Understanding environmental information is necessary for functions correlated with human activities to improve healthcare quality and reduce ecological risk. Tapered optical fibers reduce some limitations of such devices and can be considerably more responsive to fluorescence and absorption properties changes.
- tapered optical fiber
- optical sensors
- Bragg grating
- microstructure
- refractive index sensor
1. Introduction
2. Background
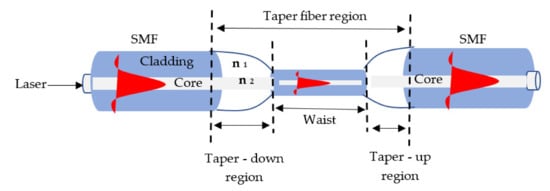
3. Overview of Tapered Fiber
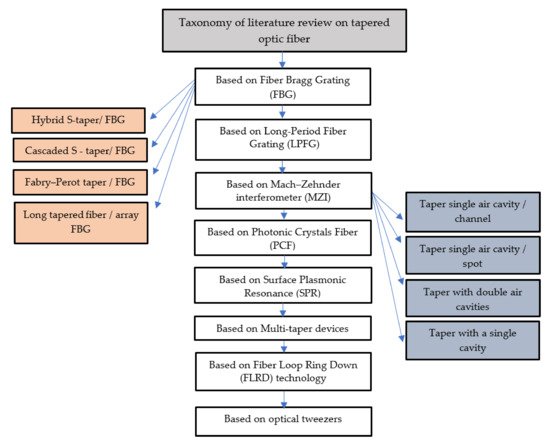
4. Taxonomy of Literature Review on Tapered Optic Fiber
5. Opportunities and Challenges
Tapered Method | Challenges | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fiber Bragg grating (FBG) | • Some spectra of reflection overlapped. | • Unstable interference wave. | • Complex configuration for grating inscription. | • Insufficient sensitivity. | |||||||
Long-period fiber grating (LPFG) | • The spectrum is limiting. | • Cross-sensitivity problem. | • The roughness of the surface. | ||||||||
Mach–Zehnder (MZI) | • Spectral band-width is limited. | • Manufacturing cost. | • Sensitivity enhancement is required. | ||||||||
Photonic crystals (PC) | • The samples given are limited. | • The manufacturing of metal layers is a complex procedure. | • Integration is expensive. | • Mechanical reliability is weak, and mass production is challenging. | |||||||
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) | • The life of the sensitive layer controls the lifetime of the device. | • Small sample size. | • There is a need for practical application, including different sample collection processes. | • The waist area is rather hard. | |||||||
Multi-taper devices | • Measured refractive index range is limited. | • Limited stability. | • The roughness of the surface. | ||||||||
Fiber loop ring-down technology | • The samples given are limited. | • Measuring accuracy depends on the high wavelength resolution of the de-modulation device. | |||||||||
Optical tweezers | • Obtain an analytical formula for the output light field is difficult. | • The trapping of optical tweezers is inadequate due to the limit of laser beam diffraction. | • Dramatic disruptions from molecular diffusion. |
References
- Newton, J. Wellbeing and the Natural Environment: A Brief Overview of the Evidence; University of Bath: Bath, UK, 2007; pp. 1–53.
- Joe, H.E.; Yun, H.; Jo, S.H.; Jun, M.B.G.; Min, B.K. A review on optical fiber sensors for environmental monitoring. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2018, 5, 173–191.
- Song, H.; Pei, H.; Zhu, H. Monitoring of tunnel excavation based on the fiber Bragg grating sensing technology. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 169, 108334.
- Guo, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, W.; Ma, Z.; Yang, T. Application of the Microclamped Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) Sensor in Rock Bolt Support Quality Monitoring. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020.
- Sahota, J.K.; Gupta, N.; Dhawan, D. Fiber Bragg grating sensors for monitoring of physical parameters: A comprehensive review. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 1.
- Wang, J.N.; Luo, C.Y. Long-period fiber grating sensors for the measurement of liquid level and fluid-flow velocity. Sensors 2012, 12, 4578–4593.
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Biswas, P.; Chiavaioli, F.; Dey, T.K.; Basumallick, N.; Trono, C.; Giannetti, A.; Tombelli, S.; Baldini, F.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Long-period fiber grating: A specific design for biosensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 9846.
- Zhao, X.W.; Wang, Q. Mini review: Recent advances in long period fiber grating biological and chemical sensors. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 140–169.
- Saghaei, H.; Elyasi, P.; Karimzadeh, R. Design, fabrication, and characterization of Mach–Zehnder interferometers. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2019, 37, 100733.
- El Shamy, R.S.; Khalil, D.; Swillam, M.A. Mid Infrared Optical Gas Sensor Using Plasmonic Mach-Zehnder Interferometer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9.
