Histamine is a key signal molecule in humans, with multiple functions, such as being a neurotransmitter or modulator of immune responses. More recent studies have shown that bacteria have evolved different mechanisms to sense histamine or histamine metabolites. Histamine sensing in the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa was found to trigger chemoattraction to histamine and to regulate the expression of many virulence-related genes.
- histamine
- signal molecule
- sensing
- histamine receptors
- chemotaxis
- gut microbiome
1. Introduction
Bacteria have evolved a large number of signal transduction systems that recognize different signals and generate, in return, adaptive responses. Major protein families include transcriptional regulators, two-component systems (TCS), chemoreceptors, proteins involved in the synthesis and hydrolysis of the c-di-GMP and c-di-AMP second messengers, extracytoplasmic function Stimuli recognized are diverse and include an enormous variety of low molecular weight compounds, pH, temperature, light or osmotic stress, among others [1][2]. Major forms of signaling responses are transcriptional regulation, chemotactic movements or alterations in second messenger levels [3].
Bacteria have evolved a large number of signal transduction systems that recognize different signals and generate, in return, adaptive responses. Major protein families include transcriptional regulators, two-component systems (TCS), chemoreceptors, proteins involved in the synthesis and hydrolysis of the c-di-GMP and c-di-AMP second messengers, extracytoplasmic function Stimuli recognized are diverse and include an enormous variety of low molecular weight compounds, pH, temperature, light or osmotic stress, among others [2,3]. Major forms of signaling responses are transcriptional regulation, chemotactic movements or alterations in second messenger levels [1].
Frequently, bacteria establish interactions with organisms of other domains like animals, humans or plants. A representative example for such central inter-species signals is the auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) that is a key plant hormone, regulating, among other processes, plant growth and development [4]. However, IAA is commonly produced and secreted by bacteria that interact with plants and plays a key role in mediating plant–bacteria interactions [5][6].
Frequently, bacteria establish interactions with organisms of other domains like animals, humans or plants. A representative example for such central inter-species signals is the auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) that is a key plant hormone, regulating, among other processes, plant growth and development [6]. However, IAA is commonly produced and secreted by bacteria that interact with plants and plays a key role in mediating plant–bacteria interactions [7,8].
There is now emerging evidence, reviewed in this article, that histamine may be another central signal molecule that mediates bacteria–host interactions. It is a human neurotransmitter, a modulator of inflammatory reactions and the immune response and a key mediator of several events in allergies and autoimmune diseases [7]. Further activities of histamine include a participation in cell proliferation, differentiation, hematopoiesis, embryonic development, secretion of pituitary hormones as well as a regulation of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and circulatory functions [8]. It is primarily secreted by mast cells and basophiles, and it exerts its function through four different types of histamine receptors, termed H1R, H2R, H3R and H4R [8].
There is now emerging evidence, reviewed in this article, that histamine may be another central signal molecule that mediates bacteria–host interactions. It is a human neurotransmitter, a modulator of inflammatory reactions and the immune response and a key mediator of several events in allergies and autoimmune diseases [10]. Further activities of histamine include a participation in cell proliferation, differentiation, hematopoiesis, embryonic development, secretion of pituitary hormones as well as a regulation of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and circulatory functions [11]. It is primarily secreted by mast cells and basophiles, and it exerts its function through four different types of histamine receptors, termed H1R, H2R, H3R and H4R [11].
A wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria were found to possess HDC-encoding genes and to synthesize histamine [9]. There appear to be two bacterial HDC superfamilies, namely those that require pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme, found primarily in Gram-negative bacteria, and those in Gram-positive species that employ a covalently bound pyruvate moiety for catalysis [9]. The regulation of the expression ofhdcgenes has been studied in several bacteria. Histidine was found to induce the expression ofhdcgenes [10][11][12][13], whereas histamine slightly repressed its expression in several lactic bacteria belonging to theLactobacillus, Pediococcus and Oenococcusgenera [11].
A wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria were found to possess HDC-encoding genes and to synthesize histamine [12]. There appear to be two bacterial HDC superfamilies, namely those that require pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme, found primarily in Gram-negative bacteria, and those in Gram-positive species that employ a covalently bound pyruvate moiety for catalysis [12]. The regulation of the expression ofhdcgenes has been studied in several bacteria. Histidine was found to induce the expression ofhdcgenes [13,14,15,16], whereas histamine slightly repressed its expression in several lactic bacteria belonging to theLactobacillus, Pediococcus and Oenococcusgenera [14].
Apart from their capacity to synthesize histamine, more recent studies have shown that some bacteria are able to metabolize histamine. The degradation of histamine coincided with the appearance of imidazole-4-acetic acid (ImAA), suggesting that the latter compound is a major intermediate in the degradation route. A six-step catabolic process converts histamine into aspartic acid that is then converted into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediate, fumaric acid [14]. To determine to which extent other bacteria may be able to degrade histamine, the authors inspected genomes for the presence ofhingenes.
