Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Birthe Nielsen and Version 2 by Catherine Yang.
There are established links between free radicals and more than sixty different human health conditions, including ageing, cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, strokes, heart attacks, and atherosclerosis. Consumption of higher levels of dietary antioxidant enzymes and antioxidant molecules-enriched food or antioxidant supplements has been found to reduce the risk of free radical-related health issues. The green halotolerant microalgae Dunaliella can grow in a wide range of saline environments and is a potential natural source for antioxidant production.
- antioxidant enzymes
- cultivation conditions
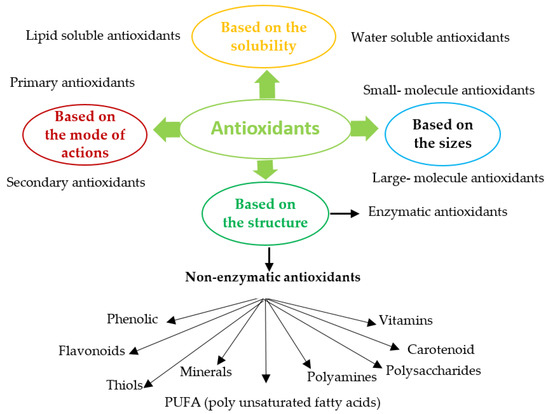
1. Classification of Antioxidants
Antioxidants (enzymatic or non-enzymatic) are classified depending on their mode of action as primary antioxidants (hydrogen or electrons donors) or secondary antioxidants (oxygen scavengers or chelating agents) [1][2][43,44]. Antioxidants can also be grouped according to size, solubility, or structure, Figure 1. Abundant enzymatic antioxidants in microalgae are superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione transferase (GST). Non-enzymatic antioxidants consist of compounds such as Vitamin C (ascorbate), glutathione, carotenoid, phenolic compounds, proline, glycine, polyamine, PUFA, and some metals (Cu, Zu) [3][4][5][45,46,47]. Most enzymatic antioxidants and some non-enzymatic antioxidants (glutathione, ascorbate) are hydrophilic and mainly present in the cellular fluids (cytosol or cytoplasmic matrix), whereas the hydrophobic antioxidants (carotenoid, tocopherol) are primary located in the cell membranes [6][48].
2. Antioxidant Enzymes
Antioxidant enzymes prevent or delay the oxidation of other molecules by neutralising reactive oxygen species (ROS) [6][48]. These enzymes eliminate ROS by reducing the energy of free radicals or by donating electrons to free radicals [10][42], and as such, constitute the first level of defence in the cell's antioxidant network. Some molecules are not involved directly in the scavenging of free radicals but rather enhance other antioxidant molecules’ activity and may also be classified as antioxidants [7][41]. The majority of antioxidant enzymes are metalloenzymes and contain a metal ion in their catalytic site [3][45].
3. Commercial Applications of Antioxidant Enzymes
Antioxidants, or antioxidant-enriched extracts, are commercially used to prevent oxidative processes and to maintain the flavor, texture, and colour of food during storage. They also find uses as refining, bleaching, deodorising agents in the food processing industries [11][12][13][14][15][51,52,53,54,55], in extending the shelf life of lubricating oil and reducing vehicular emissions [16][56] and in stabilisation of synthetic fibre, rubber, thermoplastic, and adhesives by stopping autocatalytic reactions [17][57]. In cosmeceutical products, antioxidant compounds are used to prevent skin ageing and UV-induced skin damage and treat the appearance of wrinkles and erythema [18][19][20][21][58,59,60,61]. Industrial applications of antioxidants are listed in Table 1. The global demand for antioxidants was valued at ~USD 2.25 billion in 2014 and grew at a CAGR (compounds annual growth rate) of ~5.5% between 2015 and 2020 [22][62]. This increasing global demand is driving the search for synthetic and natural-derived antioxidants.
Table 1.
