Identifying patients at increased risk of coronary artery disease, before the atherosclerotic complications become clinically evident, is the aim of cardiovascular prevention. Imaging techniques provide direct assessment of coronary atherosclerotic burden and pathological characteristics of atherosclerotic lesions which may predict the progression of disease. Atherosclerosis imaging has been traditionally based on the evaluation of coronary luminal narrowing and stenosis. However, the degree of arterial obstruction is a poor predictor of subsequent acute events. More recent techniques focus on the high-resolution visualization of the arterial wall and the coronary plaques. Most acute coronary events are triggered by plaque rupture or erosion. Hence, atherosclerotic plaque imaging has generally focused on the detection of vulnerable plaque prone to rupture.
- coronary atherosclerosis
- coronary plaque
- coronary imaging
1. Introduction
2. Non-invasive imaging
2.1. Plaque Morphology
2.2. Computed Tomography (CT)
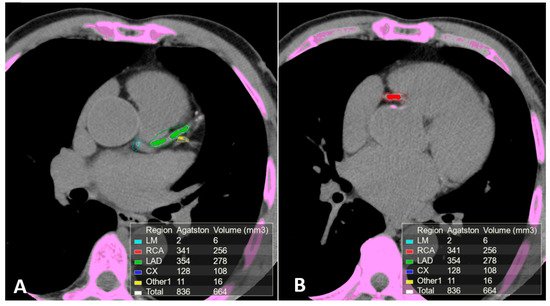
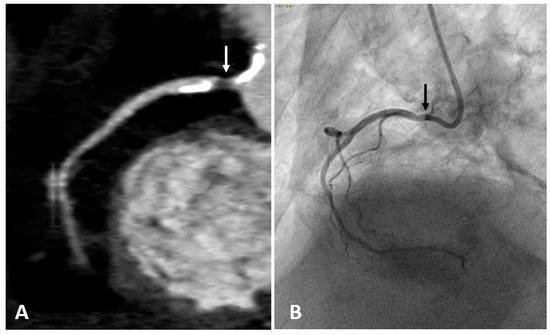
2.3. Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography (CTCA)
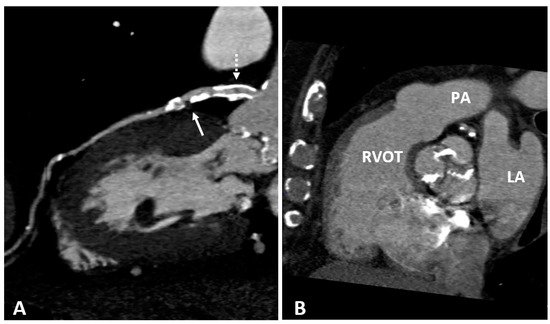
2.4. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR)
3. Disease Activity Imaging
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
References
- Libby, P.; Theroux, P. Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2005, 111, 3481–3488.
- Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Bentzon, J.F.; Daemen, M.; Falk, E.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Herrmann, J.; Hoefer, I.; Jukema, J.W.; Krams, R.; Kwak, B.R.; et al. Stabilisation of atherosclerotic plaques. Position paper of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working Group on atherosclerosis and vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 106, 1.
- Libby, P. Current Concepts of the Pathogenesis of the Acute Coronary Syndromes. Circulation 2001, 104, 365–372.
- Sandfort, A.C.V.; Lima, A.J.; Bluemke, A.D. Noninvasive Imaging of Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression: Status of Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e003316.
- Agatston, A.S.; Janowitz, W.R.; Hildner, F.J.; Zusmer, N.R.; Viamonte, M.; Detrano, R. Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast computed tomography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1990, 15, 827–832.
- Mahabadi, A.A.; Möhlenkamp, S.; Lehmann, N.; Kälsch, H.; Dykun, I.; Pundt, N.; Moebus, S.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Erbel, R. CAC Score Improves Coronary and CV Risk Assessment Above Statin Indication by ESC and AHA/ACC Primary Prevention Guidelines. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 143–153.
- Youssef, G.; Kalia, N.; Darabian, S.; Budoff, M.J. Coronary Calcium: New Insights, Recent Data, and Clinical Role. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2013, 15, 325.
- Nicoll, R.; Wiklund, U.; Zhao, Y.; Diederichsen, A.; Mickley, H.; Ovrehus, K.; Zamorano, P.; Gueret, P.; Schmermund, A.; Maffei, E.; et al. The coronary calcium score is a more accurate predictor of significant coronary stenosis than conventional risk factors in symptomatic patients: Euro-CCAD study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 207, 13–19.
- Sandfort, V.; Bluemke, D.A. CT calcium scoring. History, current status and outlook. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2017, 98, 3–10.
