Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease and tubulo-interstitial accumulation of lysine 63 (K63)-ubiquitinated (Ub) proteins drives the progression of fibrosis in DN. We previously showed that the extent of renal K63-Ub can be easily monitored through the assessment of miR-27b-3p levels in urine. In the present manuscript we explored the renoprotective effect of a specific K63-Ub inhibitor (NSC697923), alone and in combination with the ACE-inhibitor molecule Ramipril, in proximal tubular epithelial cells (in vitro) and in diabetic DBA/2J mice (in vivo).
Experimental evidence shows that NSC697923 treatment was not only able to suppress tubular accumulation of K63-Ub proteins, NSC697923 was in fact able to also inhibit hyperglycemia-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) both in vitro and in vivo reducing the expression of EMT markers such as α-SMA, Collagen I, Vimentin, FSP-1 and Collagen III along with tubulointerstitial and glomerular fibrosis.
Diabetic DBA/2J mice treated with NSC697923 also displayed recovery of urinary miR-27b-3p and restored expression of p16INK4A, indicating a protective effect on cellular senescence in tubular cells. Moreover, the combination of NSC697923 and Ramipril was effective to reduce uACR in diabetic DBA/2J mice. In conclusion, we suggest that selective inhibition of K63-Ub, when combined with the conventional treatment with ACE inhibitors, might represent a novel treatment strategy to prevent the progression of fibrosis and proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy. Finally we suggest the dosage of urinary miR-27b-3p levels to monitor treatment efficacy.
- DBA2/J mice
- lysine 63 ubiquitination
- microRNA
- renal fibrosis
- senescence
- diabetes
1. Introduction
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a renal complication of diabetes that can lead to renal failure when untreated. Several therapeutic options are currently available for the management of high blood pressure and hyperglycemia such as inhibitors of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS), hypoglycemic drugs such as metformin, sodium glucose transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists. These molecules exert beneficial effects in the context of renal damage and have also been shown to preserve renal function in animal models through their ability to inhibit pathways leading to renal fibrosis. Moreover, results from recently published clinical trials have unveiled the effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors in reducing the risk of kidney failure as well as of death from cardiovascular causes or heart failure hospitalization in chronic kidney disease patients with or without type 2 diabetes. However, no clinical data exploring renal fibrosis among other outcomes is currently available, and no targeted therapies have been developed to effectively prevent or reduce the molecular process leading to renal fibrosis.
Over the last few years, our group has described the role of lysine 63 (K63) ubiquitination in DN-related fibrosis. We showed that an increased expression of the E2 enzyme UBE2v1 (responsible for K63-linked polyubiquitin chains formation) is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) of tubular cells, increased production of extracellular matrix, and progression of kidney fibrosis in diabetic patients. This process is involved in autophagy-induced cell death and can be monitored by dosing specific urinary miRNAs, particularly miR-27b-3p and miR-1228-3p, whose expression levels inversely correlate with renal fibrosis. The beneficial effects of inhibiting this pathway in vivo however remain to be explored.
Another mechanism that drives kidney fibrosis in DN involves accelerated cellular senescence of tubular cells. DcR2, a transmembrane receptor of tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, represents a potential target to modulate the induction of cellular senescence in tubular cells. It has also been demonstrated that hyperglycemia dramatically increases the renal expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor p21, thus inducing an increase in the senescence of tubular epithelial cells. However, the role of the different mechanisms mediating kidney aging in diabetes remains to be fully clarified.
Among the different models to study diabetes and diabetic complications, Streptozotocin (STZ)-treated DBA/2J mice interestingly share common transcriptional networks with established importance in human DN. Specifically, when treated with STZ, a compound with toxic effects on the insulin-producing pancreatic beta-cells resulting in hyperglycemia, DBA/2J mice typically develop albuminuria, mesangial expansion, and GFR decline.
