Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling triggers diverse biological actions in inflammatory diseases. In tissue fibrosis, it acts as a key pathogenic regulator for promoting immunoregulation via controlling the activation, proliferation, and apoptosis of immunocytes. In cancer, it plays a critical role in tumor microenvironment (TME) for accelerating invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression. Increasing evidence suggest a pleiotropic nature of TGF-β signaling as a critical pathway for generating fibrotic TME, which contains numerous cancer-associated fibroblasts, extracellular matrix proteins, and remodeling enzymes. Better understanding the underlying mechanisms may uncover novel therapeutic targets for cancer.
- TGF-β
- tumor microenvironment
- fibrosis
- cancer
- Smad
1. TGF-β Signaling
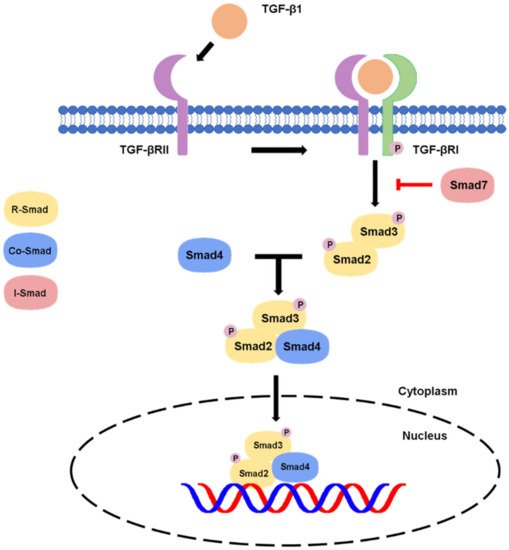
1.1. Canonical Pathway
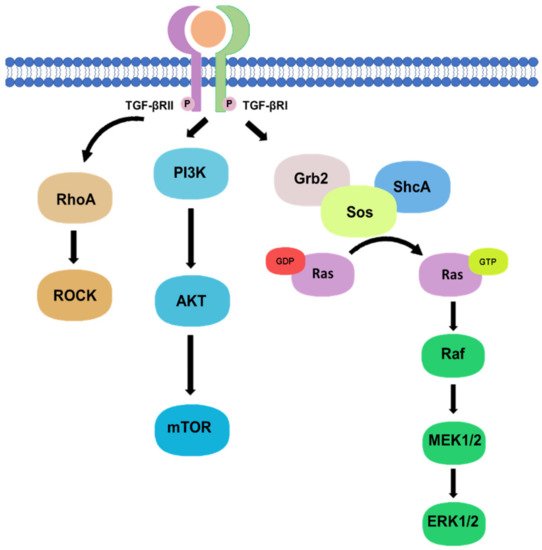
1.2. Non-Canonical Pathway
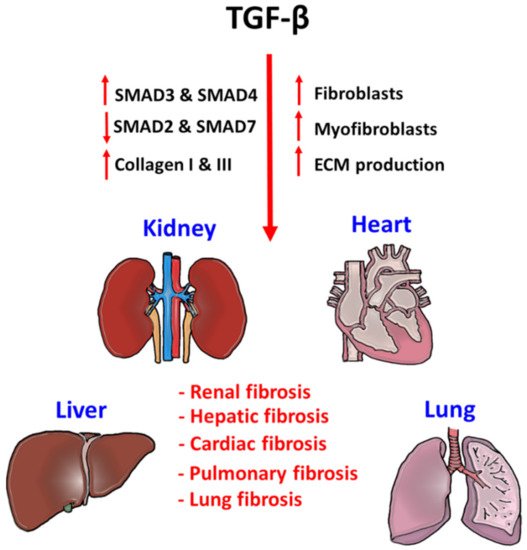
2. TGF-β Signaling in Tissue Fibrosis
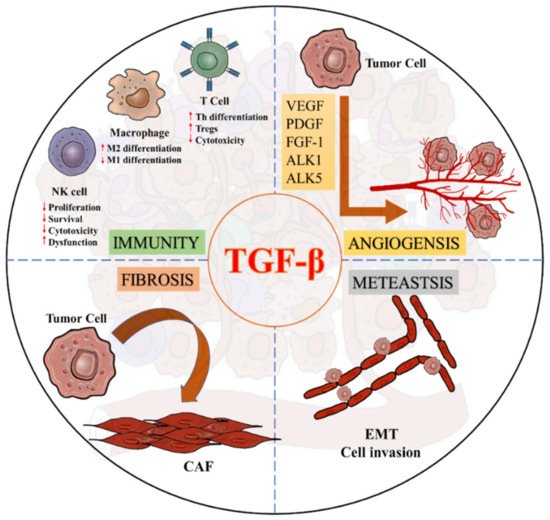
3. TGF-β Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment
References
- Bierie, B.; Moses, H.L. Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: The molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 506–520.
