Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Ali Irfan and Version 3 by Lily Guo.
The 1,2,3-thiadiazole moiety occupies a significant and prominent position among privileged heterocyclic templates in the field of medicine, pharmacology and pharmaceutics due to its broad spectrum of biological activities.
- 1
- 2
- 3-thiadiazole
- synthetic strategies
- biological activities
- antiviral
- anticancer
- antifungal
- insecticidal
1. Introduction
The fascinating aromatic 1,2,3-thiadiazole is a structurally active pharmacophore and great interest for researchers due to its versatile and wide array of biological activities in the field of medicine, pharmacology and pharmaceutics. Thiadiazoles occur naturally in four different isomeric forms, having one sulfur and two nitrogen atoms with hydrogen binding domain as presented in Figure 1 [1][2][3][4][1,2,3,4].
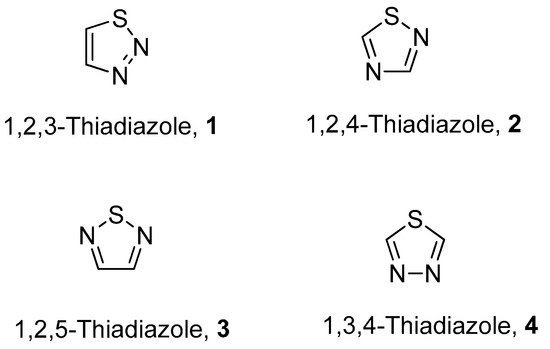
Figure 1.
Structures of different isomeric forms of thiadiazole (
1
–
4
).
Thiadiazole scaffold emerges as an interesting structural motif due to the presence of different heteroatoms in its structure and its promising therapeutic activities in the treatment and cure of several diseases. Different substitutions on the thiadiazole nucleus improve the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of thiadiazole hybrid structures to enhance its therapeutic efficacy against a wide variety of pathogens [1][5][1,5]. Thiadiazole scaffolds exhibit a wide range of biological activities including antimicrobial [6][7][8][9][10][11][6,7,8,9,10,11], carbonic anhydrase inhibitors [12][13][14][12,13,14], antifungal [15][16][17][18][19][15,16,17,18,19], antibacterial [20][21][22][23][24][25][20,21,22,23,24,25], systemic acquired resistance [26][27][26,27], insecticidal activity [28][29][28,29], antiviral [30][31][32][33][30,31,32,33], antioxidant [34][35][34,35], anticonvulsant [36][37][38][39][40][41][42][36,37,38,39,40,41,42], antihypertensive activity [43][44][43,44], anticancer and antitumor [45][46][47][48][49][50][51][45,46,47,48,49,50,51], analgesic [52][53][52,53], anti-inflammatory [54][55][56][57][58][54,55,56,57,58], plant activator [59][60][59,60], antidiabetic [61], antileishmanial activity [62][63][64][65][62,63,64,65] and antituberculosis [66][67][68][69][70][71][66,67,68,69,70,71]. The different marketed drugs of thiadiazole moiety (5–14) are given below [26][72][73][74][75][76][26,72,73,74,75,76] (Figure 2).
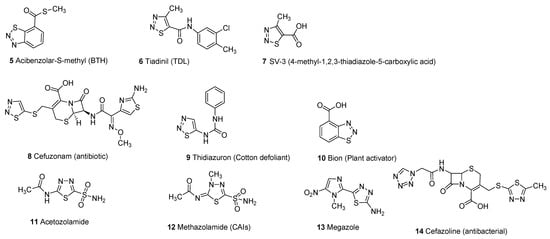
Figure 2.
Commercial drugs based on different thiadiazole scaffolds (
5
–
14
).
The bioactive 1,2,3-thiadiazole analogues display excellent and outstanding new profiles of medicinal, pharmacological and pharmaceutical activities [1][77][1,77]. In this review article, the most recent and relevant synthetic approaches and pharmacological activities of 1,2,3-thiadiazole analogues are discussed and can be classified into antiviral, insecticidal, antifungal and anticancer activities.
2. Biological Activities of 1,2,3-Thiadiazole Derivatives
The main objective of the present section is the search and presentation of the 1,2,3-thiadiazole based most potent therapeutic agents for a variety of biological and pharmacological applications with little or no side effects. In this section, 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives have been divided into classes according to their biological activity.
2.1. Antiviral Agents
Pawar et al. described antiviral drugs as such bioactive compounds which are used for the treatment of viral infections [78][96]. Rossignol et al. reported that most of the antiviral agents are specifically targeted oriented while some other antivirals have a broad spectrum against a vast variety of viral infections [79][97]. Some antiviral drugs such as ribavirin (89; Figure 3) are being used against both RNA and DNA viruses [80][81][82][98,99,100], efavirenz (90; Figure 3) used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS [83][84][85][101,102,103] and arbidol (91; Figure 3) was used against influenza viruses [86][87][104,105].
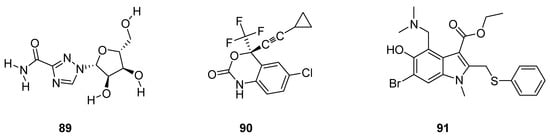

