Alkylammonium salts have been used extensively to study the structure and function of potassium channels. Here, we use the long-chain, hydrophobic tetraoctylammonium (TOA+) to shed light on the structure of the inactivated state of KcsA, a tetrameric prokaryotic potassium channel. By the combined use of a thermal denaturation assay and the analysis of homo-Förster resonance energy transfer in a mutant channel containing a single tryptophan (W67) per subunit, we found that TOA+ binds the channel cavity with high affinity, either with the inner gate open or closed. Moreover, bound TOA+ induces a decrease in the affinity for K+ in the two characteristic K+ binding events to the channel selectivity filter at pH 7.0, when the channel inner gate is in the closed conformation. This is similar to that observed in the absence of TOA+ upon acidic-pH-induced channel inactivation. Therefore, this suggests that TOA+ binding by itself causes inactivation at pH 7.0 when the inner gate is closed. Furthermore, in apparent agreement with such conclusion, the presence of bound TOA+ in the pH 4.0 samples has only modest effects on the affinity of the two binding events for K+, likely because the channel is already inactivated. Finally, we also observed that TOA+ bound at the cavity, allosterically modifies the conformation of the pore helices, leading to longer W67-W67 intersubunit distances at any K+ concentration and both at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0. The changes in the pore helix conformation, along with the decreased affinity for K+ at pH 7.0 caused by TOA+, seen in both homo-FRET and thermal denaturation experiments, are very similar to those effects caused by inactivation at pH 4.0.
- potassium channels
- tetraalkylammonium salts
- protein thermal stability
- homo-FRET
- C-type inactivation
- binding affinity
- selectivity filter conformation
- steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy
1. Introduction
Quaternary ammonium salts (QAs) have long been used as channel blockers in the characterization of K
+ channels [1,2]. Initial studies were performed on the giant squid axon and
channels [1][2]. Initial studies were performed on the giant squid axon and
D. melanogaster Shaker channels [3,4,5,6,7,8,9], and it has already been suggested that QAs bind to the conduction pore, hence impeding the K
Shaker channels [3][4][5][6][7][8][9], and it has already been suggested that QAs bind to the conduction pore, hence impeding the K
+
current. Nonetheless, the length of the alkyl chains and the hydrophobicity of the different QAs determine differences in their molecular mechanisms of blockade. Thus, while the shorter-chain QAs seem to block the channel by simply obstructing the conduction pathway, the longer-chain, more hydrophobic derivatives are also believed to induce a slow channel inactivation process [6].
The elucidation of molecular details on the interaction between QAs and K
+
channels have advanced significantly with the resolution of the X-ray structures of QAs bound to KcsA, a prokaryotic K
+
channel from
Streptomyces lividans
. This channel is a homotetrameric membrane protein, where each monomer includes two α-helical transmembrane segments (TM1 and TM2) and N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic ends (
). The four C-terminal ends are arranged as a helical bundle, with a conformation that is sensitive to pH, acting as a channel gate (inner gate) [10]. On the other hand, the channel pore includes an aqueous cavity, a short tilted helix, and a selectivity filter (SF) with the sequence TVGYG, homologous to that of the eukaryotic K
+
channels [11], that constitutes a second channel gate (outer gate). The backbone carbonyls of the SF residues conform to four K
+ binding sites (sites S1–S4, from the extracellular to the intracellular side) [11,12], which can adopt different conformations at high or low K
binding sites (sites S1–S4, from the extracellular to the intracellular side) [11][12], which can adopt different conformations at high or low K
+ concentrations [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. The conformation at a low K
concentrations [12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22]. The conformation at a low K
+
concentration shows no ions at the center of the SF (sites S2 and S3), thus adopting a “collapsed” structure that impedes ion flow through it. K
+
binds to S1 and S4 in this conformation, with an average occupancy of just one ion distributed between those two sites. However, at high K
+
concentrations, a conformational change is induced by a second K
+
entering the filter, with a final average occupancy of two K
+ ions per channel, either at the S1–S3 or the S2–S4 positions, thus enabling ion conduction [12,13,17,22]. The nonpermeant Na
ions per channel, either at the S1–S3 or the S2–S4 positions, thus enabling ion conduction [12][13][17][22]. The nonpermeant Na
+
, on the other hand, does not induce such a conformational change and shows an average occupancy of one ion per channel at the S1 and S4 sites [23].
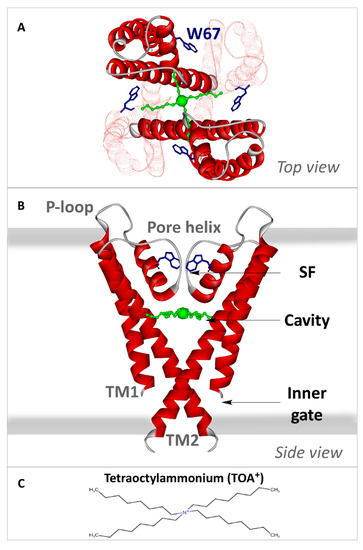
Transmembrane portion of KcsA. Crystallographic structure of the C-terminal truncated KcsA in the closed state with TOA
(green balls and sticks, with a larger ball representing the quaternary nitrogen) bound at the cavity (PDB: 2W0F). In the top view (panel (
)), two of the four subunits appear faintly drawn to facilitate the observation. The four W67 residues are depicted as blue sticks. In the side view (panel (
)), only two of the four monomers have been drawn as a solid red ribbon for the sake of clarity. Each monomer consists of two transmembrane helices (TM1 and TM2) connected by the P-loop region, a short, tilted pore helix, and the selectivity filter (SF). The thick grey lines indicate the membrane limits. Both views illustrate how the TOA
alkyl chains traverse the TM2 helix. Panel (
) represents the tetraoctylammonium ion in perspective.
