The autonomic nervous system delicately regulates the function of several target organs, including the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, nerve lesions or other nerve pathologies may cause autonomic dysfunction (AD). Some of the most common causes of AD are diabetes mellitus and α-synucleinopathies such as Parkinson’s disease. Widespread dysmotility throughout the gastrointestinal tract is a common finding in AD, but no commercially available method exists for direct verification of enteric dysfunction. Thus, assessing segmental enteric physiological function is recommended to aid diagnostics and guide treatment.
- autonomic dysfunction
- gastrointestinal
- motility
- investigations
- manometry
- breath test
- imaging
- Parkinson’s disease
- diabetes mellitus
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
Autonomic disorders may involve the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and enteric nervous systems with extensive, multisystemic consequences [1]. Among several other organ manifestations, pan-enteric gastrointestinal (GI) dysmotility is frequently seen [2]. Not only do the motility disturbances contribute to GI symptoms, they may also affect the absorption of medication used to treat the underlying disease [3][4].
Methods for assessment of GI motility are generally applicable across autonomic dysfunction (AD) etiologies despite different underlying pathophysiology. Verification of the extent of GI involvement is important to support diagnosis and guide effective treatment, especially because gastrointestinal symptoms and objective measures correlate poorly [5][6][7][8]. However, commercially available assessment methods have different inherent limitations, and better techniques are needed for evaluating GI dysfunction.
2. Clinical Presentation
2.1. Autonomic Neuropathy in Neurological Disorders
The autonomic nervous system involves sympathetic and parasympathetic neural structures in the central and peripheral nervous systems that innervate all internal organs [1]. Moreover, and often under-recognized, is the enteric nervous system that is also part of the autonomic nervous system [9]. Centrally, the autonomic nervous system is regulated by areas localized at the forebrain pontomescencephalic and bulbopontine level, and in the spinal cord. The peripheral autonomic nervous system acts via the postganglionic parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, which interact with the enteric nervous system in a complex and delicately coordinated network [10][11]. Thus, central and peripheral nerve lesions and pathology may induce AD [1]. Pure AD can manifest acutely or sub-acutely such as seen in autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy or treatment-induced neuropathy of diabetes mellitus (DM). The latter can be caused by a too fast downregulation of blood glucose in a dysregulated DM patient [12]. On the other hand, the presentation can be slowly progressing as seen in α-synucleinopathies or neuropathy of various etiologies. α-synucleinopathies are neurodegenerative diseases characterized by abnormal accumulation of aggregates of α-synuclein protein in nerve fibers or glial cells. The main types of α-synucleinopathies are Parkinson’s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies, multiple-system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure [13]. Large and small fiber sensory and autonomic neuropathy is seen in metabolic disorders (DM, hypothyroidism, uremia), cobalamin deficiency, infections, immune-mediated conditions (gammopathies, vasculitis, and coeliac disease), neurotoxic exposure (alcoholism, and pharmacological treatment), and in hereditary conditions (hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy, Fabry’s disease, and hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis) [14]. Autonomic dysfunction is also seen in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) defined by an abnormal increase in heart rate of at least 30 beats/min within 10 min of standing or during a tilt table test. The rise in heart rate is seen in the absence of orthostatic hypotension and symptoms of orthostatic intolerance must be present for at least 6 months [15]. POTS has been associated with small fiber neuropathy, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and mast cell activation syndrome [16][17].
2.2. Clinical Presentation of Autonomic Neuropathy in General
The symptoms of autonomic neuropathy are numerous and the condition is multisystemic due to the extensive parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation of multiple organs and structures such as the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, thermoregulatory, respiratory, urogenital, pupillomotor, and sudomotor systems [2]. Thus, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up may involve multiple specialties. Parasympathetic dysfunction may cause the sicca syndrome with dry eyes and mouth, light intolerance due to dilated non-responding pupils, urine retention, erectile dysfunction, resting tachycardia, and reduced GI motility. Sympathetic dysfunction is characterized by miotic pupils, orthostatic intolerance with dizziness or syncope, exercise intolerance, anhidrosis, and heat intolerance [18]. GI dysfunction may cause gastroparesis and enteropathy with constipation, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence, and may affect absorption of oral medication, see below.