Figure 3.
Structures of antiviral drugs
89
–
91
.
Zhan et al. prepared 1,2,3-thiadiazole thioacetanilide by adopting a multi-step methodology and exhibited their anti-HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) activity against MT-4 cells. Among all synthesized derivatives, the thioacetanilide based 1,2,3-thiadiazole scaffold (92; Figure 4) showed remarkably the best anti-HIV activity in terms of EC50 value 0.059 ± 0.02 µM, CC50 > 283.25 µM, SI > 4883 µM compared to the reference compounds such as NVP (nevirapine) DLV (delaviridine), EFV (Efavirenz), AZT (azidothymidine) and VRX-480773. SAR displayed that the significant enhancement in the antiviral efficacy of compound 92 was due to the introduction of the nitro group on the phenyl ring. Anilide scaffold having NO2 and halogen-substituted aryl ring at o-position took great part to enhance the anti-HIV potential, however, the case was the difference for fluorine atom which decreased activity at a certain level [88][106].
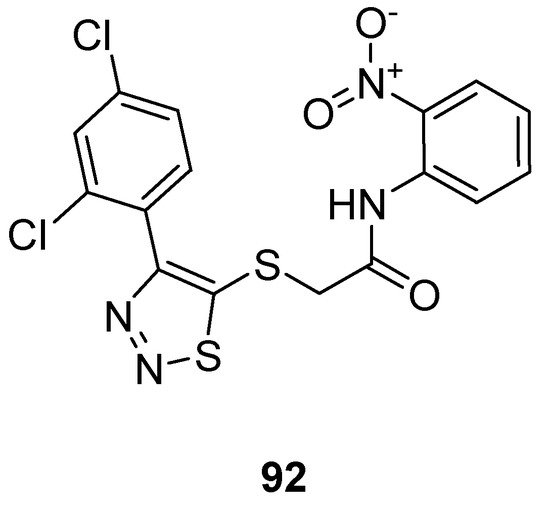

Figure 4.
Thioacetanilide based 1,2,3-thiadiazole scaffold
92
exhibiting maximum anti-HIV potential.
Zhan et al. prepared potent 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives against HIV-1. The new 1,2,3-thiadiazole (93; Figure 5) proved as the most active anti HIV-1 agent (EC50 value 0.0364 ± 0.0038 µM, CC50 > 240.08 µM and SI > 6460 µM) against MT-4 cells among the synthesized derivatives in comparison with the reference compounds NVP (EC50 0.208 µM) and DLV (EC50 0.320 µM) EFV (EC50 0.00440 µM) and AZT (EC50 0.0151 µM). Phenyl ring substituted with 2,4-Br2 group significantly increased the antiviral potential of compound 93 than all other substituents on the phenyl ring. SAR studies indicated decreasing order of antiviral strength, i.e., 2,4-Br2 > 2,4-Cl2 > 2,4-F2 [89][107].
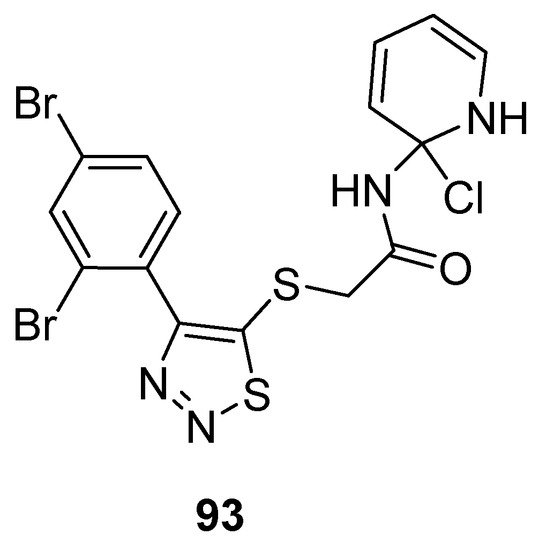

Figure 5.
Anti-HIV activity of 5-(2,4-dibromophenyl)-1,2,3-thiadiazole
93
.
Dong et al. prepared potent antiviral piperidine-based thiadiazole derivatives, and the SAR study showed that chlorine atom substituted compounds exhibited good antiviral activity and the substitution on phenyl ring affects inhibitory action. 1,2,3-thiadiazole (94; Figure 6) displayed excellent potency with IC50 3.59 μg/mL as compared to lamivudine (IC50 value 14.8 μg/mL). It was observed that compounds having p-substituents exhibited more cytotoxic potency than the o-substituted derivatives. Moreover, lowering of the selective index with higher anti-HBV potencies of the synthesized compounds was observed when comparing the results with lamivudine. Compound 94 proved to be the most active one as compared to the other derivatives [90][86].
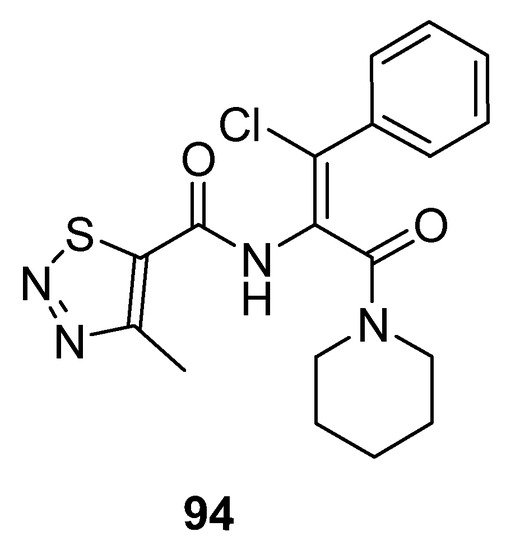