- McClelland, R.L.; Jorgensen, N.W.; Budoff, M.; Blaha, M.J.; Post, W.S.; Kronmal, R.A.; Bild, D.E.; Shea, S.; Liu, K.; Watson, K.E.; et al. 10-Year Coronary Heart Disease Risk Prediction Using Coronary Artery Calcium and Traditional Risk Factors: Derivation in the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) With Validation in the HNR (Heinz Nixdorf Recall) Study and the DHS (Dallas Heart Study). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1643–1653.
- Carr, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Terry, J.G.; Shay, C.M.; Sidney, S.; Liu, K.; Schreiner, P.J.; Lewis, C.E.; Shikany, J.M.; Reis, J.P.; et al. Association of Coronary Artery Calcium in Adults Aged 32 to 46 Years With Incident Coronary Heart Disease and DeathCoronary Artery Calcium and Incident Coronary Heart Disease and DeathCoronary Artery Calcium and Incident Coronary Heart Disease and Death. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 391–399.
- Detrano, R.; Guerci, A.D.; Carr, J.J.; Bild, D.E.; Burke, G.; Folsom, A.R.; Liu, K.; Shea, S.; Szklo, M.; Bluemke, D.A.; et al. Coronary Calcium as a Predictor of Coronary Events in Four Racial or Ethnic Groups. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1336–1345.
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.-T.; Corrà, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381.
- Hecht, H.; Blaha, M.J.; Berman, D.S.; Nasir, K.; Budoff, M.; Leipsic, J.; Blankstein, R.; Narula, J.; Rumberger, J.; Shaw, L.J. Clinical indications for coronary artery calcium scoring in asymptomatic patients: Expert consensus statement from the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2017, 11, 157–168.
- Greenland, P.; Bonow, R.O.; Brundage, B.H.; Budoff, M.J.; Eisenberg, M.J.; Grundy, S.M. ACCF/AHA 2007 clinical expert consensus document on coronary artery calcium scoring by computed tomography in global cardiovascular risk assessment and in evaluation of patients with chest pain. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 378–402.
- Stone, N.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Bairey Merz, C.N.; Blum, C.B.; Eckel, R.H.; Goldberg, A.C.; Gordon, D.; Levy, D.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2889–2934.
- Sarwar, A.; Shaw, L.J.; Shapiro, M.D.; Blankstein, R.; Hoffman, U.; Cury, R.C.; Abbara, S.; Brady, T.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Blumenthal, R.S.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Absence of Coronary Artery Calcification. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 675–688.
- Gottlieb, I.; Miller, J.M.; Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Dewey, M.; Clouse, M.E.; Sara, L.; Niinuma, H.; Bush, D.E.; Paul, N.; Vavere, A.L.; et al. The Absence of Coronary Calcification Does Not Exclude Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease or the Need for Revascularization in Patients Referred for Conventional Coronary Angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 627–634.
- Drosch, T.; Brodoefel, H.; Reimann, A.; Thomas, C.; Tsiflikas, I.; Heuschmid, M.; Schroeder, S.; Burgstahler, C. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Symptomatic Patients with Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease in the Absence of Coronary Calcifications. Acad. Radiol. 2010, 17, 1254–1258.
- Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Blankstein, R.; Agatston, A.; Rivera, J.J.; Virani, S.S.; Ouyang, P.; Jones, S.R.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Budoff, M.J.; et al. Dyslipidemia, Coronary Artery Calcium, and Incident Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2014, 129, 77–86.
- Shaw, L.J.; Giambrone, A.E.; Blaha, M.J.; Knapper, J.T.; Berman, D.S.; Bellam, N.; Quyyumi, A.; Budoff, M.J.; Callister, T.Q.; Min, J.K. Long-Term Prognosis After Coronary Artery Calcification Testing in Asymptomatic Patients: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 14–21.
- Nasir, J.K.; Rubin, J.J.; Blaha, J.M.; Shaw, N.L.; Blankstein, A.R.; Rivera, R.J.; Khan, S.A.; Berman, J.D.; Raggi, J.P.; Callister, J.T.; et al. Interplay of Coronary Artery Calcification and Traditional Risk Factors for the Prediction of All-Cause Mortality in Asymptomatic Individuals. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 467–473.
- Criqui, M.H.; Denenberg, J.O.; Ix, J.H.; McClelland, R.L.; Wassel, C.L.; Rifkin, D.E.; Carr, J.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Allison, M.A. Calcium Density of Coronary Artery Plaque and Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Events. JAMA 2014, 311, 271–278.
- Halon, D.A.; Lavi, I.; Barnett-Griness, O.; Rubinshtein, R.; Zafrir, B.; Azencot, M.; Lewis, B.S. Plaque Morphology as Predictor of Late Plaque Events in Patients With Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetes: A Long-Term Observational Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1353–1363.
