Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Eunjoo Kim and Version 2 by Amina Yu.
Falls account for a high proportion of the safety accidents experienced by hospitalized children. This entry aims to analyze the contents and effects of fall prevention programs for pediatric inpatients to develop more adaptable fall prevention programs.
- fall
- meta-analysis
- pediatric
- prevention
1. Introduction
The safety management of patients has been considered an important factor for enhancing the quality of health care worldwide. Countries around the world are promoting patient safety by implementing healthcare institution accreditation systems, and South Korea has also launched a more systematic patient safety management effort by enacting the Patient Safety Act in 2016. However, according to a 2016 patient safety incident report, the total number of fall incidents was 5562, of which 254 involved children [1]. In particular, falls accounted for 24% of pediatric safety incidents [1]. Children are highly curious and impulsive, while their physical functions and cognitive growth are still under development; hence, they have poor judgment and lack the ability to protect themselves during dangerous situations. As a result, children have a high risk of facing such accidents and have a particularly high risk of falling due to the stage of development they are in and their ambulatory ability [2].
A study that analyzed falls among pediatric inpatients reported a higher rate of falls among children aged one to three years and observed that most falls occurred from the inpatient beds and in the presence of the caregiver [3]. A study on 26 child hospitals in the US reported that 0.4–3.8 cases of pediatric fall incidents occur per 1000 days in the hospital [3]. The rate in Korea is much higher, at 0.63–2.45 cases per 1000 pediatric inpatients, highlighting the gravity of the risk of falling among pediatric inpatients in Korea [4].
Aggressive management to prevent falls among pediatric inpatients is crucial, as falls induce injuries such as abrasion (12.5%), fracture (12.5%), and hematoma (37.5%), and even lead to disability in some cases in children [5]. To this end, the importance of the appropriate evaluation, safe environment, and fall prevention education is emphasized. Previous studies have further suggested that the contents of fall prevention education should include learning about various preventive behaviors and methods and that the education programs should target not only high-risk pediatric patients but also healthcare providers and caregivers of pediatric inpatients to promote attention and interest [6]. In particular, pediatric inpatients were found to be involved in falling incidents even when their caregiver is present, which suggests that inpatient education alone cannot effectively reduce falls, further highlighting the importance of fall prevention education for caregivers such that caregivers can stay around to protect children at all times [2].
Studies that have implemented fall prevention programs have utilized audiovisual materials such as posters and videos, bulletins, and one-to-one education for children’s caregivers using PowerPoint presentations and videos. Park [2] developed and delivered a case-specific fall prevention education program one-to-one and observed significant improvements in fall-related knowledge, attitude, and fall prevention behaviors among caregivers of pediatric inpatients. Park and Ju [4] delivered fall prevention education using a leaflet and reported that fall-related knowledge and fall prevention behaviors significantly increased among the caregivers of pediatric inpatients. However, both studies delivered the educational content for only two to three sessions and for less than 15 min per session, thus lacked the evidence to ascertain whether the developed programs can effectively prevent falls in long-term pediatric inpatients. Further, fall prevention programs comprise an array of components, including views on falls as safety issues, age-specific characteristics, and factors that hinder fall prevention, which undermine their efficiency. As shown here, despite the high perceived need for fall prevention for pediatric inpatients, existing fall prevention education programs are designed only as short-term programs, calling for an evidence-based framework to identify effective fall prevention programs.
Promoting quick recovery and maintaining good quality healthcare by preventing secondary impairments and injuries is important. This can be ensured only by preventing falls among pediatric inpatients in the first place, which requires evidence-based and rational fall prevention interventions that ensure increased effectiveness. A comprehensive review of studies on fall prevention programs for pediatric inpatients needs to be conducted to identify the features and factors related to fall prevention programs and, consequently, develop more robust programs. Thus, this study aimed to conduct a literature review of existing studies on fall prevention programs for pediatric inpatients, based on which we attempted to propose a future direction for the development of effective fall prevention programs. The eventual development of such programs among pediatric inpatients would contribute to improving nursing practice.
2. Results
2.1. Features of the Studies Selected for Analysis
The characteristics of the included studies are described in Table 1. The studies selected for analysis were published between 2007 and 2017. Except for a study published in Korea and another in Singapore, all studies were published in the United States. Five studies were quality improvement (QI) or project studies, two were experimental studies, and two were retrospective chart review studies. Regarding the experimental group and control group, two studies were conducted on caregivers, while the remaining studies were conducted on pediatric inpatients in the pediatric ward or the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit to measure the number of fall events, fall rate, and fall risk.
Table 1. General characteristics of the selected studies.