Figure 6.
Antiviral activity of 1,2,3-thiadiazole
94
.
Synthesis and screening of antiviral potency of tetrazole-based 1,2,3-thiadiazoles structural against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV, anti-TMV) were evaluated [91][84]. The studies indicated that some obtained compounds (95–98; Figure 7) have higher anti-TMV activity (33.75–48.73%) than ribavirin at 100mg/mL concentration (33.23%) and comparable potency to ribavirin at 100 μg/mL. Structure 97 displayed the best protection effect among the synthesized derivatives as well as from the ribavirin—reference drug. Anti-TMV activity of synthesized scaffolds and reference drugs decreases in order of 98 > ninamycin >97 > 95 > 96 > ribavirin while the protection effect decreased in order of ninamycin > 97 > 96 > 95> ribavirin > 98. Compound 98 display a higher inhibition potential, i.e., 48.73% as compared to ninamycin and ribavirin. The SAR study showed that the 2-fluorophenyl substituent derivative 97 displayed the best protection effect among the synthesized congeners as well as from the ribavirin reference drug. The protection effect decreased in order of ninamycin > 2-fluorophenyl > cyclopropyl > isopropyl > ribavirin > 4-ethylphenyl. Overall the scaffold 97 proved to be a promising therapeutic agent, which has a better protection effect as well as the best anti-TMV activity [91][84].
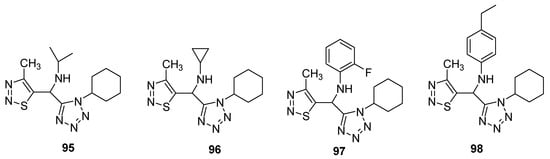

Figure 7.
Antiviral activity of terazole derivatives
95
–
98
.
Mao et al. reported the synthetic protocol to afford substituted methyl carbohydrazide-based 1,2,3-thiadiazoles and determined the anti-TMV activity. The thiophene containing carbohydrazide 1,2,3-thiadiazole (99; Figure 8) showed potent direct anti-TMV activity with 58.72% and 61.03% induction potencies at 50 µg/mL when compared with reference drugs, ninamycin and tiadinil. Both the standard reference drugs, ninamycin and tiadinil, exhibited anti-TMV activity (54.93% and 7.94%) and induction activity (18.58% and 59.25%) respectively in vivo at 50 µg/mL concentration. The scaffold 99 showed remarkably and significant higher antiviral potential than the standard reference drugs. The excellent anti-TMV activity of analogue 99 was due to the presence of thiophene moiety as compare to all the other tested compounds. The structural motif 99 showed significantly higher induction activity (61.03%) more than the induction activities of reference drugs, ninamycin and tiadinil (18.58%) and (59.25%), respectively. So the derivative 99 proved to be a plant elicitor and anti-TMV agent simultaneously [92][108].
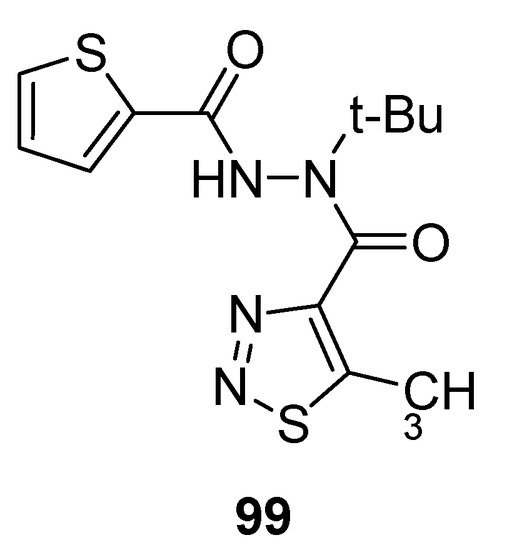

Figure 8.
Antiviral 1,2,3-thiadiazole scaffold
99
.
Another example of compounds with anti-TMV activity are structures 100 and 101 with a 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring (Figure 9) [93][109]. They showed potent curative, inactivation and protection effects against TMV. The derivative 100 displayed curative rate 54.1%, inactivation rate 90.3% and protection rate 52.8% while the compound 101 showed 47.1, 85.5 and 46.4% curative, inactivation and protection rates, respectively. The ningnanmycin was used as a standard reference drug, exhibiting a 56.1% curative rate, 92.5% inactivation rate and 59.3% protection rate. The incorporation of 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety in the skeleton of 1,2,3-thiadiazoles significantly increased the anti-TMV activity [93][109].
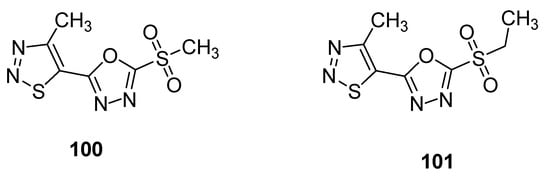

Figure 9.
1,2,3-thiadiazoles
100
and
101
with anti-TMV activity.
Other promising anti-TMV agents 102 and 103 were presented by Zheng et al. (Figure 10) [94][83]. The substituted 1,2,3-thiadiazole-4-carboxamide scaffold 102 exhibited the best antiviral curative activity of 60 and 47%, at 500 and 100 µg/mL concentrations, while the standard tiadinil showed curative activity 58 and 46% at 500 and 100 µg/mL concentrations, respectively. Compound 103 showed its potent protective effect 76 and 71% at 500 and 100 µg/mL concentrations in comparison with the standard drug tiadinil, which displayed protective 75 and 57% at 500 and 100 µg/mL. The structure 103 marked a higher protective effect than the tiadinil and 102 at 100 µg/mL concentration. The enhanced protective potential of 103 was dose-dependent and due to the presence of hyroxyphenyl moiety. The fluorophenyl, chlorophenyl and hyroxyphenyl functionalities contributed to better efficacy that led to a future investigation to develop promising anti-TMV agents [94][83].
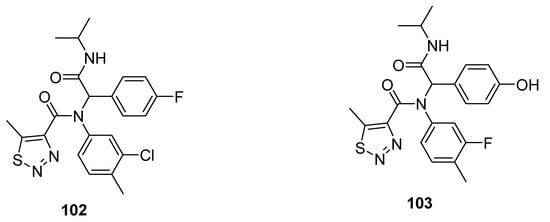

