Genetically altered stem or progenitor cells feature gross chromosomal abnormalities, inducing modified ability of self-renewal and abnormal hematopoiesis. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) regulate cell cycle progression, transcription, DNA repair and are aberrantly expressed in hematopoietic malignancies. Incorporation of CDK inhibitors (CDKIs) into the existing therapeutic regimens therefore constitutes a promising strategy. However, the complex molecular heterogeneity and different clinical presentation is challenging for selecting the right target and defining the ideal combination to mediate long-term disease control. Preclinical and early clinical data suggest that specific CDKIs have activity in selected patients, dependent on the existing rearrangements and mutations, potentially acting as biomarkers. Indeed, CDK6, expressed in hematopoietic cells, is a direct target of MLL fusion proteins often observed in acute leukemia and thus contributes to leukemogenesis. The high frequency of aberrancies in the retinoblastoma pathway additionally warrants application of CDKIs in hematopoietic neoplasms. In this review, we describe the preclinical and clinical advances recently made in the use of CDKIs. These include the FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitors, traditional and novel pan-CDKIs, as well as dual kinase inhibitors. We additionally provide an overview on molecular mechanisms of response vs. resistance and discuss open questions.
- CDK4/6 inhibitors
- predictive biomarker
- mechanisms of resistance
- pharmacological inhibition
- combination strategies
1. Introduction
Despite the clinical implementation of novel treatments like kinase inhibitors, hypomethylating agents or pathway modulators during the last decades, several hematological malignancies still face a poor prognosis. Relapsed or refractory courses are particularly difficult to manage, often exhibiting multiple drug resistances and intimidating survival rates [1–4]. The FDA approval of the cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors (CDKIs) palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib for hormone receptor positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer treatment led to numerous promising clinical studies investigating CDKIs in solid neoplasms. This provides a rationale for the emerging intensive testing in hematological malignancies, raising hopes for improving patients’ prognoses. Given their wide spectrum of cellular modulation including cell cycle control, transcription, DNA repair, epigenetic regulation, proliferation, and apoptosis, CDKs represent promising molecular targets for leukemia and lymphoma treatment [5].
Despite the clinical implementation of novel treatments like kinase inhibitors, hypomethylating agents or pathway modulators during the last decades, several hematological malignancies still face a poor prognosis. Relapsed or refractory courses are particularly difficult to manage, often exhibiting multiple drug resistances and intimidating survival rates [1][2][3][4]. The FDA approval of the cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors (CDKIs) palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib for hormone receptor positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer treatment led to numerous promising clinical studies investigating CDKIs in solid neoplasms. This provides a rationale for the emerging intensive testing in hematological malignancies, raising hopes for improving patients’ prognoses. Given their wide spectrum of cellular modulation including cell cycle control, transcription, DNA repair, epigenetic regulation, proliferation, and apoptosis, CDKs represent promising molecular targets for leukemia and lymphoma treatment [5].
Cell cycle regulation is a key mechanism to prevent malignant cell proliferation and uncontrolled cell division. Aleem and Arceci reviewed the roles of CDKs in controlling cell cycle and development of hematological malignancies in detail [6]. Here, we focus on present and future therapeutic approaches to overcome CDK-influenced cell cycle control malfunction (Table S1) and will thus only offer a short introduction on CDK pathways and their role on leukemogenesis. In brief, cell cycle control is mainly mediated by serine/threonine CDKs acting as catalytic subunit when activated by their respective cyclins. CDK activity is further modulated by physiological CDKIs and posttranslational modification, resulting in transcriptional regulation, DNA damage repair mechanisms, metabolism, or epigenetic processes. In addition to the “classical” CDKs directly influencing the cell cycle, further kinases act as indirect modulators to regulate transcription or epigenetic signaling [6].
