Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Nora Tang and Version 1 by Ahmed Abutaleb.
TiO2NFs have important applications in different fields, including catalysis. They are used as a catalyst and a photocatalyst. Most of the TiO2NF-supported catalysts were utilized as photocatalysts in the AB reaction; hence, photocatalysis will be explained in more detail before the discussion of the electrospun photocatalysts.
- electrospinning
- catalysts
- ceramic
- C NFs
- TiO NFs
- ammonia borane
- hydrogen generation
1. Characteristics of Electrospun Catalysts
Electrospun NFs have many outstanding characteristics that make them promising catalytic materials. Some of the properties of electrospun NFs are shown in Figure 1. Contrary to NPs, a mesh of fibers is self-supporting, and its high porosity and other characteristics provide several reaction sites. The stable structure of the nanofibrous membrane ensures a consistent and predictable reaction rate and poses minimum issues of the agglomeration of the catalytic material [10][1].
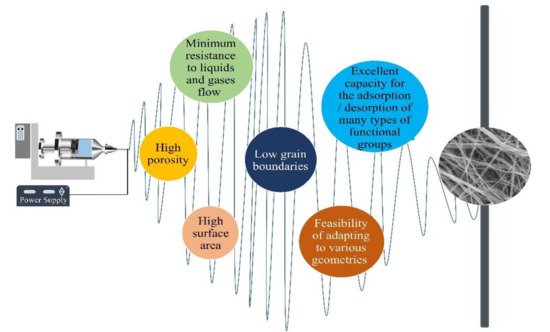
Figure 1. Properties of electrospun NFs.
2. Electrospinning Technique
Historically, several methods have been applied to produce fibers of different dimensions. These methods include drawing, self-assembly [26[2][3],27], phase separation [27[3][4],28], template synthesis [27][3], and electrospinning (ES) [9,29,30,31,32,33,34,35][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12]. Each production technique has its merits and demerits, and ES has been acknowledged as one of the most effective techniques to produce polymeric and ceramic fibers [9,31,35,36,37,38][5][8][12][13][14][15]. ES is cost-effective and can fabricate fibers continuously. This process fabricates fibers with controlled dimensions and desired structures. The diameter of the produced fibers can be achieved on the nanometer scale. The ES device generally comprises a reservoir of polymer dispersion solution with a pump, high-voltage source, nozzle, and conductive collector, as shown in Figure 2.
Organic and inorganic NFs can be fabricated using electrospinning. Polymers are involved in the fabrication of both types either as the raw material, in the case of organic NFs, or as a fabrication support, in the case of inorganic NFs.
In fact, wide ranges of natural and synthetic polymers have been electrospun to fabricate polymeric NFs for various applications. Polymers such as polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), polyacrylontrrile (PAN), poly(vinylacetate) (PVAc), polyvibyl alcohol (PVA), polyimide (PI), polyethylene oxide (PEO), polyvinylodene fluoride (PVDF), polystyrene (PS), and polyethersulfone (PES) are the most common electrospun polymers [39,40,41][16][17][18].
Polymers are also used to facilitate the fabrication of ceramic electrospun NFs. Ceramic precursor solutions do not possess sufficient viscosity to make a jet during electrospinning. Therefore, polymers are added to the electrospinning ceramic solutions to increase the viscosity to ensure successful electrospinning.
Sol–gel method, which includes a polymerization stage, is usually used in the fabrication of ceramic NFs via electrospinning. The electrospinning solution is prepared by adding ceramic precursors to a viscous polymer solution [42][19]. The metallic precursor and polymer mixture have to be completely miscible to form the gel network. Electrospinning of the sol–gel polymer solution can form either:
- i.
-
Single phase ceramic NFs obtained by removing the polymer NFs via heat treatment procedure;
- ii.
-
Polymer/ceramic hybrid NFs obtained without any heat treatment.
It is very important to note that the choice of the polymer, ceramic precursor, solvent, and additives, such as surfactants and salts, greatly affects the final properties of the electrospun polymer and ceramic NFs. For example, to prepare inorganic NFs, it is recommended to use metal acetates as a metallic precursor. Metal acetates are able to participate with the proper polymers in the polycondensation reactions to produce electrospinable sol–gels.