Figure 10.
1,2,3-Thiadiazole scaffolds
102
and
103
with anti-TMV activity.
1,2,3-Thiadiazole acetanilide hybrid structures prepared by Zhan et al. were screened for their antiviral activity against HIV-1 [95][110]. In the group of achieved derivatives structure (104; Figure 11) exhibited moderate antiviral activity (EC50 value 0.95 ± 0.33 µM) against HIV in comparison with the reference standard drugs such as: NVP (EC50 value 0.208 µM), DLV (EC50 value 0.32 µM), EFV (EC50 value 0.00440 µM) and zidovudine (EC50 value 0.0151 µM). The scaffold 104 displayed remarkable high and excellent anti-HIV-1 activity than all standards. The reason for the highest anti-HIV-I activity of structural motif 104 among the synthesized congeners was due to the 4-acetyl substituted anilide phenyl ring of 1,2,3-thiadiazole [95][110].
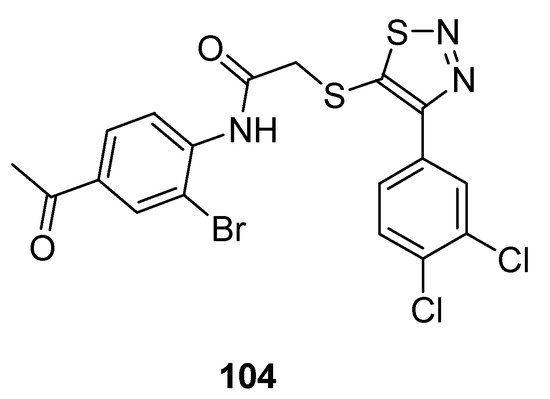

Figure 11.
Antiviral activity of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3-thiadiazole scaffold
104
.
2.2. Anticancer Agents
Cancer has drawn the attention of today’s medical science all over the world because it is the lethal, notably complex, most prominent and serious threat to human health. It forms the lump of uncontrolled growth cells called tumors or neoplasm tumor cells. The neoplasm malignant are diversified heterogeneous cells which have properties of rapid proliferation and capability to invade or spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymphatic system. Most researchers have devoted their extensive research to developing effective anticancer agents, along with the employment and application of integrated surgical procedures, radiation therapy and chemotherapy [96][97][111,112]. Great advances and many discoveries in the development of a large quantity of anticancer therapeutics such as carboplatin (105) cisplatin (106) [98][99][100][113,114,115], anastrozole (107) [101][102][116,117] and doxorubicin (108) (Figure 12), etc., have been made over the past 60 years [103][104][105][106][118,119,120,121].

Figure 12.
Clinical anticancer drugs
105
–
108
.
Noteworthy are the 4,5-diaryl-1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives obtained by Wu et al. due to their method of synthesis and anticancer properties [107][122], and results pointed out that compounds 109 and 110 are the lead compounds by exhibiting favorable activity (Figure 13). Growth inhibition rate of tumor cells (obtained from mice S180) by derivative 109 at a dose of 40 mg/kg administrated for 5 days reached 81.0%, while compound 110 displayed a tumor suppression efficacy of 64.2% (at 100 mg/kg of dose administered to mice for five days). These effects were compared with the standard reference CA-4 (combretastatin A-4), which showed a 64.2% antitumor effect at a dose of 40 mg/kg used for 4 days in a mouse model. The SAR study indicated that the reason of the highest antitumor activity of structural motif 109 than reference drug CA-4 and derivative 110 was because of OMe group at C-4 and H at C-3 of 5-phenyl ring of 1,2,3-thiadiazole, while the replacement of hydrogen at C-3 with the nitro group dropped the antitumor activity of derivative 110. The scaffold 109 could be a promising candidate due to its lower cytotoxicity and excellent antitumor effect [107][122].
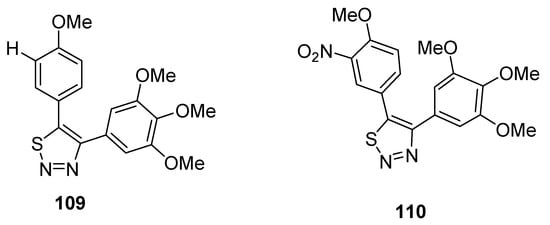

Figure 13.
Antitumor effect of 1,2,3-thiadiales
109
and
110
.
New 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives (111 and 112; Figure 14) obtained by Hosny et al. via Hurd–Mori cyclization were tested against MCF-7 tumor cells. The IC50 values of compounds 111 and 112 (IC50 = 12.8 µg/mL and 8.1 µg/mL, respectively) were comparable to doxorubicin as the standard anticancer drug with IC50 = 3.13 µg/mL. The derivative 111 showed the highest anti-breast cancer activity than the scaffold 112 and reference drug doxorubicin [108][123].
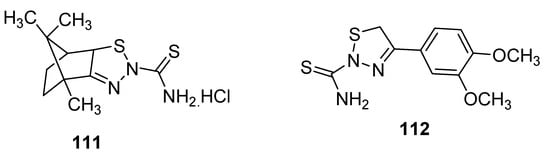

