Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Cristina Silvia Polo López and Version 3 by Catherine Yang.
Historic, listed, or unlisted, buildings account for 30% of the European building stock. Since they are complex systems of cultural, architectural, and identity value, they need particular attention to ensure that they are preserved, used, and managed over time in a sustainable way. This implies a demand for retrofit solutions able to improve indoor thermal conditions while reducing the use of energy sources and preserving the heritage significance. Often, however, the choice and implementation of retrofit solutions in historic buildings is limited by socio-technical barriers (regulations, lack of knowledge on the hygrothermal behaviour of built heritage, economic viability, etc.).
- compatible retrofit solutions
- built heritage
- energy efficiency
- sustainable preservation
1. A Whole Building Approach in the IEA-SHC Task 59 Project
As discussed in the Section 2.1, Section 2.2, Section 2.3 and Section 2.4, the different aspects of the IEA-SHC Task 59 project she Iall be seen in the broader context of the sustainable improvement of historic buildings. In this sense, a “whole building approach” is necessary, meant as an “integrated” approach that can maximize the strengths of different disciplines.
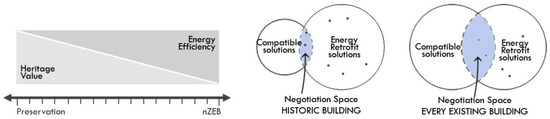
For this reason, the IEA-SHC Task 59 project has gathered a solid knowledge base on how to cost-effectively save energy in the retrofit of historic and protected buildings, thanks to the existing research and new findings shared by the partners involved in this interdisciplinary collaboration. The new approach developed to change the negotiation space of suitable retrofit measures was presented in a paper resulting from the IEA-SHC Task 59 [1][23] (Figure 1).
For existing buildings without any heritage values to be considered during the renovation process, the choice of suitable solutions is much more extensive than for historic buildings. For the latter instead, the negotiation space includes all interventions that are considered compatible with the building characteristics and it strongly depends on the interaction of the involved stakeholders. The integration of all compatible solutions in this negotiation space would result in the lowest possible energy demand of the building.
The concept of “lowest possible energy demand” introduced in [1][23] acknowledges that in historic buildings the preservation of the heritage building value may sometimes result in absolute constraints on certain interventions. Similarly, it also spans a space from the concept of reducing energy demand close to the nZEB standard but do this with a focus on preserving as much as possible of the buildings aesthetic value to that of reducing the energy demand as much as possible while preserving all the buildings heritage values. Reality will lie in between, depending on the value of the building, and it will also consider additional parameters like comfort and economic feasibility [1][23].
2. Towards a Sustainable Approach in the EN 16883:2017 Standard
The European Committee for Standardisation has developed a suitable procedure to improve the energy performance of historical buildings, detailed in the EN 16883:2017 [2][21] standard “Conservation of cultural heritage-Guidelines for improving the energy performance of historic buildings”. The guidelines are meant to be used by building owners, practitioners, and public sector to select appropriate solutions in the planning stage.
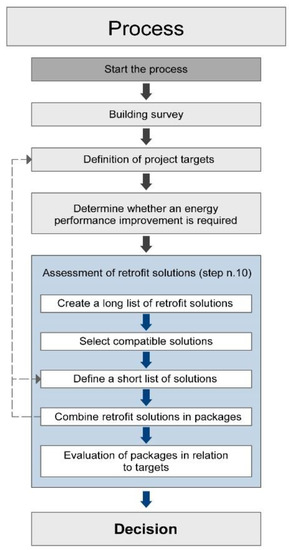
The procedure (Figure 2) helps in the selection of interventions, based on investigation, analysis and documentation of the building including its heritage significance. Rather than specifying general solutions beforehand, the EN 16883:2017 provides a procedure to facilitate the best decision for each individual building. The main goal is to find a sustainable equilibrium between the use of the building, its energy performance, and its conservation.