Recognizing AD is important because of the increased morbidity and mortality associated with reduced heart rate variability, arrhythmias, increased blood pressure variability, and neurogenic orthostatic hypotension [19][20]. Acute development of AD can be the first sign of an underlying paraneoplastic condition. Furthermore, early recognition is important to ensure early initiation of conservative or pharmacological treatments targeting orthostatic or postprandial hypotension, supine hypertension, erectile dysfunction, and gastroenteropathy as these conditions may have a negative impact on the quality of life if left untreated. Finally, autonomic testing can monitor the course of dysautonomia and the response to treatment.
2.3. Clinical Presentation of Gastrointestinal Autonomic Neuropathy
Studies of GI function in patients with AD have mainly included patients with DM or PD. However, pan-enteric autonomic neuropathy is also seen in the less commonly described etiologies, and principles for clinical evaluation and treatment will be largely similar across etiologies. All segments of the GI tract may be affected, contributing to a highly variable inter-individual clinical presentation and intra-individual symptom fluctuation with time, the latter especially seen in patients with DM [21]. Common GI symptoms, such as dysphagia, nausea, vomiting, bloating, early satiety, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, weight loss, and fecal incontinence may be present, combined or solitary, and they may substantially affect the quality of life [22][23][24]. In patients with DM, symptoms of gastroparesis are present in up to 18%, diarrhea in 20%, and constipation in up to 60%. Furthermore, fecal incontinence is frequently reported [25][26]. The prevalence of symptoms of gastroparesis and constipation in PD reaches 50%. Furthermore, 72% have anorectal dysfunction expressed as straining for defecation, but also incomplete emptying, with symptoms becoming more severe during disease progression [27][28]. Constipation is reported in 50% of patients with pure autonomic failure and in up to 82% of patients with multiple system atrophy [3]. Orthostatic symptoms in POTS often coexist with severe GI symptoms, with nausea, abdominal pain and constipation reported in more than 70% [29][30]. Prominent multi-segmental GI symptoms are also commonly seen in the hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and in the mast cell activation syndrome, which is relevant as a differential diagnosis [16][17]. However, prevalence measures vary across studies in all the above-mentioned disorders. While several AD etiologies are associated with GI symptoms, studies on motility across multiple GI segments are primarily performed in PD and DM. Thus, motility disturbances in PD and DM will gain most attention in this review, but dysmotility findings in other diseases will be mentioned when available.
Pan-enteric dysmotility has been documented, and the abnormalities in each segment of the GI tract are presented in
. Aperistalsis and uncoordinated contractions are common in the esophagus [7][31]. Gastric dysmotility presents as delayed or accelerated gastric emptying time and reduced postprandial accommodation [21][30]. Dysmotility, prolonged transit time, and a higher prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) are seen within the small intestine [32][33]. Delayed colonic transit time is frequently seen in PD and primarily caused by a combination of slow transit constipation and anorectal outlet obstruction [27]. Anorectal dysfunction in PD is primarily due to dystonia and pathological contractions of the external sphincter during defecation [27]. Both colonic hypo- and hypermotility have been shown in DM and a dysfunctional internal sphincter combined with rectal hyposensitivity contributes to fecal incontinence [34][35][36].
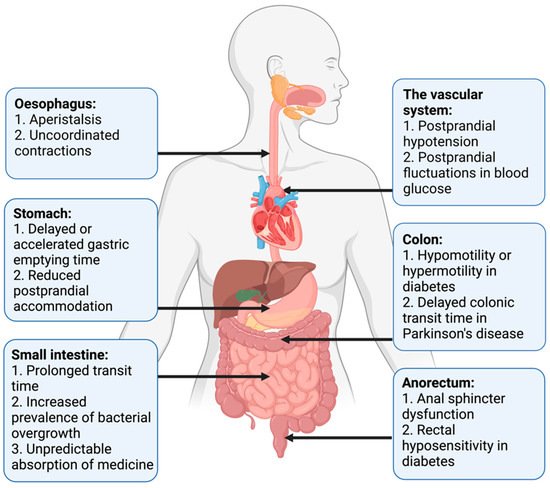
Motility disturbances related to autonomic dysfunction in each gastrointestinal segment.