Apart from their capacity to synthesize histamine, more recent studies have shown that some bacteria are able to metabolize histamine. The degradation of histamine coincided with the appearance of imidazole-4-acetic acid (ImAA), suggesting that the latter compound is a major intermediate in the degradation route. A six-step catabolic process converts histamine into aspartic acid that is then converted into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediate, fumaric acid [18]. To determine to which extent other bacteria may be able to degrade histamine, the authors inspected genomes for the presence ofhingenes.
The detection of signal molecules by bacteria can serve several purposes: (i) they can indicate the presence of a compound of metabolic value or toxicity, or (ii) For a number of signal molecules, the physiological purposes of sensing appear to be tightly interwoven and include the metabolic aspect as well as the aspect of gaining information on the ecological niche. Histamine may be one of these signals. In the first part of this article, we reviewed studies illustrating the histamine sensing capacity of bacteria, whereas we focused attention, in the second part, on the consequences of bacterial histamine secretion on the host.
2. Histamine Sensing by Bacteria
It is an opportunistic pathogen that infects virtually any tissue [15] and is the leading cause of nosocomial infections, particularly in immunocompromised, cancer, burn-wound and cystic fibrosis patients [16] and a frequent cause of bacteremia [17]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has placedP. aeruginosasecond on the global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery and development of new antibiotics and has rated the development of new antimicrobial agents againstP. aeruginosaas critical [18]. Strain PAO1 was found to be able to grow on histamine as a sole carbon and nitrogen source, indicating that it harbors a functional histamine degradation pathway [19]. In a subsequent study, it was found that the histamine catabolic pathway described in the non-pathogenicP. putidaU [14] is also highly conserved in the opportunistic human pathogenPseudomonas aeruginosa (
It is an opportunistic pathogen that infects virtually any tissue [19] and is the leading cause of nosocomial infections, particularly in immunocompromised, cancer, burn-wound and cystic fibrosis patients [20] and a frequent cause of bacteremia [21]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has placedP. aeruginosasecond on the global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery and development of new antibiotics and has rated the development of new antimicrobial agents againstP. aeruginosaas critical [22]. Strain PAO1 was found to be able to grow on histamine as a sole carbon and nitrogen source, indicating that it harbors a functional histamine degradation pathway [23]. In a subsequent study, it was found that the histamine catabolic pathway described in the non-pathogenicP. putidaU [18] is also highly conserved in the opportunistic human pathogenPseudomonas aeruginosa(
Figure 1
).
The effect of histamine on bacterial gene transcript levels was assessed, for the first time, usingP. aeruginosaPAO1 as a model system [20], the primary reference strain for this pathogen. RNA-seq experiments were conducted, comparing the wild-type (wt) strain in the absence and presence of 2 mM histamine, and samples were taken 3 h after histamine addition. This study showed that the transcript levels of approximately 8.5% of the PAO1 genes showed at least a three-fold change. There were, in total, 301 upregulated and 178 downregulated genes, a selection of which is shown in
The effect of histamine on bacterial gene transcript levels was assessed, for the first time, usingP. aeruginosaPAO1 as a model system [24], the primary reference strain for this pathogen. RNA-seq experiments were conducted, comparing the wild-type (wt) strain in the absence and presence of 2 mM histamine, and samples were taken 3 h after histamine addition. This study showed that the transcript levels of approximately 8.5% of the PAO1 genes showed at least a three-fold change. There were, in total, 301 upregulated and 178 downregulated genes, a selection of which is shown in
Table 1
.
The authors selected nine genes and determined histamine-induced changes in transcript levels using quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR), and the results obtained were consistent with RNA-seq data. Furthermore, additional RT-qPCR studies showed significant changes in the transcript levels of thehinD,hinF, pvdSandpqsAgenes at a 1000-fold lower histamine concentration (2 µM), indicative of high-affinity signal recognition [20].
The authors selected nine genes and determined histamine-induced changes in transcript levels using quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR), and the results obtained were consistent with RNA-seq data. Furthermore, additional RT-qPCR studies showed significant changes in the transcript levels of thehinD,hinF, pvdSandpqsAgenes at a 1000-fold lower histamine concentration (2 µM), indicative of high-affinity signal recognition [24].
Histamine exposure caused significant changes in histamine-related genes, such as genes encoding enzymes for histamine metabolism (HinCDFLHG), transport (HinA) and regulation (HinK) (
Table 1
,
Figure 1
).
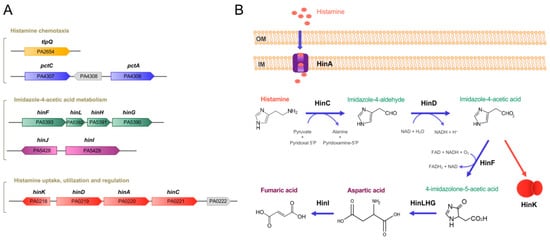
Figure 1. Genes and proteins involved in histamine metabolism, transport, regulation and chemotaxis in P. aeruginosa PAO1. (A) Genetic organization of genes. (B) The proposed histamine catabolic pathway. Data are based on [14][19][20][18,23,24].