Since the standard was intentionally kept very general, IEA-SHC Task 59 has been working on further developing this procedure with a focus in two areas:
-
Multidisciplinary Planning Process (Subtask B): The scope of this thrust of the project is to increase the use and usability of the European guidelines to improve the energy performance of historic buildings and support professionals in the decision-making process. The main outcome is a handbook for the planning of energy retrofits in historic buildings.
-
Conservation Compatible Retrofit Solutions and Strategies (Subtask C): This part of the project aims at further developing the assessment criteria (corresponding to step number 10) in the EN 16883:2017 that support the selection of solutions for energy refurbishment (Figure 2). The activity carried out in IEA-SHC Task 59 first led to the compilation of a long list of retrofit possibilities, identified from the information gathered through examples of good practice and research shared by experts and affiliated partners. Below, the general evaluation criteria available in the EN standard have been analysed and refined to make them specific to each building-element category of intervention and support the definition of a short list of solutions.
3. Conservation Compatible Retrofit Solutions and Strategies
One of the main objectives of the IEA-SHC Task 59 project was to identify, document, and assess replicable renovation solutions from different sources such as case studies, research projects (past and present) and innovative products from industry. The scope was making available to a larger audience a collection of already existing technical solutions to overcome some of the identified barriers (see Section 2).
As it has been anticipated in Section 1.1, IEA-SHC Task 59 is a task-sharing project that benefits from a large international network of researchers and practitioners working in the field of sustainability and heritage.
A collaborative information seeking methodology was adopted to collect retrofit solutions [4][5][19,22]. The IEA-SHC Task 59 members worked collaboratively on the shared task of collecting and organising retrofit solutions considered compatible for historic buildings. The collection of retrofit solutions was compiled from case studies gathered and reviewed by this large network of experts.
Partners also had the opportunity to provide information about retrofit solutions they had been working on in the past, for their validation and assessment under a common framework. As such, the uniqueness of this exercise is that it drew on the valuable source of information and long-term experience of the project participants.
A standardised procedure was defined to ensure that consistent information was collected for each case study submitted, and that all solutions included in the appraisal complied with the overall aim of the IEA-SHC Task 59.
These solutions should fulfil three main points:
-
conservation compatibility with historic buildings,
-
energy efficiency goals towards lowest possible energy demand and CO2 emissions (nZEB),
-
technical compatibility and functionality.
According to the EPBD Recast 2010/31/EU [6][38], nZEB is achieved when an energy balance is reached by bringing together architectural design, energy efficiency and local use of renewables. The goal of IEA-SHC Task 59, however, is not to present the equalized balance as absolute threshold, but as the intended target with the above threefold approach.
Specifically, the solutions had to demonstrate an increase in the energy efficiency of the building towards its lowest possible energy demand while ensuring their technical performance and the protection of heritage values.
To tackle the limited access to tested retrofit solutions that can ensure heritage compatibility and long-term performance, IEA-SHC Task 59 focused the review of retrofit measures compatible for historic buildings, on the following thematic areas:
-
wall solutions: Thermal enhancement of external walls.
-
window solutions: Conservation and restoration of historic windows with enhanced energy efficiency and user comfort.
-
heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems: Ventilation systems and technical conditioning installations compatible for historic buildings.
-
Solar technologies: thermal or photovoltaic systems, integrated or not, for historic buildings.
Every solution (Table 1) was documented following a common template. The first section aimed at collecting a brief overview of the solution with a description of the proposed intervention. Solutions included short information about the building context, pictures, and technical details.
Table 1. Number of documented solutions for each category in the IEA-SHC Task 59 Project.
The next, and most important section, focused on the justification of why that solution would be feasible for the retrofit of a historic building from an energy, conservation, and technical point of view. A description of the case study where the solution was implemented was subsequently collected, as well as any link (if available) to existing information and publications [1][23] to complement the documentation.