Cell cycle regulation is a key mechanism to prevent malignant cell proliferation and uncontrolled cell division. Aleem and Arceci reviewed the roles of CDKs in controlling cell cycle and development of hematological malignancies in detail [6]. Here, we focus on present and future therapeutic approaches to overcome CDK-influenced cell cycle control malfunction and will thus only offer a short introduction on CDK pathways and their role on leukemogenesis. In brief, cell cycle control is mainly mediated by serine/threonine CDKs acting as catalytic subunit when activated by their respective cyclins. CDK activity is further modulated by physiological CDKIs and posttranslational modification, resulting in transcriptional regulation, DNA damage repair mechanisms, metabolism, or epigenetic processes. In addition to the “classical” CDKs directly influencing the cell cycle, further kinases act as indirect modulators to regulate transcription or epigenetic signaling [6].
Hematopoietic stem cells are relatively quiescent to prevent stem cell exhaustion [7][8][9]. Once these stem cells initiate cell cycle induction, the cells proliferate extensively to provide hematopoiesis [10]. Therefore, the cell cycle of hematopoietic stem cells must be controlled thoroughly. Dysregulation of CDKs and associated cyclins is frequently observed in hematological malignancies. CDK6 is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cell types and loss of CDK6 results in impaired generation of several blood cell types. In contrast, overexpression and chromosomal translocation of CDK6 is observed in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma. CDK4/6 inhibition is achieved by physiological CDKI p16
Hematopoietic stem cells are relatively quiescent to prevent stem cell exhaustion [7–9]. Once these stem cells initiate cell cycle induction, the cells proliferate extensively to provide hematopoiesis [10]. Therefore, the cell cycle of hematopoietic stem cells must be controlled thoroughly. Dysregulation of CDKs and associated cyclins is frequently observed in hematological malignancies. CDK6 is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cell types and loss of CDK6 results in impaired generation of several blood cell types. In contrast, overexpression and chromosomal translocation of CDK6 is observed in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma. CDK4/6 inhibition is achieved by physiological CDKI p16
INK4A
, the most frequently deleted locus in human cancer. Translocations of the
MLL
gene locus are common in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and account for most infant ALL cases. CDK6 is a direct target of MLL fusion proteins and thus activated. Finally, CDK6 can be activated by
FLT3
-ITD-mediated down-regulation of cyclins D2 and D3. Besides CDK6, other CDKs are also involved in leukemogenesis. For example, the AML driver mutation
FLT3-ITD is an activator of CDK1. Further, mutations and deletions of the cyclin C and CDK19 locus on 6q21 result in altered Notch1 regulation especially in T-ALL [11].
-ITD is an activator of CDK1. Further, mutations and deletions of the cyclin C and CDK19 locus on 6q21 result in altered Notch1 regulation especially in T-ALL [6].
21. CDK4/6 Inhibitors
While the pan CDKI flavopiridol was the first CDK inhibitor applied clinically [12], recent CDKIs are more specific, with most drugs targeting only a subset of CDKs. CDK6 has a central role in hematopoiesis and CDK6-deficient mice show reduced production of erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and thrombocytes, as well as thymic atrophy [6]. Neutropenia is therefore the most common and dose-limiting adverse event in the clinical use of CDK6 inhibitors [13]. CDK6 is also a direct target of MLL fusion proteins which are common in AML and ALL [14][15]. This results in transcriptional activation of CDK6 and subsequent initiation of leukemic processes [15][16][17]. Further, CDK6 can be activated via
FLT3-ITD-mediated upregulation of cyclins D2 and D3 [18]. In mantle cell lymphoma, the characteristic t(11;14) translocation induces ectopic cyclin D1 expression, also resulting in CDK6 and CDK4 upregulation [19]. In pediatric B-ALL, p16
INK4A deletions, especially occurring during relapse, are a key feature of dysfunctional CDK4/6 control and an associated dismal prognosis [20].
21.1. Palbociclib
FLT3-ITD [18][21] and TKD mutations [22],
RUNX1/ETO translocation [23] and
MLL rearrangement [16][24]. In a recent study investigating de novo transformation of granulocyte/macrophage progenitor cells to AML, Chen et al. demonstrated that transient palbociclib application is capable of halting progenitor cell proliferation and preferentially abrogated the most proliferative progenitor cell subsets. Palbociclib further reduced the progenitor cell transformation in vivo, resulting in reduced AML burden and prolonged survival. This suggests that cell cycle inhibition decreases the likelihood of malignant transformation in vivo [25].