Table 1. The effect of histamine on P. aeruginosa PAO1 transcript levels. Shown is a selection of genes with altered transcript levels in an RNA-seq study comparing the wt strain in the absence and presence of 2 mM histamine. Many of these genes play a role in virulence. In total, approximately 8.5% of the P. aeruginosa genes showed at least a three-fold change. Data were taken from [20][24].
| Gene ID | Name | Log2 Fold Change | Description | Function/ Comment |
Ref. Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine-mediated upregulation | |||||
| Histamine metabolism, transport and regulation | |||||
| PA5390 | hinG | 7.9 | Probable peptidic bond hydrolase | Histamine utilization | [20][24] |
| PA5391 | hinH | 10.9 | Hypothetical protein | ||
| PA5392 | hinL | 10.7 | Conserved hypothetical protein | ||
| PA5393 | hinF | 11.1 | Conserved hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0219 | hinD | 10.0 | Probable aldehyde dehydrogenase | ||
| PA0221 | hinC | 10.0 | Probable aminotransferase | ||
| PA0220 | hinA | 9.5 | Histamine transporter | Histamine transport | |
| PA0218 | hinK | 4.8 | Transcriptional regulator | Histamine-mediated regulation | |
| PA0222 | 8.7 | Solute-binding protein | Possibly transport | ||
| Iron acquisition | |||||
| PA0931 | pirA | 3.2 | Ferric enterobactin receptor PirA | [21][25] | |
| PA2385 | pvdQ | 6.3 | 3-oxo-C12-homoserine lactone acylase PvdQ | Siderophore pyoverdin synthesis, secretion, regulation and pyoverdin-Fe uptake | [22][26] |
| PA2386 | pvdA | 7.5 | L-ornithine N5-oxygenase | ||
| PA2389 | pvdR | 2.6 | PvdR | ||
| PA2390 | pvdT | 2.4 | PvdT | ||
| PA2392 | pvdP | 4.1 | PvdP | ||
| PA2394 | pvdN | 5.9 | PvdN | ||
| PA2395 | pvdO | 6.3 | PvdO | ||
| PA2396 | pvdF | 3.4 | Pyoverdine synthetase F | ||
| PA2397 | pvdE | 6.3 | Pyoverdine biosynthesis protein PvdE | ||
| PA2398 | fpvA | 6.0 | Ferripyoverdine receptor | ||
| PA2399 | pvdD | 2.9 | Pyoverdine synthetase D | ||
| PA2400 | pvdJ | 3.0 | PvdJ | ||
| PA2413 | pvdH | 5.6 | L-2,4-diaminobutyrate:2-ketoglutarate 4-aminotransferase | ||
| PA2424 | pvdL | 5.8 | PvdL | ||
| PA2425 | pvdG | 6.2 | PvdG | ||
| PA2426 | pvdS | 5.7 | Sigma factor PvdS | ||
| PA0472 | fiuI | 3.1 | ECF sigma factor FiuI | Ferrichrome activated | [23][27] |
| PA2468 | foxI | 2.5 | ECF sigma factor FoxI | Ferrioxamine activated | [24][28] |
| PA3410 | hasI | 2.9 | ECF sigma factor HasI | Heme activated | [25][29] |
| PA4168 | fpvB | 3.3 | Second ferric pyoverdine receptor FpvB | Pyoverdine transport | [26][30] |
| PA4221 | fptA | 1.7 | Fe(III)-pyochelin outer membrane receptor precursor | Siderophore pyochelin synthesis and transport | [27][31] |
| PA4226 | pchE | 3.1 | Dihydroaeruginoic acid synthetase | ||
| PA4228 | pchD | 4.1 | Pyochelin biosynthesis protein PchD | ||
| PA4229 | pchC | 3.6 | Pyochelin biosynthetic protein PchC | ||
| PA4230 | pchB | 2.7 | Salicylate biosynthesis protein PchB | ||
| PA4231 | pchA | 2.3 | Salicylate biosynthesis isochorismate synthase | ||
| PA4687 | hitA | 3.3 | Ferric iron-binding periplasmic protein HitA | Iron transport | [28][32] |
| PA4688 | hitB | 3.2 | Iron (III)-transport system permease HitB | ||
| Quorum sensing | |||||
| PA0996 | pqsA | 3.4 | Probable coenzyme A ligase | Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) quorum sensing system | [29][33] |
| PA0997 | pqsB | 3.8 | PqsB | ||
| PA0998 | pqsC | 3.8 | PqsC | ||
| PA0999 | pqsD | 3.8 | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase III | ||
| PA1000 | pqsE | 3.6 | Quinolone signal response protein | ||
| PA1001 | phnA | 3.5 | Anthranilate synthase components I and II (important for PQS synthesis) | PQS synthesis | [30][34] |
| PA1002 | phnB | 3.0 | |||
| Secretion system | |||||
| PA1718 | pscE | 2.3 | Type III export protein PscE | Type III secretion apparatus | [31][35] |
| PA1721 | pscH | 1.9 | Type III export protein PscH | ||
| PA1715 | pscB | 1.8 | Type III export apparatus protein | ||
| Regulation | |||||
| PA0707 | toxR | 1.9 | Transcriptional regulator ToxR | Exotoxin A expression | [32][36] |
| PA0612 | ptrB | 2.0 | Repressor PtrB | Type III secretion system expression | [33][37] |