A set of 131 solutions has been documented so far, most of which with a link to real case studies of retrofitted historic buildings in Europe. This set is thought to be easily implemented as more solutions are available. Considering how much the context of a retrofit can change, this set of solutions is thought to be further adapted to the specific building and its location during the retrofit design process.
A parallel aim of the IEA-SHC Task 59 project was to propose a list of criteria to assess the suitability of the solution when applied to a specific historic building. For this purpose, the risk criteria listed in the EN 16883:2017 standard were adopted in this work as starting point.
In the EN standard, the definition of these risk criteria is based on a risk–benefit scheme and considers: technical compatibility (e.g., hygrothermal risk, structural risk, or corrosion risk), heritage significance of the building (estimated as visual, spatial, and physical impact on the heritage), economic viability (cost–benefit evaluation), energy (primary energy demand), environment (sustainability of products), indoor environmental quality (thermal comfort levels and air quality assessment), impact on the outdoor environment (impact on the building context) and aspects of use (impact on building management issues).
These criteria, however, are not solution-specific and their application is not always immediate. Within the IEA-SHC Task 59 project, partners were organised in working groups to refine and adapt these criteria in support of the assessment of retrofit solutions for the different building-element categories explored: walls, windows, HVAC systems, and solar technologies. More information on the different categories and how the assessment was carried out is presented in the following sections.
3.1. Walls Solutions
The collection of solutions for improving the energy efficiency of external walls was clustered in five categories with different characteristics and impact on the historic building integrity: (i) reversible systems; (ii) internal wall insulation; (iii) cavity insulation (behind internal lining); (iv) frame infill insulation; and (v) external wall insulation.
This collection is characterized by a wide variety of materials: mineral wool, cellulose, wood fibre, cork, calcium silicate, perlite, aerogel, phenolic foam, rigid polyurethane (PUR), etc. The insulation materials selected also present different behaviour and characteristics (e.g., insulation systems with vapour control layers, and capillary-active systems).
Of the 37 solutions documented, two solutions are considered reversible systems: one solution for a reversible façade element installed on the outside, and one of a thin wooden panelling using straw insulation.
Sixteen examples of internal insulation are documented. They are divided between solutions with capillary active insulation materials (12 solutions, such as perlite panel, or wet blown cellulose applied between frames); solutions with vapour retarder (4 solutions, using insulation materials such as mineral wool, cellulose and sheep wool).
Four different solutions of cavity insulation behind internal lining have been documented, including blow in materials, like aerogel-based material, cellulose, and injected foam insulations.
Examples of external insulations are also documented in the collection (nine solutions), including solutions with mineral wool (four solutions), with vacuum insulation panels (one solution), and in combination with thin internal insulation (reed mat, multiport, and wood fibre) (four solutions).
The collection also includes two examples of frame infill insulation, one of a half-timbered building with hemp concrete and another one with timber walls and wood fibre.
Advanced solutions still under development are also included in the collection, like reflective coating, aerogel-based textile wallpaper, or reversible external façade systems. For these special and innovative solutions, the related documentation has been reviewed by the IEA-SHC Task 59 members from scientific and grey literature papers.
Twenty-four solutions of the whole set were implemented on a historic building and are documented as best practices; five of them have even been further assessed with simulations and on-site measurements.
General topics such as driving rain protection and wall drying are also documented in the majority of the collected examples.
The assessment of these solutions in the specific case studies was carried out by adapting the criteria in EN 16883:2017 standard (listed in Section 3.3) to the requirements for walls. Specifically, the criteria recommended by the EN standard were extended by tailoring the description to walls of historic buildings and should thus facilitate practical application. This aspect are discussed more in detail in a companion paper within the IEA-SHC Task 59 frame of activities [7][95].
3.2. Windows Solutions
Two main criteria were considered for the collection of window solutions. The first criterion concerns the identification of the most common historic window types. Four types were pinpointed: single window, single window with winter window, coupled window, and box-type window. The interventions applicable to these types of historic windows were then grouped into four levels of increasing impact on the character and visual appearance of the building, which is the second criterion considered.