Based on the electrostatic field between the nozzle and collector, the electrospun fibers are collected on the surface of the collector screen. Many parameters influence ES operations and the characteristics of the produced fibers, including the type and nature of the collector, the voltage applied, the distance between the nozzle and collector, and the dispersion flow rate.
Electrospun fibers have extensive applications in industries such as air filtration, water purification [43[20][21],44], fabrication of sensors and biosensors [45][22], medical and biomedical applications (e.g., soft-tissue engineering, encapsulation of bioactive species, regenerative medicine, drug delivery fuel, and cell membranes) [45[22][23],46], antibiotics [47[24][25][26][27],48,49,50], environmental protection [51][28], smart textiles, surface coatings, and energy harvesting [33,52][10][29], conversion, catalysis [34[11][30],53], and storage, among others. Several valuable reviews have been published for the utilization of electrospun NFs in different application areas; a list of some of them is provided in Table 1. Nonetheless, there are no recent comprehensive reviews on the applications of electrospun ceramic NFs in catalysis for H2 production from AB yet. In this paper, an effort has been made to develop such a comprehensive review of the published literature on the applications of electrospun NFs as AB hydrolysis catalysts. It worth mentioning that the studies by Ayman et al. and Nasser et al. have contributed the most in the search for effective electrospun catalysts for AB hydrolysis [13,54][31][32].
Table 1. A list of reviews published for various applications of electrospun NFs.
| Review | Covered Application | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. | Drug delivery | 2014 | [55][33] |
| Advances in nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications: From electrospinning to self-assembly. | Biomedical. | 2014 | [56][34] |
| Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food-based applications. | Food Industry. | 2014 | [57][35] |
| Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. | Tissue engineering. Energy harvesting and Storage, Filtration. |
2014 | [58][36] |
| Electrospinning for regenerative medicine: a review of the main topics. | Tissue engineering. | 2014 | [59][37] |
| Hierarchical electrospun nanofibers for energy harvesting, production, and environmental remediation. | Photovoltaics and photocatalysis. Hydrogen energy Harvesting, Fuel cells. |
2014 | [60][38] |
| Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers for tissue regeneration. | Medical. | 2015 | [61][39] |
| Fundamentals of electrospinning as a novel delivery vehicle for bioactive compounds in food nanotechnology. | Food technology. | 2015 | [62][40] |
| A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. | Water treatment. | 2015 | [63][41] |
| A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. | Biomedical and biotechnology. | 2015 | [64][42] |
| Recent trends in electrospinning of polymer nanofibers and their applications in ultra-thin layer chromatography. | Chromatography. | 2016 | [65][43] |
| Melt electrospinning today: An opportune time for an emerging polymer process. | Energy, environment, filtration, and separation. Biomedical. |
2016 | [66][44] |
| A comprehensive review: electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. | Water treatment. | 2016 | [67][45] |
| A review of polymer nanofibres by electrospinning and their application in oil-water separation for cleaning up marine oil spills. | Oil–water separation. | 2016 | [68][46] |
| Electrospinning: A versatile technique for making of 1D growth of nanostructured nanofibers and its applications: An experimental approach. | Energy conversion and storage. Environmental. Biomedical. |
2017 | [69][47] |
| Electrospinning: A novel nano-encapsulation approach for bioactive compounds. | Encapsulation of different types of bioactive compounds by biopolymer matrixes. | 2017 | [70][48] |
| Recent advances in multiaxial electrospinning for drug delivery. | Drug delivery. | 2017 | [71][49] |
| Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. | Tissue engineering. Organ function regeneration. Drug delivery. |
2017 | [72][50] |
| Fibers for hearts: A critical review on electrospinning for cardiac tissue engineering. | Cardiac tissue engineering. | 2017 | [73][51] |
| Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration | Air Filtration. | 2017 | [74][52] |
| Electrospinning-based (bio)sensors for food and agricultural applications: A review. | Biosensor (Analysis of food/and agricultural products). | 2017 | [75][53] |
