In the field of energy storage, recently investigated nanocomposites show promise in terms of high hydrogen uptake and release with enhancement in the reaction kinetics. Among several, carbonaceous nanovariants like carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerenes, and graphitic nanofibers reveal reversible hydrogen sorption characteristics at 77 K, due to their van der Waals interaction. The spillover mechanism combining Pd nanoparticles on the host metal-organic framework (MOF) show at room temperature uptake of hydrogen. Metal or complex hydrides either in the nanocomposite form and its subset, nanocatalyst dispersed alloy phases illustrate the concept of nanoengineering and nanoconfinement of particles with tailor-made properties for reversible hydrogen storage. Another class of materials comprising polymeric nanostructures such as conducting polyaniline and their functionalized nanocomposites are versatile hydrogen storage materials because of their unique size, high specific surface-area, pore-volume, and bulk properties. The salient features of nanocomposite materials for reversible hydrogen storage are reviewed and discussed.
- nanocomposite materials
- carbon nanotubes
- nanocatalyst
- nanoparticles
- ball-milling
- hydrogen storage system
- complex hydrides
- sorption kinetics
1. Introduction
The increased deployment of fossil fuels produces an exorbitant amount of greenhouse gases such as CO
The increased deployment of fossil fuels produces an exorbitant amount of greenhouse gases such as CO2 [1][2][3], which has already caused an increase in the Earth’s temperature and will continue to do so unless CO
[1,2,3], which has already caused an increase in the Earth’s temperature and will continue to do so unless CO2 emissions are significantly curtailed. In addition to the occurrence of global warming due to the combustion of fossil-based fuels, there is wide agreement that these fossil fuels are running out [4], therefore increasing the urgency of finding new energy alternatives. One such alternative, especially for use in mobile applications, is hydrogen [5][6]. Hydrogen is an ideal fuel, particularly for transportation because it has the highest energy density per mass (149 MJ∙g
emissions are significantly curtailed. In addition to the occurrence of global warming due to the combustion of fossil-based fuels, there is wide agreement that these fossil fuels are running out [4], therefore increasing the urgency of finding new energy alternatives. One such alternative, especially for use in mobile applications, is hydrogen [5,6]. Hydrogen is an ideal fuel, particularly for transportation because it has the highest energy density per mass (149 MJ∙g−1) among the known fuel sources, and it is a safe, environmentally friendly fuel source that can be easily transformed to useful work without releasing harmful emissions. If burned in internal combustion engines (ICE), hydrogen can be combusted at high compression ratios, which leads to improved engine efficiencies, and substantially reduced pollutants compared to fossil fuels [7][8][9]. A better alternative to utilize hydrogen in mobile platforms is to burn it catalytically with oxygen using fuel cells to obtain the desired work output. This catalytic conversion of hydrogen and oxygen to working produces primarily to heat and water vapor as byproducts [10]. Hydrogen storage is a vital component between hydrogen production and utilization, for a full-fledged hydrogen economy as shown in
) among the known fuel sources, and it is a safe, environmentally friendly fuel source that can be easily transformed to useful work without releasing harmful emissions. If burned in internal combustion engines (ICE), hydrogen can be combusted at high compression ratios, which leads to improved engine efficiencies, and substantially reduced pollutants compared to fossil fuels [7,8,9]. A better alternative to utilize hydrogen in mobile platforms is to burn it catalytically with oxygen using fuel cells to obtain the desired work output. This catalytic conversion of hydrogen and oxygen to working produces primarily to heat and water vapor as byproducts [10]. Hydrogen storage is a vital component between hydrogen production and utilization, for a full-fledged hydrogen economy as shown inFigure 1 [11][12][13][14]. Hydrogen economy will be realized only when the hydrogen production, transportation/distribution, storage, and utilization (see
[11,12,13,14]. Hydrogen economy will be realized only when the hydrogen production, transportation/distribution, storage, and utilization (seeFigure 1) are streamlined [15][16][17].
) are streamlined [15,16,17].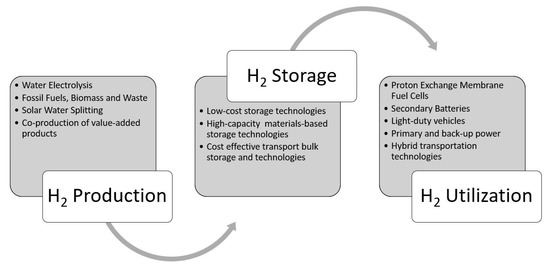
Figure 1. Storing hydrogen in the molecular or atomic form is a challenging task and equally important like producing it from clean sources and utilizing for stationary and vehicular applications (reproduced with permission from [18], Cambridge University Press, 2008).