Widespread dysmotility and varying transit times, especially prolonged gastric emptying time, can make the absorption of oral medication unpredictable and reduce the effectiveness of some drugs [3][4]. Additionally, abnormal postprandial fluctuations in blood glucose, related to a mismatch between insulin administration and food availability in the small intestine, may be harmful to patients with DM [21]. Postprandial hypotension, mainly related to autonomic neuropathy, is also more frequent in patients with DM than in healthy controls [37].
No commercially available in vivo diagnostic test of enteric neuropathy exists. Furthermore, GI symptoms are generally not predictive of the objective motility dysfunction, with objective dysmotility occurring more frequently than subjective symptoms. This necessitates objective assessment to verify the extent of GI dysmotility to support the diagnosis of enteric neuropathy and guide treatment [5][6][7][8]. However, even though a verification of GI dysmotility in a patient with AD significantly increases the likelihood of enteric neuropathy, some patients may have enteric neuropathy despite normal motility measurements.
The underlying pathophysiology of AD varies across patient groups, but assessment methods of the pan-enteric dysfunction are overall identical. Thus, established and emerging methods for assessment of gut function in autonomic disorders and the most relevant general assessment methods of autonomic neuropathy will be reviewed below. The assessment-guided treatment approach will be described at the end of this review.
3. Established Methods for Assessment of Gastroenteropathy
3.1. Exclusion of Differential Diagnoses
When enteric neuropathy is suspected in a patient with an autonomic disorder, the primary approach is to exclude other plausible causes of the gastrointestinal symptoms, such as gastrointestinal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, exocrine pancreas insufficiency, bile acid malabsorption, coeliac disease, and porphyria. Furthermore, it is important to substitute medication if side effects are suspected to be the cause of GI symptoms.
3.2. Assessment of Symptoms
The Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index is a sub-score in the larger questionnaire PAGI-SYM (patient assessment of upper gastrointestinal disorders-symptom severity index) [38]. It is a symptom severity scale assessing gastroparesis and consists of nine items grouped into three subscales including nausea/vomiting, postprandial fullness/early satiety, and bloating. The severity of each symptom is rated on a Likert scale ranging from 0 (no symptoms) to 5 (very severe symptoms), and the recall period is two weeks. The Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index is reliable, valid, and responsive to change [39][40]. However, gastroparesis can be asymptomatic and previous studies suggest that delayed gastric emptying cannot be predicted by the severity of symptoms alone [41][42].
The Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale is a well-validated, responsive, and reliable instrument for assessing GI symptoms. It has been used in several clinical trials mainly for dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux disease, but also in patients with DM [43][44][45]. It consists of 15 items covering five symptom clusters: reflux, abdominal pain, indigestion, diarrhea, and constipation. A 7-point Likert-type response scale is used to grade the severity of symptoms, ranging from 1 (no symptoms) to 7 (very troublesome symptoms), and the recall period is the past week [43].
Specific constipation scoring systems have also been used in autonomic disorders. The Cleveland Constipation Score consists of eight items, and a total score above 15 represents constipation. Symptoms are graduated from mild to severe, which allows for monitoring of symptom fluctuation [46]. The ROME IV criteria for constipation are commonly used to define functional constipation and combine a detailed description of colonic and anorectal symptoms [47]. They are, however, not directly applicable in patients with AD-related gastroenteropathy.
The Diabetes Bowel Symptom Questionnaire is validated for assessment of GI symptoms, glycemic control, and quality of life in patients with DM, but has been used only sporadically [48]. Questionnaires addressing the broad spectrum of non-motor-symptoms in PD have been developed. These do not cover pan-enteric GI dysfunction in detail but are useful as screening tools [27].