| Electrospinning in solid oxide fuel cells–A review. | Solid oxide fuel cells. | 2017 | [76][54] |
| Polymer-based composites by electrospinning: Preparation & functionalization with nanocarbons | Tissue engineering Chemical Biosensors Environmental remediation. |
2018 | [77][55] |
| An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors, and wearable/flexible electronics. | Wearable/flexible electronics. | 2017 | [78][56] |
| Recent advances in energy materials by electrospinning. | Energy-related devices. | 2018 | [79][57] |
| Non-precious nanostructured materials by electrospinning and their applications for oxygen reduction in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. | Fuel cell (Oxygen reduction reaction in a fuel cell). | 2018 | [80][58] |
| Designing function-oriented artificial nanomaterials and membranes via electrospinning and electrospraying techniques. | Tissue engineering and medicine. Membrane filtration. Lithium battery. |
2018 | [81][59] |
| Electrospinning: An enabling nanotechnology platform for drug delivery and regenerative medicine. | Biomedical. Regenerative medicine. |
2018 | [82][60] |
| Emulsion electrospinning: Fundamentals, food applications, and prospects. | Food. | 2018 | [83][61] |
| Electrospinning and electrospray of bio-based and natural polymers for biomaterials development. | Food Industry. Enzyme immobilization. Tissue engineering. Drug delivery. Wound dressing. |
2018 | [84][62] |
| Comprehensive review on the electrospinning of starch polymer for biomedical applications. | Biomedical applications. | 2018 | [85][63] |
| Electrospinning tissue engineering and wound dressing scaffolds from polymer-titanium dioxide nanocomposites. | Tissue engineering. Wound dressing. |
201 | [86][64] |
| Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: a review. | Reinforced composites. | 2018 | [87][65] |
| ZnO-based ceramic nanofibers: Preparation, properties and applications | ZnO-based CNF applications. | 2019 | [88][66] |
| A review on electrospinning nanofibers in the field of microwave absorption | Microwave Absorption. | 2020 | [89][67] |
References
- Barakat, N.A. Catalytic and photo hydrolysis of ammonia borane complex using Pd-doped Co nanofibers. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 451, 21–27.
- Liao, H.-S.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Jin, A.; Chen, X.S. Self-assembly mechanisms of nanofibers from peptide amphiphiles in solution and on substrate surfaces. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14814–14820.
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Arnold, L. Recent advances in nanofibre fabrication techniques. Text. Res. J. 2011, 82, 129–147.
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Cheng, B.; Liu, H. Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membranes by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation along with Hydrogen Gas Formation Using a Single Orifice Spinneret. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700282.
- Yousef, A.; Brooks, R.M.; El-Halwany, M.; Abutaleb, A.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun CoCr7C3 -supported C nanofibers: Effective, durable, and chemically stable catalyst for H2 gas generation from ammonia borane. Mol. Catal. 2017, 434, 32–38.
- Lolla, D.; Lolla, M.; Abutaleb, A.; Shin, H.U.; Reneker, D.H.; Chase, G.G. Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols. Materials 2016, 9, 671.
- Shin, H.U.; Abutaleb, A.; Lolla, D.; Chase, G.G. Effect of Calcination Temperature on NO–CO Decomposition by Pd Catalyst Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina Nanofibers. Fibers 2017, 5, 22.
- Abutaleb, A.; Lolla, D.; Aljuhani, A.; Shin, H.U.; Rajala, J.W.; Chase, G.G. Effects of Surfactants on the Morphology and Properties of Electrospun Polyetherimide Fibers. Fibers 2017, 5, 33.
- Yousef, A.; Brooks, R.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.H. Low Temperature Synthesis of Cobalt–Chromium Carbide Nanoparticles-Doped Carbon Nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2938–2942.
- Abutaleb, A. Electrochemical Oxidation of Urea on NiCu Alloy Nanoparticles Decorated Carbon Nanofibers. Catalysts 2019, 9, 397.
- Lolla, D.; Abutaleb, A.; Kashfipour, M.A.; Chase, G.G. Polarized Catalytic Polymer Nanofibers. Materials 2019, 12, 2859.
- Abutaleb, A.; Lolla, D.; Aljuhani, A.; Shin, H.U.; Ali, M.A.; Hassan, A.A.Y.; Maafa, I.M.H.; Chase, G.G. Liquid Phase Selective Hydrogenation of Phenol to Cyclohexanone over Electrospun Pd/PVDF-HFP Catalyst. Fibers 2019, 7, 28.
- Rodaev, V.V.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Golovin, Y.I. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun ZrO2/Al2O3 nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16023–16026.