- Criqui, M.H.; Knox, J.B.; Denenberg, J.O.; Forbang, N.I.; McClelland, R.L.; Novotny, T.E.; Sandfort, V.; Waalen, J.; Blaha, M.J.; Allison, M.A. Coronary Artery Calcium Volume and Density: Potential Interactions and Overall Predictive Value: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 845–854.
- Yoon, H.-C.; Emerick, A.M.; Hill, J.A.; Gjertson, D.W.; Goldin, J.G. Calcium Begets Calcium: Progression of Coronary Artery Calcification in Asymptomatic Subjects. Radiology 2002, 224, 236–241.
- Baron, K.B.; Choi, A.D.; Chen, M.Y. Low Radiation Dose Calcium Scoring: Evidence and Techniques. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 2016, 9, 12.
- Thomsen, C.; Abdulla, J. Characteristics of high-risk coronary plaques identified by computed tomographic angiography and associated prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 120–129.
- Thomas, I.C.; Forbang, N.I.; Criqui, M.H. The evolving view of coronary artery calcium and cardiovascular disease risk. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 144–150.
- Saremi, F.; Achenbach, S. Coronary Plaque Characterization Using CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W249–W260.
- Taylor, A.J.; Cerqueira, M.; Hodgson, J.M.; Mark, D.; Min, J.; O’Gara, P.; Rubin, G.D. ACCF/SCCT/ACR/AHA/ASE/ASNC/NASCI/SCAI/SCMR 2010 Appropriate Use Criteria for Cardiac Computed Tomography: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1864–1894.
- Gilard, M.; Le Gal, G.; Cornily, J.-C.; Vinsonneau, U.; Joret, C.; Pennec, P.-Y.; Mansourati, J.; Boschat, J. Midterm Prognosis of Patients With Suspected Coronary Artery Disease and Normal Multislice Computed Tomographic Findings: A Prospective Management Outcome Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1686–1689.
- Min, J.K.; Shaw, L.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Okin, P.M.; Weinsaft, J.W.; Russo, D.J.; Lippolis, N.J.; Berman, D.S.; Callister, T.Q. Prognostic Value of Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography for Prediction of All-Cause Mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 1161–1170.
- Jiang, B.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Cai, W. Prognostic Value of Cardiac Computed Tomography Angiography in Patients with Suspected Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Cardiology 2014, 128, 304–312.
- Fischer, C.; Hulten, E.; Belur, P.; Smith, R.; Voros, S.; Villines, T.C. Coronary CT angiography versus intravascular ultrasound for estimation of coronary stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque burden: A meta-analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2013, 7, 256–266.
- Voros, S.; Rinehart, S.; Qian, Z.; Joshi, P.; Vazquez, G.; Fischer, C.; Belur, P.; Hulten, E.; Villines, T.C. Coronary Atherosclerosis Imaging by Coronary CT Angiography: Current Status, Correlation With Intravascular Interrogation and Meta-Analysis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 4, 537–548.
- Bittencourt, S.M.; Hulten, P.E.; Ghoshhajra, A.B.; O’leary, L.D.; Christman, J.M.; Montana, W.P.; Truong, J.Q.; Steigner, F.M.; Murthy, F.V.; Rybicki, F.F.; et al. Prognostic Value of Nonobstructive and Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease Detected by Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography to Identify Cardiovascular Events. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 282–291.
- Butler, J.; Shapiro, M.; Reiber, J.; Sheth, T.; Ferencik, M.; Kurtz, E.G.; Nichols, J.; Pena, A.; Cury, R.C.; Brady, T.J.; et al. Extent and distribution of coronary artery disease: A comparative study of invasive versus noninvasive angiography with computed angiography. Am. Heart J. 2007, 153, 378–384.
- Pathan, F.; Negishi, K. Prediction of cardiovascular outcomes by imaging coronary atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 322–339.
- de Knegt, M.C.; Linde, J.J.; Fuchs, A.; Pham, M.H.C.; Jensen, A.K.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Kelbæk, H.; Køber, L.V.; Heitmann, M.; Fornitz, G.; et al. Relationship between patient presentation and morphology of coronary atherosclerosis by quantitative multidetector computed tomography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 20, 1221–1230.
- Shishikura, D. Noninvasive imaging modalities to visualize atherosclerotic plaques. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 340–353.
- Xie, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Pang, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Yang, Q.; Wei, J.; Nguyen, C.T.; Deng, Z.; Choi, B.W.; Fan, Z.; et al. Coronary Atherosclerosis T1-Weighed Characterization with Integrated Anatomical Reference: Comparison with High-Risk Plaque Features Detected by Invasive Coronary Imaging. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 637–648.