Figure 14.
Anticancer activity of 2-thioamide-1,2,3-thiadiazole
111
and
112
.
Cikotiene et al. reported the synthetic protocol to achieve the substituted 4,5-diaryl-1,2,3-thiadiazoles as Hsp90 chaperone protein inhibitors. This protein plays a significant part in developing tumor cells, so its inhibition is the main target of many anticancer drugs. The Hsp90 chaperone stabilizes a number of proteins that are essential for the growth of tumors, due to which researchers all over the world are interested in the development of Hsp90 inhibitors which would be investigated as anticancer agents. In the group of tested derivatives, structure 113 deserves special attention as an inhibitor of cancer cells with GI50 value of 0.69 µM for U2OS (osteosarcoma) cells and 0.70 µM for HeLa (cervical carcinoma) cells (Figure 15) [109][124]. Isothermal titration calorimetry was used to determine the binding affinity of compound (113) to Hsp90F and Hsp90N. The derivative (39) acted as a binder to both Hsp90N andHsp90F with the observed Kd of about 42 nM and 37 nM, while for the reference compound17-AAG [17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin] Kd was 200 nM and 240 nM, respectively [109][124].
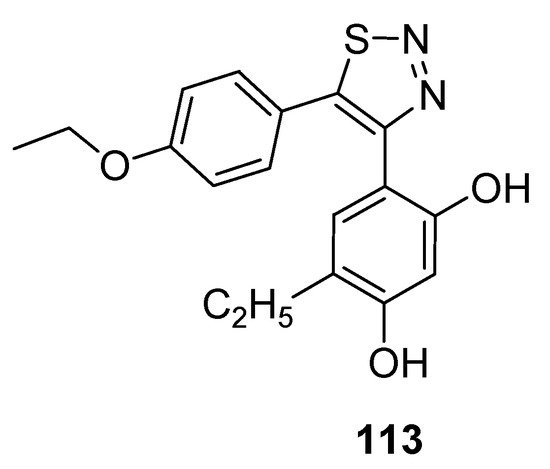

Figure 15.
Anticancer activity of 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivative
113
against U2OS and HeLa cell lines.
Synthesized by Cui et al., dehydroepiandrosterone derivatives of thiadiazoles were investigated against T47D and HAF cell lines for their antitumor activity applying the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay. In this group of compounds, derivative 114 (Figure 16) focuses particular attention, due to its strong antitumor and antimetastatic activities, in vitro and in vivo. Its IC50 value for T47D cells was 0.058 ± 0.016 µM and for HAF cells IC50 = 21.1 ± 5.06 µM. Moreover, the selectivity of compound 114 (SI = 364) was 214 folds better than adriamycin (positive control) (ADM; SI = 1.7). The SAR study showed that the introduction of 1,2,3-thiadiazole and D-proline chemical entities in derivative 114 significantly enhanced antiproliferative activity than the parent DHEA. The SI of scaffold 114 was 214 folds better than SI of ADM standard drugs. The derivative 114 could be used as the promising and novel class of anticancer agent due to its low cytotoxicity, high selectivity index and excellent antitumor and antiproliferative activities (Figure 16) [110][125].
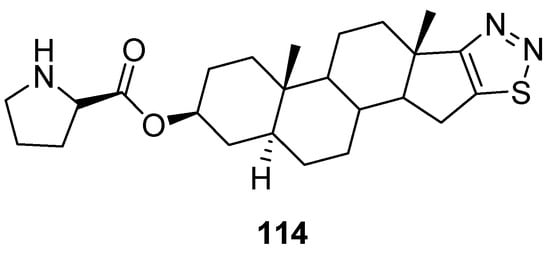

Figure 16.
1,2,3-Thiadiazole dehydroepiandrosterone derivative
114
as new antitumor agents.
2.3. Insecticidal Agents
Insecticides are the designed substances of either chemical or biological origin that used to regulate the insect behaviour, control insects, cause death, dysfunction and moving away [111][112][126,127]. Some of the insecticidal agents, such as tebufenozide (115) act as molting hormones primarily against caterpillar pests [113][128]; imidacloprid (116) is the most well-known broad spectrum insecticide, which used as an insect neurotoxin [114][115][116][129,130,131], and neuroactive pymetrozine (117) is a novel class of pyridineazomethine insecticide used for the control of aphids and whiteflies in crop fields (Figure 17) [117][132].
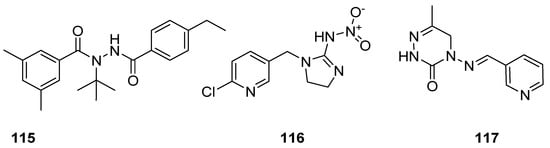

Figure 17.
Known insecticidal agents
115
–
117
.
An interesting example of 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives with insecticidal properties are two groups of N-tert-butyl-N,N′-diacylhydrazines obtained by Wang et al. [29] and tested their activity against Plutella xylostella L. and Culex pipiens pallens. Derivative 118 (Figure 18) displayed remarkable and significantly the highest insecticidal potential (79% mortality at 200 μg/mL) against Plutella xylostella L., while 119 exhibited 68% mortality against the same insects at concentration 200 μg/mL. Insecticidal activity of reference agent, i.e., tebufenozide, was 40%. The scaffold 118 displayed excellent and the highest insecticidal potency, 79% more than the insecticidal potencies of reference drug tebufenozide (40%) and derivative 119 (68%). The EWD group chloro increased the insecticidal activity of scaffold 118, while ED group methyl decreased the insecticidal potency of scaffold 119 [29].
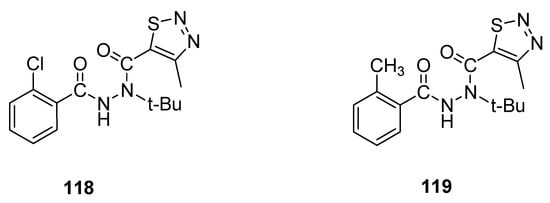

Figure 18.
Insecticidal activity of
N
-
tert
-butyl-
N
,
N
′-diacylhydrazines
118
and
119
.
Zhang et al. designed the (E)-β-farnesene based carboxamides of thiadiazoles and checked their aphicidal behavior against Myzus persicae [118][133]. The three compound 120–122 (Figure 19) exhibited LC50 values of 33.4 μg/mL, 50.2 μg/mL and 61.8 μg/mL, respectively. The 1,2,3-thiadiazole carboxamide analogues showed significantly higher aphicidal activity than (E)-ß-farnesene, but lesser insecticidal activity than pymetrozine insecticide (LC50 = 7.1 μg/mL). It was observed that fluoro or difluoro groups on phenyl moiety enhanced the aphicidal potential significantly in novel chemical entities of Eβf 1,2,3-thiadiazole 120 and 121 while the methyl substitution led to lower aphicidal activity of scaffold 122 [118][133].
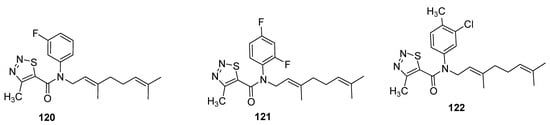