In terms of functional activity, KcsA undergoes a cycle that includes four main different states, which reveals the concerted action of the two channel gates. At neutral pH and in the presence of K
+, the channel is in a closed/conductive resting state, whereby the cytoplasmic inner gate impedes ion flow, while the SF (the outer gate) displays a conductive form. At acidic pH, the inner gate opens, allowing ion flow in this open/conductive state and making KcsA a proton-activated channel [24,25,26]. However, this is not a stable state, and the outer gate evolves to a conformation reminiscent of C-type inactivation in eukaryotic K
, the channel is in a closed/conductive resting state, whereby the cytoplasmic inner gate impedes ion flow, while the SF (the outer gate) displays a conductive form. At acidic pH, the inner gate opens, allowing ion flow in this open/conductive state and making KcsA a proton-activated channel [24][25][26]. However, this is not a stable state, and the outer gate evolves to a conformation reminiscent of C-type inactivation in eukaryotic K
+ channels [27,28,29], which impedes ion flow in this open/inactivated form [27,28,30]. Such an inactivation process is modulated by a network of interactions that includes the so-called inactivation triad, i.e., residues E71, D80, and W67 from each subunit [17]. The cycle is completed when the pH returns to neutrality, which closes the inner gate, causing the transient closed/inactivated state to evolve to the initial closed/conductive resting state [31].
channels [27][28][29], which impedes ion flow in this open/inactivated form [27][28][30]. Such an inactivation process is modulated by a network of interactions that includes the so-called inactivation triad, i.e., residues E71, D80, and W67 from each subunit [17]. The cycle is completed when the pH returns to neutrality, which closes the inner gate, causing the transient closed/inactivated state to evolve to the initial closed/conductive resting state [31].
The crystallographic studies on KcsA complexed to different QAs reveal that the QA binding site for the hydrophilic ammonium head group is located in the internal water-filled cavity of the channel, directly underneath the innermost cation binding site (S4) of the SF (see
). The QAs are further stabilized in the cavity through the insertion of their alkyl chains of varying lengths into the hydrophobic channel wall so that this hydrophobic component becomes an important source of binding stability. Thus, hydrophobic compounds such as TBA
+
(tetrabutylammonium), THA
+
(tetrahexylammonium) and TOA
+ (tetrabutylammonium) bind to KcsA with very high affinity (nM range) [32,33]. In the particular case of TOA
(tetrabutylammonium) bind to KcsA with very high affinity (nM range) [32][33]. In the particular case of TOA
+
–KcsA complexes, the X-ray structure also reveals that the channel SF is in a collapsed conformation at pH 7.0 and high K
+
concentrations, i.e., the S2 and S3 K
+
binding sites are absent, similar to that previously seen in the collapsed X-ray structure of the channel alone in the presence of very low K
+
concentrations. This led those authors to conclude that such a collapsed structure is an inactivated state induced by the binding of TOA
+. However, those X-ray studies used an L90C KcsA mutant without the C-terminal domain, in which the additional presence of a Fab fragment bound to the extracellular channel loop is suspected to restrict the conformational plasticity of the SF [17,34]. Indeed, previous studies from our laboratory on several inactivated models of KcsA, some of which were also predicted as collapsed from X-ray studies, have shown that the stack of K
. However, those X-ray studies used an L90C KcsA mutant without the C-terminal domain, in which the additional presence of a Fab fragment bound to the extracellular channel loop is suspected to restrict the conformational plasticity of the SF [17][34]. Indeed, previous studies from our laboratory on several inactivated models of KcsA, some of which were also predicted as collapsed from X-ray studies, have shown that the stack of K
+
binding sites in the inactivated filters remains accessible to cations, as in the resting channel. Therefore, rather than being collapsed, the inactivated SF seems “resting-like” [35]. In apparent agreement with our observations, other authors found only modest conformational changes in the G77 residue during inactivation compared to the resting state [36], further supporting the tenet that the SF remains “resting-like” upon inactivation, with all four K
+
binding sites accessible to cations. Our goal in this paper is to contribute to the elucidation of this controversy on the conformation of the SF in the inactivated channel state by studying in detail the effects of TOA
+
binding to the KcsA channel, which, up to now, was believed to result in an inactivated channel with a collapsed SF [33].
2. TOA
+
Binds to Wild-Type KcsA with High Affinity and Diminishes the Thermal Stability of the Channel
An assay based on the thermal denaturation of the KcsA protein was previously developed to study the binding of different channel ligands to KcsA, including permeant or nonpermeant cations, membrane lipids, and others [35,37,38,39,40].
An assay based on the thermal denaturation of the KcsA protein was previously developed to study the binding of different channel ligands to KcsA, including permeant or nonpermeant cations, membrane lipids, and others [35][37][38][39][40].
A,B shows examples of thermal denaturation curves to illustrate that the addition of TOA
+
at micromolar concentrations to the detergent-solubilized channel leads to a concentration-dependent decrease in the thermal stability of the wild-type protein, both at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0. Because of the destabilizing effects of TOA
+
on KcsA, these experiments were always conducted at a constant 10-mM concentration of Na
+
to ensure that the tetrameric channel does not dissociate into monomers at the different TOA
+
concentrations tested (
A,B insets).
