Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Ken Yamaguchi and Version 2 by Ron Wang.
Ovarian clear cell carcinoma (CCC) exhibits unique characteristics, including slow growth, glycogen accumulation in the cytoplasm, and poor prognosis for stress resistance. Several molecular targeting agents have failed to treat ovarian CCC. Recent reports have identified metabolic alterations through HNF1B, which is highly expressed in ovarian CCC. The Warburg effect, GSH synthesis, and mitochondrial regulation occur in CCC. The metabolic behaviors of ovarian CCC resemble the evolution of life to survive in stressful environments. Understanding the fundamental biology of ovarian CCC might help in the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
- ovarian clear cell carcinoma
- metabolism
- mitochondrion
- Warburg effect
- glutathione synthesis
1. Introduction
Ovarian cancer is the worst gynecologic malignancy and includes heterogeneous histological and biomolecular features [1][2][3][1,2,3]. Clear cell carcinoma (CCC) of the ovary is the second most common ovarian cancer, after high-grade serous carcinoma in Japan, and exhibits unique characteristics, including endometriosis, slow growth, association with thromboembolism, glycogen accumulation in the cytoplasm, and poor prognosis in advanced cases due to chemoresistance [4][5][6][7][8][9][10][4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Recently, the molecular biological features of CCC have been reported using next-generation sequencing technology. Mutations in AT-rich interacting domain-containing protein 1A (ARID1A) and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit alpha (PIK3CA) genes have been found in approximately half of the cases [11][12][13][11,12,13]. There are single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs11651755) in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1-beta (HNF1B) gene, which is highly expressed in ovarian CCC [14][15][14,15]. In addition, a detailed mutation status during each process of endometriosis-related carcinogenesis has been reported [11][12][13][11,12,13]. Interestingly, there are similar gene mutations in the orthotopic endometrium and ovarian endometriosis [16][17][16,17], and the possibility of carcinogenesis due to two hits in the ovary, as the same mutation has been found in eutopic endometrium, endometriotic cyst, and ovarian CCC [16]. Thus, the development of CCC has rapidly been understood from genetic analysis; however, the reasons for CCC being more frequent in endometriosis-related ovarian cancer and its unique characteristics are not clear. This review describes the roles of the carcinogenic environment leading to the development of CCC in endometriotic cysts and highlights the importance of metabolic regulation in sculpting the unique biology of ovarian CCC. Regulation of metabolism contributes to energy homeostasis from the onset of life. The tumor microenvironment can be considered a battlefield between cancer and host defense, competing for energy supply and metabolism [18]. Because mitochondria have been fundamental in evolution to produce energy, cancer cells utilize mitochondria for survival. In this review, we hypothesize that the evolution of ovarian CCC is a reason for the metabolic alterations that occur in ovarian CCC.
2. Endometriotic Cyst as a Carcinogenic Environment for Ovarian Cancer
Endometriosis is one of the most common gynecological disorders, affecting approximately 15% of women in their reproductive years [19]. Although endometriosis is a benign condition dependent on estrogen, endometriosis is a risk factor for ovarian cancer [20]. Although 1.3% of women in the general female population will develop ovarian cancer in their lifetime, the lifetime risk of ovarian cancer among women with endometriosis is 1.8% [21]. Large epidemiological studies showed an increased risk for ovarian cancer in patients who were hospitalized for endometriosis (SIR 1.9, 95% CI 1.3–2.8, and SIR 1.43, 95% CI 1.49–1.71, respectively) [20]. Genomic sequencing was used to identify cancer-associated mutations in endometriosis. Known somatic cancer-driver mutations in ARID1A, PIK3CA, and KRAS have been identified in deep endometriosis, indicating that endometriosis is a neoplastic disease [22]. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs11651755) in HNF1B were found to be associated with endometriosis and modified the risk of ovarian cancer, as well as endometriosis [14][15][14,15]. These findings indicate that endometriosis is a precursor and a neoplastic disease.3. Two Hypothetical Theories for Carcinogenesis Process among Endometriosis-Related Ovarian Cancer