Figure 19.
Insecticide Eβf 1,2,3-thiadiazole carboxamides
120
–
112
.
Pyrazole oxime derivatives, as a new Fenpyroximate analogue bearing a thiadiazole moiety, were synthesized by Dai et al. and then their insecticidal, acaricidal and cytotoxic activities were examined. The best insecticidal properties possessed oximes 123 and 124 (Figure 20) against Aphis craccivora at 100 μg/mL with 90% of the mortality rate. The structure–activity relationship study revealed that due to the insertion of F- and Me-groups at p-position of phenoxy moiety attached to the pyrazole oxime 123 and 124 displayed good insecticidal activities but slightly lower than commercial drug imidacloprid [119][134].
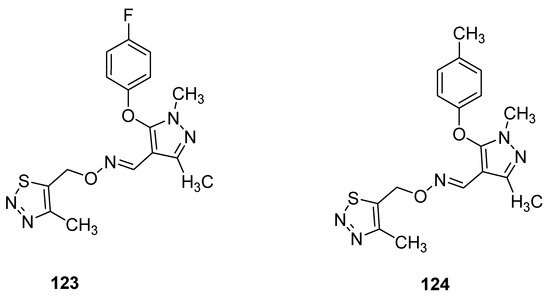

Figure 20.
Ethers of pyrazole oximes
123
and
124
with insecticidal properties.
Another interesting example of insecticidal compounds are hybrids of substituted triazole and 1,2,3-thiadizole scaffold that were investigated for their activity against Aphis laburni and TMV by Li et al. [120][135]. Preliminary bioassays indicated compounds 125 and 126 (Figure 21) as lead compounds by depicting enhanced activity against Aphis laburni at 100mg/mL (mortality ≥ 95%) while the derivative 127 represent the least active compound (due to CF3 substituted triazole ring) that displayed only 25.25% mortality. The structure–activity study indicated that scaffolds with aromatic moieties attached to the carbonyl carbon of triazole ring have higher insecticidal activity than scaffolds with alkyl moieties [120][135].
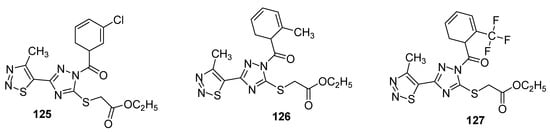

Figure 21.
Substituted 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives with insecticidal properties against
Aphis laburni
.
2.4. Amoebicidal Agents
A parasitic disease caused by a protozoa Entamoeba histolytica is known as amoebiasis. E. histolytica has infected 40 to 50 million people worldwide and led to the development of amoebic colitis or extraintestinal abscess that has resulted in 100,000 deaths annually [121][122][123][136,137,138]. The tissue amoebiasis is treated by different drugs such as metronidazole, chloroquine, tinidazole, dehydroemetine and nitazoxanide, while the diloxanide furoate and iodoquinoline drugs are used to treat luminal infections (Figure 22) [124][125][126][127][128][139,140,141,142,143].
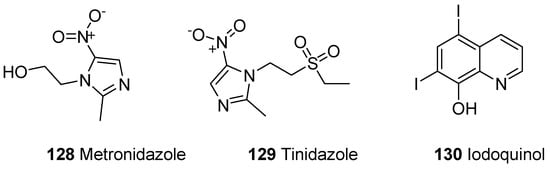

Figure 22.
Amoebicidal commercial dugs
128
–
130
.
Hayat et al. reported the synthetic route to achieve substituted 1,2,3-thiadiazole scaffolds from the cyclization of quinoline-based hydrazone. All substituted 1,2,3-thiadiazole hybrids and quinoline-based hydrazones were evaluated for antiamoebic activity against HM1 and IMSS strains of E. histolytica. The scaffold 4-bromo phenyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole (131, Figure 23) and furan based 1,2,3-thiadiazole (132, Figure 23) exhibited potent antiamoebic activity (IC50 = 0.24 µM and IC50 = 0.23 µM, respectively) when compared with metronidazole (IC50 = 1.80 µM). The parent intermediate quinoline-based hydrazone displayed better antiamoebic potential than the targeted derivatives of 1,2,3-thiadizoles. The SAR study revealed that the significant loss of antiamoebic potential in scaffolds 131 and 132 was due to the absence of quinoline acetohydrazone moiety in final thiadiazoles [129][87].
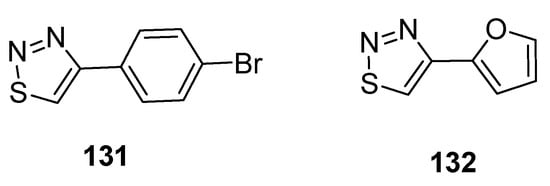

Figure 23.
The most active antiamoebic 1,2,3-thiadiazoles
131
and
132
.
2.5. Plant Activator Agents
Plant activators are synthetic or natural chemicals entities that protect plants from different pathogens. Among them, pyrimidin-type plant activator 2 (PPA2 133; Figure 24) significantly enhanced plant defense system against bacterial infections unlikely traditional commercially available plant activators (INA 134, BABA 135, BHT 7; Figure 24). Plant activators not only showed their therapeutic potential against wide variety of pathogens but also increased growth of plants, rate of photosynthesis and overall yield of crops [130][131][132][133][134][144,145,146,147,148].
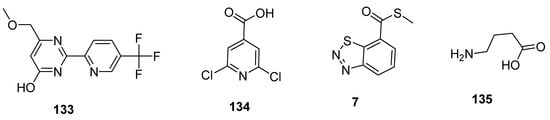