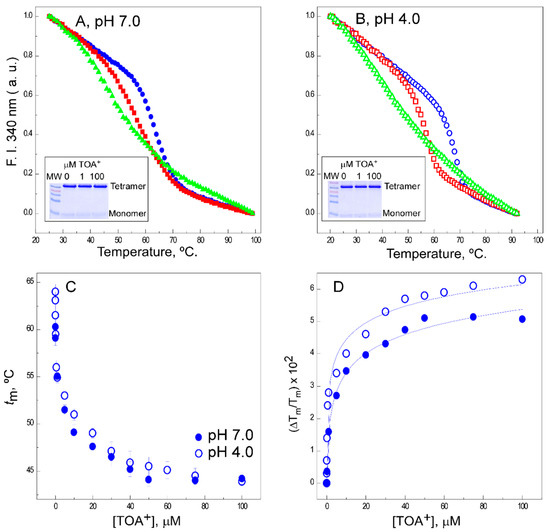
Effects of tetraoctylammonium (TOA
) on the thermal denaturation of wild-type (WT) KcsA. The intrinsic fluorescence at pH 7.0 (panel (
)) and pH 4.0 (panel (
)) and in the absence of TOA
(full and empty circles, respectively) or upon the addition of 1 µM (full and empty squares, respectively) or 100 µM (full and empty triangles, respectively) of TOA
. The insets show SDS-PAGE analysis of the different samples to illustrate the integrity of tetrameric WT KcsA at room temperature. Panel (
) shows the dependence of the midpoint temperature of the protein denaturation process (
) of WT KcsA with increasing concentrations of TOA
, either at pH 7.0 (●) or pH 4.0 (○). The results are the average
(in Celsius) ± S.D. from three independent titrations. Panel (
) illustrates the fitting of Equation (1) to the experimental data from Panel (
) (see Methods). The apparent dissociation constants for the TOA
-channel complexes and their 95% confidence intervals estimated at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0 were 1.8 (0.54–6.02) × 10
M and 3.6 (1.89–6.98) × 10
M, respectively. The observed differences between such dissociation constant (K
) values were not statistically significant.
The midpoint temperatures (
tm
s) from the thermal denaturation curves at different TOA
+
concentrations were used to build titration binding curves, such as those shown in
C. The fitting of such curves to a simple two-state binding equilibrium (see Methods) allows us to estimate the apparent dissociation constants (K
D
s) for the binding of TOA
+
to WT KcsA, which were in the 10
−7
and 10
−8
M range at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0, respectively (
D). These indicate that TOA
+
has a very high affinity for binding to the channel under either experimental condition. This is in contrast with previous observations on the binding to KcsA of tetrabutylammonium (TBA
+
), a shorter acyl chain QA, for which the binding affinity at pH 7.0 (K
D
~5 × 10
−9
M) is similar to that reported here for TOA
+
but drops five orders of magnitude at pH 4.0 (K
D
~3.5 × 10
−4 M) [35]. Such a dramatic difference in binding affinities could be rationalized based on the crystallographic information on the binding site for these compounds in the channel protein [12,32,33,41] As indicated in our introduction, the channel-bound QAs are further stabilized at the cavity through the interaction of their alkyl chains with the hydrophobic channel wall. In fact, the long alkyl chains of TOA
M) [35]. Such a dramatic difference in binding affinities could be rationalized based on the crystallographic information on the binding site for these compounds in the channel protein [12][32][33][41] As indicated in our introduction, the channel-bound QAs are further stabilized at the cavity through the interaction of their alkyl chains with the hydrophobic channel wall. In fact, the long alkyl chains of TOA
+
completely traverse the channel protein wall [33], so that hydrophobic interactions become particularly important to stabilize the TOA
+
–KcsA complex.
3. The Presence of TOA
+
in the Cavity Diminishes the Affinity of WT KcsA to Bind K
+
in the Closed Channel State
The availability of cation binding sites in the SF of the TOA
+
–KcsA complex has been explored by thermal denaturation experiments of such complexes in the presence of increasing concentrations of either permeant K
+
or nonpermeant Na
+
. In these experiments, an excess TOA
+
concentration of 100 µM, identical to that used in the crystallographic studies referenced above, was maintained constant throughout the titrations with the cations.
A,C shows representative binding curves for Na
+
, at both pH 7.0 and pH 4.0, respectively. Binding curves for Na
+
to WT KcsA in the absence of TOA
+
[37] are also included in all panels to facilitate comparison.
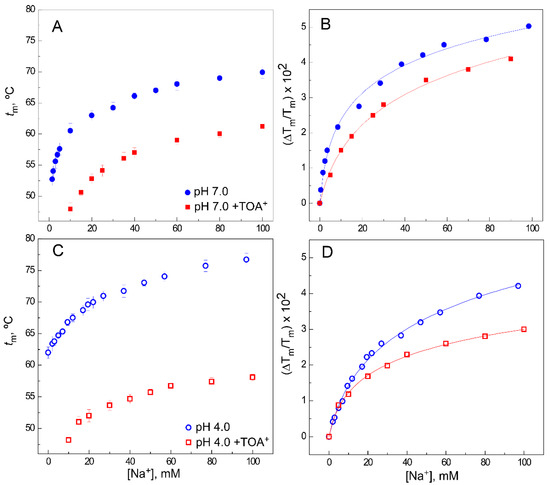
Effect of TOA
on Na
binding to WT KcsA. Panels (
,
) illustrate Na
binding to the WT KcsA channel at pH 7.0 (panel (
)) or pH 4.0 (panel (
)), in the absence (circles) and presence (squares) of 100 µM TOA
, monitored through the Na
-concentration-dependence of the midpoint temperature of the protein denaturation process (
). Each experimental point is the average
(in Celsius) ± S.D. (
= 3). Panels (
,
) show the fitting of Equation (1) to the experimental data from panels (
,
), respectively (see Methods). The apparent K
values estimated for the above binding events are given in
.
Apparent dissociation constants (K
s) for the binding of Na
and K
to the WT KcsA channel at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0 in the absence or presence of 100 µM TOA
. Mean K
values given here come from the experiments reported in
,
and Figure 5. Since the estimated K
values are derived from a logarithmic function (Equation (1)), we used the 95% confidence intervals of these values for statistical comparisons instead of giving mean ± S.D. values since only parametric analysis is appropriate on the logarithmic scale for such data.
Significant difference with respect to the same sample in the absence of TOA
(
< 0.05).