| PA1431 | rsaL | 2.0 | Regulatory protein RsaL | Virulence and biofilm formation | [34][38] |
| PA2227 | vqsM | 2.4 | Transcriptional regulator VqsM | Quorum sensing and virulence | [35][39] |
| PA2686 | pfeR | 3.1 | PfeR response regulator | Enterobactin receptor | [36][40] |
| PA2687 | pfeS | 2.6 | PfeS sensor kinase | ||
| PA3006 | psrA | 1.8 | Transcriptional regulator PsrA | Type III secretion system | [37][41] |
| PA4315 | mvaT | 2.3 | Transcriptional regulator MvaT | Type III secretion system | [38][42] |
| PA5124 | ntrB | 4.0 | NtrB kinase | Invasiveness and Virulence | [39][43] |
| PA5125 | ntrC | 3.7 | NtrC response regulator | ||
| Others | |||||
| PA4760 | dnaJ | 3.2 | Heat shock protein | Pyocyanin production | [40][44] |
| PA4761 | dnaK | 3.7 | Chaperone DnaK | Translocation across the intestinal epithelia cells | [41][45] |
| Histamine-mediated downregulation | |||||
| Regulation | |||||
| PA0173 | cheB2 | −2.1 | CheB2 methylesterase | Che2 pathway, unknown function, involved in virulence | [42][43][46,47] |
| PA0174 | cheD | −2.2 | CheD deamidase | ||
| PA0175 | cheR2 | −2.4 | CheR2 methyltransferase | ||
| PA0176 | mcpB/aer2 | −2.3 | Aer2/McpB chemoreceptor | ||
| PA0177 | cheW | −1.9 | CheW coupling protein | ||
| PA4293 | pprA | −2.5 | Sensor kinase PprA | Quorum sensingregulation | [44][48] |
| PA4296 | pprB | −1.6 | Response regulator PprB | ||
| Motility | |||||
| PA1930 | mcpS | −2.1 | Chemoreceptor McpS | Chemotaxis | [45][49] |
| PA2561 | ctpH | −2.4 | Inorganic phosphate (Pi) specific chemoreceptor CtpH | Pi is a major virulence signal | [46][47][50,51] |
| Others | |||||
| PA4299-4306 | Flp-tad-rcp locus | −2.3 to −4.8 | Formation of type IVb pili | Aggregation and biofilm formation | [48][52] |
| PA4236 | katA | −2.1 | Major catalase KatA | Osmoprotection and virulence | [49][53] |
Of note are the large changes that have been observed for the genes involved in histamine metabolism that ranged from a 240- to 2200-fold increase in the presence of histamine [20]. A large number of the upregulated genes were associated with iron uptake, such as those encoding proteins for the synthesis and secretion of the pyoverdin and pyochelin siderophores, iron transport or different ECF sigma factors (
Of note are the large changes that have been observed for the genes involved in histamine metabolism that ranged from a 240- to 2200-fold increase in the presence of histamine [24]. A large number of the upregulated genes were associated with iron uptake, such as those encoding proteins for the synthesis and secretion of the pyoverdin and pyochelin siderophores, iron transport or different ECF sigma factors (
Table 1
). Another group of upregulated genes had regulatory functions, such as the transcriptional regulators ToxR, PtrB, MvaT, VqsM, PsrA and RsaL (
Table 1) that regulate diverse processes, such as the expression of genes encoding the primary toxin endotoxin A [32], quorum sensing proteins [35] or the type III secretion system [37]. Alternatively, several of the downregulated genes also had regulatory functions (
) that regulate diverse processes, such as the expression of genes encoding the primary toxin endotoxin A [36], quorum sensing proteins [39] or the type III secretion system [41]. Alternatively, several of the downregulated genes also had regulatory functions (
Table 1
)
Among the genes that were upregulated in the presence of histamine washinK, encoding a LysR-type transcriptional regulator. In PAO1, thehinKgene was found to be next to thehinDACgenes that were involved in histamine metabolism and transport (
Figure 1). To assess the role of HinK in the histidine-mediated regulation, the authors conducted RNA-seq experiments, comparing the wt with thehinKmutant in the presence of histamine, showing a significantly changed pattern in the gene transcript levels with respect to the experiment comparing the histamine-free and -supplemented wt strain [20]. In the wt strain, the addition of histamine caused an important increase in the transcriptional activity, whereas no changes were observed in thehinKmutant, a phenotype reversed by mutant complementation [20].
