually stable and present at constant levels throughout the cell cycle; however, its depletion leads to filamentous growth [79][223]. Ccn1 and Cln3 levels in yeast cells are high in the G1 phase, coinciding with bud emergence and apical growth, and decline in the early G2 phase. Clb2 levels peak in the early G2/M phase, while Clb4 levels reach their peak in the mid-G2/M phase [80][224]. Levels of both B-cyclins start to decline in the M phase and disappear during exit from mitosis [52][80][185,224].
In hyphal cells, polarized growth continues at the apical site throughout the cell cycle, indicating the decoupling of cell elongation from the cell cycle. Ccn1 and Cln3 levels are accumulated earlier and persist for a longer time during hyphal growth [80][81][224,225], extending the G1 phase in the early germ tube. Accumulation of the mitotic cyclins, Clb2 and Clb4, is delayed in hyphal cells. Although it is not required for the initiation of hyphal growth, high levels of Ccn1 are required for maintenance of hyphal growth, along with Cln3. The forkhead family transcription factor, Fkh2, usually undergoes cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation to induce the expression of genes that regulate cell cycle progression [82][83][226,227]. However, upon hyphal induction, Fkh2 is phosphorylated by Ccn1/Cln3-Cdc28 and Mob2-Cbk1 in a cell cycle-independent manner, redirecting it to enhance the expression of hyphal-specific genes such as the hyphal-specific G1 cyclin HGC1 ( Figure 36 ) [82][83][226,227]. fkh2Δ/Δ mutants grow constitutively as pseudohyphae under both yeast and hyphal-inducing conditions [82][83][226,227]. During hyphal growth, Ccn1-Cdc28 and Cln3-Cdc28 complexes phosphorylate Mob2, the activator of Cbk1, the cell wall integrity kinase, inhibiting the activation of Ace2 ( Figure 36 ) [84][228]. Cln3-Cdc28 complex regulates cortical actin patches via phosphorylation of Sla1 [69][206].
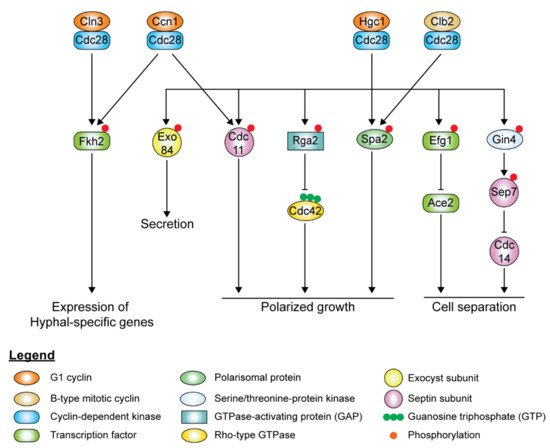
The hyphal-specific G1 cyclin Hgc1 does not regulate the cell cycle but plays a critical role in hyphal morphogenesis ( Figure 36 ) [47][169]. Besides suppression by Tup1 and Nrg1, the expression of HGC1 is positively regulated by the transcription factor Ume6, which ensures that Hgc1 is expressed throughout the cell cycle as long as the inducing conditions remain [47][169]. Hgc1 interacts with Cdc28, forming a complex regulating by phosphorylation regulators and components of cell polarity, membrane trafficking, and cell separation, which is required to maintain hyphal growth ( Figure 36 ). The Hgc1-Cdc28 complex phosphorylates and inactivates Rga2, sequestering it from the hyphal tip to allow Cdc42 localization at the hyphal tip to persist during polarized growth [85][86][217,229]. Hgc1-Cdc28, together with Clb2-Cdc28, phosphorylates Spa2, localizing the polarisome to the hyphal tip [87][230]. Hgc1-Cdc28 complex phosphorylates the exocyst subunits Exo84 and Sec2, allowing them to be recycled at the growing hyphal tip [56][88][194,231]. The Hgc1-Cdc28 complex phosphorylates Efg1, leading to Efg1 competitively binding to promoters of Ace2 target genes, thereby repressing the expression of cell separation activators to prevent cell separation after cytokinesis [89][232]. The Hgc1-Cdc28 complex also plays a role in regulating the septin ring dynamics during hyphal growth via Sep7 [90][175].
The cyclins Pcl1 and Pcl5 and the CDK Pho85, although not essential for cell cycle progression, contribute to morphogenesis in response to environmental cues. The Pcl1-Pho85 complex is required for temperature-dependent filamentation induced by Hsp90 inhibition [91][233]. The transcription factor Hms1 is required for filamentation induced by high temperatures. The Pcl1-Pho85 complex phosphorylates Hms1, which then binds to hyphal-specific genes. It also regulates the degradation of the transcription factor Gcn4, which is indirectly involved in filamentous growth in response to amino acid starvation [92][234]. Gcn4 induces PCL5 expression, and the Pcl5-Pho85 complex phosphorylates Gcn4, leading to its degradation [93][94][235,236].