- Wakefield, L.M.; Hill, C.S. Beyond TGFbeta: Roles of other TGFbeta superfamily members in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 328–341.
- Zhao, H.; Wei, J.; Sun, J. Roles of TGF-beta signaling pathway in tumor microenvirionment and cancer therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89 Pt B, 107101.
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-beta: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338.
- Neuzillet, C.; Tijeras-Raballand, A.; Cohen, R.; Cros, J.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E.; de Gramont, A. Targeting the TGFbeta pathway for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147, 22–31.
- David, C.J.; Massague, J. Contextual determinants of TGFbeta action in development, immunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 419–435.
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad Signaling Pathways of the TGF-beta Family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022129.
- Finnson, K.W.; Almadani, Y.; Philip, A. Non-canonical (non-SMAD2/3) TGF-beta signaling in fibrosis: Mechanisms and targets. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 101, 115–122.
- Reich, N.; Maurer, B.; Akhmetshina, A.; Venalis, P.; Dees, C.; Zerr, P.; Palumbo, K.; Zwerina, J.; Nevskaya, T.; Gay, S.; et al. The transcription factor Fra-2 regulates the production of extracellular matrix in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 280–290.
- Xia, H.; Ooi, L.L.; Hui, K.M. MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer. Hepatology 2013, 58, 629–641.
- Yang, W.L.; Wang, J.; Chan, C.H.; Lee, S.W.; Campos, A.D.; Lamothe, B.; Hur, L.; Grabiner, B.C.; Lin, X.; Darnay, B.G.; et al. The E3 ligase TRAF6 regulates Akt ubiquitination and activation. Science 2009, 325, 1134–1138.
- Thuault, S.; Valcourt, U.; Petersen, M.; Manfioletti, G.; Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. Transforming growth factor-beta employs HMGA2 to elicit epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 175–183.
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196.
- Valcourt, U.; Kowanetz, M.; Niimi, H.; Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell transition. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1987–2002.
- Xie, L.; Law, B.K.; Chytil, A.M.; Brown, K.A.; Aakre, M.E.; Moses, H.L. Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 603–610.
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040.
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. Inflammatory processes in renal fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 493–503.
- Eddy, A.A.; Neilson, E.G. Chronic kidney disease progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2964–2966.
- Liu, Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 684–696.
- Tang, P.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chan, M.K.; Lam, W.W.; Chung, J.Y.; Kang, W.; To, K.F.; Lan, H.Y.; Tang, P.M. The Emerging Role of Innate Immunity in Chronic Kidney Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4018.
- Tang, P.M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Hung, J.S.; Chung, J.Y.; Huang, X.R.; To, K.F.; Lan, H.Y. DPP4/CD32b/NF-kappaB Circuit: A Novel Druggable Target for Inhibiting CRP-Driven Diabetic Nephropathy. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 365–375.
- Meng, X.M.; Tang, P.M.; Li, J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-beta/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 82.
- Tang, P.C.; Chan, A.S.; Zhang, C.B.; Garcia Cordoba, C.A.; Zhang, Y.Y.; To, K.F.; Leung, K.T.; Lan, H.Y.; Tang, P.M. TGF-beta1 Signaling: Immune Dynamics of Chronic Kidney Diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 628519.
- Lan, H.Y. Tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation mechanisms in proximal tubule cells. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2003, 12, 25–29.
- Meng, X.M.; Chung, A.C.; Lan, H.Y. Role of the TGF-beta/BMP-7/Smad pathways in renal diseases. Clin. Sci. 2013, 124, 243–254.