Commercial uses of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant.
| Antioxidants | Applications | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|
4. Generation and Detoxification of ROS
ROS is a collective term for oxygen-derived products (free radicals and non-radicals reactive derivatives of oxygen). They are produced in cellular compartments either exogenously (in response to environmental stress such as UV radiation or xenobiotics) or endogenously (from the intracellular metabolic pathway, enzymatic activities, mitochondrial respiration, or photosynthesis) [26][66]. Accumulation of ROS leads to oxidative stress in cells and causes damage to cellular macromolecules, including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and DNA [51][89]. Various sources of ROS and corresponding modes of biochemical metabolism are summarised in Table 2.
Table 2.
Production of ROS in cells during biological metabolism and their corresponding neutralising antioxidants.
| ROS | Reaction | Life Span | Function | Sources of ROS | Scavenging Antioxidants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural antioxidants | SOD | Added to cosmetic products to protect against skin damage | O | 2 | + Fe | 2+ | [8][12][20][23][24] | [49,52 |
| Singlet ( | 1 | O | 2 | ) First excited electronic state of O | 2 | Chlorophyll triplet state (Chl) is generated sue to insufficient energy dissipation during photosynthesis Chl + | 3 | O | 2 | → | ,60,63,64] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 µs (appx.) | 4 µs in H | 2 | O 100 µs in polar solvents |
Gene up-regulation, molecular defense against photo-oxidative stress | Chloroplast | β-carotene, lycopene, tocopherol, ASc, plastoquinone, and proline | Protect against lipid peroxidation, heat, and cold stress in poultry production | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Superoxide radical (O | 2•− | ) One electron reduction of | 3 | O | 2 | Reduction of oxygen ( | 3 | O | 2 | ) during electron transport during the photosynthesis process in chloroplasts or during oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria | 3 | O | 2 | + e | − | → O | 2•− | 3 | O | 2 | + Xanthine ( | Xanthine oxidase | ) → O | 2•− | + uric acid | 3 | O | 2 | + NADPH ( | NADPH oxidase | ) → O | 2•− | + NADP | + | + H | + | 2–4 µs | Triggering the formation of more ROS which further participates in membrane lipid peroxidation | PSI in Chloroplast oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria Peroxisomes Plasma membrane |
SOD, ASc, glutathione (GSH), flavonoids, Cu | As a therapeutic agent for treatment of inflammatory disorders | |
| H | 2 | O | 2 | Two electron reduction of | 3 | O | 2 | or univalent reduction of O | 2•− | Protonation reaction (acidic conditions) O | 2•− | + H | + | + HO | 2 | Normal cells protector during radiotherapy for cancer patients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | O | 2 | Reduction of transition metal (Fe | • | →H | 2 | O | 2 | + 2O | 2 | Glycolate + O | 2 | ( | Glycolate oxidase | ) → H | 2 | O | 2 | + Glyoxylate Fatty acids ( | β−oxidation | ) → Acetyl coenzyme + H | 2 | O | 2 | 1 ms | Act as a signaling molecule (low concentration of H | 2 | O | 2 | ), at high concentration of H | 2 | O | 2 | triggers tolerance to various stress, as a regulator of physiological processes (photorespiration and photosynthesis) | Chloroplast, Mitochondria, and Peroxisome |
CAT, POD (GPX and APX), peroxiredoxin, ASc, tocopherol, GSH, β-carotene, Se flavonoids, lipoic acid, | ||||||
| HO | 2 | • | Protonation of superoxide ions O | 2•− | + H | + | → HO | 2• | Attacks PUFA in the negatively charged membrane surface | Mitochondria, microsomes and peroxisomes | CAT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HO• (Three electron reduction of | 3 | O | 2 | )Eliminate excessive H | 2 | O | 2 | in the textile industry, pulp, and paper industry used for bleaching fibres and pulp, and as a bactericidal disinfectant in food processing and the pharmaceutical industry | Fenton reaction: H | 2 | O | 2 | + Fe | 2+ | → HO | • | + HO | − | + Fe | 3+ | Haber-Weiss reactions: O | 2•− | + H | 2 | O | 2 | → HO | • | + HO | − | + O | 2 | [11][17][25] | [51,57,65] | ||||||||