Storing hydrogen in the molecular or atomic form is a challenging task and equally important like producing it from clean sources and utilizing for stationary and vehicular applications (reproduced with permission from [18], Cambridge University Press, 2008).The hydrogen storage system is an essential part of any fuel cell or hydrogen-ICE automobile [19][20]. The roadblocks for the widespread commercialization of the hydrogen-powered automobile are the development of safe and reliable hydrogen storage and transportation systems. The required properties of hydrogen storage systems for automotive applications are low cost, high volumetric and gravimetric storage capacity, favorable cycling kinetics, and near-ambient operation temperature. Improving these properties requires a better understanding of the fundamental physicochemical processes of solid-gas reactions at the nanoscale.
The hydrogen storage system is an essential part of any fuel cell or hydrogen-ICE automobile [19,20]. The roadblocks for the widespread commercialization of the hydrogen-powered automobile are the development of safe and reliable hydrogen storage and transportation systems. The required properties of hydrogen storage systems for automotive applications are low cost, high volumetric and gravimetric storage capacity, favorable cycling kinetics, and near-ambient operation temperature. Improving these properties requires a better understanding of the fundamental physicochemical processes of solid-gas reactions at the nanoscale.There are four major approaches to storing hydrogen: (i) compressed-gaseous, (ii) liquefied, (iii) solid-state (on-board regenerable), and (iv) chemical (off-board regenerable) [21]. Compressed-gaseous and liquefied hydrogen storage systems are considered as physical hydrogen storage methods. Both of these methods are mature and compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage is the only method employed in commercially available fuel-cell vehicles such as Honda Clarity, Toyota Mirai, and Hyundai Nexo. The main disadvantages of compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage are a high energy penalty for compression, which consumes 15% of the total internal energy of hydrogen for pressures up to 350 bar, and high-cost carbon-fiber wound cylinders to withstand pressures up to 700 bar [22]. Storing hydrogen at such a large pressure is acceptable to users as long as safety is demonstrated, which is a considerable challenge. Liquefied hydrogen is the other major form of physical hydrogen storage. It provides a compact medium for on-board storage [23], but again, the energy penalty for liquefaction is quite high (liquefaction process consumes around 30% of total internal energy of hydrogen) and it is impossible to prevent the loss of hydrogen through boil-off during long dormancy periods [24]. Liquefied hydrogen tanks operate at atmospheric pressures, and they are perfectly insulated to minimize heat transfer to hydrogen at 20 K from the surroundings. There is a promising hybrid physical-chemical storage method called cryo-compressed hydrogen storage [25]. In this method, high storage capacity, on par with liquefied hydrogen, can be achieved at a lower energy penalty because hydrogen is cooled to 77 K as opposed to 20 K required for liquefaction and hydrogen is compressed to pressures around 100 bar, which is significantly lower than the compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage. Another advantage of this physical storage method is to extend the dormancy period almost indefinitely. However, high surface area porous materials are required to store hydrogen inside a tank. The third method, solid-state storage, relies on storing hydrogen inside a host material, and the main promise of this method is the ability to refill hydrogen on-board. Significant research efforts have been devoted to this area during the last two decades to improve storage capacity, kinetics, reversibility, and safety of these materials. There are mainly two sub-categories of solid-state storage; (a) chemical storage via metal/complex hydrides and (b) physisorption based high surface area materials such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The last method is chemical storage in liquid organic compounds such as methanol and in boron-nitrogen based compounds such as ammonia-borane. These materials are off-board regenerable adding complexity and cost to hydrogen storage and distribution infrastructure. Though each storage method possesses desirable characteristics, no single method provides the volumetric and gravimetric storage capacities, cost, and safety requirements for transportation. The third and most researched method of hydrogen storage is by using metal hydrides. The chemical bonding between the metal and hydrogen is weakened by adjusting the temperature and pressure parameters so the hydrogen is released from the metal-hydrogen (M–H) systems. Metal hydrides, though investigated for decades, still not qualified as a reliable method for hydrogen storage. The hydrogen sorption kinetics are often very slow with low usable capacity (<2 wt.%). Various hydrogen storage methods are presented and discussed by Züttel [19].