3.3. Tests of Esophageal Motility
Within recent years,
has been the method of choice for examining esophageal dysfunction in neurological disorders [49]. When an upper endoscopy with biopsies does not explain the underlying cause of symptoms such as dysphagia and regurgitation, esophageal manometry may be performed. The manometry catheter contains up to 36 pressure sensors distributed 1 cm apart. These sensors provide spatiotemporal, topographic maps of the propagating motor patterns by measuring amplitudes of contractile events within the regions of interest [50]. The clinical performance and interpretation of these data can be challenging. Therefore, when high-resolution esophageal manometry is used to assess AD, it is normally restricted to specialized centers [51]. Esophageal motor dysfunction is present in half of all patients with type 1 DM and dysphagia [52]. In addition, esophageal dysmotility is frequently seen in the α-synucleinopathies, most often as generally reduced peristalsis with ineffective swallows [31][33]. Absent or impaired esophageal activity is documented in POTS with conventional esophageal manometry and with high-resolution esophageal manometry in the Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome, hypermobility type [53][54].
The
can also be utilized in the diagnosis of these disorders. This examination permits the dynamic visualization of content movements through the upper GI system in real time with the use of videofluoroscopy [55]. The role of the modified barium swallowing test is not limited to the diagnose of dysmotility but can add to the understanding of the physiologic swallowing deficit, which can be useful to maximize the benefit of swallowing therapy [56]. Unfortunately, this examination suffers a highly variable inter- and intra-rater reliability, requires considerable resources, and is associated to radiation exposure as well as aspiration risks [55][57]. The modified barium swallowing test demonstrated slower initiation of airway closure in patients with PD [56]. The test is utilized in the diagnostics of esophageal dysmotility in other causes of autonomic dysfunction as well but the literature on this area is still scarce [58].
3.4. Gastric Emptying Tests
Assessment of gastric emptying time is indicated when patients with an autonomic disorder suffer from nausea, early satiety, lack of appetite, vomiting, postprandial pain, unpredictable absorption of orally administered medication, or large postprandial blood glucose fluctuations in DM. Various assessment techniques exist, and the choice of method primarily depends on its availability at each center performing the procedure.
is the gold standard for measuring gastric emptying time. An ingested, standardized radiolabeled meal is followed by sequential gamma camera images at minimum 0, 1, 2, and 4 h after meal ingestion [59][60]. The region of interest is drawn manually on each image, and the percentage of activity remaining in the stomach at each time-point expresses gastric emptying [61]. The advantage of this technique is its effective and non-invasive character that does not interfere with normal gastric motility. However, exposure to radiation, high cost, and limited availability are major drawbacks for all scintigraphic measurements. Scintigraphy has shown delayed or rapid gastric emptying time in patients with DM, and delayed gastric emptying time in patients with multiple system atrophy and PD [8][62]. In patients with POTS gastric emptying time is more frequently rapid than delayed [63].
is a simple, inexpensive, non-invasive, and radiation-free technique to measure gastric emptying time. A solid meal containing the non-radioactive isotope
C is ingested and rapidly absorbed when it enters the small intestine. Gastric emptying is the rate-limiting step in the metabolic pathway for
CO
; and after metabolization in the liver,
CO
is exhaled through the respiratory tract, whereby the accumulation of
CO
in the breath samples indirectly reflects gastric emptying time [64]. Gastric emptying time measures from the gastric emptying breath test are reproducible and correlate with findings from gastric emptying scintigraphy in patients with DM [21][65]. The disadvantage of this technique is the multiple steps required from ingestion to exhalation, which may make the test less accurate. Normal lung and liver function are also a prerequisite. Patients with multiple system atrophy have significantly prolonged gastric emptying time when investigated with gastric emptying breath test [66]. Unfortunately, a recent meta-analysis showed that gastric emptying time obtained with gastric emptying scintigraphy and gastric emptying breath test correlate poorly in patients with PD, and the validity of the test is questioned in this disease [67].
3.5. Assessment of Gastric and Small Intestinal Motility
can distinguish abnormal from normal motility patterns within the distal stomach, pylorus, and duodenum. The method is performed only at a few and highly specialized centers and usually as a supplement to gastric emptying tests. Specific motility patterns can be demonstrated in both fasting and postprandial states. However, different disorders may share common dysmotility patterns. Antropyloroduodenal manometry is in general seen as a valuable diagnostic tool and can guide treatment in various motility disorders [68]. The method has been used in patients with DM, but the clinical evidence is otherwise sparse in gastroenteropathy related to AD [68][69].