Significant difference with respect to the same sample in the absence of TOA
at pH 4.0 (
< 0.05).
| Tested Cation | Sets of Binding Sites Detected | WT KcsA, pH 7.0 | WT KcsA, pH 4.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Added TOA+ | +100 µM TOA+ | No Added TOA+ | +100 µM TOA+ | ||||||
| KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | ||
| Na+ | 1 | 3.3 × 10−3 | (2.5−4.3) × 10−3 b | 1.4 × 10−2 | (0.9–2.1) × 10−2 a,b | 7.7 × 10−3 | (6.6–8.9) × 10−3 | 1.3 × 10−2 | (0.9–1.8) × 10−2 a,b |
| K+ | 2 | 2.8 × 10−7 | (2.0–3.9) × 10−7 b | 5.0 × 10−5 | (3.3–7.5) × 10−5 a,b | 3.8 × 10−4 | (2.1–6.9) × 10−4 | 1.9 × 10−4 | (0.9–4.9) × 10−4 |
| 4.2 × 10−3 | (3.2–5.4) × 10−3 b | 1.6 × 10−3 | (1.2–2.1) × 10−2 a,b | 1.1 × 10−1 | (0.7–1.5) × 10−1 | 1.0 × 10−1 | (0.8−1.4) × 10−1 | ||
| W67 KcsA, pH 7.0 | W67 KcsA, pH 4.0 | ||||||||
| KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | ||
| K+ | 2 | 1.0 × 10−5 | (0.7–1.5) × 10−5 b | 3.2 × 10−5 | (1.2–8.6) × 10−5 b | 4.8 × 10−4 | (2.7–8.7) × 10−4 | 1.2 × 10−4 | (1.0−1.4) × 10−4 a,b |
| 9.4 × 10−4 | (5.8–14.0) × 10−4 b | 5.2 × 10−3 | (3.3–8.1) × 10−3 a,b | 1.4 × 10−2 | (1.1–1.7) × 10−2 | 8.6 × 10−3 | (7.1–10.4) × 10−3 a,b | ||
| KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | ||
| K+ | 1 | 4.5 × 10−4 | (3.6–5.4) × 10−4 b | 4.3 × 10−3 | (3.4–5.2) × 10−3 a,b | 4.4 × 10−2 | (4.3–4.6) × 10−2 | 1.9 × 10−2 | (1.2–2.5) × 10−2 a,b |
In these conditions, it is known that Na
+
binds to a single set of sites provided by the S1 and S4 crystallographic sites in a nonconductive pore conformation [23] (PDB 2ITC). This binding process has a K
D
in the millimolar range, slightly higher at pH 4.0 than at pH 7.0 (
), which should correspond to the overall K
D
for Na
+
binding to the alluded S1 and S4 sites. In the TOA
+
–KcsA complex, access to the S4 site is blocked by the presence of TOA
+
; however, there is still Na
+
binding to the available S1 site (
A,C), although the extent of thermal stabilization (on top of the thermal destabilization caused by TOA
+
) is lower and its K
D
decreases an order of magnitude compared to the samples in the absence of TOA
+
(
B,D and
). These observations on Na
+
binding to the available S1 site in the QA–KcsA complex are quite similar at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0 and analogous to the results previously seen in the presence of TBA
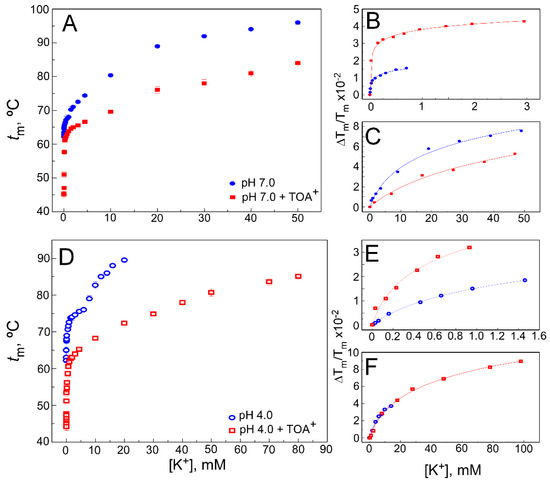
Effect of TOA
on K
binding to WT KcsA. Panels (
,
) illustrate K
binding to the WT KcsA channel in the absence (circles) and presence of 100 µM TOA
(squares) at pH 7.0 (panel (
)) or pH 4.0 (panel (
)), monitored through the K
-concentration-dependence of the midpoint temperature of the protein denaturation process (
). Each experimental point is the average
m (in Celsius) ± S.D. (
= 3). When the low (panels (
,
)) and high (panels (
,
)) K
concentration ranges are analyzed separately, Equation (1) adequately fits the data from panels (
,
), indicating that two different sets of K
binding sites are present in the WT KcsA. The apparent K
values estimated for the above binding events are given in
.
Experiments similar to the above were also conducted at increasing K
+
concentrations instead of Na
+
. As reported previously in the absence of QAs [37], K
+
binds to two different sets of binding sites in WT KcsA at pH 7.0 (
Figure 3A), which is consistent with crystallographic evidence on the ability of permeant cations to induce concentration-dependent transitions between nonconductive and conductive conformations of the SF [12,13]. The first set of such sites, assigned to the crystal S1 and S4 sites, shows a high affinity for K
A), which is consistent with crystallographic evidence on the ability of permeant cations to induce concentration-dependent transitions between nonconductive and conductive conformations of the SF [12][13]. The first set of such sites, assigned to the crystal S1 and S4 sites, shows a high affinity for K
+
(micromolar K
D
), thus securing displacement of potentially competing nonpermeant cations. The second set of sites results from the contribution of all S1 to S4 crystallographic sites, is available only to permeant cations when the filter is in the conductive conformation and shows low affinity (millimolar K
D
) to favor cation dissociation and permeation.