The windows solutions documented are divided into (i) low-impact interventions (four solutions), i.e., conservative options potentially applicable to any window with no visual, material or spatial impact on the historic building (e.g., inserting a sealant, repairing, etc.); (ii) interventions with impact on the inside (six solutions), i.e., addition or substitution of single window elements with limited impact on the building character and appearance from the internal side of the façade (e.g., installing an internal new window layer); (iii) interventions with impact on the outside (four solutions), i.e., addition or substitution of single window elements with limited impact on the building character and appearance from the external side of the façade (e.g., replacing outer glass, installing an external new window layer); (iv) strategies with a profound impact on the building character and appearance (two solution), i.e., replacement of the window with a new component. The solutions revised not only concerned interventions on the window components (i.e., frame, and glass), but were also extended to shading systems (such as shutters, blinds, and curtains), which can have a strong influence on the thermal performance of the window itself.
The subdivision proposed makes it easier for the building owner to find a viable solution; if the elements to be preserved are limited to the façade, it will be possible to select interventions focused on changing only single elements with impact on the internal appearance and vice versa. For listed buildings, the available options might be limited to minimal interventions, like repairing original windows or improving their airtightness.
For 13 out of 16 solutions, at least one practical case study was collected. In some cases, a detailed energy assessment has also been carried out.
An assessment of window solutions adapting the criteria in the EN 16883:2017 standard was also developed as an output of this activity, which allows a systematic evaluation of different solutions.
3.3. HVAC Solutions
HVAC solutions focused on two main areas: ventilation systems, and heating/cooling systems. Solutions capable of producing positive effects on energy efficiency, indoor air quality and climate were considered. The review focused on minimal invasive solutions suitable to the future use of the building, while reducing risks for the built heritage conservation (e.g., moisture damage, especially in conjunction with internal wall insulation).
For ventilation systems, the documented solutions range from natural ventilation and space-saving (such as active overflow systems or the push pull system) to artificial ventilation solutions in historic buildings. Three documented solutions deal with the airtightness of buildings, a fundamental requirement for the installation of mechanical ventilation systems. Five examples of central ventilation systems with suspended ceilings are also collected. There are also two examples where the distribution takes place through the floor construction.
Decentralised systems such as ventilation with monoblocks air handling units and room-by-room systems include four examples. Furthermore, one example of alternative possibilities (i.e., facade-integrated ventilation, air supply via chimney/shafts and active overflow systems) were documented. Thus, a total of 17 solutions for the integration of ventilation systems in historic buildings were collected.
For heating/cooling solutions they were collected examples with heat pumps (four solutions), pellet (two solutions), and wood chip boilers (one solution) and cogeneration system (four solutions). Examples of biogas and district heating were described and documented in connection with different distribution systems, like floor heating (four examples), wall heating (one example), and normal radiators (three examples). In addition to that, separate examples such as radiators with visible piping, air heating and infrared heating panels with general descriptions have been included in the collection.
In all the cases involving heating solutions, the integration of the distribution system may be particularly challenging. For this reason, different systems like conventional floor heating, wall heating, radiators, air heating, infrared heating panels, etc., were assessed. In total 18 ventilation solutions, 12 distribution solutions, and 13 production solutions were documented.
On the basis of the assessment criteria in the EN 16883:2017 standard, an approach for tailoring the selection of solutions on a case by case has been developed. A detailed description and an application of this assessment method for HVAC solutions are presented and discussed in companion paper within the IEA-SHC Task 59 framework [8][96].
3.4. Solar Technologies
New technical solutions with high-performance levels may allow an efficient use of solar energy while preserving the character, heritage and architectural quality of historic buildings and sites. The documented solar energy solutions (37) mainly concerned solar thermal collectors and photovoltaic systems compatible with historic buildings.
The collected case studies demonstrate that most solutions used to date in historic buildings are roof-integrated systems (22 solutions out of 37).