Usually, water-perfused or solid-state catheters are used with pressure sensors spaced 5–10 cm in the duodenal region and 0.5–1 cm in the antral and pyloric region. The recording period is often 6 h and includes the ingestion of a meal. However, ambulatory recording can be performed over 24 h, which may reduce variability among individuals but increases the risk of catheter displacement [70]. The method is reproducible and the interobserver agreement is comparable to that of other commonly used methods [68][71]. Normative values are available [72]. However, it may be unpleasant for the patients to carry the catheter, and expertise is needed to perform the investigations and to analyze data. Application of the high-resolution esophageal manometry catheter in the antropyloroduodenal region can demonstrate more detailed motility patterns than antropyloroduodenal manometry, but these catheters are expensive and more sensitive to external noise, such as cough and movements [73].
3.6. Tests of Small Intestinal and Colonic Transit
Assessment of small intestinal or colonic transit times is mainly indicated in patients with abdominal bloating and pain or in patients with symptoms of constipation. It may also be relevant in patients where symptoms of constipation or diarrhea coexist in order to obtain information on the underlying physiology and aid the choice of treatment, see
.
is established for measuring transit times through the small bowel, colon, and whole gut [74]. The basic principles are similar to those of gastric emptying scintigraphy. However, for small bowel transit time gamma images are continued for 6 h after ingestion, and single images at 24, 48, and 72 h are used to determine colonic transit time [61]. Only a few normative data with a wide normal range are available for small bowel transit time and the interpretation is potentially affected by abnormal gastric or colonic motility. Lack of standardization in clinical practice and time-consuming protocols are drawbacks for intestinal scintigraphy in general [60]. Thus, the method has only gained limited use in AD-related gastroenteropathies [75].
are the most commonly used method for assessment of whole gut transit time, which in clinical practice can be seen as an approximation of colonic transit time. The method is simple, repeatable, well-tolerated, inexpensive, and easy to perform. In addition, good correlation has been demonstrated for colonic transit time measured with radio-opaque markers, Wireless Motility Capsule, and scintigraphy [76][77]. Usually, the markers are taken on a single day and visualized by an X-ray on day 5. If quantitative data are needed, a capsule containing 10 markers is ingested on 6 consecutive days with an abdominal X-ray on day 7 [78][79]. Estimation of segmental colonic transit times also requires ingestion of radio-opaque markers at consecutive days, and patient compliance has to be optimal. Other limitations are the radiation exposure and the lack of method standardization between centers, which challenges comparison of the results [60]. Assessment with radio-opaque markers in patients with PD, multiple system atrophy and DM showed significantly prolonged colonic transit time, especially within the left and rectosigmoid colon [5][27][80][81].
can quantify orocecal transit time as a combined measure of gastric and small intestinal transit. The test is usually used as a supplement to assessment of colonic transit time with radiopaque markers and mainly in patients with bloating, abdominal discomfort, or diarrhea. When in contact with colonic bacteria, ingested non-absorbable carbohydrates undergo fermentation and release gases, such as hydrogen and methane, which are excreted through respiration within 3 min. Orocecal transit time is defined as the time interval between oral intake of carbohydrates (often 10 g lactulose) and a registered peak in expired gases by gas chromatography. The hydrogen and methane breath tests are simple, non-invasive, inexpensive, and without exposure to radiation. However, the correlation between the hydrogen breath test and scintigraphy is variable [82][83]. In addition, several other sources of error exist. The natural osmotic activity of lactulose potentially accelerates small intestinal transit and decelerates gastric emptying. The presence of SIBO may complicate the interpretation of orocecal transit time [60]. In both DM and PD, orocecal transit time was significantly prolonged compared with healthy controls when using the hydrogen breath test [84][85].