- Andrews, J.P.M.; Fayad, Z.A.; Dweck, M.R. New methods to image unstable atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 2018, 272, 118–128.
- Matsumoto, K.; Ehara, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Otsuka, K.; Yoshikawa, J.; Shimada, K. Localization of Coronary High-Intensity Signals on T1-Weighted MR Imaging: Relation to Plaque Morphology and Clinical Severity of Angina Pectoris. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, 1143–1152.
- Jansen, C.H.P.; Perera, D.; Wiethoff, A.J.; Phinikaridou, A.; Razavi, R.M.; Rinaldi, A.; Marber, M.S.; Greil, G.F.; Nagel, E.; Maintz, D.; et al. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of ruptured coronary plaques in patients with acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188292.
- Hamdan, A.; Asbach, P.; Wellnhofer, E.; Klein, C.; Gebker, R.; Kelle, S.; Kilian, H.; Huppertz, A.; Fleck, E. A Prospective Study for Comparison of MR and CT Imaging for Detection of Coronary Artery Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 4, 50–61.
- Sakuma, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Chino, S.; Hirano, T.; Makino, K.; Takeda, K. Detection of Coronary Artery Stenosis with Whole-Heart Coronary Magnetic Resonance Angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1946–1950.
- Kato, S.; Kitagawa, K.; Ishida, N.; Ishida, M.; Nagata, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Katahira, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Seo, K.; Ochiai, R.; et al. Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease Using Magnetic Resonance Coronary Angiography: A National Multicenter Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 983–991.
- Robson, P.M.; Dweck, M.R.; Trivieri, M.G.; Abgral, R.; Karakatsanis, N.A.; Contreras, J.; Gidwani, U.; Narula, J.P.; Fuster, V.; Kovacic, J.C.; et al. Coronary Artery PET/MR Imaging: Feasibility, Limitations, and Solutions. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 1103–1112.
- Wurster, T.; Landmesser, U.; Engel, L.-C.; Bigalke, B.; Makowski, M. Coronary Vessel Wall Imaging: State of the Art and Future Directions. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 2019, 12, 16.
- Evans, N.R.; Tarkin, J.M.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Warburton, E.A.; Rudd, J.H.F. PET Imaging of Atherosclerotic Disease: Advancing Plaque Assessment from Anatomy to Pathophysiology. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18.
- Joshi, N.V.; Vesey, A.T.; Williams, M.C.; Shah, A.S.V.; Calvert, P.A.; Craighead, F.H.M.; Yeoh, S.E.; Wallace, W.; Salter, D.; Fletcher, A.M.; et al. 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography for identification of ruptured and high-risk coronary atherosclerotic plaques: A prospective clinical trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 705.
- Robson, P.M.; Dey, D.; Newby, D.E.; Berman, D.; Li, D.; Fayad, Z.A.; Dweck, M.R. MR/PET Imaging of the Cardiovascular System. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 1165–1179.
- Ben-Haim, S.; Kupzov, E.; Tamir, A.; Israel, O. Evaluation of 18F-FDG Uptake and Arterial Wall Calcifications Using 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1816–1821.
- Adamson, P.D.; Vesey, A.T.; Joshi, N.V.; Newby, D.E.; Dweck, M.R. Salt in the wound: (18)F-fluoride positron emission tomography for identification of vulnerable coronary plaques. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2015, 5, 150–155.
- Fiz, F.; Morbelli, S.; Piccardo, A.; Bauckneht, M.; Ferrarazzo, G.; Pestarino, E.; Cabria, M.; Democrito, A.; Riondato, M.; Villavecchia, G.; et al. F-18-NaF Uptake by Atherosclerotic Plaque on PET/CT Imaging: Inverse Correlation Between Calcification Density and Mineral Metabolic Activity. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1019–1023.
- Dweck, M.R.; Aikawa, E.; Newby, D.E.; Tarkin, J.M.; Rudd, J.H.F.; Narula, J.; Fayad, Z.A. Noninvasive Molecular Imaging of Disease Activity in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 330–340.
- Kwiecinski, J.; Dey, D.; Cadet, S.; Lee, S.-E.; Tamarappoo, B.; Otaki, Y.; Huynh, P.T.; Friedman, J.D.; Dweck, M.R.; Newby, D.E.; et al. Predictors of 18F-sodium fluoride uptake in patients with stable coronary artery disease and adverse plaque features on computed tomography angiography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 58–66.
- Kitagawa, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Toshimitsu, S.; Sasaki, K.; Senoo, A.; Kubo, Y.; Tatsugami, F.; Awai, K.; Hirokawa, Y.; Kihara, Y. 18F-sodium fluoride positron emission tomography for molecular imaging of coronary atherosclerosis based on computed tomography analysis. Atherosclerosis 2017, 263, 385–392.