In this study, we investigated whether the in vitro and in vivo inhibition of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains accumulation, using the specific E2 complex inhibitor compound NSC697923, alone and in combination with the RAAS inhibitor Ramipril, has beneficial effects in terms of preventing kidney fibrosis and reducing albuminuria. We also explored the possibility to use specific circulating miRNAs as biomarkers to monitor the efficacy of different therapeutic treatments.
2. K63-Ub inhibition with NSC697923 prevents high-glucose induced EMT in vitro
In vitro experiments confirmed that short exposure of tubular cells to high glucose media is associated to a marked increase of a-SMA, Collagen I and Vimentin, indicating that EMT actively contributes to the synthesis of extracellular matrix components. While stimulation of tubular cells with Ramipril was able to reduce Vimentin expression, it had no effect in the suppression of Collagen I synthesis. Interestingly, treatment of tubular cells with NSC697923, alone and in combination with Ramipril, completely restored the epithelial phenotype.
3. K63-Ub inhibition with NSC697923 reduced renal fibrosis in vivo in diabetic DBA/2J mice
DBA/2J mice were used as our in vivo model of DN. Animals were initially injected with either STZ or PBS, and then treated with Ramipril and NSC697923, alone and in combination.
The effects of in vivo treatment with NSC697923 and Ramipril on the development of tubule-interstitial fibrosis within the renal cortex, renal medulla, and glomeruli was investigated by Collagen III and FSP-I immunohistochemistry as well as Sirius Red and Fast Green staining, and PAS staining. For the quantification of each staining associated with computerized image analysis, the perivascular regions as well as the limits of each biopsy were excluded from the analysis of the cortical and medullary compartments, while the Bowman’s capsule was excluded when analyzing the glomerular area. Diabetic mice showed an increased amount of Collagen III deposition, both in the renal cortex, at the tubulo-interstitial (Figure 2L) and glomerular (Figure 2Q) levels, and in the renal medulla (Figure 2V), when compared with non-diabetic mice (Figure 2K,P,U, respectively). Interestingly, packed Collagen III fibers were accumulated in the glomerular mesangium (Figure 2Q), suggesting the development of renal damage comparable to human DN. In diabetic mice, treatment with Ramipril resulted in a slight reduction in Collagen III expression at the tubulo-interstitial level and medulla (Figure 2M,W, respectively), which was significant only at the glomerular level (Figure 2R) when compared to untreated diabetic mice (Figure 2P). Interestingly, NSC697923 alone (Figure 2N,S,X) or in combination with Ramipril (Figure 2O,T,Y) preserved the integrity of the renal parenchyma by significantly reducing Collagen III deposits at both the tubulo-interstitial and glomerular levels and in the medullary region, so that levels were comparable to those in non-diabetic mice. Control mice, both untreated (Figure 2K,P,U) and treated (Supplementary Figure S3), showed similar amounts of Collagen III fibers in all compartments of renal parenchyma.
Additionally, FSP-1 expression, another myofibroblast marker, almost absent in non-diabetic mice both in the cortex (Figure 2Z) and in the medulla (Figure 2AE), was significantly increased in diabetic mice (Figure 2AA,AF). Ramipril treatment did not significantly reduce FSP-1 expression in both the cortex (Figure 2AB) and in the medulla (Figure 2 AG). NSC697923 both alone (Figure 2AC,AH) or in combination with Ramipril (Figure 2AD,AI) significantly reduced FSP-1 expression in the tubular compartment in the cortex (Figure 2AC,AD, respectively) and in the medulla (Figure 2AH,AI, respectively) once again to levels comparable to those in non-diabetic mice.