Using expression microarrays of ovarian cancer, we identified a gene set composed of 320 genes which are specific to ovarian CCC and named them ovarian CCC signatures [23][32]. These genes include many genes related to HNF1B signaling. We assessed whether the signature is involved in the stressful environment of carcinogenesis in endometriotic cysts. When cells were cultured with stressful factors, such as the contents of endometriotic cysts and iron, the ovarian CCC signature was upregulated [23][32], suggesting that genes specific for ovarian CCC are induced under a stressful carcinogenic environment. Recently, ferroptosis, which is a cell death caused by lipid ROS in an iron-dependent manner, was identified and is considered to be different from apoptosis and necrosis. Ferroptosis is induced by erastin, through the reduction of glutathione levels by directly inhibiting the cystine/glutamate antiporter system Xc−activity in ectopic endometrial stromal cells, whereas the influence of erastin on normal endometrial stromal cells was only slight [24][35]. Our previous report identified that immunohistochemistry using 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), a marker of oxidative stress-induced DNA damage, was higher in CCC than in other histological subtypes [25][24], suggesting that ovarian CCC can grow in oxidative stress environments. We also evaluated the lipid ROS damage marker to evaluate the ferroptosis status. Our preliminary data showed that the lipid damage marker tended to be stronger in endometrioid carcinoma than in CCC (data not yet published). These findings indicate that CCC exhibits different responses against oxidative stress from endometrioid carcinoma, although both subtypes develop in an oxidative stress environment, suggesting that ferroptosis is suppressed in CCC. Zou et al. reported that inhibition of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) exhibits the highest selectivity and potency in killing renal and ovarian CCC cells, suggesting an intrinsic vulnerability to ferroptosis [26][36]. In their study, they identified that cells with clear cell morphology exhibit GPX4 dependency. These findings indicate that CCC requires distinct mechanisms to survive ferroptosis compared to other histological subtypes.4. Unique Characteristics of Ovarian CCC Induced in Carcinogenic Environments
The third question is why CCC possesses unique characteristics, including glycogen accumulation in the cytoplasm, slow growth, and chemoresistance. The genomic alterations in endometriosis-related ovarian cancer are distinct from those induced by free iron. Free iron frequently induces p16 gene mutations in a rat renal carcinogenesis model [27][28][29][38,39,40], whereas approximately half of ovarian CCC cases possess ARID1A and PIK3CA mutations [11][12][13][11,12,13]. These findings suggest that gene mutations in iron-rich environments are not the reason for the initiation of carcinogenesis in endometriotic cysts, although iron-induced oxidative stress is an environment that affects carcinogenesis. The ovarian CCC signature includes many genes related to oxidative stress, glycogen (glucose metabolism), coagulation, and HNF1B signaling [23][32]. Oxidative stress, glucose metabolism, and coagulation are consistent with the characteristics of ovarian CCC, indicating that the ovarian CCC signature reflects the unique biology of ovarian CCC. In addition, HNF1B signaling, which forms a network in the ovarian CCC signature, may be involved in ovarian CCC properties. HNF1B expression is associated with physiopathological cytoplasmic glycogen accumulation in ovarian CCC, endometrial CCC, and non-neoplastic endometrium in the mid-to-late secretory phase of the menstrual cycle and gestation [30][41]. A bioinformatics assessment also identified an association between HNF1B, glycogen accumulation, and thrombosis [23][31][32,42]. As shown in the previous section, the stressful carcinogenic environment in endometriotic cysts may induce the unique biology of ovarian CCC. These results suggest that HNF1B is a key factor in regulating the features of ovarian CCC; we will describe the role of HNF1B in a later section.5. Genomic and Epigenetic Alterations in Ovarian CCC