3.7. Assessment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Patients with intestinal dysmotility, and among these patients with AD-related gastroenteropathy, are predisposed to SIBO [24][86]. The prevalence of SIBO depends on the choice of diagnostic method [32][87]. Assessment of this condition is primarily needed when abdominal discomfort, bloating, and diarrhea are present in patients with AD. The most valid method for diagnosing SIBO is a luminal, jejunal aspirate for culture retrieved by endoscopy, but this method is invasive, subject to contamination, and may underestimate the intraluminal amount of microbiota. In addition to their use for assessment of orocecal transit time,
are frequently used as an indirect and non-invasive method to detect SIBO. When SIBO is present, an early peak of expired hydrogen or methane gas is recognized due to fermentation within the small intestine [32]. A North American consensus provides a practical guide to a standardized performance and interpretation of breath tests, and these tests are widely used in clinical practice [88]. However, recent studies have questioned the utility of breath tests for diagnosing SIBO [89]. Simultaneously performed scintigraphy and breath test showed that rapid orocecal transit time and hereby early colonic fermentation with production of hydrogen or methane gas could erroneously be interpreted as SIBO [90]. Jejunal aspirates for culture did not correlate well with the breath test, and in general methods for diagnosing SIBO lack sensitivity, specificity, reproducibility, and standardization [89].
3.8. Tests of Anorectal Motility
and
are increasingly used in clinical practice to evaluate continence and regulation of defecation, primarily in patients with either difficult evacuation of stools or fecal incontinence who do not respond to standard treatment modalities [91]. A consensus guideline for standardization of the methods was recently published [92]. Compared with conventional manometry, additional pressure sensors are closely incorporated within either a solid-state or a water-perfused catheter (often ≥8 sensors). A high-definition rigid catheter containing 256 pressure sensors arranged in a circumferential grid has also been developed [91][93]. In combination with anorectal sensibility tests or other diagnostic investigations, contractions in the distal rectum and anal canal in response to various stimuli may establish a diagnosis and direct different treatment modalities [92]. Normative values based on large datasets exist for both high-resolution and high-definition anorectal manometry [94][95]. Limitations to both techniques are their fragility and costs. Moreover, data analysis is challenging, limiting their use to investigation at specialized centers. High-resolution anorectal manometry has been used to evaluate anorectal dysfunction in PD, especially revealing dystonic contractions in the external anal sphincter as a pathophysiological mechanism for unsuccessful attempts of defecation [96][97]. Reduced anorectal sensibility and internal sphincter dysfunction contribute to fecal incontinence in patients with DM [35].
3.9. Whole Gut Assessment
When pan-enteric dysmotility is suspected, often due to combined upper and lower GI symptoms,
(Smartpill Monitoring System; Medtronic) is considered the method of choice. An ingested capsule measures pH, intraluminal pressure, and temperature while it passes through the GI tract and transmits this information to a wireless receiver [98]. Accurate measures of the total and regional transit times are provided by using specific pH changes as a surrogate for GI physiological landmarks and temperature to verify expulsion, as seen in
[36][98]. The advantages of this test are the availability of substantive normative data and its ambulatory, non-invasive, and radiation-free character [99][100]. Results from the wireless motility capsule correlate with established methods for measuring regional and whole gut transit times [101][102][103]. Lack of information on segmental colonic transit times is a drawback for the wireless motility capsule investigation. In addition, it only provides information on localized intestinal pressure changes rather than detecting a peristaltic wave, whereas external noise, such as a cough and body movements, can be misinterpreted as bowel movements. The SmartBar, ingested along with the wireless motility capsule, has a high sugar content, which may induce hyperglycemia and by this a slower gastric emptying in patients with DM [104]. Evidence suggests multi-segmental dysmotility in the GI system of both patients with POTS and DM, and a recent study showed that test results led to treatment changes in 73% of patients with DM [6][105]. In patients with PD, multi-segmental delayed transit times determined by the wireless motility capsule can also guide treatment [106]. Hence, evaluation of the entire GI tract with only one examination seems like a reasonable choice in AD-related gastroenteropathy [6][36][107].
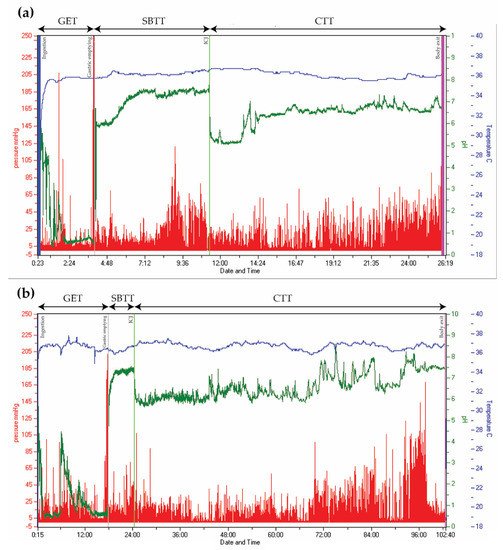
Wireless Motility Capsule recordings from two patients with type 2 diabetes. Time is displayed on the x-axis, pressure on the left y-axis (red), pH on the right y-axis (green), and temperature on the right y-axis (blue). (
) Normal transit times. (
) Delayed gastric emptying time (18 h) and colonic transit time (78 h). (GET = Gastric emptying time. SBTT = Small bowel transit time. CTT = Colonic transit time. ICJ = Ileocolic junction).