B,C also shows that in the presence of a saturating concentration of TOA
+
, two different sets of sites are still available for K
+
binding in the TOA
+
–KcsA complex, which, therefore, is clearly noncollapsed. This indicates that the TOA
+
-bound channel retains the ability to undergo K
+
concentration-dependent transitions between different conformations of its SF. Despite such similarity, it is observed that the binding curve, mainly in the lower K
+
concentration range, shows a lower slope than in the absence of TOA
+
, indicating a loss in K
+
binding affinity. Indeed,
shows that the K
D
values for the two K
+
binding events in the TOA
+
–KcsA complex are increased with respect to those in the absence of the QA. This is particularly noticeable in the first, high affinity K
+
binding event in which the K
D
values differed by approximately two orders of magnitude. It should be noted that in the presence of TOA
+
, the entrance to the channel’s SF through the S4 site is permanently blocked by the bound TOA
+
. In the first K
+
binding event, which takes place in the low K
+
concentration range, the SF is in a nonconductive state, collapsed at the S2/S3 sites. This, along with the TOA
+
blockade of the S4 site, indicates that the decreased affinity for K
+
under the TOA
+
blockade should be attributed to the binding of K
+
to the S1 site in the nonconductive channel state. Nonetheless, as the K
+
concentration increases, a second K
+
binding event takes place, causing the filter to undergo a conformational transition in which the permeant cation reaches internal binding sites within the pore to provide the characteristic increase in thermal stability to the protein.
D shows the results from experiments similar to those described in the previous paragraph but now conducted at pH 4.0 to induce channel inactivation. These experiments are further complicated because pH 4.0 causes an additional thermal stabilization of the channel protein compared to pH 7.0 [35]. Still, as described above for the resting channel at pH 7.0, both in the WT KcsA alone or when complexed to TOA
+
, the two sets of K
+
binding sites are also detected in the K
+
titrations of all samples at pH 4.0, when the channel is inactivated (
E,F). This was previously reported as a common feature in three different models of inactivated KcsA channels [35]. As expected for an inactivated state, all WT KcsA samples at pH 4.0 show a decrease in the affinity for K
+
. Indeed,
shows that when compared to the pH 7.0 samples, the K
D
s for K
+
binding at pH 4.0 increase approximately three and two orders of magnitude, respectively, for the first and second K
+
binding events. Such effects on the binding affinity caused by pH-induced channel inactivation are comparable to those caused by the presence of TOA
+
bound to the resting state of the channel at pH 7.0. Interestingly, in contrast to TOA
+
, the shorter chain-length TBA
+ does not critically change the interaction between the SF and the permeant cations [32,33,39].
does not critically change the interaction between the SF and the permeant cations [32][33][39].
4. Discussion
In this paper, a combined approach using thermal denaturation and homo-FRET assays was used to characterize the effects of TOA
+
binding to KcsA. The addition of TOA
+
to the channel protein induces a concentration-dependent decrease in protein thermal stability, opposite to the stabilizing effect observed of a shorter-chain QA, TBA
+ [35,39]. When comparing the binding of these two QAs at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0, we observed that the closed-channel state at pH 7.0 exhibits a similar K
[35][39]. When comparing the binding of these two QAs at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0, we observed that the closed-channel state at pH 7.0 exhibits a similar K
D
for both TOA
+
and TBA
+
. On the other hand, when the inner gate is open by pH 4.0, the affinity for TOA
+
remains unaffected, while that for TBA
+
decreases five orders of magnitude [35]. Since the only difference between these QA blockers is the length of their alkyl chains, it is concluded that the four extra carbon atoms in TOA
+ are critical for better hydrophobic interaction with the protein channel wall. There is no crystallographic information on QA–KcsA complexes at pH 4.0, but based on related evidence [42,43,44], it seems reasonable to expect that the widening of the channel cavity accompanies the acidic-pH-induced untangling of the cytoplasmic α-helical bundle and the bending of the TM2 segment away from the symmetry axes of the channel. Such a widening of the cavity could diminish the hydrophobic component in the binding of the shorter TBA
are critical for better hydrophobic interaction with the protein channel wall. There is no crystallographic information on QA–KcsA complexes at pH 4.0, but based on related evidence [42][43][44], it seems reasonable to expect that the widening of the channel cavity accompanies the acidic-pH-induced untangling of the cytoplasmic α-helical bundle and the bending of the TM2 segment away from the symmetry axes of the channel. Such a widening of the cavity could diminish the hydrophobic component in the binding of the shorter TBA
+
, making it prompt to dissociate from the complex. However, the longer acyl chains of TOA
+
extend further so as to traverse the channel protein wall completely [33]. This should keep it firmly associated with the hydrophobic residues even in the open conformation at pH 4.0, thus explaining why it maintains a high binding affinity. The X-ray crystallographic data at pH 7.0 also revealed that while TBA
+
establishes van der Waals interactions with I100 and F103 residues from the cavity wall (TM2 helix), TOA
+
adds interactions with L36 (from the TM1 helix), T74 (near the SF), and G99 and S102 (from the TM2 helix) [33]. These additional interactions between the protein and the QA should be involved in providing a higher affinity for the binding of TOA
+
to the open state of the channel compared to TBA
+, thus preventing its dissociation from the complex, as suggested by the earlier electrophysiological studies [5,6]. Another difference in the interaction between these two QAs with the channel consists of a change on the side-chain rotamer of the F103 residue in the TOA
, thus preventing its dissociation from the complex, as suggested by the earlier electrophysiological studies [5][6]. Another difference in the interaction between these two QAs with the channel consists of a change on the side-chain rotamer of the F103 residue in the TOA
+
–bound complex. The possible relevance of such observation is discussed below.