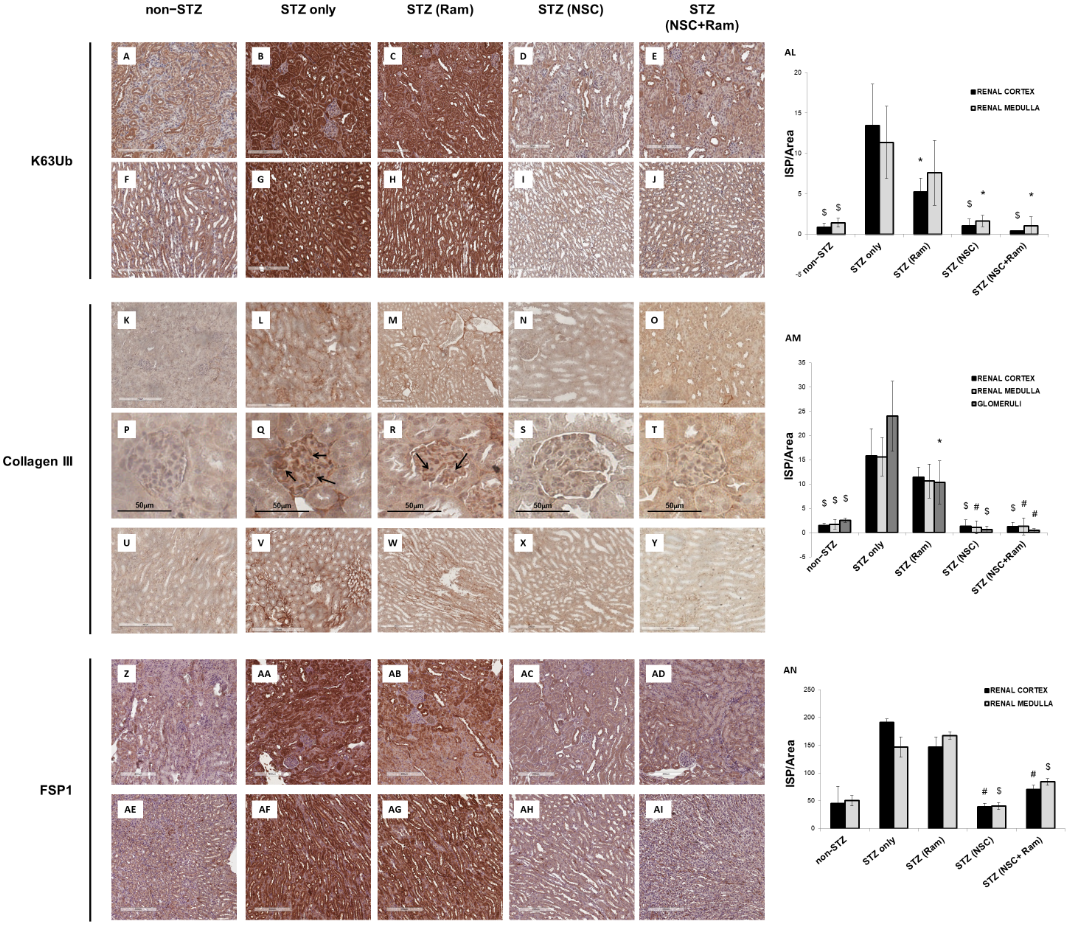
Figure 2. NSC697923, alone and in combination with Ramipril, reduced K63-ubiquitination, Collagen III expression. and FSP-1 expression in the renal cortex and medulla of STZ-treated DBA/2J mice. Error bars indicate standard deviation. * p < .05 vs. STZ only; $ p < .005 vs. STZ only; # p < .0005 vs. STZ only.
4. Effect of NSC697923, alone or in combination with Ramipril, on albuminuria and on the concentration of urinary miR-27b-3p in diabetic mice
In order to evaluate the effects of Ramipril and NSC697923 on STZ-induced albuminuria in diabetic mice, we performed quantification of urinary albumin and normalization with urinary creatinine (Figure 4A). As expected, the mean urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (uACR) was higher in the diabetic compared to control mice. Moreover, NSC697923, better than Ramipril alone and the combination of both, was able to mitigate STZ-induced albuminuria, however no statistical significance was observed, probably due to the reduced number of animals available for this analysis.