). To assess the role of HinK in the histidine-mediated regulation, the authors conducted RNA-seq experiments, comparing the wt with thehinKmutant in the presence of histamine, showing a significantly changed pattern in the gene transcript levels with respect to the experiment comparing the histamine-free and -supplemented wt strain [24]. In the wt strain, the addition of histamine caused an important increase in the transcriptional activity, whereas no changes were observed in thehinKmutant, a phenotype reversed by mutant complementation [24].
a DNA binding- and ligand-binding domain (LBD), and experiments were conducted to identify the signal that binds and activates HinK. Several pieces of evidence indicate that HinK does not recognize histamine directly but instead imidazole-4-acetic acid (ImAA), which corresponds to an intermediate in the metabolic pathway converting histamine into aspartic acid, as described above (
Figure 1B). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays revealed that micromolar concentrations of ImAA caused HinK binding at its target DNA, namelyhinDandhinFpromoters, an observation that was not made using a variety of related compounds, including histamine [20]. The authors reported the three-dimensional structure of the apo HinK protein and ImAA binding studies to site-directed HinK mutants indicate that the ligand binds between both lobes of the LBD in a manner similar to other LysR type transcriptional regulators [20].
B). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays revealed that micromolar concentrations of ImAA caused HinK binding at its target DNA, namelyhinDandhinFpromoters, an observation that was not made using a variety of related compounds, including histamine [24]. The authors reported the three-dimensional structure of the apo HinK protein and ImAA binding studies to site-directed HinK mutants indicate that the ligand binds between both lobes of the LBD in a manner similar to other LysR type transcriptional regulators [24].
They showed that the deletion ofP. aeruginosa hinAsignificantly reduced the transcriptional activity from thehinDpromoter that was found to be controlled by HinK in response to histamine, which supports the notion that HinA is the primary histamine transporter. In close vicinity to thehinAgene is a gene encoding a solute-binding protein, PA0222 (
Figure 1
A), and histamine was found to increase its transcript levels by 400-fold (
Table 1). However, microcalorimetric titrations of purified PA0222 showed that it bound γ-aminobutyrate with nanomolar affinity but failed to recognize histamine [50]. The potential role of PA0222 in histamine transport is thus unclear.
). However, microcalorimetric titrations of purified PA0222 showed that it bound γ-aminobutyrate with nanomolar affinity but failed to recognize histamine [55]. The potential role of PA0222 in histamine transport is thus unclear.
Based on the observation that histamine induces the expression of many virulence-related genes, Wang et al. conducted experiments to elucidate, in more detail, the role of histamine inP. aeruginosavirulence [20]. Using theDrosophila melanogastermodel, the authors showed that histamine treatment increased bacterial virulence, whereas no change in virulence was noted for thehinKmutant, a phenotype that was reversed by complementation withhinK. In accordance with the above data, the deletion ofhinKcaused a significant reduction in virulence as compared to the wt and the complemented mutant strain [20].
Based on the observation that histamine induces the expression of many virulence-related genes, Wang et al. conducted experiments to elucidate, in more detail, the role of histamine inP. aeruginosavirulence [24]. Using theDrosophila melanogastermodel, the authors showed that histamine treatment increased bacterial virulence, whereas no change in virulence was noted for thehinKmutant, a phenotype that was reversed by complementation withhinK. In accordance with the above data, the deletion ofhinKcaused a significant reduction in virulence as compared to the wt and the complemented mutant strain [24].
Experimentation with a number of chemoreceptor mutants revealed that the histamine chemotaxis was not based on a single chemoreceptor, like for many other chemoeffectors studied, but on the concerted action of the TlpQ, PctA and PctC chemoreceptors [19]. Therefore, the combined action of three chemoreceptors with different sensitivities broadened the response range, a finding reminiscent of the action of the CtpL and CtpH chemoreceptors for inorganic phosphate [46][51]. PctA and PctC have previously been shown to bind and mediate chemoattraction to different proteinogenic amino acids and γ-aminobutyrate [52][53][54]. It was thus suggested that histamine recognition by both receptors occurs via the binding of solute-binding proteins [19], an indirect mechanism for the activation of different bacterial sensor proteins that appears to be widespread among bacteria [55].
Experimentation with a number of chemoreceptor mutants revealed that the histamine chemotaxis was not based on a single chemoreceptor, like for many other chemoeffectors studied, but on the concerted action of the TlpQ, PctA and PctC chemoreceptors [23]. Therefore, the combined action of three chemoreceptors with different sensitivities broadened the response range, a finding reminiscent of the action of the CtpL and CtpH chemoreceptors for inorganic phosphate [50,57]. PctA and PctC have previously been shown to bind and mediate chemoattraction to different proteinogenic amino acids and γ-aminobutyrate [59,60,61]. It was thus suggested that histamine recognition by both receptors occurs via the binding of solute-binding proteins [23], an indirect mechanism for the activation of different bacterial sensor proteins that appears to be widespread among bacteria [63].