MLL or BCR-ABL1 rearrangements, palbociclib controlled cell growth via G1 arrest and Rb dephosphorylation both in vitro and in vivo [15][26][27][28][29]. A phase I clinical trial investigating palbociclib in relapsed ALL children is currently underway.
Similar promising antitumoral effects were observed in multiple myeloma, anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, where palbociclib was also capable of overcoming ibrutinib resistance [30][31][32][33][34][35]. In a study with 17 relapsed mantle cell lymphoma patients, palbociclib achieved one complete remission (CR) and two partial responses (PR), five patients had a progression-free survival of at least one year with reduced tumor metabolism and proliferation [36]. A phase I study in non-Hodgkin lymphoma showed stable disease (SD) in one third of the participants and two out of 68 patients had PR [37].
Palbociclib was then evaluated in several combinations both preclinically and clinically. The combination with proteasome inhibitor bortezomib was effective in an immunocompetent myeloma mouse model. Inhibition of CDK4/6 by palbociclib induced G1 arrest and enhanced bortezomib susceptibility via increased mitochondrial depolarization [31]. This combination was also evaluated in a clinical phase I/II trial in refractory/relapsed (R/R) myeloma together with dexamethasone, demonstrating an overall response rate of 20% and SD in 44% of the participants [38]. A phase I trial in R/R mantle cell lymphoma with palbociclib and bortezomib achieved CR in one out of 19 patients [39]. Combined palbociclib and ibrutinib treatment has been evaluated in R/R mantle cell lymphoma. From 27 patients in this phase I study, 67% responded and 37% had CR [40].
Figure 1) [41]. Besides cell cycle regulation, CDK6 also controls gene expression of oncogenic kinases by directly binding promoter sites. These include, among others, AURORA and AKT, both of which are known mediators of drug resistance.
FLT3
FLT3-ITD and TKD mutated AML cells [22].
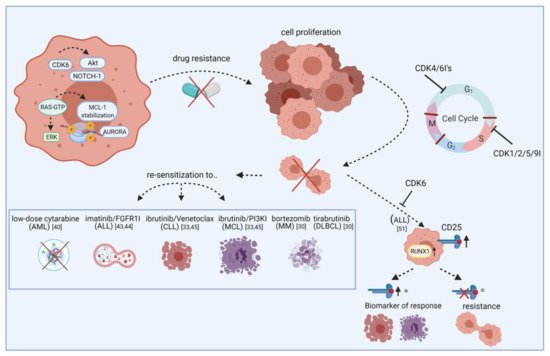
Figure 1.
Although there is a clear connection between BCR-ABL1 fusion and cell cycle regulation, only very limited data is available for the evaluation of CDKIs in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Rangatia and Bonnet have shown that lack of BCR-ABL1 leads to G1 phase arrest and a decrease in cyclin D1. Physiological CDKIs p21 and p27 subsequently exhibited increased gene expression [42]. Schneeweiss-Gleixner et al. recently reported that palbociclib synergizes with tyrosine kinase inhibitor ponatinib in BCR-ABL1
T315I mutated CML, via reducing proliferation and inducing G1 arrest. This is of importance because tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance is frequently observed in this CML subtype, leading to challenging clinical problems [43]. In ALL, palbociclib synergizes with fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor PD-173074 and imatinib (Gleevec) [44][45]. Increased apoptosis rates compared to palbociclib mono application were achieved with PI3Kδ inhibitor GS-1101 and BET protein bromodomain antagonist JQ1 in mantle cell lymphoma [46][47]. In myeloma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, synergism was achieved with dexamethasone and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor tirabrutinib [30][48].