To evaluate the effect of NSC697923, alone or in combination with Ramipril, on the expression of candidate biomarkers of diabetes-induced renal injury in vivo, we assessed the urinary levels of miR-27b-3p in our animal model. We focused on the analysis of miR-27b-3p, since this miRNA, unlike miR-1228-3p, is evolutionarily conserved in mice. Interestingly, miR-27b-3p was significantly downregulated in diabetic mice (STZ-only) compared to the control group (non-STZ) (Figure 4B) as observed in Human samples. Treatment with Ramipril did not affect miR-27b-3p levels in urine of DBA/2J diabetic mice, however, the treatment with NSC697923, alone and in combination with Ramipril, was associated with the restoration of miR-27b-3p levels. Interestingly, we observed a moderate but very significant inverse correlation between uACR and urinary miR-27b-3p (Figure 4C), thus further supporting the role of miR-27b-3p as a biomarker of renal function decline in diabetes.
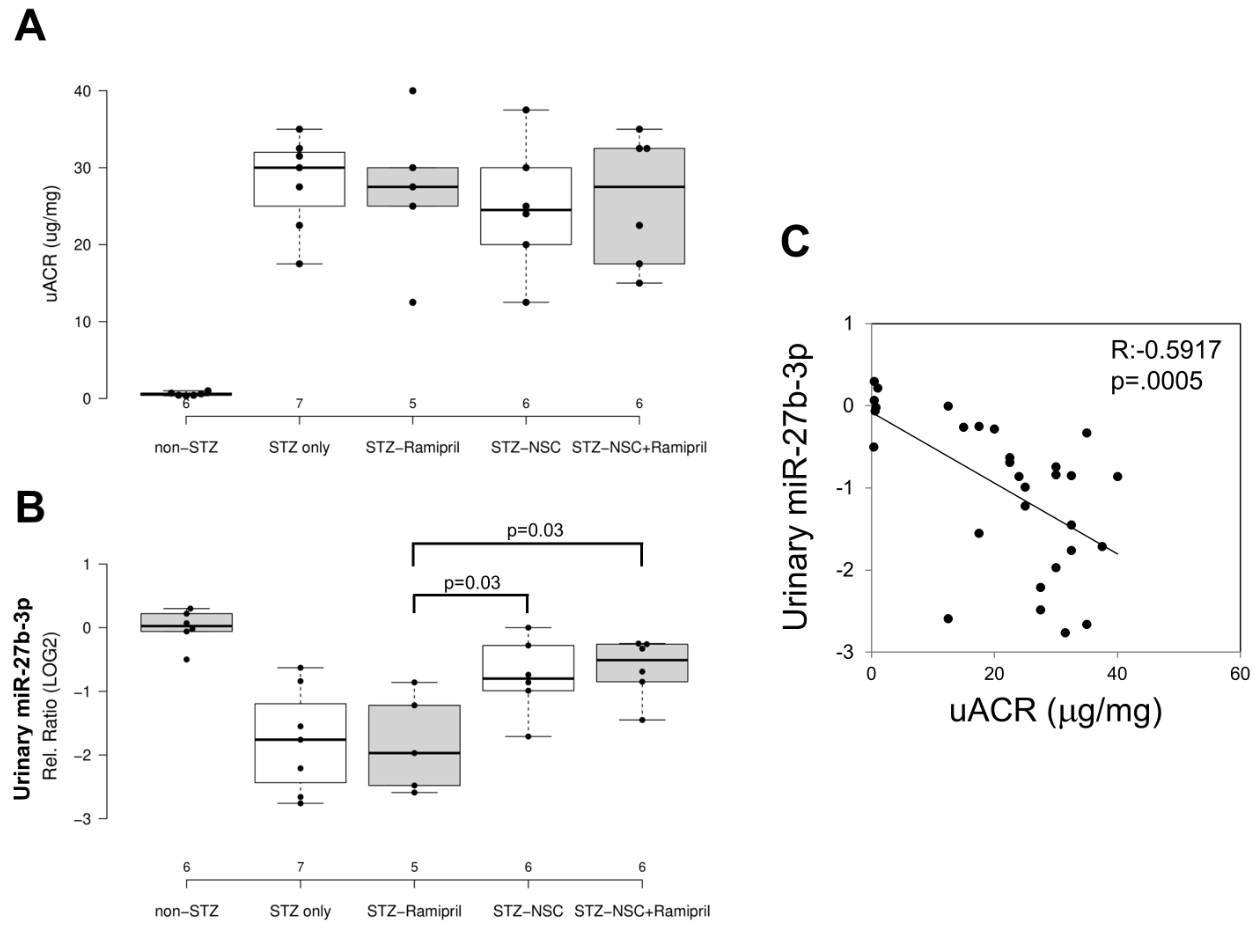
Figure 4. Effects of NSC697923, alone and in association with Ramipril, on uACR (A) and urinary miR-27b-3p levels (B) and correlation among both (C).