- Vindevoghel, L.; Lechleider, R.J.; Kon, A.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Uitto, J.; Roberts, A.B.; Mauviel, A. SMAD3/4-dependent transcriptional activation of the human type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) promoter by transforming growth factor beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14769–14774.
- Chen, S.J.; Yuan, W.; Mori, Y.; Levenson, A.; Trojanowska, M.; Varga, J. Stimulation of type I collagen transcription in human skin fibroblasts by TGF-beta: Involvement of Smad 3. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 49–57.
- Yuan, W.; Varga, J. Transforming growth factor-beta repression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in dermal fibroblasts involves Smad3. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 38502–38510.
- Hall, M.C.; Young, D.A.; Waters, J.G.; Rowan, A.D.; Chantry, A.; Edwards, D.R.; Clark, I.M. The comparative role of activator protein 1 and Smad factors in the regulation of Timp-1 and MMP-1 gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10304–10313.
- Meng, X.M.; Huang, X.R.; Chung, A.C.; Qin, W.; Shao, X.; Igarashi, P.; Ju, W.; Bottinger, E.P.; Lan, H.Y. Smad2 protects against TGF-beta/Smad3-mediated renal fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1477–1487.
- Gomez-Puerto, M.C.; Iyengar, P.V.; Garcia de Vinuesa, A.; Ten Dijke, P.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signal transduction in human disease. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 9–20.
- Meng, X.M.; Huang, X.R.; Xiao, J.; Chung, A.C.; Qin, W.; Chen, H.Y.; Lan, H.Y. Disruption of Smad4 impairs TGF-beta/Smad3 and Smad7 transcriptional regulation during renal inflammation and fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 266–279.
- Ebisawa, T.; Fukuchi, M.; Murakami, G.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Imamura, T.; Miyazono, K. Smurf1 interacts with transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor through Smad7 and induces receptor degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12477–12480.
- Chong, P.A.; Lin, H.; Wrana, J.L.; Forman-Kay, J.D. An expanded WW domain recognition motif revealed by the interaction between Smad7 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17069–17075.
- Liu, F.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Peng, Y.M.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.H. Arkadia regulates TGF-beta signaling during renal tubular epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 588–594.
- Park, N.H.; Song, I.H.; Chung, Y.H. Molecular Pathogenesis of Hepatitis-B-virus-associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2007, 1, 101–117.
- Xu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. TGF-beta/SMAD Pathway and Its Regulation in Hepatic Fibrosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2016, 64, 157–167.
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603.
- Khan, R.; Sheppard, R. Fibrosis in heart disease: Understanding the role of transforming growth factor-beta in cardiomyopathy, valvular disease and arrhythmia. Immunology 2006, 118, 10–24.
- Yue, Y.; Meng, K.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, X. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) mediates cardiac fibrosis and induces diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 133, 124–130.
- Khalil, H.; Kanisicak, O.; Prasad, V.; Correll, R.N.; Fu, X.; Schips, T.; Vagnozzi, R.J.; Liu, R.; Huynh, T.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Fibroblast-specific TGF-beta-Smad2/3 signaling underlies cardiac fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3770–3783.
- Kalchiem-Dekel, O.; Galvin, J.R.; Burke, A.P.; Atamas, S.P.; Todd, N.W. Interstitial Lung Disease and Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Practical Approach for General Medicine Physicians with Focus on the Medical History. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 476.
- Flanders, K.C. Smad3 as a mediator of the fibrotic response. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2004, 85, 47–64.
- Chanda, D.; Otoupalova, E.; Smith, S.R.; Volckaert, T.; De Langhe, S.P.; Thannickal, V.J. Developmental pathways in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 56–69.
- Francisco, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jeong, J.I.; Mizushima, W.; Ikeda, S.; Ivessa, A.; Oka, S.; Zhai, P.; Tallquist, M.D.; Del Re, D.P. Blockade of Fibroblast YAP Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis and Dysfunction Through MRTF-A Inhibition. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 931–945.
- Batlle, E.; Massague, J. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940.
- Eshima, K.; Misawa, K.; Ohashi, C.; Iwabuchi, K. Role of T-bet, the master regulator of Th1 cells, in the cytotoxicity of murine CD4(+) T cells. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 348–356.
- Gorelik, L.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 46–53.