There are four major approaches to storing hydrogen: (i) compressed-gaseous, (ii) liquefied, (iii) solid-state (on-board regenerable), and (iv) chemical (off-board regenerable) [21]. Compressed-gaseous and liquefied hydrogen storage systems are considered as physical hydrogen storage methods. Both of these methods are mature and compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage is the only method employed in commercially available fuel-cell vehicles such as Honda Clarity, Toyota Mirai, and Hyundai Nexo. The main disadvantages of compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage are a high energy penalty for compression, which consumes 15% of the total internal energy of hydrogen for pressures up to 350 bar, and high-cost carbon-fiber wound cylinders to withstand pressures up to 700 bar [22]. Storing hydrogen at such a large pressure is acceptable to users as long as safety is demonstrated, which is a considerable challenge. Liquefied hydrogen is the other major form of physical hydrogen storage. It provides a compact medium for on-board storage [23], but again, the energy penalty for liquefaction is quite high (liquefaction process consumes around 30% of total internal energy of hydrogen) and it is impossible to prevent the loss of hydrogen through boil-off during long dormancy periods [24]. Liquefied hydrogen tanks operate at atmospheric pressures, and they are perfectly insulated to minimize heat transfer to hydrogen at 20 K from the surroundings. There is a promising hybrid physical-chemical storage method called cryo-compressed hydrogen storage [25]. In this method, high storage capacity, on par with liquefied hydrogen, can be achieved at a lower energy penalty because hydrogen is cooled to 77 K as opposed to 20 K required for liquefaction and hydrogen is compressed to pressures around 100 bar, which is significantly lower than the compressed-gaseous hydrogen storage. Another advantage of this physical storage method is to extend the dormancy period almost indefinitely. However, high surface area porous materials are required to store hydrogen inside a tank. The third method, solid-state storage, relies on storing hydrogen inside a host material, and the main promise of this method is the ability to refill hydrogen on-board. Significant research efforts have been devoted to this area during the last two decades to improve storage capacity, kinetics, reversibility, and safety of these materials. There are mainly two sub-categories of solid-state storage; (a) chemical storage via metal/complex hydrides and (b) physisorption based high surface area materials such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The last method is chemical storage in liquid organic compounds such as methanol and in boron-nitrogen based compounds such as ammonia-borane. These materials are off-board regenerable adding complexity and cost to hydrogen storage and distribution infrastructure. Though each storage method possesses desirable characteristics, no single method provides the volumetric and gravimetric storage capacities, cost, and safety requirements for transportation. The third and most researched method of hydrogen storage is by using metal hydrides. The chemical bonding between the metal and hydrogen is weakened by adjusting the temperature and pressure parameters so the hydrogen is released from the metal-hydrogen (M–H) systems. Metal hydrides, though investigated for decades, still not qualified as a reliable method for hydrogen storage. The hydrogen sorption kinetics are often very slow with low usable capacity (<2 wt.%). Various hydrogen storage methods are presented and discussed by Züttel [19].The most critical challenges for improving hydrogen storage technologies are increasing their gravimetric and volumetric storage capacity while reducing their cost [19]. For a full tank charging, the mileage range of hydrogen-fueled hybrid vehicles are in par with the gasoline-based vehicles (for example, Toyota Mirai can get 312 miles with a full tank, Honda Clarity fuel-cells claims 360 miles range and Hyundai Nexo of the 380 miles range), however, the lack of hydrogen filling stations, the transportation, and distributions looks critical [26]. The energy required to get hydrogen in and out of storage is an issue for reversible solid-state materials storage systems. In addition, the energy associated with compression and liquefaction must be factored in when considering compressed and liquid hydrogen storage technologies. The durability of some hydrogen storage systems is inadequate. Materials and components are needed that allow hydrogen storage systems with a lifetime in excess of 1500 refueling cycles. Refueling times are currently too long as for as the solid-state chemical hydrides are concerned. There is a need to develop hydrogen storage systems with refueling times of less than five minutes over the lifetime of the system (
The most critical challenges for improving hydrogen storage technologies are increasing their gravimetric and volumetric storage capacity while reducing their cost [19]. For a full tank charging, the mileage range of hydrogen-fueled hybrid vehicles are in par with the gasoline-based vehicles (for example, Toyota Mirai can get 312 miles with a full tank, Honda Clarity fuel-cells claims 360 miles range and Hyundai Nexo of the 380 miles range), however, the lack of hydrogen filling stations, the transportation, and distributions looks critical [26]. The energy required to get hydrogen in and out of storage is an issue for reversible solid-state materials storage systems. In addition, the energy associated with compression and liquefaction must be factored in when considering compressed and liquid hydrogen storage technologies. The durability of some hydrogen storage systems is inadequate. Materials and components are needed that allow hydrogen storage systems with a lifetime in excess of 1500 refueling cycles. Refueling times are currently too long as for as the solid-state chemical hydrides are concerned. There is a need to develop hydrogen storage systems with refueling times of less than five minutes over the lifetime of the system (Table 1). Overall, the economic and technical challenges in developing all of the hydrogen storage technologies mentioned above demand new approaches and methodologies.