A thermal denaturation assay was also used to characterize the interaction of WT KcsA with Na
+
and K
+
in the presence of TOA
+
, in terms of both the number of binding events detected and their respective affinities. In the case of Na
+
, a single binding event with a slightly lower affinity than the control, in the absence of TOA
+
(see
), was observed, which corresponds to Na
+
binding to its only available site, the extracellular S1 binding site. These observations on Na
+
binding were quite similar at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0, or in the presence of TBA
+
, as indicated by the results. In contrast, the K
+
binding studies indicated that the presence of bound TOA
+
specifically affects the binding of the permeant species and is sensitive to the inner gate opening by the acidic pH. Thus, it is concluded that the effect of TOA
+
on the ion–protein interactions specifically affects the binding to the channel of the permeant K
+
, and, therefore, monitoring of K
+
binding becomes a useful tool to detect both the acidic pH-induced conformational change of the SF to an inactivated state and the changes induced by TOA
+
. As mentioned in the Introduction section, binding of K
+
to WT KcsA is described by two consecutive binding events, with dissociation constants in the µM and mM range, respectively. Here, it is shown that in the presence of TOA
+
bound to the channel cavity, the two K
+
binding events still remain, suggesting that the SF, rather than collapsing, retains the ability to accommodate K
+
at the stack of K
+
binding sites and to undergo the K
+
-concentration-dependent conformational transition. Nonetheless, bound TOA
+
induces a decrease in the affinity for K
+
in both binding events at pH 7.0 when the inner gate is in the closed conformation. This is similar to that observed in the absence of TOA
+
upon acidic-pH-induced channel inactivation. Therefore, this suggests that TOA
+
binding by itself causes inactivation at pH 7.0 when the inner gate is closed. Indeed, a similar decrease in the affinity of the channel for K
+ at pH 7.0 was also detected in mutant channels where the inactivation process is favored [35,45]. Furthermore, in apparent agreement with such conclusion, the presence of bound TOA
at pH 7.0 was also detected in mutant channels where the inactivation process is favored [35][45]. Furthermore, in apparent agreement with such conclusion, the presence of bound TOA
+
in the pH 4.0 samples has only modest effects on the affinity of the two binding events for K
+
, likely because the channel is already inactivated. We have no evidence to propose a molecular mechanism to explain how TOA
+
induces channel inactivation at neutral pH, but it could be speculated that the change on the side-chain rotation of the F103 residue in the TOA
+–bound complex indicated above could be involved. The reason to speculate on such a possibility is that F103 is believed to be an essential residue in the allosteric crosstalk between the inner and outer channel gates [46,47,48] involved in the regulation of the channel’s functional cycle.
–bound complex indicated above could be involved. The reason to speculate on such a possibility is that F103 is believed to be an essential residue in the allosteric crosstalk between the inner and outer channel gates [46][47][48] involved in the regulation of the channel’s functional cycle.
In order to gain structural information on the KcsA–TOA
+
–K
+
complex, we use the quadruple mutant KcsA W26, 68, 87, 113F, which carries a single tryptophan (W67) as a fluorescent reporter of the SF conformation and dynamics. In this WT–like mutant channel, the homo-FRET process between the W67 residues from each subunit allows us to estimate the changes in steady-state anisotropy and the intersubunit lateral distances according to the type and concentration of cations within the SF [34]. Here, we first characterize in detail the acidic-pH-induced inactivated state in the absence of QAs. Even though the thermal denaturation assay from above detected two consecutive binding events for K
+
at pH 4.0, the homo-FRET process is only sensitive to the transition from the nonconductive to the inactivated state. The analysis of this latter event shows a clear decrease in K
+
binding affinity at intermediate concentrations of the cation, although the final conformation at saturating amounts of K
+
is almost identical to that observed in the closed-conductive state.
As to the effects of TOA
+
binding on the W67 mutant channel, we observed that TOA
+
bound at the cavity allosterically modifies the conformation of the pore helices, leading to longer W67–W67 intersubunit distances at any K
+
concentration at both pH 7.0 and pH 4.0. This loosening in the outer mouth packing seems consistent with the observed decrease in the thermal stability of the protein. The changes in the pore helix conformation, along with the decreased affinity for K
+
at pH 7.0 caused by TOA
+
, seen in both homo-FRET and thermal denaturation experiments, are very similar to those effects caused by inactivation at pH 4.0. Therefore, as in the WT channel, it is concluded that TOA
+
binding at pH 7.0 also causes channel inactivation in the W67 KcsA mutant.
The intersubunit distances determined from the time-resolved anisotropy decays can be compared to those calculated from the published X-ray data, which are usually obtained in the presence of Fab fragments bound to the channel to improve crystal resolution. Even though there are no X-ray data on WT KcsA at pH 4.0, some constitutively open mutant channels were successfully crystallized in different conditions [24,47,49].
The intersubunit distances determined from the time-resolved anisotropy decays can be compared to those calculated from the published X-ray data, which are usually obtained in the presence of Fab fragments bound to the channel to improve crystal resolution. Even though there are no X-ray data on WT KcsA at pH 4.0, some constitutively open mutant channels were successfully crystallized in different conditions [24][47][49].
summarizes the W67–W67 distances calculated from the time-resolved anisotropy decays and compares them to the W67–W67 Cδ2-Cε2 lateral distances derived from X-ray data.
It is observed that the W67–W67 lateral distances calculated from the anisotropy decays of the open/inactivated W67 KcsA channel at pH 4.0 and high K
+
concentrations (15.3 ± 0.1 Å) are almost identical to those W67–W67 Cδ2-Cε2 distances determine from X-ray data obtained in the presence of an intracellular Fab fragment (15.2 Å; PDB 3PJS), but not when an extracellular Fab was used to form the crystals (17.7 Å; PDB 3F5W). These results highlight how the binding of the extracellular Fab fragment alters the conformation of the extracellular loop and the SF dynamics. In fact, the same Fab fragment has been described to have a profound effect on KcsA inactivation [17]. In this respect, it should be noted that the available X-ray data on the TOA
+
–KcsA complex was obtained in the presence of the extracellular Fab fragment [33]. Based on such data, the authors concluded that the SF conformation in the TOA
+
–inactivated channel is a collapsed structure, similar to that detected in KcsA alone at low K
+
concentrations [50] (PDB 1K4D), where the inner S2 and S3 K
+
binding sites are absent. In contrast to such a conclusion, we find that the stack of K
+
binding sites, although with a lower affinity, remains accessible in the TOA
+
–KcsA complex and that the W67–W67 intersubunit distances are very much like those found in the resting channel in the absence of TOA
+
. We attribute such discrepancies to the perturbing effects of the extracellular Fab fragment and/or to the C-terminal deletion on the X-ray data and conclude that rather than being collapsed, the inactivated TOA
+
–bound state of the SF at pH 7.0 and high K
+
has a “resting-like” conformation. This is not unique to the inactivated TOA
+–induced state as it is shared by several inactivated models of KcsA [35,51,52], and it seems, therefore, a general feature of the inactivated SF of KcsA.