- Tzachanis, D.; Freeman, G.J.; Hirano, N.; van Puijenbroek, A.A.; Delfs, M.W.; Berezovskaya, A.; Nadler, L.M.; Boussiotis, V.A. Tob is a negative regulator of activation that is expressed in anergic and quiescent T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1174–1182.
- Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Fu, B.; Yachida, S.; Luo, M.; Abe, H.; Henderson, C.M.; Vilardell, F.; Wang, Z.; Keller, J.W.; Banerjee, P.; et al. DPC4 gene status of the primary carcinoma correlates with patterns of failure in patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1806–1813.
- Rodell, C.B.; Arlauckas, S.P.; Cuccarese, M.F.; Garris, C.S.; Li, R.; Ahmed, M.S.; Kohler, R.H.; Pittet, M.J.; Weissleder, R. TLR7/8-agonist-loaded nanoparticles promote the polarization of tumour-associated macrophages to enhance cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 578–588.
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Bu, X.; Cai, S.; et al. TGF-beta induces M2-like macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52294–52306.
- Regis, S.; Dondero, A.; Caliendo, F.; Bottino, C.; Castriconi, R. NK Cell Function Regulation by TGF-beta-Induced Epigenetic Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 311.
- Tang, P.M.; Zhou, S.; Meng, X.M.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, C.J.; Lian, G.Y.; Huang, X.R.; Tang, Y.J.; Guan, X.Y.; Yan, B.P.; et al. Smad3 promotes cancer progression by inhibiting E4BP4-mediated NK cell development. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14677.
- Rybinski, B.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Cukierman, E. The wound healing, chronic fibrosis, and cancer progression triad. Physiol. Genom. 2014, 46, 223–244.
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1650–1659.
- Hawinkels, L.J.; Paauwe, M.; Verspaget, H.W.; Wiercinska, E.; van der Zon, J.M.; van der Ploeg, K.; Koelink, P.J.; Lindeman, J.H.; Mesker, W.; ten Dijke, P.; et al. Interaction with colon cancer cells hyperactivates TGF-beta signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene 2014, 33, 97–107.
- Untergasser, G.; Gander, R.; Lilg, C.; Lepperdinger, G.; Plas, E.; Berger, P. Profiling molecular targets of TGF-beta1 in prostate fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transdifferentiation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 59–69.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Jing, S. Notch and TGF-beta/Smad3 pathways are involved in the interaction between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 379–385.
- Shi, X.; Young, C.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling in Fibrotic Diseases and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1666.
- Evans, R.A.; Tian, Y.C.; Steadman, R.; Phillips, A.O. TGF-beta1-mediated fibroblast-myofibroblast terminal differentiation-the role of Smad proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 282, 90–100.
- Ronnov-Jessen, L.; Petersen, O.W. Induction of alpha-smooth muscle actin by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in quiescent human breast gland fibroblasts. Implications for myofibroblast generation in breast neoplasia. Lab. Investig. 1993, 68, 696–707.
- Lamprecht, S.; Sigal-Batikoff, I.; Shany, S.; Abu-Freha, N.; Ling, E.; Delinasios, G.J.; Moyal-Atias, K.; Delinasios, J.G.; Fich, A. Teaming Up for Trouble: Cancer Cells, Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 Signaling and the Epigenetic Corruption of Stromal Naive Fibroblasts. Cancers 2018, 10, 61.
- Costanza, B.; Umelo, I.A.; Bellier, J.; Castronovo, V.; Turtoi, A. Stromal Modulators of TGF-beta in Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 7.
- Lin, S.; Xie, J.; Gong, T.; Shi, S.; Zhang, T.; Fu, N.; Lin, Y. Smad signal pathway regulates angiogenesis via endothelial cell in an adipose-derived stromal cell/endothelial cell co-culture, 3D gel model. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 412, 281–288.
- Cunha, S.I.; Pietras, K. ALK1 as an emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer. Blood 2011, 117, 6999–7006.
- Welch-Reardon, K.M.; Ehsan, S.M.; Wang, K.; Wu, N.; Newman, A.C.; Romero-Lopez, M.; Fong, A.H.; George, S.C.; Edwards, R.A.; Hughes, C.C. Angiogenic sprouting is regulated by endothelial cell expression of Slug. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 9, 2017–2028.
