Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Sazan Rasul and Version 2 by Dean Liu.
The [177Lu]Lu-PSMA radioligand therapy (PSMA-RLT) has emerged as a successful treatment option in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
- PSMA-RLT
- 177Lu-PSMA
- PSA
- mCRPC
- prostate cancer
1. Introduction
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers and one of the leading oncologic causes of death in men in western countries. In these patients, particularly in those with aggressive, metastatic or castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), the levels of prostate-specific membrane antigen, also called glutamate carboxypeptidase type II and abbreviated as PSMA, are elevated up to 1000 times the normal value and are inversely correlated with the levels of androgens [1]. These receptors are a highly potent target in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with prostate tumors. Therefore, radionuclides targeting these peptides, such as [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 ligand positron emission tomography (68Ga-PSMA PET), which is widely applied as a non-invasive molecular method for imaging prostate cancer, and [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 radio-ligand therapy (PSMA-RLT), which has emerged as a valuable treatment in patients with mCRPC, are currently available. Although this novel therapy has not yet been approved for clinical use, it has been successfully administered to patients with mCRPC, based on the results of numerous studies [2][3][4][5][2,3,4,5]. Despite encouraging favorable outcomes of these trials on the efficacy and safety of PSMA-RLT [2][6][2,6], this therapy is presently used in mCRPC patients only as a last therapy option when other available standard medical procedures have failed to show clinical improvement. The therapeutic protocol in many centers, however, is quite heterogenous with treatments differing between two to six cycles of 3.7–9.3 GBq PSMA-RLT every 6 to 8 weeks [7]. Most recently, the TheraP study, a multicenter, unblinded, randomized phase 2 trial involving 11 centers in Australia, demonstrated a more frequent PSA response in mCRPC men treated with PSMA-RLT than in patients receiving cabazitaxel at the same stage of the disease. In addition, the results of this study reported fewer serious adverse events in men treated with PSMA-RLT than with cabazitaxel [8].
2. Response Rate and Clinical Clinical Effects of SEffects of Second PSMA-RLT Course
TIn Table 2, the laboratory parameters of the entire studied mCRPC patients before and 1 month after the third last cycle of the second course of PSMA-RLT applied every 4 weeks have been compared. The PSA levels of the treated patients decreased significantly after three cycles of PSMA-RLT compared with baseline, median PSA 40.8 (range 0.87–1358 µg/L) vs. 20.2 (range 0.6–1926 µg/L), p = 0.002. Overall, 26 out of 43 (60.5%) patients demonstrated any decrease in PSA levels, 18 out of 43 (42%) had a PSA decline of ≥50%, and 8 of 43 (19%) patients showed a PSA decrease of ≥80%. The percentage of the PSA decline after both treatment courses of highly standardized PSMA-RLT, each three cycles with a 4-week interval, in all patients studied are depicted in Figure 1.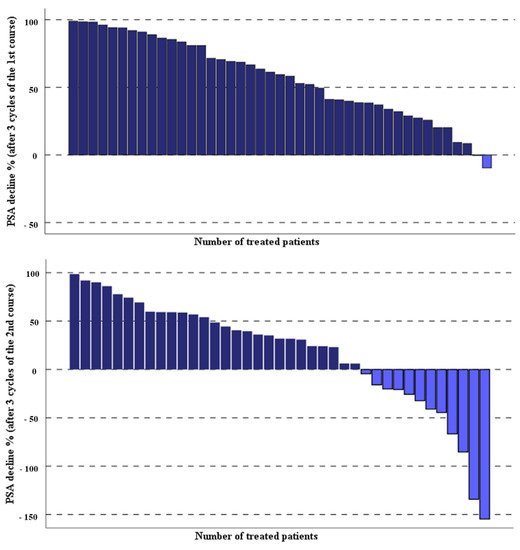
Figure 1. Percentage of PSA change in the studied patients after two courses of the highly standardized PSMA-RLT, each three cycles with 4-week interval.
Table 12. Comparison of laboratory parameters of the studied mCRPC patients before and after the second course of three cycles of PSMA-RLT every 4 weeks.
| Parameters | Before Therapy | After Therapy | q -Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| * PSA µg/L | 40.8 (0.87–1358) | 20.2 (0.60–1962) | 0.002 |
| Hemoglobin g/dL (mean ± SD) | 11.5 ± 1.7 | 11 ± 1.6 | 0.006 |
| Thrombocyte g/L (mean ± SD) | 208 ± 63 | 185 ± 63 | 0.002 |
| * Leucocyte g/L | 5.4 (1.17–14.3) | 4.8 (2.1–14.1) | n.s. |
| * Creatinine mg/dL | 0.96 (0.54–2.24) | 0.94 (0.61–2.6) | n.s. |
| * Alkaline phosphatase U/L | 78 (42–995) | 84 (47–1345) | n.s. |
| * LDH U/L | 205 (96–278) | 194 (86–551) | n.s. |
PSA: prostate-specific antigen; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; n.s.: not significant; (*) data not normally distributed, presented in median and range and log10 transferred for analysis.
Moreover, levels of hemoglobin (Hb) (11.5 ± 1.7 g/dL vs. 11 ± 1.6 g/dL, p = 0.006) and platelets (208 ± 63 g/L vs. 185 ± 63 g/L, p = 0.002) one month after the third cycle were significantly lower compared to the baseline (Table 12). However, only two cases of grade 3 anemia and one case of grade 3 thrombocytopenia were observed among all the treated patients (Table 23). In addition, no statistically significant changes in the levels of leukocyte, creatinine, alkaline phosphatase, and lactate dehydrogenase were observed when we compared their basal values with those one month after treatment with three cycles of PSMA-RLT (Table 12). No patients with severe gastrointestinal adverse events, as well as no patients with acute parotitis and myelodysplastic syndrome, were reported during the second PSMA-RLT course.
Table 23.
Evaluation of treatment toxicities based on CTCAE version 4.0.
| Parameters | Before Therapy | After Therapy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicity (n) | Toxicity (n) | |||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | |
| Hemoglobin g/dL | 18 | 7 | 0 | 15 | 9 | 2 |
| Thrombocyte g/L | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 1 |
| Leucocyte g/L | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Creatinine mg/dL | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
(n): number of reported cases.
(References would be added automatically after the entry is online)