General characteristics of the selected studies.
| Author (Year) | Nation | Design | Setting | Experimental (n or Period) | Control (n or Period) | Program | Intervention Period | Result | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooper and Nolt (2007) [7] | Cooper and Nolt (2007) [9] | USA | Project-a prospective descriptive chart review | General pediatric unit 0–21 years | Not described | Not described | Pediatric Fall Prevention Program for inpatients or outpatients | January–June 2006 | Not described in detail | |||
| 2010–2014 | ||||||||||||
| (1) Decreased fall rate 8.84/1000 patient days, 1.79/1000 patient days (χ | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| = 17.23, | ||||||||||||
| p | = 0.0001) | (2) Decreased falls with caregivers (χ | 2 | = 6.25, | p | = 0.012) | ||||||
| Park and Ju (2017) [4] | Korea | Non-equivalent control group, non-synchronized design | Pediatric ward | 31 (caregivers) | 31 (caregivers) | Pediatric Fall Prevention Education: A leaflet and picture book | August–October 2013 | (1) There was a difference in fall-related knowledge between the experimental group and control group (t = −3.05, | p | = 0.048) (2) There was no difference in the preventive behaviors for patients at risk of falls between the experimental group and control group (t = −1.91, | p | = 0.065) |
1 Pediatric intensive care unit. 2 Cardiac incentive care unit.
2.2. Specific Contents of the Pediatric Inpatient Fall Prevention Programs in the Selected Studies
Table 2 provides details of the fall prevention programs investigated in the nine selected studies. Four out of nine studies divided the patients into a high-risk fall group and a low-or medium-risk fall group to apply the corresponding protocol. Using the high-risk sign/sticker was a common protocol guideline in all studies concerning the high-risk fall group. Cooper and Nolt, Hill-Rodriguez et al., Kim et al., Neiman et al., Rouse et al., and Stubbs and Sikes [7][8][9][12][14][15][9,10,11,14,16,17] recommended the signs to be shown on the bed and outside the ward, while Lee et al. [11][13] recommended that patients wear a green tag on the wrist or ankle. The next guideline was close observation. Neiman et al., and Murray et al. [9][13][11,15] stressed the importance of hourly rounding and one-to-one observation, while Cooper and Nolt, Hill-Rodriguez et al., and Rouse et al. [7][8][12][9,10,14] suggested placing patients close to the registered nurse (RN) station and leaving the room door open. The next important guideline was to assist with patients’ ambulation. The guidelines suggested frequently checking and safely supporting the patients. The general protocol applied to the low-and moderate-risk group included educating patients and their families, using low beds, always leaving the bed rails up with locked breaks, and never leaving the child alone.
Table 2. The detailed contents of the inpatient fall prevention programs.
The detailed contents of the inpatient fall prevention programs.
| Author (Year) | Program | High Risk Protocol | Low Risk Protocol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooper and Nolt (2007) [7] | Cooper and Nolt (2007) [9] | Pediatric Fall Prevention Program for inpatients |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hill-Rodriguez et al. (2009) [8] | Hill-Rodriguez et al. (2009) [10] | USA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hill-Rodriguez et al. (2009) [ | Matched case-control design | 8] | Hill-Rodriguez et al. (2009) [10] | Patient Falls Safety Protocol |
| In-patient units, PICU | 1 | , CICU | 2 | 153 |
| 153 | Humpty Dumpty Procedure: Low/High program |
| 2005–2006 |
| Fall events: Odds ratio = 1.87; confidence interval = 1.01, 3.53 ( | p | = 0.03) | ||||||||
|
| Neiman et al. (2011) [9] | Neiman et al. (2011) [11] | USA | Retrospective case-control study | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neiman et al. (2011) [9] | Neiman et al. (2011) [11] | I’m SAFE fall Prevention Program |
| Inpatient encounter | Low-risk intervention |
| 59 | 177 | I’M SAFE fall risk tool/prevention/evaluation |
| January 2004–September 2005 |
| Decreased fall rate = 0.67/1000 patient days >0.51/1000 ( | p | = 0.015) | ||||||||||||
| Lyren et al. (2013) [10] | Lyren et al. (2013) [12] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lyren et al. (2011) | USA | QI project | Children’s hospitals | [10 | 45 | 127 | Ohio Children’s Hospital Association | January 2010–October 2012 | Decreased severe safety event (70/127->18/45) | ||||||||||||||||||