5. NSC697923, alone and in combination with Ramipril, modulates cellular Senescence, both in vitro and in vivo
Premature senescence is a key cellular event in renal fibrosis and is associated with the progression of diabetic nephropathy therefore we evaluated whether NSC697923 might affect hyperglycemia-induced tubular cell senescence in vitro. To this purpose, we stimulated tubular cells with high glucose for 48 h both in the absence (Figure 5B) and in the presence of Ramipril (Figure 5C), or NSC697923 (Figure 5D), or the combination (Figure 5E). Interestingly, high glucose stimulated tubular cells acquired a senescent phenotype as determined by significant increase in SA-β-GAL positivity compared to the basal conditions (Figure 5A,B,P). Interestingly under hyperglycemic conditions in the presence of Ramipril, tubular cells did not show a significant reduction in hyperglycemia-induced SA-βGAL positivity (Figure 5C,P), while NSC697923 both alone (Figure 5D,P) and in association (Figure 5E,P) significantly reduced cellular senescence and SA-βGAL positivity (Figure 5P). Moreover, we investigated the expression of the senescent marker p16INK4A and its potential association with the accumulation of K63-ubiquitinated proteins in vivo.
Non-diabetic mice displayed few p16INK4A positive tubular cells in renal parenchyma (Figure 5F). In contrast, p16INK4A staining was greatly increased in diabetic mice (Figure 5G). NSC697923, alone (Figure 5I) and in combination with Ramipril (Figure 5J), significantly reduced the expression of the senescence-related p16INK4A marker (Figure 5P). Ramipril treatment induced a significant reduction of p16INK4A expression when compared to untreated diabetic mice, but this effect was less evident compared to NSC697923 (Figure 5H,Q).
To further evaluate the role of K63-ubiquitinated protein accumulation in tubular senescence, we performed a double immunofluorescence staining for p16INK4A and K63-ubiquitinated proteins in all animal groups. The expression of K63-ubiquitinated proteins co-localized with p16INK4A-positive tubules in the diabetic mice (Figure 5L), and no significant differences in the co-staining were observed following treatment with Ramipril (Figure 5M,R). Remarkably, the use of NSC697923 alone (Figure 5N) or in combination with Ramipril (Figure 5O) significantly reduced K63-ubiquitinated proteins/p16INK4A double positive cells, indicating diminished renal senescence (Figure 5R). Collectively, these data indicate that NSC697923 alone or in association with Ramipril could interfere with diabetes-induced senescence and prevent kidney fibrosis and progression of kidney damage.