In contrast to PctA and PctC, the LBD of the TlpQ chemoreceptor bound histamine directly [19]. In addition to histamine, TlpQ also recognized structurally related polyamines, namely putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine, agmatine and ethylenediamine, with a similarly high affinity [19]. As stated above, the magnitude of histamine chemotaxis inP. putidaKT2440 was inferior to that ofP. [56], recognizes histamine with a 40-fold lower affinity [19].
In contrast to PctA and PctC, the LBD of the TlpQ chemoreceptor bound histamine directly [23]. In addition to histamine, TlpQ also recognized structurally related polyamines, namely putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine, agmatine and ethylenediamine, with a similarly high affinity [23]. As stated above, the magnitude of histamine chemotaxis inP. putidaKT2440 was inferior to that ofP. [65], recognizes histamine with a 40-fold lower affinity [23].
Like PctA and PctC, the TlpQ chemoreceptor has a dCache type LBD, and its 3D structure in a complex with histamine has been solved by X-ray crystallography [19] (
Like PctA and PctC, the TlpQ chemoreceptor has a dCache type LBD, and its 3D structure in a complex with histamine has been solved by X-ray crystallography [23] (
Figure 2). The TlpQ-LBD is composed of two structural α/β modules, and histamine was bound at the membrane distal module, like in the very large majority of other characterized dCache domains [52][56][57][58][59]. The molecular detail of histamine recognition by human receptors has recently been deciphered by reporting three dimensional structures of the Histamine H1 receptor [60] and the β3 GABAAreceptor in a complex with histamine [61]
). The TlpQ-LBD is composed of two structural α/β modules, and histamine was bound at the membrane distal module, like in the very large majority of other characterized dCache domains [59,65,66,67,68]. The molecular detail of histamine recognition by human receptors has recently been deciphered by reporting three dimensional structures of the Histamine H1 receptor [69] and the β3 GABAAreceptor in a complex with histamine [70]
The comparison of TlpQ-LBD with the two human receptors thus shows that the proteins involved in histamine sensing in bacteria and humans are entirely different. In the human H1 receptor, histamine is recognized within the membrane by several transmembrane helices, whereas histamine is bound to the extracytosolic part of the β3 GABAAreceptor, where it is recognized by a curved β-sheet. Although the 3D structures of the three histamine receptors are entirely different, there was a certain parallelism between TlpQ and the β3 GABAAreceptor in the molecular detail of ligand recognition that is illustrated in
Figure 3
.
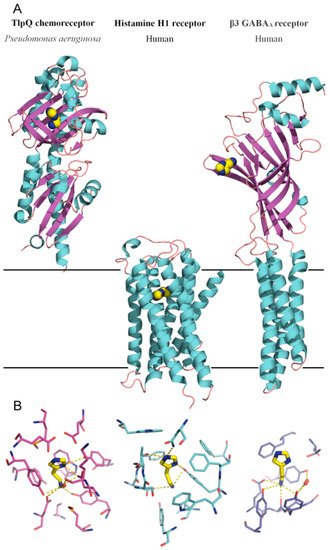
Figure 2.
Bacterial and human histamine receptors. (
A
) Shown is the ligand-binding domain of the TlpQ chemoreceptor from
P. aeruginosa
PAO1 (PDB ID 6FU4), the human histamine H1 receptor (PDB ID 7DFL) and the human β3 GABA
A receptor (PDB ID 7A5V). Bound histamine is shown in stick mode in the lower part of the figure. These structures have been published in [19][60][61]. (
receptor (PDB ID 7A5V). Bound histamine is shown in stick mode in the lower part of the figure. These structures have been published in [23,69,70]. (
B
) Zoom on the histamine binding sites of the receptors shown above.
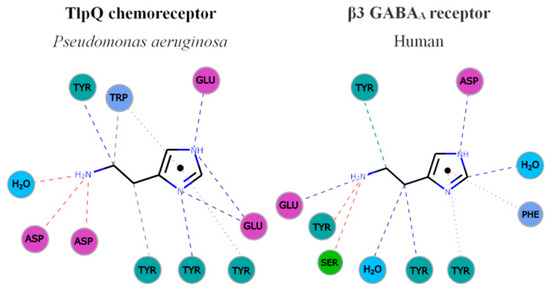
Figure 3. Parallelism in the mode of histamine recognition by P. aeruginosa TlpQ-LBD and the human β3 GABAA receptor. The interaction of histamine within the different binding pocket was automatically generated at the PDBe, using Arpeggio [62][71]. Non-covalent interactions are shown by the following colored dashed lines: red, hydrogen bonds; green, hydrophobic interactions; brown, weak hydrogen bonds; and purple, pi-pi interactions. The thickness of each dash is related to the interaction-distance. Hydrophobic, negatively charged, aromatic and polar residues are colored in blue, magenta, green and cyan, respectively. For clarity, only some representative interactions are shown.