–induced state as it is shared by several inactivated models of KcsA [35][51][52], and it seems, therefore, a general feature of the inactivated SF of KcsA.
In summary, the results obtained by the combination of the thermal denaturation assay and the analysis of the homo-FRET process among the W67 residues of each subunit in KcsA reinforce the argument that the long chain QA TOA
+ stabilizes an inactivated conformation of the SF, as suggested by earlier electrophysiological studies [5,6], which is characterized by a lower affinity for K
stabilizes an inactivated conformation of the SF, as suggested by earlier electrophysiological studies [5][6], which is characterized by a lower affinity for K
+
without affecting the interaction with Na
+
. However, in contrast to the conclusion from the X-ray studies, this inactivated state is not collapsed but, rather, in a “resting-like” conformation, where the differences between the conductive and inactivated SFs are more subtle. However, if the inactivated SF is “resting-like”, what makes it nonconductive? Earlier electrophysiological work concluded that inactivation is associated with a loss of K
+ from the selectivity filter in potassium channels [53,54] and that the presence of the cations inside the selectivity filter is fundamental to stabilizing it in the conductive conformation [55,56,57]. In this respect, the drop in K
from the selectivity filter in potassium channels [53][54] and that the presence of the cations inside the selectivity filter is fundamental to stabilizing it in the conductive conformation [55][56][57]. In this respect, the drop in K
+
affinity detected in our thermal denaturation and homo-FRET experiments would increase the probability of partial K
+
depletion from the filter, thus hampering ion conduction.
References
- Yellen, G. The moving parts of voltage-gated ion channels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1998, 31, 239–295.
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes; Mass Sinauer Assoc. Inc.: Sunderland, UK, 2001; p. 5. ISBN 0-87893-321-2.
- Armstrong, C.M.; Binstock, L. Anomalous rectification in the squid giant axon injected with tetraethylammonium chloride. J. Gen. Physiol. 1965, 48, 859–872.
- Hille, B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J. Gen. Physiol. 1967, 50, 1287–1302.
- Armstrong, C.M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1969, 54, 553–575.
- Armstrong, C.M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1971, 58, 413–437.
- Choi, K.L.; Aldrich, R.W.; Yellen, G. Tetraethylammonium blockade distinguishes two inactivation mechanisms in voltage-activated K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5092–5095.
- Heginbotham, L.; MacKinnon, R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron 1992, 8, 483–491.
- Choi, K.L.; Mossman, C.; Aubé, J.; Yellen, G. The internal quaternary ammonium receptor site of Shaker potassium channels. Neuron 1993, 10, 533–541.
- Uysal, S.; Vasquez, V.; Tereshko, V.; Esaki, K.; Fellouse, F.A.; Sidhu, S.S.; Koide, S.; Perozo, E.; Kossiakoff, A. Crystal structure of full-length KcsA in its closed conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6644–6649.
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais, C.J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The structure of the potassium channel: Molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77.
- Zhou, Y.; Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Kaufman, A.; MacKinnon, R. Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 Å resolution. Nature 2001, 414, 43–48.
- Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Zhou, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Energetic optimization of ion conduction rate by the K+ selectivity filter. Nature 2001, 414, 37–42.
- Wylie, B.J.; Bhate, M.P.; McDermott, A.E. Transmembrane allosteric coupling of the gates in a potassium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 185–190.
- Zhou, Y.; MacKinnon, R. The occupancy of ions in the K+ selectivity filter: Charge balance and coupling of ion binding to a protein conformational change underlie high conduction rates. J.Mol.Biol. 2003, 333, 965–975.
- Chill, J.H. NMR study of the tetrameric KcsA potassium channel in detergent micelles. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 684–698.
- Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Cuello, L.G.; Zhao, Y.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Roux, B.; Perozo, E. Molecular determinants of gating at the potassium-channel selectivity filter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 311–318.
- Baker, K.A.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Kwiatkowski, W.; Choe, S.; Riek, R. Conformational dynamics of the KcsA potassium channel governs gating properties. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 1089–1095.
- Ader, C.; Schneider, R.; Hornig, S.; Velisetty, P.; Vardanyan, V.; Giller, K.; Ohmert, I.; Becker, S.; Pongs, O.; Baldus, M. Coupling of activation and inactivation gate in a K-channel: Potassium and ligand sensitivity. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2825–2834.
- Bhate, M.P.; Wylie, B.J.; Tian, L.; McDermott, A.E. Conformational dynamics in the selectivity filter of KcsA in response to potassium ion concentration. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 401, 155–166.
- Imai, S.; Osawa, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Shimada, I. Structural basis underlying the dual gate properties of KcsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6216–6221.
- Cheng, W.W.L.; McCoy, J.G.; Thompson, A.N.; Nichols, C.G.; Nimigean, C.M. Mechanism for selectivity-inactivation coupling in KcsA potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5272–5277.
- Lockless, S.W.; Zhou, M.; MacKinnon, R. Structural and thermodynamic properties of selective ion binding in a K+ channel. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e121.
- Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Jogini, V.; Sompornpisut, A.; Perozo, E. A molecular mechanism for proton-dependent gating in KcsA. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1126–1132.
- Hirano, M.; Onishi, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Ide, T. Role of the KcsA channel cytoplasmic domain in pH-dependent gating. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2157–2162.
- Posson, D.J.; Thompson, A.N.; McCoy, J.G.; Nimigean, C.M. Molecular interactions involved in proton-dependent gating in KcsA potassium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 142, 613–624.
- Hoshi, T.; Zagotta, W.N.; Aldrich, R.W. Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: Effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron 1991, 7, 547–556.
- Liu, Y.; Jurman, M.E.; Yellen, G. Dynamic rearrangement of the outer mouth of a K+ channel during gating. Neuron 1996, 16, 859–867.