| 1 ps | Attack unsaturated fatty acids in membranes | Mitochondria | ASc, GSH, flavonoids, lipoic acid, proline | In aesthetics (mask treatment) to increase cellular oxygenation in the upper layers of facial epidermis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nitric oxide (NO•) | L-arginine + O | 2 | Nitric oxide synthase | → NO | • | + Citrulline | Intercellular messenger, the quencher of O | 2•− | , defense against various protozoa, fungi, and mycobacteria | Peroxisome, cytosol | GSHReducing the risk of diabetes mellitus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peroxynitrite (ONOO | − | ) | NO | • | + O | 2•− | → ONOO | − | React with amino acids residues in enzymes causing inactivation | Peroxiredoxin, Uric acid | GPX | Immune system booster | [10][26] | [42,66] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lipid hydroperoxide | Oxidation of PUFA | Tissue injuries and diseases | Mitochondrial membrane PUFA | GST | Protective role against neurogenerative diseases | [26][ | [66 | 27] | ,67] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Decreases the risk of tumours of the head and neck, oral, cavity and colon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glutathione | Anti-wrinkle formation, and as a modifier of skin smoothness | [28] | [68] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitamins | As a food preservative and bread improver, protective activity against heart diseases, reduced the risk of colorectal adenomas and prostate cancer, reduction of thyroid hormone levels | [29][30][31][32][33] | [69,70,71,72,73] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flavonoids | As cancer preventive agents, protection against type 2 diabetes Functional food additive | [34][35][36][37] | [74,75,76,77] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carotenoid | Anticancer agents, additive to cosmetics and multivitamin preparation Food colouring agent, pro-vitamin A in food and animal feed |
[38][39][40] | [29,38,78] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PUFA | Prevention of heart and inflammatory diseases | [41][42] | [79,80] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthetic Antioxidants | BHA | Extending the shelf life of vegetable oil, frying oil, animal feed, cereals, chewing gum, potato flakes and cosmetic products | [43][44][45] | [81,82,83] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BHT | Increasing the shelf life of animal fats, chewing gum, animal feed, vegetable oils | [44][45] | [82,83] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TBHQ | Used as preservative for enhancing storage stability of vegetable oils, margarine, fish oil, fried foods, essential oils, nuts, edible animal fats, butterfat, and packed fried foods | [44] | [82] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propyl gallate | As an antioxidant agent in foods and vegetable oil | [44] | [82] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BHA = butylated hydroxyl anisole; TBHQ = tert-butylhydroquinone; BHT = butylated hydroxyl toluene | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercially, synthetic antioxidants such as butylated hydroxyl anisole (BHA), butylated hydroxyl toluene (BHT), α-tocopherol and propyl gallate are used in foods, food packaging, cosmetics and pharmaceutical products [44][46][82,84]. However, the physical properties of BHT and BHA (high volatility and instability at elevated temperature), strict legislation on the use of synthetic food additives, and the carcinogenic nature of some synthetic antioxidants [47][48][49][50][85,86,87,88] have shifted the attention to finding antioxidants from natural sources that are pharmacologically potent and have low or no toxicity.
| 3+ |
| ) | ||||||
| O | 2•− | + Fe | 3+ | → | 1 |
The majority of ROS are generated when electrons leak from the chloroplastic electron transport systems during photosynthesis, from the mitochondrial electron transport chain during photorespiration, and from the peroxisomal membrane electron transport chain (Figure 2) [52][90]. Within plant cells, 1–2% of O2 consumption leads to the formation of superoxide (O2•−), and 1–5% of mitochondrial O2 consumption leads to the generation of H2O2 [3][45]. O2•− is generated during oxidisation of unsaturated fatty acids [53][91], from the activity of cytochrome P450 [54][92] and the cytochrome b5 family members [55][56][93,94]. Also, O2•− is produced in the peroxisome where xanthine oxidases catalyse the oxidation of xanthine and hypoxanthine to uric acid [3][45], and in the plasma membrane due to the reduction of O2 by NADPH oxidases [8][49].