- Yuan, K.; Jin, X.; Yu, Z.; Gan, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, L.; Xu, N. Electrospun mesoporous zirconia ceramic fibers for catalyst supporting applications. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 282–289.
- Asadi-Pakdel, K.; Aghdam, R.M.; Asl, M.S.; Sani, M.A.F. Synthesis and morphology optimization of electrospun SiBNC nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 6052–6059.
- Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Cabeza, L.; Perazzoli, G.; Díaz, A.; López-Romero, J.M.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Electrospun Nanofibers: Recent Applications in Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 656.
- Ognibene, G.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Spitaleri, L.; Gulino, A.; Purrello, R.; Cicala, G.; Fragalà, M.E. Role of the surface composition of the polyethersulfone–TiiP–H2T4 fibers on lead removal: From electrostatic to coordinative binding. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8023–8033.
- Jung, J.-W.; Lee, C.-L.; Yu, S.; Kim, I.-D. Electrospun nanofibers as a platform for advanced secondary batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 703–750.
- Esfahani, H.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Ceramic Nanofiber Mats Today: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1238.
- Gangemi, C.M.A.; Iudici, M.; Spitaleri, L.; Randazzo, R.; Gaeta, M.; D’Urso, A.; Gulino, A.; Purrello, R.; Fragalà, M.E. Polyethersulfone Mats Functionalized with Porphyrin for Removal of Para-nitroaniline from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2019, 24, 3344.
- Yousefa, A.; Hameed, R.A.; Shaikh, S.F.; Abutalebd, A.; Halwanye, M.-; Al-Enizi, A.M. Enhanced electro-adsorption desalination performance of graphene by TiC. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117602.
- Su, Z.; Ding, J.; Wei, G. Electrospinning: A facile technique for fabricating polymeric nanofibers doped with carbon nanotubes and metallic nanoparticles for sensor applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52598–52610.
- Salmeri, M.; Ognibene, G.; Saitta, L.; Lombardo, C.; Genovese, C.; Barcellona, M.; D’Urso, A.; Spitaleri, L.; Blanco, I.; Cicala, G.; et al. Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Growth on Polyetheresulfone Electrospun Mats to Promote Antibacterial Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 1696.
- Zafar, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Vazirzadeh, M.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, B.; Sefat, F. Potential of Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomedical and Dental Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 73.
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of Chitosan-Based Solutions for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407.
- Ansari, M.A.; Albetran, H.M.; Alheshibri, M.H.; Timoumi, A.; Algarou, N.A.; Akhtar, S.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; AlAhmari, F.S.; Baykal, A.; et al. Synthesis of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers and Characterization of Their Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Potential against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 572.
- AlAhmari, F.; Rehman, S.; Almessiere, M.; Khan, F.; Slimani, Y.; Baykal, A. Synthesis of Ni0.5Co0.5-xCdxFe1.78Nd0.02O4 (x ≤ 0.25) nanofibers by using electrospinning technique induce anti-cancer and anti-bacterial activities. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 1–8.
- Shin, H.U.; Lolla, D.; Abutaleb, A.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chase, G.G. CO Oxidation over Pd-Au Alloy Nanoparticle Doped Fibrous TiO2-Support Media. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanoeng. 2018, 4, 12–23.
- Hameed, R.A.; Mohamed, I.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Shaikh, S.F.; Yousef, A. Fabrication of electrospun nickel sulphide nanoparticles onto carbon nanofibers for efficient urea electro-oxidation in alkaline medium. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 12944–12960.
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Nafady, A.; El-Halwany, M.; Brooks, R.M.; Abutaleb, A.; Yousef, A. Electrospun carbon nanofiber-encapsulated NiS nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 21716–21725.
- Barakat, N.A. Effective Co–Mn–O nanofibers for ammonia borane hydrolysis. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 229–232.
- Yousef, A.; Barakat, N.; El-Newehy, M.; Kim, H.Y. Chemically stable electrospun NiCu nanofibers for highly efficient dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17715–17723.
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21.
- Wade, R.J.; Burdick, J.A. Advances in nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications: From electrospinning to self-assembly. Nano Today 2014, 9, 722–742.
- Bhushani, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33.
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Duvail, J.-L.; Jiang, X.; Yin, H. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890.