To demonstrate their anti-leukemic potential, CDK4/6 inhibitors rely on expression of downstream signaling protein Rb. Intrinsic or acquired lack of Rb function results in resistance towards therapeutic CDK4/6 targeting [13]. Additionally, palbociclib treatment can lead to p27 downregulation, thus reactivating CDK2 and cell cycle progression. Transcription factor
FOXO3A
p27
FOXO3A
p27
p27
p27
p27
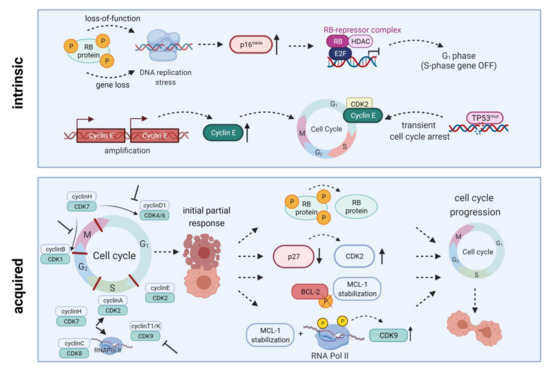
Figure 2.
INK4A
TP53
21.2. Ribociclib
Ribociclib (LEE011) is another CDK4/6 inhibitor that demonstrated significant anti-proliferative and apoptosis-inducing effects in AML and B-ALL cell lines and primary samples, probably mediated via G1 arrest and senescence [49]. A recent study on pediatric B-ALL evaluated ribociclib in combination with dexamethasone. They found significant basal overexpression of CDK6 in B-ALL cells. Subsequent inhibition of CDK4/6 using ribociclib resulted in G1 phase arrest, reduced cell proliferation, and apoptosis induction accompanied by Rb dephosphorylation. Adding dexamethasone synergistically improved anti-neoplastic effects in B-ALL cell lines as well as primary samples [50].
NOTCH1-mutant and wildtype T-ALL and found both subtypes sensitive to the inhibitor. The combination with glucocorticoid dexamethasone and mTOR inhibitor everolimus acted synergistically in vitro and in vivo. In contrast, antagonistic effects were observed with several drugs used in T-ALL standard chemotherapy including methotrexate, mercaptopurine, asparaginase, or doxorubicin [51].
CD25
RUNX1
Figure 1) [52]. A clinical phase I study examined ribociclib in solid neoplasms and lymphoma and found SD in ten out of 70 patients [53].
21.3. Abemaciclib
While ribociclib was mainly analyzed in acute leukemias, abemaciclib (LY2835219) has been more widely evaluated in lymphoma. Here, inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis was reported in germinal center-derived B-cell lymphoma cell lines, but not in activated B-cell like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines [54]. In a clinical trial, 71% of the participating R/R mantle cell lymphoma patients achieved SD and 36% had PR [55]. A subsequent phase II study with 28 patients reached CR in two patients and an overall response rate of 36% with an overall survival of 16 months [56]. Another clinical trial is currently evaluating abemaciclib with fulvestrant in advanced or metastatic solid tumors and lymphomas.
MLL-rearranged AML cell lines and xenografts [57] as well as myeloma cell lines [58]. Nakatani et al. recently identified that t(8;21) rearranged AML cell lines are more vulnerable to palbociclib and abemaciclib than non-t(8;21) AML cells [59]. Molecularly, this is due to higher cyclin D2 levels, a common response marker towards abemaciclib. In t(8;21) rearranged AML cells, abemaciclib induced the expected G1 arrest, leading to impaired cell proliferation and decreased MAPK and AKT pathway signaling. Another interesting finding of this study was autophagosome formation which significantly increased apoptosis induction upon combined application of abemaciclib and autophagy inhibitors [59].
21.4. Lerociclib
The novel CDK4/6 inhibitor lerociclib (G1T38) was capable of decreasing Rb phosphorylation and induced G1 cell cycle arrest in leukemia and lymphoma cell lines in vitro. Of note, lerociclib demonstrated a superior efficacy compared to palbociclib and did not induce severe neutropenia in an estrogen receptor positive breast cancer dog animal model, which is a common side effect of CDK4/6 inhibitors. Using mouse xenograft models, the authors further demonstrated that lerociclib accumulated within the tumor but not in plasma, implying less severe effects on myeloid progenitor cells compared to palbociclib therapy. Indeed, plasma concentrations after palbociclib treatment were significantly higher than the concentration needed to inhibit cell proliferation in several cell lines. In contrast, after lerociclib treatment, plasma concentrations dropped faster. The authors thus claim that palbociclib-induced neutropenia is a product of CDK4/6 inhibition in the bone marrow, preventing proliferation of healthy bone marrow cells [60].