Pan-enteric assessment methods, such as the wireless motility capsule, are not widely available. Thus, the initial assessment of motility-disturbances is commonly performed by combining a gastric emptying test (for example the gastric emptying scintigraphy), a breath test for SIBO (for example the hydrogen and methane breath tests) and a test of colonic transit time (for example the radio-opaque markers). Furthermore, guided by symptoms and objective motility findings, it may be relevant to perform one of the mentioned manometric investigations.
References
- Benarroch, E.E. Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Autonomic Nervous System. Continuum 2020, 26, 12–24.
- Mathias, C.J.B.R. Autonomic Failure. A Textbook of Clinical Disorders of the Autonomic Nervous System, 5th ed.; University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013.
- Chung, K.A.; Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in the synucleinopathies. Clin. Auton. Res. 2020.
- Müller, T.; Erdmann, C.; Bremen, D.; Schmidt, W.E.; Muhlack, S.; Woitalla, D.; Goetze, O. Impact of gastric emptying on levodopa pharmacokinetics in Parkinson disease patients. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 29, 61–67.
- Knudsen, K.; Fedorova, T.D.; Bekker, A.C.; Iversen, P.; Østergaard, K.; Krogh, K.; Borghammer, P. Objective Colonic Dysfunction is Far more Prevalent than Subjective Constipation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Colon Transit and Volume Study. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, 359–367.
- Rouphael, C.; Arora, Z.; Thota, P.N.; Lopez, R.; Santisi, J.; Funk, C.; Cline, M. Role of wireless motility capsule in the assessment and management of gastrointestinal dysmotility in patients with diabetes mellitus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29.
- Gustafsson, R.J.; Littorin, B.; Berntorp, K.; Frid, A.; Thorsson, O.; Olsson, R.; Ekberg, O.; Ohlsson, B. Esophageal dysmotility is more common than gastroparesis in diabetes mellitus and is associated with retinopathy. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2011, 8, 268–275.
- Bharucha, A.E.; Camilleri, M.; Forstrom, L.A.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Relationship between clinical features and gastric emptying disturbances in diabetes mellitus. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 70, 415–420.
- Karemaker, J.M. An introduction into autonomic nervous function. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, R89–R118.
- Costa, M.; Brookes, S.J. The enteric nervous system. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, S129–S137.
- Meldgaard, T.; Olesen, S.S.; Farmer, A.D.; Krogh, K.; Wendel, A.A.; Brock, B.; Drewes, A.M.; Brock, C. Diabetic Enteropathy: From Molecule to Mechanism-Based Treatment. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 3827301.
- Gibbons, C.H.; Freeman, R. Treatment-induced neuropathy of diabetes: An acute, iatrogenic complication of diabetes. Brain 2015, 138, 43–52.
- Coon, E.A.; Cutsforth-Gregory, J.K.; Benarroch, E.E. Neuropathology of autonomic dysfunction in synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 349–358.
- Terkelsen, A.J.; Karlsson, P.; Lauria, G.; Freeman, R.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. The diagnostic challenge of small fibre neuropathy: Clinical presentations, evaluations, and causes. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 934–944.
- Benarroch, E.E. Postural tachycardia syndrome: A heterogeneous and multifactorial disorder. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 1214–1225.
- Weinstock, L.B.; Pace, L.A.; Rezaie, A.; Afrin, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome: A Primer for the Gastroenterologist. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020.
- Beckers, A.B.; Keszthelyi, D.; Fikree, A.; Vork, L.; Masclee, A.; Farmer, A.D.; Aziz, Q. Gastrointestinal disorders in joint hypermobility syndrome/Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type: A review for the gastroenterologist. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29.