In both cases, the primary and secondary histamine amino groups are coordinated by negatively charged amino acids and a series of tyrosine residues that interact with the linear and cyclic parts of histamine.
On the other hand, the AtoC response regulator is a member of the NtrC-NifA family of transcriptional regulators and is composed of an N-terminal receiver domain, followed by an AAA+_ATPase and DNA-binding domain [63]. SCFAs are important signal molecules in the human gut microbiome. They are produced in the colon following microbial fermentation of dietary fibers, are important energy sources for colonocytes and regulate the assembly and organization of tight junctions [64]. Abnormalities in SCFA levels, either caused by dysbiosis (i.e., alteration of gut microbiota homeostasis) or diet, were suggested to play a role in a number of pathologies, such as type-2 diabetes, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer or allergy [65].
On the other hand, the AtoC response regulator is a member of the NtrC-NifA family of transcriptional regulators and is composed of an N-terminal receiver domain, followed by an AAA+_ATPase and DNA-binding domain [74]. SCFAs are important signal molecules in the human gut microbiome. They are produced in the colon following microbial fermentation of dietary fibers, are important energy sources for colonocytes and regulate the assembly and organization of tight junctions [78]. Abnormalities in SCFA levels, either caused by dysbiosis (i.e., alteration of gut microbiota homeostasis) or diet, were suggested to play a role in a number of pathologies, such as type-2 diabetes, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer or allergy [79].
In addition, AtoSC also contributes to the regulation of flagellar gene expression and was thus shown to modulate motility and chemotaxis [66]. Spermidine and acetoacetate are the effectors of the AtoSC system [67][68]. Multiple pieces of evidence have suggested that AtoSC activity is modulated by Ca2+that may act as a co-signal [69][70]. However, the molecular detail and the corresponding sensor domains of these effectors have so far not been established.
In addition, AtoSC also contributes to the regulation of flagellar gene expression and was thus shown to modulate motility and chemotaxis [81]. Spermidine and acetoacetate are the effectors of the AtoSC system [82,83]. Multiple pieces of evidence have suggested that AtoSC activity is modulated by Ca2+that may act as a co-signal [84,85]. However, the molecular detail and the corresponding sensor domains of these effectors have so far not been established.
Evidence has been presented showing that histamine interferes with AtoSC activity. Histamine was shown to increaseatoCtranscription and to reduce cPHB biosynthesis [69][71]. cPHB biosynthesis requires SCFAs [68], and the interference of histamine with SCFA metabolism and levels may play a regulatory role in the gut. Furthermore, low concentrations of histamine enhanced motility and chemotaxis inE. coli, whereas the opposite effect was noted when histamine was present at higher levels [66].
Evidence has been presented showing that histamine interferes with AtoSC activity. Histamine was shown to increaseatoCtranscription and to reduce cPHB biosynthesis [84,86]. cPHB biosynthesis requires SCFAs [83], and the interference of histamine with SCFA metabolism and levels may play a regulatory role in the gut. Furthermore, low concentrations of histamine enhanced motility and chemotaxis inE. coli, whereas the opposite effect was noted when histamine was present at higher levels [81].
3. Histamine Release by Bacteria and Its Consequences
Apart from the fact that bacteria sense histamine, there is evidence that bacterial-derived histamine has multiple consequences, for example, on host health [64] and food safety [72]. In fact, histamine levels are monitored in a number of different foods as a measure of food freshness [73][74]. This is particularly relevant for seafood products, where bacteria-secreted histamine can provoke food poisoning [72]. The list of microorganisms that secrete histamine in seafood is long and includes Gram-positive and Gram-negative species.
Apart from the fact that bacteria sense histamine, there is evidence that bacterial-derived histamine has multiple consequences, for example, on host health [78] and food safety [87]. In fact, histamine levels are monitored in a number of different foods as a measure of food freshness [88,89]. This is particularly relevant for seafood products, where bacteria-secreted histamine can provoke food poisoning [87]. The list of microorganisms that secrete histamine in seafood is long and includes Gram-positive and Gram-negative species.
The effect of histamine secretion by human intestinal bacteria on its host is a more recent but rapidly expanding field of research. Initial in vitro studies showed that histamine suppressed the chemokine and proinflamatory cytokine secretion in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells [75]. Administration of anotherLactobacillusspecies,L. saerimneri,that is able to secrete approximately 100-fold more histamine as compared toL. rhamnosus, resulted, next to a variety of immune responses, in animal weight loss and signs of deteriorating health [76]. The authors suggested that the amount of histamine secreted by a microbe may be critical in determining the nature of the effect.
The effect of histamine secretion by human intestinal bacteria on its host is a more recent but rapidly expanding field of research. Initial in vitro studies showed that histamine suppressed the chemokine and proinflamatory cytokine secretion in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells [90]. Administration of anotherLactobacillusspecies,L. saerimneri,that is able to secrete approximately 100-fold more histamine as compared toL. rhamnosus, resulted, next to a variety of immune responses, in animal weight loss and signs of deteriorating health [91]. The authors suggested that the amount of histamine secreted by a microbe may be critical in determining the nature of the effect.