| ] | Lyren et al. (2011) [12] | Collaborative Organizational Framework-High Reliability Implementation | The error prevention task force The leadership methods task force The cause analysis task force The lessons learned task-communication, risk management All organizations have developed mechanisms to routinely share safety stories The safety governance task forces |
Lee et al. (2013) [11] | Lee et al. (2013) [13] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lee et al. (2013) | Singapore | [11 | Experimental study | ] | Lee et al. (2013) [13] | The JBI Practical Application of Clinical Evidence System (PACES) |
| Pediatric wards | 30 (caregivers) | None |
|
| The JBI Practical Application of Clinical Evidence System (PACES) and Getting Research into Practice (GRiP) Programmes |
| March–June 2011 |
| (1) The fall risk preventative interventions and high-risk fall event did not differ between the experimental and control groups ( | p | = 0.110) (2) The behavior of patients at risk of fall did not differ between the experimental and control group ( | p | = 0.039) | ||||||
| Rouse et al. (2014) [12] | Rouse et al. (2014) [14] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rouse et al. (2014) | USA | [12 | QI project | Pediatric unit | Not described | Not described | Patient Falls Safety protocol | June 2011 | Not described | ||||||||||||||||||
| ] | Rouse et al. (2014) [14] | Patient Fall Safety Protocol | Similar to Cooper and Nolt’s (2007) protocol | Murray et al. (2016) [13] | Murray et al. (2016) [15] | USA | QI project | Pediatric ward/PICU | 1 | January–June 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| Murray et al. (2016) [ | January–June 2015 | 13] | Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) | Murray et al. (2016) [15 | January–June 2016 | Decreased fall rate 4.5% per 1000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ] | Fall Risk Assessment, prevention program | Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA)-6-bed ward, PICU, 0–18 months, Fall Risk Assessment, Prevention program/HDFS (administered once a shift/family) and patient education, sign, orientation to the unit, environment safety, patient rounding hourly (high risk) | Stubbs and Sikes (2017) [14] | Stubbs and Sikes (2017) [16] | USA | QI project | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stubbs and Sikes (2017) [14] | Inpatient pediatric neuro rehabilitation center | 2014 | 2009 | Stubbs and Sikes (2017) [16] | PDSA method: interdisciplinary intervention—red light, green light | Red Green light Interdisciplinary care involving physical therapist, nurse manager, educator Family training session, red-green light Staff education/nursing staff education | PDSA Method: Interdisciplinary intervention-green light, green light | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Park and Ju (2017) [4] | Pediatric fall prevention education | Pediatric fall prevention education: Leaflet and picture book |
1 PFE: Patient and Family Engagement.
2.3. Meta-Analysis Results
Figure 2a presents a forest plot of the seven studies. The studies showed very low homogeneity (I2 = 70.3) and showed an odds ratio of 0.95 (95% Cl 0.550~1.640); hence, it was not significant at a z-value of −0.184 (p = 0.854). Figure 2b presents the forest plot of only four studies in which the number or the rate of inpatient falls is the outcome. The I2 of these four studies was 32.13, showing a random effect, while the odds ratio of the fall prevention programs was 0.561 (95% Cl 0.333~0.945, z-value = −2.173, p = 0.030).
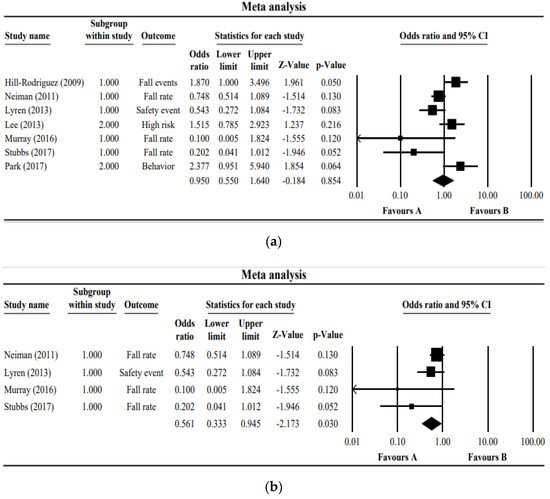

Figure 2. (a) Forest plot of the studies included in the meta-analysis. (b) Forest plot of the studies measuring the number or the rate of inpatient falls as an outcome. The boxes in the graphs show the effect estimates from the single studies, while the diamond symbol shows the pooled result.
In other words, the fall-prevention programs for inpatients have been effective in reducing the fall rate. It was confirmed that there was no publication bias because the corrected effect size and the original effect size were the same by adding a study to be symmetrical through funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s trim and fill method (Figure 3).
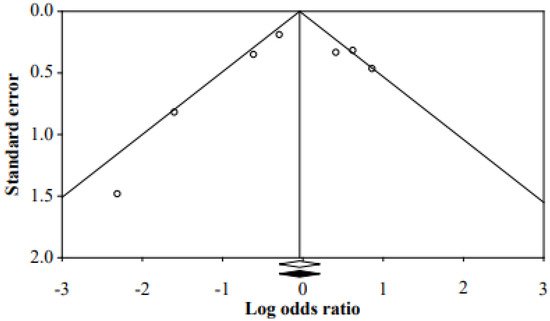

Figure 3. Funnel plot of the studies.