How is the expression of the ovarian CCC signature regulated? A comprehensive DNA methylation analysis showed that CCC had a profile distinct from that of other histological subtypes [14][32][14,43]. This profile involved many genes involved in HNF1 transcription. Both expression and DNA methylation analyses revealed that the HNF1B signal is activated through decreased methylation in ovarian CCC. In contrast, ERa signaling is activated in endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary. In our previous report, whole exome sequencing using ovarian CCC revealed genomic abnormalities in many signals, as well as genes belonging to the HNF1B signal in ovarian CCC [33][44]. Mutations and amplification of PIK3CA were found to occur in 54% and 26% of cases, respectively, and mutations and amplification of KRAS were identified in 10% and 18% of ovarian CCC cases, respectively [33][44]. Genomic abnormalities in KRAS-PI3K signaling were identified in 82% of ovarian CCC cases; furthermore, 79% of CCC cases show copy number alterations in MYC-RB signaling, including MYC amplification and RB1 deletion in 81% and 31% of CCC cases, respectively [33][44]. The TP53 gene was deleted, and MDM2 and MDM4 were amplified in ovarian CCC. ARID1A mutations were identified in 62% of cases, and SMARCA2 and SMARCA4 were deleted in 21% and 41% of CCC cases, respectively [33][44]; moreover, genes belonging to the SWI/SNF complex exhibited genomic abnormalities in 85% of the CCC cases. These findings suggest that the activation of KRAS-PI3K signaling, MYC-RB signaling, and the suppression of the TP53 network and the SWI/SNF complex are associated with ovarian CCC [33][44]. Other studies have also identified similar frequent genomic alterations in ovarian CCC. In total, 40–62% and 33–51% of CCC cases show ARID1A and PIK3CA mutations [34][35][45,46]. KRAS mutations are identified in 9–17% of cases, and TP53 mutations are observed in 5–15% of ovarian CCC cases [34][35][36][37][45,46,47,48]. The frequency of single-nucleotide variants was significantly lower in ovarian CCC than in high-grade serous carcinoma, whereas the ratio of whole-arm copy number variants (CNVs) among all CNVs in CCC was significantly higher than that in high-grade serous carcinoma [38][49]. Chromosome 20q13.2, including the ZNF217 (Zinc finger protein 217) locus, is frequently amplified in ~36% of CCC cases [39][50]. Amplifications of the MET (chr7q31) and AKT2 (chr19q13.2) oncogenes have been identified in 31% and 24% of ovarian CCC, respectively, and deletions of the CDKN2A/2B (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A/2B) tumor suppressor genes have been detected in 17% of cases [39][40][41][50,51,52]. We confirmed the protein levels of activated signals in ovarian CCC. HNF1B is highly expressed, and ERa is poorly expressed in ovarian CCC [42][43][30,31]. The expression of pAKT, which reflects PI3K signaling, is high, and pMAPK, which reflects KRAS signaling, is also highly expressed, similar to the genomic characteristics. Based on the immunohistochemistry of nine subunits belonging to the SWI/SNF complex, 61% of the cases exhibited the loss of at least one SWI/SNF complex subunit; thus, genomic and epigenetic abnormalities occur in ovarian CCC, which differs from the other histological types.
6. Regulation of the Unique Characteristics and Mitochondrial Metabolism by HNF1B in Ovarian CCC
From the distinct gene expression profile of ovarian CCC compared to other histologic subtypes [23][38][32,49], HNF1B is the most abundantly upregulated transcription factor in CCC [23][32] and in 40% of endometriotic cysts without malignancy [44][53]. The OCCC signature contained many genes related to oxidative stress, glucose metabolism, and HNF1B transcript signaling, as described above [23][32]. HNF1B mutations cause maturity-onset diabetes in the young type five [45][54]; therefore, we next considered the influence of HNF1B on metabolism in CCC.
HNF1B induces glucose uptake into ovarian CCC cell lines through glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and activates glycolysis flux and lactate secretion [46][55]. Comprehensive metabolome analysis using the HNF1B-suppressed CCC cell line revealed that HNF1B increased lactic acid levels and decreased citric acid levels, indicating that anaerobic metabolism is enhanced and the TCA cycle is decreased [47][56]. This phenomenon commonly occurs in cancer cells and is called the Warburg effect. The Warburg effect, first reported in 1956, refers to the enhanced anaerobic metabolism in cancer cells, even under aerobic conditions [48][57]; however, the reason for the Warburg effect in cancer cells remains controversial.