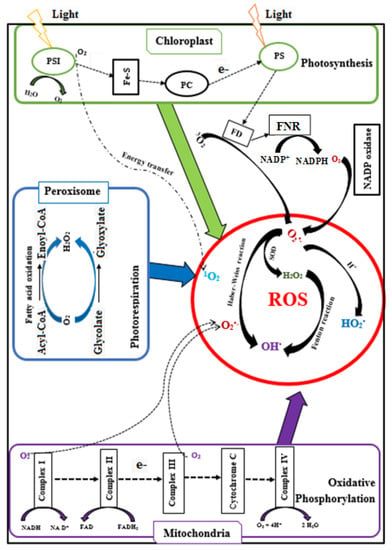
Superoxide ions (O2•−) are converted into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by the catalytic activity of SOD. H2O2 is also produced in peroxisomes when glycolate from the photorespiration is recycled. In addition, H2O2 can be formed by D-amino acid oxidase, urate oxidase, flavin oxidase, L-α-hydroxy acid oxidase, and fatty acyl-CoA oxidase, and by cell wall peroxidases. Reactive OH• is produced from the reaction of O2•− and H2O2 at neutral pH and ambient temperature (Haber–Weiss reaction) or from H2O2 during the Fenton reaction [58][96]. In contrast, a proton (H+) addition to O2•− generates perhyroxyl radicals (HO2•). In some cases, intracellular ROS could also form during auto-oxidation of small molecules (epinephrine, flavins, and hydroquinones) [59][60][97,98]. The singlet oxygen (1O2) is generated from the reaction of oxygen (3O2) with the triplet state of chlorophyll produced by the dissipation of insufficient energy during photosynthesis [3][45].
Under normal physiological conditions, ROS is neutralised by the cells’ antioxidant systems where antioxidant enzymes and antioxidant molecules maintain the delicate intracellular redox balance and mitigate undesirable cellular damage caused by ROS, Table 2 [6][9][48,50].
Different isozymes of SOD exist (Mn-SOD in mitochondria and peroxisome, Fe-SOD in the chloroplast, and Cu/Zn-SOD isozyme in cytosol) but they all participate in scavenging of O2•−. In addition to SOD, some antioxidants molecules (Vitamin C, glutathione, etc.) also eliminate O2•− [3][45]. Further, the individual or cumulative catalytic activity of catalase or peroxidases decomposes H2O2 into H2O and O2. CAT, peroxidases (GPX, APX), and SOD show a synergistic effect in the scavenging of O2•−. In addition to eliminating H2O2, GPX can protect cells by preventing intracellular lipid peroxidation [6][48]. APX may be more efficient compared to CAT or GPX in detoxification of H2O2 due to its higher affinity for H2O2. APX reduces H2O2 into H2O in chloroplasts, cytosol, mitochondria, and peroxisomes, and in the apoplastic space using Ascorbic acid (ASc) as an electron donor [61][99].
Algal cells accumulate ASc with 30–40% remaining in the chloroplast. Ascorbic acid is water-soluble and acts as a potent antioxidant because of its ability to donate electrons in enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions [62][100]. It protects cells by directly scavenging O2•−, HO2•− and regenerating the tocopherol from tocopheroxyl radicals [63][101]. All intracellular compartments generate the reduced form of glutathione, which plays a role as an excellent scavenger of many ROS such as O2•−, HO•, O3, NO2, lipid hydroperoxides [9][50] due to the redox-active thiol group that becomes oxidised when GSH reduces ROS [64][102]. Carotenoid also protects cells from light-induced oxidative stress by quenching 1O2 or dissipating excess heat (excitation energy) or scavenging peroxy radicals [3][6][45,48].
As the accumulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants in the cell depends on the external environment, manipulating cultivation conditions could enhance the intracellular antioxidant levels.