- Inan, H.; Poyraz, M.; Inci, F.; Lifson, M.A.; Baday, M.; Cunningham, B.T.; Demirci, U. Photonic crystals: Emerging biosensors and their promise for point-of-care applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 366–388.
- Long, H.; Bao, L.; Habeeb, A.A.; Lu, P. Effects of doping concentration on the surface plasmonic resonances and optical nonlinearities in AGZO nano-triangle arrays. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 1–8.
- Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors for food allergen detection in food matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111449.
- Salam, A.O.A.; Sheriff, R.E.; Al-Araji, S.R.; Mezher, K.; Nasir, Q. Multi-taper spectrum-based estimator for cognitive radio using multiple antennas and STBC techniques. IET Circ. Dev. Syst. 2018, 12, 133–143.
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Han, Q.; Yan, W.; Yu, L. Fiber loop ring-down cavity integrated U-bent single-mode-fiber for magnetic field sensing. Photonics Res. 2016, 4, 322.
- Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Fiber loop ring down for static ice pressure detection. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 36, 312–316.
- Killian, J.L.; Ye, F.; Wang, M.D. Optical Tweezers: A Force to Be Reckoned With. Cell 2018, 175, 1445–1448.
- Crozier, K.B. Quo vadis, plasmonic optical tweezers? Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 4–9.
- Kao, K.C.; Hockham, G.A. Dielectric-Fibre Surface Waveguides for Optical Frequencies; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1966.
- Culshaw, B. Optical Fiber Sensor Technologies: Opportunities and-Perhaps-Pitfalls. J. Lightwave Technol. 2004, 22, 39–50.
- Taha, B.A.; Mashhadany, Y.A.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Zan, M.S.D.B.; Arsad, N. An analysis review of detection coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on biosensor application. Sensors 2020, 20, 6764.
- Taha, B.A. Perspectives of Photonics Technology to Diagnosis COVID-19 Viruses: A Short Review. J. Appl. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 1, 1–6.
- Taha, B.A.; Al Mashhadany, Y.; Bachok, N.N.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Zan, M.S.D.B.; Arsad, N. Detection of COVID-19 Virus on Surfaces Using Photonics: Challenges and Perspectives. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1119.
- Elgaud, M.M.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Ghaith, A.A.; Naim, N.F.; Arsad, N.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Azeman, N.H.; Zan, M.S.D. Pulse compressed time domain multiplexed fiber bragg grating sensor: A comparative study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 64427–64434.
- Rao, Y.-J.; Deng, M.; Duan, D.-W.; Yang, X.-C.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, G.-H. Micro Fabry-Perot interferometers in silica fibers machined by femtosecond laser. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 14123.
- Fernandes, L.A.; Grenier, J.R.; Herman, P.R.; Aitchison, J.S.; Marques, P.V.S. Femtosecond laser fabrication of birefringent directional couplers as polarization beam splitters in fused silica. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 11992.
- Jung, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.H.; Oh, K. Ultracompact in-line broadband Mach–Zehnder interferometer using a composite leaky hollow-optical-fiber waveguide. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2934–2936.
- Leng, Y.; Yun, V.E.; Goldhar, J. UV laser fabrication and modification of fiber Bragg gratings by stitching sub-gratings with in situ fluorescence monitoring. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 6977–6981.
- Morales, A.M.; Lieber, C.M. A laser ablation method for the synthesis of crystalline semiconductor nanowires. Science 1998, 279, 208–211.
- Westwater, J. Growth of silicon nanowires via gold/silane vapor–liquid–solid reaction. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 1997, 15, 554.
- Chen, J.; Reed, M.A.; Rawlett, A.M.; Tour, J.M. Large on-off ratios and negative differential resistance in a molecular electronic device. Science 1999, 286, 1550–1552.
- Giallorenzi, T.G.; Dandridge, A. Optical Fiber Sensor Technology. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 1982, 30, 472–511.
- Mehrvar, M.; Bis, C.; Scharer, J.M.; Moo-Young, M.; Luong, J.H. Fiber-optic biosensors-Trends and advances. Anal. Sci. 2000, 16, 677–692.
- Arnold, M.A. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64.
- Seitz, W.R. Chemical sensors based on fiber optics. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, A16–A34.
- Jarzebinska, R.; Korposh, S.; James, S.; Batty, W.; Tatam, R.; Lee, S.W. Optical Gas Sensor Fabrication Based on Porphyrin-Anchored Electrostatic Self-Assembly onto Tapered Optical Fibers. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 1297–1309.
- Jarzebinska, R.; Cheung, C.S.; James, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Response of the transmission spectrum of tapered optical fibres to the deposition of a nanostructured coating. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 34001.