HNF1B also contributes to glutathione synthesis [39][50]. An HNF1B-suppressed CCC cell line showed increased ROS and higher sensitivity to cisplatin compared to an HNF1B-retained CCC cell line [47][56]. This regulation was induced by glutathione synthesis through the cystine transporter SLC3A1, regulated by HNF1B [47][56]. HNF1B also regulates glutathione levels in renal cell carcinoma [49][58]. ARID1A deficiency, which is identified in approximately half of ovarian CCC cases, suppresses glutathione synthesis. ARID1A-deficient cancer cells are specifically vulnerable to inhibitors of the antioxidant glutathione metabolic pathway and the glutamate–cysteine ligase synthetase catalytic subunit, a rate-limiting enzyme for glutathione synthesis [50][59]. These results imply that antioxidant glutathione synthesis is regulated by HNF1B and ARID1A deficiency.
HNF1B suppresses cell proliferation [51][60] and represses cyclin D1 through direct suppression of SMAD6 expression, which is repressed by CDKN2A as an HNF1B-interacting protein [51][60]. HNF1B induces aberrant retention of the G2 checkpoint, indicating chemoresistance of ovarian CCC [52][61]. These functions are compatible with the clinical behavior of the slow growth of ovarian CCC.
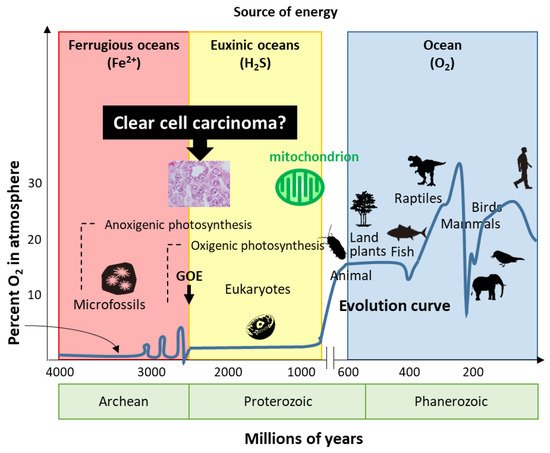
7. Hypothesis—Evolution or Reversion of Mitochondrial Metabolism in Ovarian CCC
Life has evolved for energy homeostasis. The earth was formed ~4.6 billion years ago, and is defined by four eons, including the Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic eons [53][68]. The Hadean eon, named after Hades, was inhospitable because of the excessively hot and anoxic conditions. Life began 3.8 billion years ago in the Archean eon [53][68]. In the Archean eon, which was filled with warm and ferruginous (anoxic and Fe2+ dominated) oceans, other than possibly a few “whiffs”, atmospheric O2 was essentially nil until the great oxidation event (GOE) 2.3 billion years ago (Figure 1). The Proterozoic eon began 2.5 billion years ago; atmospheric oxygen increased several times to ~2%, while the oceans remained essentially anoxic in the GOE. In the Proterozoic eon, eukaryotes first appeared 1.5 billion years ago in euxinic oceans and developed until O2 production by oxygenic cyanobacteria and plants ~600 million years ago. Although oxygen production increased tremendously by the combined activity of cyanobacteria and plants, the oxygen was immediately reduced by the large amounts of H2S and Fe2+; subsequently, the oceans were oxidized, atmospheric oxygen increased to the present values, and led to an end to H2S as an energy source. In the Phanerozoic eon, the earth is supported by solar energy and an abundance of atmospheric oxygen. Mitochondria have evolved to give organisms the energy to exploit new, more complex morphologies interacting in increasingly complex ecosystems. Eukaryotic organisms with nuclei acquire mitochondria to use oxygen to efficiently produce energy; however, the abundance of oxygen poses a new threat to life. Mitochondria simultaneously emit oxidative stress which animals are forced to deal with. H2S-dependent animals either became extinct, retreated to isolated sulfide niches, or adapted. Mass extinctions were often associated with a fall in ambient O2 and an increase in H2S, perhaps providing a biological filter for descendants that retained some degree of tolerance to hypoxia and sulfide.
Figure 1. Evolution of life. Based on energy production, ovarian clear cell carcinoma seems to show evolution or reversion because of traditional energy metabolism. GOE: great oxidation event.