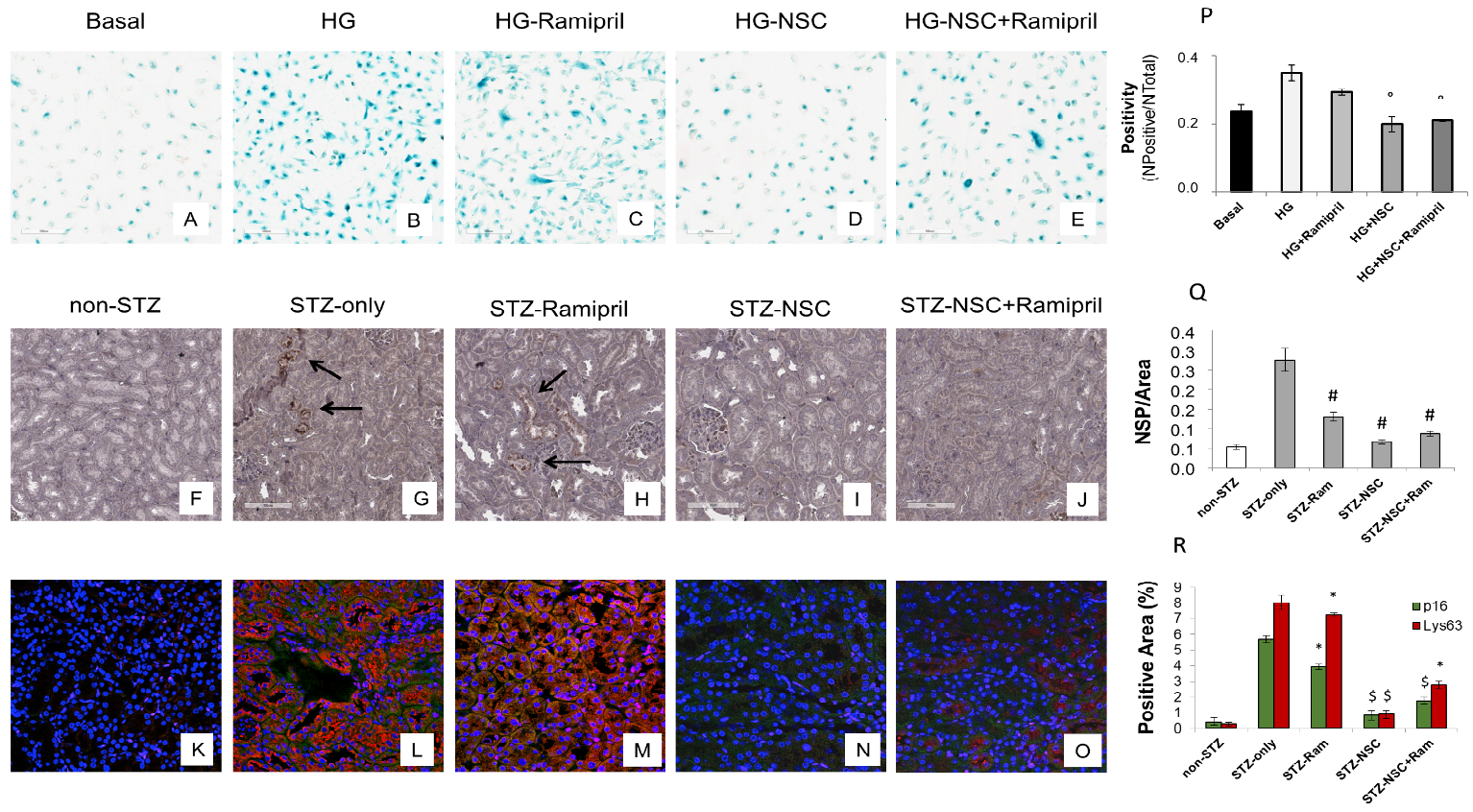
Figure 5. Treatment with NSC697923 modulated cellular senescence and renal expression of p16INK4A in vitro in RPTEC cells and in vivo in DBA/2J mice. Histograms are indicative of mean values while error bars are indicative of the standard deviation. ° p <.05 vs. HG; * p <.05 vs. STZ only; $ p < .005 vs. STZ only; # p < .0005 vs. STZ only.
6. Conclusions
Pre-clinical studies can be leveraged to ameliorate current therapeutic approaches since they allow the identification of novel therapeutic targets. In this scenario, we showed that the selective inhibition of K63 ubiquitination by NSC697923 could be considered as a novel treatment option to halt the process leading to kidney fibrosis in experimental diabetes. In addition, the additive effect of the association of conventional ACE inhibitor treatment with NSC697923 with regard to a reduction of fibrosis and the potential role of NSC697923 in the reduction of albuminuria, as well as its effect on miRNA-27b-3p modulation, can represent a novel approach to tackle the multifactorial pathophysiology of renal complication in diabetes.
Patents
The methods and results described in the present manuscript are included in patent no. 102018000004126.