Pitched roofs and steep-roofed houses, widely built until the 20th century, are not only characterized by their shape and contours but also by the construction, nature and characteristic colours of the surface materials used (e.g., ceramic or slate tiles, copper or zinc roofs, etc.).
In seven case studies, the solar thermal and photovoltaic systems have the same colours as the roof and therefore were well concealed. In another three cases, systems are not visible from the street and sometimes they are just part of the architectural concept.
Four solutions describe systems attached to the roof, which are mostly not visible from the street and, therefore, may result more compatible in historic contexts (such as in historic city centres) due to the lower visual impact on the appearance of the historic building.
Three wall-integrated systems are also documented, with several interesting examples of their application to valuable historic building. These case studies demonstrate that a harmonization between conservation and renewable energy sources is possible. Alternative solutions with free standing systems are documented as well for cases where one of the solutions above may not be a possibility.
To complete the collection and to provide alternatives for special cases, four models for sharing renewables, i.e., shared solar energy projects for building complexes/communities, are also documented.
All solutions have been assessed adapting the criteria in the EN 16883:2017 standard to analyse their strengths and weakness.
4. A Decision-Support Tool for the Identification of Solutions
A tool named “HiBERtool” (Historic Building Energy Retrofit tool) is being jointly developed between the IEA-SHC Task 59 and the Interreg Alpine Space ATLAS project [3][9][18,97] to help end users (whether architects, engineers, or building owners) identifying a list of suitable solutions.
The webtool interface guides the user to a set of suitable solutions, depending on their needs and requirements. A decision tree was created for each of the different building components presented in this paper (walls, windows, HVAC systems, and solar technologies) (Figure 3). The trees should enable the user to narrow down all the solutions to those suitable for the specific case study (in correspondence with the assessment of solutions approach proposed in the EN 16883:2017 standard—Figure 2).
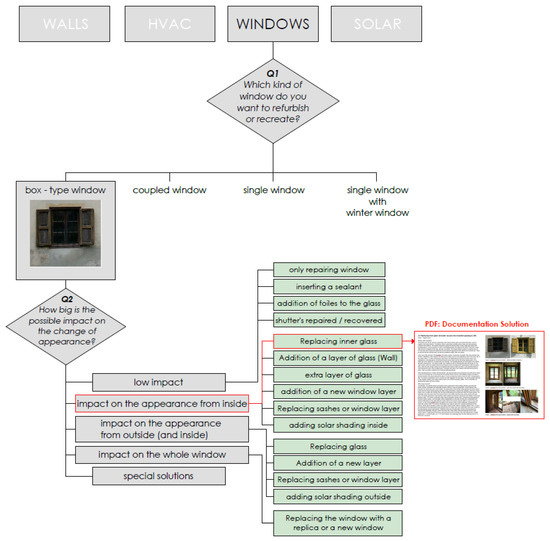
Figure 3. Application of the decision tree for windows in the HIBERtool.
In the online tool, retrofit solutions are selected from those available in the repository by answering simple questions about the building, its context, or the level of conservation.
Figure 3 illustrates one of this decision trees and how based on a series of simple questions the user is guided in the choice of a retrofit solution for an historic window. With the first question, a classification is made according to the type of element to be refurbished. The second level asks about the limits on the modification of the window. The number of questions asked depends on the category. For instance, the HVAC tree presents a series of up to five questions to identify the suitable solution. These choices lead in the decision tree to a list of possible measures. A detailed description of the selected solution can be saved as a PDF file.
The HiBERtool offers a comprehensive and structured access to implemented solutions. Furthermore, the solutions presented are linked to exemplary retrofits documented in the HiBERatlas online platform (a separate output from the same projects) [10][11][16,98]. In contrast with general categories of solutions [12][99], practical tested solutions offer the advantage of the experience gained during their implementation.
The tool, with 131 solutions will thus serve as an inspiration and provide a useful basis for the planning process. In order to allow for the integration of future documentation into the tool, a structure was designed to be continuously expanded as desired.