32. CDK7/8/9 Inhibitors
MLL
HOX gene promoters and inducing abnormal CDK9 expression, cell growth, and proliferation [61]. Another role for CDK9 is transcriptional regulation of MCL-1, it may thus influence intrinsic apoptosis induction (
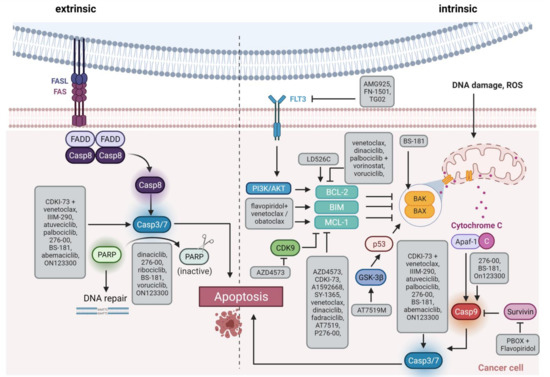
Figure 3.
32.1. AZD4573
So far, AZD4573 is the only selective CDK9 inhibitor invested clinically in hematological malignancies. A preclinical study on different hematological neoplasms proved significant induction of apoptosis via MCL-1 suppression in vitro and in vivo [63]. The same study also evaluated the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax as combination partner to overcome treatment failure or leukemic progress after AZD4573 cessation. Both, MCL-1 and BCL-2 are anti-apoptotic members of the intrinsic apoptosis initiation cascade. Combined therapy with AZD4573 and venetoclax induced long-term inhibition of leukemic cell proliferation in all animals, even in models intrinsically resistant to either monotherapy (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma SU-DHL-4; AML model OCI-AML3) [63].
32.2. CDKI-73
The non-selective CDK9 inhibitor CDKI-73 proved anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic capacity in chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL) [64], diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [65], ALL and AML [66] cells, as well as in animal models. Walsby et al. evaluated the anti-neoplastic potential of CDKI-73 together with fludarabine in CLL and found decreased
MCL1
MCL1
XIAP
CCND1
CCND2. Of note, synergistic effects were also observed under CD40L-expressing pro-survival co-culture conditions with initial fludarabine resistance [64]. In diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, CDK9 inhibitors including CDKI-73 frequently induce histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation, which is associated with tumor progression. A recent study therefore evaluated CDKI-73 with histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitors EPZ6438 and GSK126 and found synergistic anti-proliferative effects. The authors also identified drastically increased apoptosis and DNA damage in response to combined treatment [65]. The same group previously evaluated combinatorial effects of CDKI-73 with venetoclax in ALL and AML and elucidated synergistic induction of apoptosis via PARP and caspase 3 cleavage as well as XIAP downregulation [66]. Many more CDK9 inhibitors have been preclinically evaluated in a broad range of hematological malignancies [67][68][69][70][71][72].
32.3. CDK8 Inhibitors
CDK8 regulates transcription as part of the mediator complex or by phosphorylation of transcription factors [73]. In primary AML and ALL samples with BCR-ABL1 translocation, Menzl et al. found that mTOR signaling is usually deregulated in CDK8-deficient cells. They subsequently developed the small molecule YKL-06-101, targeting both CDK8 and mTOR, which had significant anti-leukemic potential in vitro and in vivo [74]. Another selective CDK8 inhibitor, SEM120, is effective in AML in vitro and in vivo and currently evaluated in a phase Ib clinical trial in AML and myelodysplastic syndrome [75].
32.4. CDK7 Inhibitors
RUNX1/ETO rearranged cell line [76]. A preclinical study investigating the effect of THZ1 in myeloma revealed decreased cell proliferation and survival as well as RNA polymerase II, CDK 1, 2, and 9, MCL-1, BCL-XL, and c-MYC downregulation in vitro and in vivo. Addition of venetoclax or carfilzomib significantly increased the antitumor efficacy [77].