Figure 24. Structures of commercially available plant activators 133–135.
Du et al. reported a synthetic pathway for the preparation of carboxylate derivatives of thiadiazoles as potential plant activators against seven plant diseases [135][90]. The 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives 136 and 137 (Figure 25) proved to be good plant activators and displayed excellent inhibition activities against diseases such as M. melonis, (90% for 136 and 69% for 137), C. cassiicola (77% for 136 and 52% for 137), P. syringae pv. Lachrymans (42% for 136 and 42% for 137) and P. infestans (81% for 136 and 67% for 137) when results were compared with commercial BTH plant activator. The structural motifs 136 and 137 displayed significantly better therapeutic efficacy than BHT commercial drug, but the scaffold 136 had better plant activating potency than scaffold 137 [136][88].
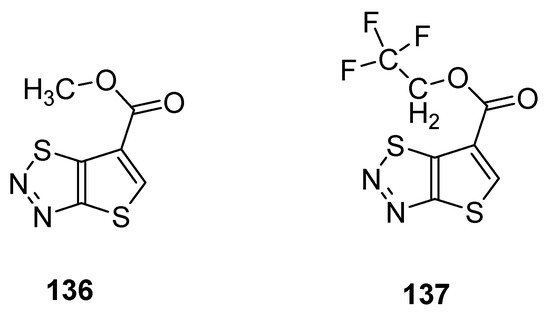

Figure 25.
Potential new plant activator with thieno [2,3-
d
]-1,2,3-thiadiazoles
136
and
137
.
2.6. Fungicidal Agents
The chemical agents that have the potential to control and eradicate fungal infections are termed as fungicides or antifungal drugs [137][149]. The commercial antifungal agents are chlorothalonil (65) which is a non-systemic fungicide [138][139][150,151], fluconazole (66) [140][152] and ketoconazole (67) (Figure 26) [141][153].

Figure 26.
Structures of commercial antifungal drugs
138
–
140
.
As the first example, it is worth bring up oxadiazoles containing thiadiazole derivatives [142][154]. In this group, two oxadiazole derivatives 141 and 142 (Figure 27) displayed the best antifungal activity against Puccinia triticina at a concentration of 500 μg/mL. Both structures showed a remarkable high growth inhibition activity (98 and 83%, respectively) which was slighter lower than the standard drug chlorothalonil with 100% fungal growth inhibition activity. The remarkable high and excellent antifungal activity of scaffold 141 could lead to the development of novel oxadiazole-based 1,2,3-thiadiazole fungicides [142][154].
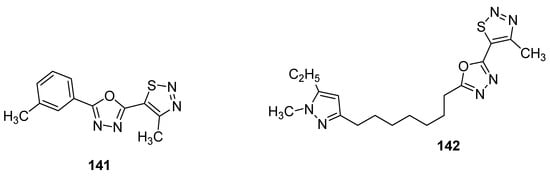

Figure 27.
Novel potent 1,2,3-thiadiazole fungicides
141
and
142
.
Another example of compounds with good antifungal activities are new structures designed by Sun et al., which are 1,2,4-triazole derivatives substituted with a 1,2,3-thiadiazole ring [143][82]. One of the synthesized compounds 143 (Figure 28), exhibited remarkably high fungicidal 93.19% against Corynespora cassiicola, while reference compounds iprodione, validamycin and topsin-M possessed 78.20, 53.52 and 78.75% antifungal activity, respectively. The authors declared that compound containing phenyl group on triazole ring 143 exhibited higher activity, however, the results were different in the case of Pseudoperonospora cubensis as compound 144 containing cyclopropyl group displayed higher activity than that of 143. The most active compound with regard to Pseudoperonospora cubensis was 144, which inhibited the growth of this pathogen in 81.62%. However, SAR analysis did not clear the results against pseudomonas syringae pv. Lachrymans. Both the scaffolds showed excellent and the highest antifungal potential than all three commercial reference drugs that will lead to the development of promising antifungal agents [143][82].
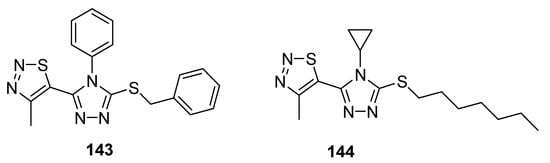

Figure 28.
Antifungal activity of triazole moiety containing 1,2,3-thiadiazolew
143
and
144
.
Less antifungal activity was observed in the derivative 145 (Figure 29) reported by Tan et al. [144][155]. Its inhibition rates to Phytophthora infestans (Mont) de Bary, Alternaria solani, Gibberella sanbinetti, Physalospora piricola Nose, Botrytis cinerea, Phytophthora capsici Leonian, Cercospora arachidicola, Rhizoctonia solanii and Fusarium oxysporum reached 32.3, 17.4, 32.3, 25.8, 43.5%, 36.1, 15.8, 30.3 and 26.9% at 50 μg/mL respectively. The results indicated that the structural motif 145 proved to be broad-spectrum fungicide because it exhibited significant antifungal activity against different fungal strains [144][155].
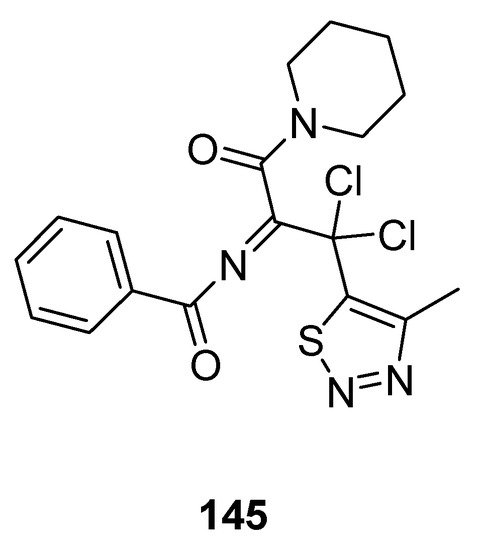