- Mackenzie, H.S.; Payne, F.P. Evanescent Field Amplification in a Tapered Single-Mode Optical Fibre. Electron. Lett. 1990, 26, 130–132.
- Massaro, A.; Pierantoni, L.; Rozzi, T. Far-field radiation of optical fibers with tapered end. J. Lightwave Technol. 2006, 24, 3162–3168.
- Latifi, H.; Zibaii, M.I.; Hosseini, S.M.; Jorge, P. Nonadiabatic tapered optical fiber for biosensor applications. Photonic Sens. 2012, 2, 340–356.
- Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Recent developments in micro-structured fiber optic sensors. Fibers 2017, 5, 3.
- Jabbar, A.A.; Haider, A.J.; Haider, M.J.; Al-Azawi, K.F. Preparation and characterization of NiO/PSi as self-cleaning surface. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15123–15131.
- Birks, T.A.; Li, Y.W. The Shape of Fiber Tapers. J. Lightwave Technol. 1992, 10, 432–438.
- Leung, A.; Rijal, K.; Shankar, P.M.; Mutharasan, R. Effects of geometry on transmission and sensing potential of tapered fiber sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2202–2209.
- McCulloch, S.; Uttamchandani, D. Development of a fibre optic micro-optrode for intracellular pH measurements. IEE Proc. Optoelectron. 1997, 144, 162–167.
- International, S.M.; Nishitani, R.; Umeno, T.; Kasuya, A.; Nishina, Y. Correlation Between Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM)-Induced Photon Map and the STM Topography of Nanometer-Size Metal Particles. eCM J. 1998, 12, 113.
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, N.; Shi, Y.; Xin, H.; Li, B. Optical fiber tweezers: A versatile tool for optical trapping and manipulation. Micromachines 2020, 11, 114.
- Abushagur, A.A.G.; Arsad, N.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Bakar, A.A.A. High Sensitive Microsurgical Force Sensor Using Spectral-Width of Tapered Fiber Bragg Gratings. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on BioPhotonics (BioPhotonics), Taipei, Taiwan, 15–18 September 2019; pp. 1–2.
- Sun, D.; Ran, Y.; Wang, G. Label-free detection of cancer biomarkers using an in-line taper fiber-optic interferometer and a fiber bragg grating. Sensors 2017, 17, 2559.
- Mitschke, F. Fiber Optics: Physics and Technology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783662527641.
- Chen, G.Y.; Wu, X.; Kang, Y.Q.; Yu, L.; Monro, T.M.; Lancaster, D.G.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. Ultra-fast Hygrometer based on U-shaped Optical Microfiber with Nanoporous Polyelectrolyte Coating. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7.
- Zhu, S.; Pang, F.; Huang, S.; Zou, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T. High sensitivity refractive index sensor based on adiabatic tapered optical fiber deposited with nanofilm by ALD. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13880.
- He, F.; Liao, Y.; Lin, J.; Song, J.; Qiao, L.; Cheng, Y.; He, F.; Sugioka, K. Femtosecond laser fabrication of monolithically integrated microfluidic sensors in glass. Sensors 2014, 14, 19402–19440.
- Correia, R.; James, S.; Lee, S.W.; Morgan, S.P.; Korposh, S. Biomedical application of optical fibre sensors. J. Opt. 2018, 20.
- Black, R.J.; Lacroix, S.; Gonthier, F.; Love, J.D. Tapered single-mode fibres and devices Part 2. Experimental and theoretical quantification. IEE Proc. Part J Optoelectron. 1991, 138, 355–364.
- Harun, S.W.; Lim, K.S.; Tio, C.K.; Dimyati, K.; Ahmad, H. Theoretical analysis and fabrication of tapered fiber. Optik 2013, 124, 538–543.
- Korposh, S.; James, S.W.; Lee, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Tapered Optical Fibre Sensors: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Sensors 2019, 19, 2294.
- Maragò, O.M.; Jones, P.H.; Gucciardi, P.G.; Volpe, G.; Ferrari, A.C. Optical trapping and manipulation of nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 807–819.
- Tong, L. Micro/nanofibre optical sensors: Challenges and prospects. Sensors 2018, 18, 903.
- Lakomski, M.; Guzowski, B.; Wozniak, A. Fabrication of ultra-long tapered optical fibers. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 221, 111193.
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, F. Multifunctional integration on optical fiber tips: Challenges and opportunities. Adv. Photonics 2020, 2, 1–24.
- Hu, Q.; Li, C. The New Tapered Fiber Connector and the Test of Its Error Rate and Coupling Characteristics. Int. J. Opt. 2017, 2017.
- Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Lou, X.; Yu, L. A refractive index sensor based on h-shaped photonic crystal fibers coated with ag-graphene layers. Sensors 2020, 20, 741.