). Overall, the economic and technical challenges in developing all of the hydrogen storage technologies mentioned above demand new approaches and methodologies.Table 1. Selected US Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) hydrogen storage systems-targets for 2020 and 2025. Adapted with web policies copyright, restrictions, and permissions notice of DOE [15].
Selected US Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) hydrogen storage systems-targets for 2020 and 2025. Adapted with web policies copyright, restrictions, and permissions notice of DOE [15].| Storage Parameter. | 2020 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Gravimetric Hydrogen Storage Capacity (kg H2∙kg−1 material) |
0.045 | 0.055 |
| Volumetric Hydrogen Storage Capacity (kg H2∙L−1 material) |
0.030 | 0.040 |
| Hydrogen Delivery Temperature (°C) | −40/85 | −40/85 |
| System Fill Time (min; for 5 kg of H2) | 3–5 | 3–5 |
| Cycle Life (1/4 Tank to Full; non-dim) | 1500 | 1500 |
Different hydrogen storage systems namely metal hydrides, complex hydrides, chemical hydrides, high surface area porous materials (metal-organic frameworks and similar), and nanovariants [27][28][29][30][31][32] have been investigated for hydrogen storage applications. However, none of these materials fulfill all the hydrogen storage criteria set by US Department of Energy (DOE) such as (1) high hydrogen content; (2) favorable thermodynamics to achieve system fill-time less than 5 min; (3) operation below 85 °C and above −40 °C for hydrogen delivery; and (5) cyclic reversibility (1500 cycles) at ambient temperatures.
Different hydrogen storage systems namely metal hydrides, complex hydrides, chemical hydrides, high surface area porous materials (metal-organic frameworks and similar), and nanovariants [27,28,29,30,31,32] have been investigated for hydrogen storage applications. However, none of these materials fulfill all the hydrogen storage criteria set by US Department of Energy (DOE) such as (1) high hydrogen content; (2) favorable thermodynamics to achieve system fill-time less than 5 min; (3) operation below 85 °C and above −40 °C for hydrogen delivery; and (5) cyclic reversibility (1500 cycles) at ambient temperatures.Carbon-based materials, on the other hand, possess salient properties that make them interesting for storing hydrogen. Due to the abundance of carbon and the simplicity by which one can produce various forms of it, such as carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, nanobel1s, or graphite [33][34], there is virtually an unlimited amount of materials that can be investigated for hydrogen storage. One of the most important advantages of carbon-based materials is that they do not need to be kept in an inert atmosphere. It was initially thought that carbon materials are environmentally friendly and benign to humans, however, recent reports on the health risks of carbon nanotubes need considerable attention [35][36]. Graphite nanofibers, in its herringbone structure, have been shown to store hydrogen [37], though the exact structure required to store the hydrogen is still being investigated. Hydrogen storage in carbon nanotubes [38], carbon nanobel1s [39], carbon nanofibers [40], and especially doped carbon nanotubes [41][42] have shown reversible hydrogen storage at 77 K. Carbon-based materials possess another important feature, namely a hydrogen binding energy between 10 and 50 kJ∙mol
Carbon-based materials, on the other hand, possess salient properties that make them interesting for storing hydrogen. Due to the abundance of carbon and the simplicity by which one can produce various forms of it, such as carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, nanobel1s, or graphite [33,34], there is virtually an unlimited amount of materials that can be investigated for hydrogen storage. One of the most important advantages of carbon-based materials is that they do not need to be kept in an inert atmosphere. It was initially thought that carbon materials are environmentally friendly and benign to humans, however, recent reports on the health risks of carbon nanotubes need considerable attention [35,36]. Graphite nanofibers, in its herringbone structure, have been shown to store hydrogen [37], though the exact structure required to store the hydrogen is still being investigated. Hydrogen storage in carbon nanotubes [38], carbon nanobel1s [39], carbon nanofibers [40], and especially doped carbon nanotubes [41,42] have shown reversible hydrogen storage at 77 K. Carbon-based materials possess another important feature, namely a hydrogen binding energy between 10 and 50 kJ∙mol−1
. This is an ideal value for the binding of hydrogen, since a material with weak bonding of molecular hydrogen with binding energy <10 kJ∙mol−1
is not a suitable candidate material, as the hydrogen can be readily and accidentally released. Materials that have high energy hydrogen bonds, such as chemical hydrides (400 kJ∙mol−1
) or metal hydrides (50–100 kJ∙mol−1), can store a large amount of hydrogen, but they will require excessive energy, either as heat or pressure difference, to store or release the hydrogen. The carbon structures that possess this binding energy namely graphene, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. This enhanced physisorption, “spillover”, and “Kubas” binding represent the ideal hydrogen bonds. In this review, among the different storage options, we have compared and contrast the salient features and underlying applications of nanostructured variants for the reversible hydrogen storage.