Figure 29.
Piperidine based 1,2,3-Thiadiazole
145
with moderate antifungal activity.
Another group reported the fungicidal properties of 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives against Alternaria solani (AS), Botrytis cinerea (BC), Cercospora arachidicola (CA), Cercospora beticola (CB), Colletotrichum lagenarium (CL), Fusarium oxysporum (FO), Gibberella zeae (GZ), Macrophoma kuwatsukai (MK), Phytophthora infestans(Mont) de Bary (PI), Physalospora piricola (PP), Pellicularia sasakii (Shirai) (PS), Puccinia triticina Eriks (PT) and Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn (RS) [145][156]. The most active occurred to be structure 146 (Figure 30) showed potent fungicidal inhibitory activity 84.8, 83.9, 83.3, 78.9, 75.0, 71.4, 70.7, 66.7, 64.7 and 63.6% against PS, PP, RS, PT, FO, CB, PI, AS, CL and CA, respectively. On the other hand, the propyl containing fused 1,2,4-triazolo[1,3,4]thiadiazole 147 (Figure 30) exhibited the best fungicidal inhibition activity 93.0% for FO, 84.9% for BC, 77.8% for PS, 75.8% for PI, 75.0% for GZ, 62.1% for CA, 50.0% for CL, 40.5% for PP, 34.4% for AS and 33.3% for CB. The results of the antifungal study showed that fused 1,2,4-triazolo[1,3,4]thiadiazole led to the development of wide-spectrum antifungal agents [145][156].
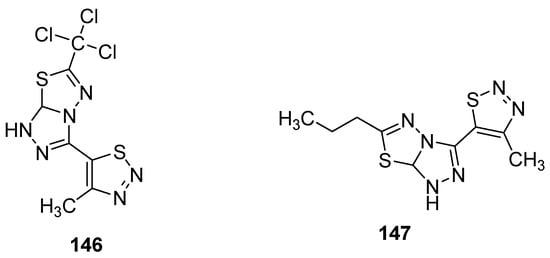

Figure 30.
1,2,3-thiadiazoles with broad antifungal activity.
Wang et al. reported a synthetic approach to new series of organotin 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-carboxylates and benzo[1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-carboxylates [146][157] and antifungal properties against P. piricola and Gibberella zeae. The triethyltin-based 1,2,3-thiadiazole carboxylate analogue 148 (Figure 31) displayed antifungal efficacy EC50 = 0.12 μg/mL and 0.16 μg/mL against P. piricola, and Gibberella zeae, respectively. The overall results of the present study indicated the antifungal effectiveness of organotin-based benzo-1,2,3-thiadiazole or 1,2,3-thiadiazoles analogues proved to be broad-spectrum fungicides [146][157].
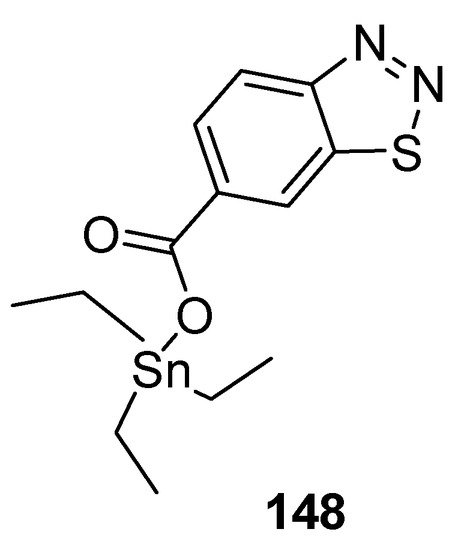

Figure 31.
Antifungal benzo[1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-carboxylate derivative
148
.
Antifungal properties have also been determined for carboxamide derivatives of thiadiazoles obtained by Zuo et al. utilized one-pot four-component Ugi reaction strategy under green synthetic conditions [147][158]. All the synthesized analogues were investigated against eleven fungal strains to develop novel fungicidal candidates. The 1,2,3-thiadiazole containing carboxamide moiety 149 (Figure 32) displayed broad-spectrum fungicidal inhibition activities against CA 71%, AS 100%, GZ 62%, PP 85%, PG 14%, PS, 74%, CL 95%, PI 88% and RS 97%. Similarly good antifungal activity was observed for scaffold 150 that exhibited fungicidal inhibition against various fungal strains such as: CB (Cercospora beticola) 67%, CA 79%, AS 44%, GZ 34%, PP 53%, PG 57%, PS 16%, CL 43%, RS 51% and PI 57%. The scaffold 149 displayed maximum fungicidal potential 100, 97 and 95% against fungal strains AS, RS and CL, respectively, while the zero percent antifungal activity was shown against CB and FO fungal strains, just as scaffold 150 displayed the best antifungal potential 67% against CB fungal strains and 0% against FO [147][158].
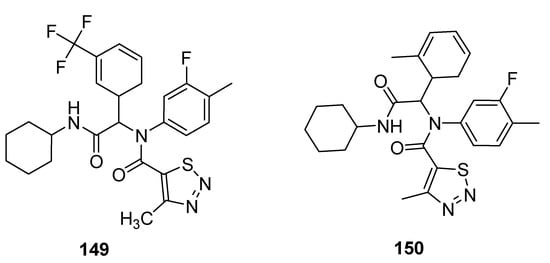

Figure 32.
The most active 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-carboxamides.