SY-1365, which is under clinical investigation for solid tumors, decreased MCL-1 protein levels and induced transcriptional changes mainly of oncogenic transcription factor genes and members of cell cycle and DNA damage repair related pathways. Of note, this inhibitor was more effective in cells with low BCL-XL expression. When combined with BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax, antitumor effects were synergistically increased in vitro and in vivo [78]. Finally, BS-181 inhibited CDK7 and induced apoptosis in Jurkat T-ALL cells [79].
43. Pan CDK Inhibitors
43.1. Flavopiridol
Flavopiridol (alvocidib) is a first generation pan CDK inhibitor, targeting CDKs 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, and 9. It induces cell cycle arrest in ALL and AML cell lines as well as leukemia and lymphoma animal models [80][81]. Preclinical studies of flavopiridol in combination with BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax or pan BH3 mimetic obatoclax revealed synergistic anti-apoptotic effects in vitro and in vivo, probably mediated via MCL-1, BIM, and NOXA regulation [82][83]. Flavopiridol has also been tested in CML and acted synergistically with pro-apoptotic pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine compounds in imatinib-resistant cells. The observed induction of apoptosis was likely due to deactivation of the CDK1/cyclin B1 complex [84].
Clinical efficacy was observed in hematological neoplasms including CLL and AML, especially in AML as part of the FLAM regimen (flavopiridol followed by cytarabine and mitoxanthrone) [6][85]. Clinical investigation in CLL with early trials using flavopiridol achieved PR in almost half of the patients [86]. Further, a clinical trial is currently evaluating the potential of flavopiridol and decitabine in myelodysplastic syndrome. However, the use of flavopiridol proved difficult in the clinical setting, offering a complex pharmacokinetic profile, a wide range of side effects and an unclear mechanism of action [13].
Figure 2). Mahoney et al. identified endoplasmatic reticulum stress-mediated death of CLL cells as a novel mode of action for flavopiridol. However, induction of autophagy decreased cytotoxic effects while autophagy inhibition supported stress-mediated anti-leukemic effects, highlighting autophagy as a potential mechanism of flavopiridol resistance [87]. Besides, members of the BCL-2/MCL-1 apoptosis signaling cascade are involved in flavopiridol resistance. Data by Yeh et al. indicated that prolonged MCL-1 stability, in line with RNA polymerase II phosphorylation and CDK9 kinase domain upregulation, contributes to resistance in B-ALL cell line 697. MCL-1 upregulation was probably mediated via MAPK/ERK signaling. Knockdown of MCL-1 restored flavopiridol sensitivity and induced cytotoxicity [88]. Besides MCL-1, BCL-2 is another anti-apoptotic signaling molecule involved in flavopiridol metabolism. Decker et al. demonstrated that a truncated BCL-2 protein lacking the phosphorylation loop domain results in flavopiridol resistance in U937 AML cells [89].
43.2. Dinaciclib
MLL rearrangement, primary patient cells, and in vivo models [90][91][92][93]. A phase II study found reduced numbers of circulating blasts but no bone marrow remission in AML and ALL patients [92].
In CLL, dinaciclib downregulates MCL-1 gene and protein expression and potently induces apoptosis in patient-derived cells [94]. Interestingly, this effect was also present when the cells were cultured with cytokines produced by microenvironment cells but not with direct stromal cell contact. This lack of therapeutic efficacy was overcome by addition of PI3Kα inhibitor PIK-75 but not inhibitors of other PI3K isoforms [94]. Chen et al. subsequently characterized dinaciclib-induced effects on signaling pathways, elucidating caspase 8 and 9-mediated apoptosis induction with MCL-1 and BCL-XL suppression. They further detected inhibition of oncogenic pathways including STAT3, NFkB, p38, PI3K/AKT, and MAPK [95]. In addition, dinaciclib enhanced ibrutinib and venetoclax sensitivity. When combined with SYK inhibitor entospletinib, no synergistic effect was seen. Two phase I clinical trials evaluated the effect of dinaciclib in R/R CLL; combined with rituximab, four out of five patients had SD and one achieved CR [96]. In combination with ofatumumab, a median progression-free survival of 322 days was observed [97].