), can store a large amount of hydrogen, but they will require excessive energy, either as heat or pressure difference, to store or release the hydrogen. The carbon structures that possess this binding energy namely graphene, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. This enhanced physisorption, “spillover”, and “Kubas” binding represent the ideal hydrogen bonds. In this review, among the different storage options, we have compared and contrast the salient features and underlying applications of nanostructured variants for the reversible hydrogen storage.2. Nanocomposite Materials for Hydrogen Storage
Nanocomposite materials are the combination of two or more elements, phases, or compounds in which at least one of these constituents has features at the nanoscale. Nanocomposites make it possible to achieve superior material properties due to nanoscale interactions such as nanoconfinement and spillover enhancement. Nanocomposite materials such as nanoparticles hold promise in hydrogen storage because of their unique features such as high specific surface area [43,44]. Nanostructured and nanoscale materials strongly influence the kinetics of hydrogen sorption due to their high surface area [45]. However, nanoparticle agglomeration due to repeated cooling/heating and contraction/expansion during cycling might result in degraded performance over time. Nevertheless, the nanoscale systems enable controlling the property of materials beyond what is possible in their bulk counterparts. Additionally, these nanoscale materials lead to the design and development of lightweight hydrogen storage systems with affordable characteristics for an onboard application. Some of the prominent nanoparticulate systems for hydrogen storage are discussed in the following subsections.Nanocomposite materials are the combination of two or more elements, phases, or compounds in which at least one of these constituents has features at the nanoscale. Nanocomposites make it possible to achieve superior material properties due to nanoscale interactions such as nanoconfinement and spillover enhancement. Nanocomposite materials such as nanoparticles hold promise in hydrogen storage because of their unique features such as high specific surface area [43][44]. Nanostructured and nanoscale materials strongly influence the kinetics of hydrogen sorption due to their high surface area [45]. However, nanoparticle agglomeration due to repeated cooling/heating and contraction/expansion during cycling might result in degraded performance over time. Nevertheless, the nanoscale systems enable controlling the property of materials beyond what is possible in their bulk counterparts. Additionally, these nanoscale materials lead to the design and development of lightweight hydrogen storage systems with affordable characteristics for an onboard application. Some of the prominent nanoparticulate systems for hydrogen storage are discussed in the following subsections.
3. Conclusions
Nanostructured materials exhibit excellent properties for hydrogen storage due to desired and tunable specific surface area along with many others. These functional smart nanosystems offer superior properties for the physical and chemical reactions, such as surface interactions, adsorption on the active surface while maximizing the bulk absorption, fast reaction kinetics, low-temperature hydrogenation and dehydrogenation, hydrogen atom dissociation on the nanocatalytic surface, and molecular diffusion via the active polymeric chain. The huge surface to volume ratio and exclusive hydrogen adsorbing properties of nanophase materials can facilitate the dissociation of gaseous hydrogen effectively, Similarly, the small volume of individual nanoparticles can produce short diffusion paths to the materials’ interiors, therefore enhances the hydrogen atomic transport between the granular composites. The use of nanosized catalytic doping agents provides a higher dispersion of the catalytically active species and thus participates in higher mass transfer reactions. Nanocomposites based on polyaniline nanofibers and further functionalized with carbon nanotubes possess a unique microstructure for hydrogen storage for onboard vehicular applications.
Nanostructured materials exhibit excellent properties for hydrogen storage due to desired and tunable specific surface area along with many others. These functional smart nanosystems offer superior properties for the physical and chemical reactions, such as surface interactions, adsorption on the active surface while maximizing the bulk absorption, fast reaction kinetics, low-temperature hydrogenation and dehydrogenation, hydrogen atom dissociation on the nanocatalytic surface, and molecular diffusion via the active polymeric chain. The huge surface to volume ratio and exclusive hydrogen adsorbing properties of nanophase materials can facilitate the dissociation of gaseous hydrogen effectively, Similarly, the small volume of individual nanoparticles can produce short diffusion paths to the materials’ interiors, therefore enhances the hydrogen atomic transport between the granular composites. The use of nanosized catalytic doping agents provides a higher dispersion of the catalytically active species and thus participates in higher mass transfer reactions. Nanocomposites based on polyaniline nanofibers and further functionalized with carbon nanotubes possess a unique microstructure for hydrogen storage for onboard vehicular applications.