- Braghirolli, D.I.; Steffens, D.; Pranke, P. Electrospinning for regenerative medicine: A review of the main topics. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 743–753.
- Kumar, P.S.; Sundaramurthy, J.; Sundarrajan, S.; Babu, V.J.; Singh, G.; Allakhverdiev, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Hierarchical electrospun nanofibers for energy harvesting, production and environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3192–3222.
- Jiang, T.; Carbone, E.J.; Lo, K.W.-H.; Laurencin, C.T. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers for tissue regeneration. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 46, 1–24.
- Ghorani, B.; Tucker, N. Fundamentals of electrospinning as a novel delivery vehicle for bioactive compounds in food nanotechnology. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 227–240.
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30.
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188.
- Moheman, A.; Alam, M.S.; Mohammad, A. Recent trends in electrospinning of polymer nanofibers and their applications in ultra thin layer chromatography. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 1–24.
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning today: An opportune time for an emerging polymer process. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 56, 116–166.
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Nguyen, N.C.; Nguyen, H.T. A comprehensive review: Electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85495–85514.
- Sarbatly, R.; Krishnaiah, D.; Kamin, Z. A review of polymer nanofibres by electrospinning and their application in oil–water separation for cleaning up marine oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 8–16.
- Patil, J.; Mali, S.S.; Kamble, A.S.; Hong, C.K.; Kim, J.H.; Patil, P. Electrospinning: A versatile technique for making of 1D growth of nanostructured nanofibers and its applications: An experimental approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 641–674.
- Wen, P.; Zong, M.-H.; Linhardt, R.J.; Feng, K.; Wu, H. Electrospinning: A novel nano-encapsulation approach for bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 56–68.
- Khalf, A.; Madihally, S.V. Recent advances in multiaxial electrospinning for drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 1–17.
- Cheng, J.; Jun, Y.; Qin, J.; Lee, S.-H. Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 121–143.
- Kitsara, M.; Agbulut, O.; Kontziampasis, D.; Chen, Y.; Menasché, P. Fibers for hearts: A critical review on electrospinning for cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 20–40.
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353.
- Mercante, L.; Scagion, V.P.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.; Correa, D. Electrospinning-based (bio)sensors for food and agricultural applications: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 91–103.
- Aruna, S.; Balaji, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Prakash, B.S. Electrospinning in solid oxide fuel cells—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 673–682.
- Lee, J.K.Y.; Chen, N.; Peng, S.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Thakor, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Polymer-based composites by electrospinning: Preparation & functionalization with nanocarbons. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 40–84.
- Chinnappan, A.; Baskar, C.; Baskar, S.; Ratheesh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors and wearable/flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12657–12673.
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y. Recent advances in energy materials by electrospinning. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1825–1858.
- Rauf, M.; Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, P.; Iqbal, W.; Qu, J.; Li, Y. Non-precious nanostructured materials by electrospinning and their applications for oxygen reduction in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2018, 408, 17–27.
- Zong, H.; Xia, X.; Liang, Y.; Dai, S.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Kong, F.; Pan, J.H. Designing function-oriented artificial nanomaterials and membranes via electrospinning and electrospraying techniques. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 1075–1091.
- Chen, S.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Xie, J. Electrospinning: An enabling nanotechnology platform for drug delivery and regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 188–213.
- Zhang, C.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Emulsion electrospinning: Fundamentals, food applications and prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 175–186.
- Soares, R.M.; Siqueira, N.; Prabhakaram, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning and electrospray of bio-based and natural polymers for biomaterials development. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 969–982.
- Hemamalini, T.; Dev, V.R.G. Comprehensive review on electrospinning of starch polymer for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 712–718.
- Ghosal, K.; Agatemor, C.; Špitálsky, Z.; Thomas, S.; Kny, E. Electrospinning tissue engineering and wound dressing scaffolds from polymer-titanium dioxide nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1262–1278.
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720.
- Pascariu, P.; Homocianu, M. ZnO-Based ceramic nanofibers: Preparation, properties and applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 11158–11173.
- Huang, W.; Tong, Z.; Wang, R.; Liao, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Lyu, P.; Ma, Y. A review on electrospinning nanofibers in the field of microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26441–26453.
More