Metabolomic studies revealed higher histamine concentrations in the DEC group as compared to healthy children, and altered histamine levels were associated to certain gut microbiota species More recent studies have suggested that bacterial histamine release in the gut does not only cause a local modulation of the host immune system, but can also have immunological consequences at distant mucosal sites, such as in the lung [77].E. coliwas engineered to secrete histamine and administered orally to mice [77]. Gut bacteria of theMorganella morganiiandLactobacillus reuterispecies were found to produce histamine in vivo during the colonization of the mouse intestine, and L-His dietary supplementation increased histamine production by these bacteria. In this study, the authors found that bacteria-derived histamine was associated with increased mice colon motility and fecal output and that treatment with histamine receptor antagonists largely blocked the effect of bacterial histamine on colon motility [78].
Metabolomic studies revealed higher histamine concentrations in the DEC group as compared to healthy children, and altered histamine levels were associated to certain gut microbiota species More recent studies have suggested that bacterial histamine release in the gut does not only cause a local modulation of the host immune system, but can also have immunological consequences at distant mucosal sites, such as in the lung [94].E. coliwas engineered to secrete histamine and administered orally to mice [94]. Gut bacteria of theMorganella morganiiandLactobacillus reuterispecies were found to produce histamine in vivo during the colonization of the mouse intestine, and L-His dietary supplementation increased histamine production by these bacteria. In this study, the authors found that bacteria-derived histamine was associated with increased mice colon motility and fecal output and that treatment with histamine receptor antagonists largely blocked the effect of bacterial histamine on colon motility [95].
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder, and accumulating evidences at both preclinical and clinical levels indicates an involvement of enteric microbiota in its pathogenesis [79]. These analyses revealed that IBS patients presented higher levels of histamine and bacterialhdcgenes [78]. Subsequent studies also showed that supernatants from colonic samples of IBS patients contained increased histamine levels, and expression levels of the histamine receptors H1R and H2R were upregulated in IBS patients [80]. The authors thus hypothesized that a dysbiosis with increased histamine-secreting or HDC-containing bacteria was potentially associated with the development and aggravation of IBS [79].
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder, and accumulating evidences at both preclinical and clinical levels indicates an involvement of enteric microbiota in its pathogenesis [96]. These analyses revealed that IBS patients presented higher levels of histamine and bacterialhdcgenes [95]. Subsequent studies also showed that supernatants from colonic samples of IBS patients contained increased histamine levels, and expression levels of the histamine receptors H1R and H2R were upregulated in IBS patients [97]. The authors thus hypothesized that a dysbiosis with increased histamine-secreting or HDC-containing bacteria was potentially associated with the development and aggravation of IBS [96].
4. Outlook
The knowledge available on the role of histamine as a bacterial signal molecule is summarized in Figure 4.
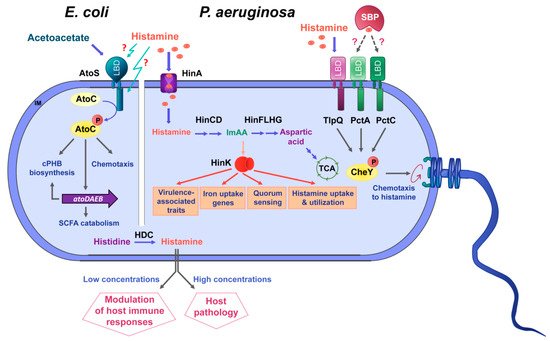
Figure 4. Summary of data available on histamine sensing and secretion by bacteria. On the left, histamine sensing by the TCS AtoSC in E. coli. On the right, histamine assimilation and chemotaxis in P. aeruginosa. Lower part: Many bacteria synthesize histamine by a decarboxylation of histidine using the histidine decarboxylase (HDC) and secrete histamine. Blue arrows: metabolic pathways; orange arrows: gene expression regulation; grey arrows: activation of biological processes; dotted lines: hypothetical interaction; LBD: ligand-binding domain; SBP: solute-binding protein; ImAA: imidazole-4-acetic acid; HinA: permease for the histamine uptake; HinCD: enzymes for the conversion of histamine to ImAA; HinFLHG: enzymes for the conversion of ImAA to aspartic acid; HinK: LysR-family response regulator; IM: inner membrane.
The elucidation of the role of histamine as a signal molecule for inter-domain communication is an emerging field of research that requires future efforts. So far, the information on histamine sensing is restricted toP. aeruginosa, P. putidaandE. coli, and studies need to be conducted to determine to which extent other species show similar responses. For key signal molecules that are of metabolic value, like histamine, it has to be determined whether the primary motivation of chemotaxis is related to metabolism or the capacity to infect hosts. In this context, important gaps in knowledge to be closed are the determination of environmental factors that may trigger histamine release and to determine the capacity of histamine release for strains typically found in the gut microbiome.