- Gao, L.; Mi, X.; Paajanen, V.; Wang, K.; Fan, Z. Activation-coupled inactivation in the bacterial potassium channel KcsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17630–17635.
- Li, J.; Ostmeyer, J.; Cuello, L.G.; Perozo, E.; Roux, B. Rapid constriction of the selectivity filter underlies C-type inactivation in the KcsA potassium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 1408–1420.
- Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Perozo, E. The gating cycle of a K+ channel at atomic resolution. Elife 2017, 6, e28032.
- Yohannan, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Crystallographic Study of the Tetrabutylammonium Block to the KcsA K+ Channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 806–814.
- Lenaeus, M.J.; Burdette, D.; Wagner, T.; Focia, P.J.; Gross, A. Structures of KcsA in complex with symmetrical quaternary ammonium compounds reveal a hydrophobic binding site. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5365–5373.
- Renart, M.L.; Giudici, A.M.; Poveda, J.A.; Fedorov, A.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Prieto, M.; Díaz-García, C.; González-Ros, J.M.; Coutinho, A. Conformational plasticity in the KcsA potassium channel pore helix revealed by homo-FRET studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6215–6228.
- Giudici, A.M.; Renart, M.L.; Díaz-García, C.; Morales, A.; Poveda, J.A.; González-Ros, J.M. Accessibility of cations to the selectivity filter of KcsA in the inactivated state: An equilibrium binding study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 689.
- Devaraneni, P.K.; Komarov, A.G.; Costantino, C.A.; Devereaux, J.J.; Matulef, K.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Semisynthetic K+ channels show that the constricted conformation of the selectivity filter is not the C-type inactivated state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15698–15703.
- Renart, M.L.; Triano, I.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Gómez, J.; González Ros, J.M. Ion binding to KcsA: Implications in ion selectivity and channel gating. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9480–9487.
- Triano, I.; Barrera, F.N.; Renart, M.L.; Molina, M.L.; Fernandez-Ballester, G.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernandez, A.M.; Encinar, J.A.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Otzen, D.; et al. Occupancy of nonannular lipid binding sites on KcsA greatly increases the stability of the tetrameric protein. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5397–5404.
- Renart, M.L.; Montoya, E.; Giudici, A.M.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Morales, A.; González-Ros, J.M. Selective exclusion and selective binding both contribute to ion selectivity in KcsA, a model potassium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15552–15560.
- Montoya, E.; Lourdes Renart, M.; Marcela Giudici, A.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Morales, A.; González-Ros, J.M. Differential binding of monovalent cations to KcsA: Deciphering the mechanisms of potassium channel selectivity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 779–788.
- Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Kutluay, E.; Jogini, V.; Zhao, Y.; Heginbotham, L.; Roux, B. Mechanism of Intracellular Block of the KcsA K+ Channel by Tetrabutylammonium: Insights from X-ray Crystallography, Electrophysiology and Replica-exchange Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 649–662.
- Perozo, E.; Marien Cortes, D.; Cuello, L.G. Three-dimensional architecture and gating mechanism of a K+ channel studied by EPR spectroscopy. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 459–469.
- Perozo, E.; Cortes, D.M.; Cuello, L.G. Structural rearrangements underlying K+-channel activation gating. Science 1999, 285, 73–78.
- Iwamoto, M.; Shimizu, H.; Inoue, F.; Konno, T.; Sasaki, Y.C.; Oiki, S. Surface structure and its dynamic rearrangements of the KcsA potassium channel upon gating and tetrabutylammonium blocking. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28379–28386.
- Renart, M.L.; Montoya, E.; Fernandez, A.M.; Molina, M.L.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Ayala, J.L.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Gomez, J.; Morales, A.; et al. Contribution of ion binding affinity to ion selectivity and permeation in KcsA, a model potassium channel. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 3891–3900.
- Cuello, L.G.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Pan, A.C.; Gagnon, D.G.; Dalmas, O.; Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Chakrapani, S.; Roux, B.; Perozo, E. Structural basis for the coupling between activation and inactivation gates in K+ channels. Nature 2010, 466, 272–275.
- Cuello, L.G.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Perozo, E. Structural mechanism of C-type inactivation in K+ channels. Nature 2010, 466, 203–208.
- Pan, A.C.; Cuello, L.G.; Perozo, E.; Roux, B. Thermodynamic coupling between activation and inactivation gating in potassium channels revealed by free energy molecular dynamics simulations. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 138, 571–580.
- Uysal, S.; Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Koide, S.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Perozo, E. Mechanism of activation gating in the full-length KcsA K+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11896–11899.
- Zhou, M.; Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Mann, S.; MacKinnon, R. Potassium channel receptor site for the inactivation gate and quaternary amine inhibitors. Nature 2001, 411, 657–661.
- Matulef, K.; Komarov, A.G.; Costantino, C.A.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Using protein backbone mutagenesis to dissect the link between ion occupancy and C-Type inactivation in K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17886–17891.
- Matulef, K.; Annen, A.W.; Nix, J.C.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Individual Ion Binding Sites in the K+ Channel Play Distinct Roles in C-type Inactivation and in Recovery from Inactivation. Structure 2016, 24, 750–761.
- Baukrowitz, T.; Yellen, G. Modulation of K+ current by frequency and external [K+]: A tale of two inactivation mechanisms. Neuron 1995, 15, 951–960.
- Xu, Y.; Bhate, M.P.; McDermott, A.E. Transmembrane allosteric energetics characterization for strong coupling between proton and potassium ion binding in the KcsA channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8788–8793.
- Swenson, R.P.; Armstrong, C.M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature 1981, 427–429.
- Rasmusson, R.L.; Morales, M.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Campbell, D.L.; Brahmajothi, M.V.; Strauss, H.C. Inactivation of voltage-gated cardiac K+ channels. Circ. Res. 1998, 739–750.
- Santos, J.S.; Syeda, R.; Montal, M. Stabilization of the conductive conformation of a voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channel: The lid mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16619–16628.