In mantle cell lymphoma, Höring et al. pursued a combined MCL-1 inhibiting and NOXA stabilizing approach using dinaciclib and fatty acid synthase inhibitor orlistat. They observed synergistically-induced NOXA-dependent apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma cell lines and primary samples along with tumor growth inhibition in vivo [98]. In advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma, B-CLL, and myeloma, no PR, CR, or SD was observed in a clinical phase I study with dinaciclib alone [99]. A different study reported SD in eight out of 61 advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma or myeloma patients treated with dinaciclib in combination with aprepitant, ondansetron, and dexamethasone [100].
Further preclinical evaluation detected increased doxorubicin response rates in myeloma cell lines after low dose dinaciclib treatment, boosting growth inhibition and promoting senescence [101]. Interestingly, and in contrast to several other studies of dinaciclib in hematological neoplasms, this work did not observe apoptosis induction but accelerated senescence via increased p16 signaling. Additionally, dinaciclib may have reduced doxorubicin-induced ATM/Chk2/p53/p21 senescence-modulating signaling. Further investigation in myeloma was conducted by Alagpulinsa et al. who combined dinaciclib with PARP inhibitor ABT-888, based on the idea of impaired homologous recombination during PARP-mediated DNA double strand break repair after dinaciclib [102]. Dinaciclib-treated myeloma cells had increased DNA damage and reduced repair gene expression. Cotreatment with PARP inhibitor ABT-888 synergistically reduced tumor cell proliferation in vitro as well as in vivo using myeloma xenograft models. A subsequent phase I/II study found an overall response rate of 11% in myeloma patients receiving dinaciclib alone [103]. A combinatory approach with bortezomib is currently being evaluated in a phase I plasma cell myeloma study.
43.3. Other Pan CDK Inhibitors Investigated in Clinical Trials
Further pan CDK inhibitors are now also tested in the clinical setting. Besides the CDKs targeted by dinaciclib (CDK1, 2, 5, 9), AT7519M also inhibits CDK4, still inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo and reducing proliferation in myeloma and CLL [104][105]. Two clinical trials investigating AT7519M in non-Hodgkin lymphoma as well as R/R CLL and mantle cell lymphoma observed SD in at least half of the patients enrolled and PR in three out of 12 R/R mantle cell lymphoma cases [106][107].
Voruciclib (P1446A), a CDK1/2/4/5/6/8/9 inhibitor, was evaluated in a phase I study recruiting follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, small lymphocytic lymphoma, CLL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and AML patients after demonstrating significant potential in preclinical studies [62][108]. Combined application of voruciclib and BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax was synergistic in preclinical AML models. Notably, venetoclax-mediated
MCL-1
c-Myc downregulation was only reached in an intermittent drug administration schedule that should be considered in clinical practice [109].
The CDK1/4/9 inhibitor P276-00 showed promising in vitro and in vivo results in AML [110], myeloma [111], and mantle cell lymphoma [112] but only achieved SD in two out of 13 R/R mantle cell lymphoma patients in a phase II clinical trial [113].
Roniciclib (BAY1000394) targets the same CDKs as flavopiridol (1, 2, 4, 6, 7, and 9) and achieved SD in three out of seven patients with lymphoid neoplasms [114]. Of note, this is the only clinical trial so far investigating CDKIs in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Earlier studies suggested that there is a relation between apoptosis-induction, DNA fragmentation, survival, and expression of cell cycle regulators p27 and p21 [115], providing a rationale for CDK targeting in Hodgkin lymphoma. Sánchez-Aguilera et al. further identified CDK regulator p18
INK4C as a potential tumor suppressor gene in Hodgkin lymphoma [116]. Finally, loss of p16
INK4A expression has been observed in Reed–Sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma cases [117].