- Benarroch, E.E. The clinical approach to autonomic failure in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 396–407.
- Soedamah-Muthu, S.S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Witte, D.R.; Stevens, L.K.; Porta, M.; Fuller, J.H. Relationship between risk factors and mortality in type 1 diabetic patients in Europe: The EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study (PCS). Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1360–1366.
- Spallone, V. Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet. Diabetes Metab J. 2019, 43, 3–30.
- Bharucha, A.E.; Kudva, Y.C.; Prichard, D.O. Diabetic Gastroparesis. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1318–1352.
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch. Int. Med. 2001, 161, 1989–1996.
- Talley, N.J.; Young, L.; Bytzer, P.; Hammer, J.; Leemon, M.; Jones, M.; Horowitz, M. Impact of chronic gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus on health-related quality of life. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 71–76.
- Fasano, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Liu, L.W.; Lang, A.E.; Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 625–639.
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Hammer, J.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. GI symptoms in diabetes mellitus are associated with both poor glycemic control and diabetic complications. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 604–611.
- Feldman, M.; Schiller, L.R. Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 378–384.
- Knudsen, K.; Krogh, K.; Østergaard, K.; Borghammer, P. Constipation in parkinson’s disease: Subjective symptoms, objective markers, and new perspectives. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 94–105.
- Verbaan, D.; Marinus, J.; Visser, M.; van Rooden, S.M.; Stiggelbout, A.M.; van Hilten, J.J. Patient-reported autonomic symptoms in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2007, 69, 333–341.
- Wang, L.B.; Culbertson, C.J.; Deb, A.; Morgenshtern, K.; Huang, H.; Hohler, A.D. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in postural tachycardia syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 359, 193–196.
- DiBaise, J.K.; Harris, L.A.; Goodman, B. Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) and the GI Tract: A Primer for the Gastroenterologist. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1458–1467.
- Claus, I.; Suttrup, J.; Muhle, P.; Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Siemer, M.L.; Lenze, F.; Dziewas, R.; Warnecke, T. Subtle Esophageal Motility Alterations in Parkinsonian Syndromes: Synucleinopathies vs. Tauopathies. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2018, 5, 406–412.
- Rao, S.S.C.; Bhagatwala, J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Clinical Features and Therapeutic Management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00078.
- Knudsen, K.; Borghammer, P. Imaging the Autonomic Nervous System in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 79.
- Brock, C.; Søfteland, E.; Gunterberg, V.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Lelic, D.; Brock, B.; Dimcevski, G.; Gregersen, H.; Simrén, M.; Drewes, A.M. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy affects symptom generation and brain-gut axis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3698–3705.
- Azpiroz, F.; Malagelada, C. Diabetic neuropathy in the gut: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 404–408.
- Farmer, A.D.; Pedersen, A.G.; Brock, B.; Jakobsen, P.E.; Karmisholt, J.; Mohammed, S.D.; Scott, S.M.; Drewes, A.M.; Brock, C. Type 1 diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy have pan-enteric prolongation of gastrointestinal transit times and an altered caecal pH profile. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 709–718.
- Pavelić, A.; Krbot Skorić, M.; Crnošija, L.; Habek, M. Postprandial hypotension in neurological disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2017, 27, 263–271.
- Rentz, A.M.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J.; de la Loge, C.; Trudeau, E.; Dubois, D.; Revicki, D.A. Development and psychometric evaluation of the patient assessment of upper gastrointestinal symptom severity index (PAGI-SYM) in patients with upper gastrointestinal disorders. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 1737–1749.
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI): Development and validation of a patient reported assessment of severity of gastroparesis symptoms. Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 2004, 13, 833–844.
- Nilsson, M.; Poulsen, J.L.; Brock, C.; Sandberg, T.H.; Gram, M.; Frokjaer, J.B.; Krogh, K.; Drewes, A.M. Opioid-induced bowel dysfunction in healthy volunteers assessed with questionnaires and MRI. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 514–524.
- Jones, K.L.; Russo, A.; Stevens, J.E.; Wishart, J.M.; Berry, M.K.; Horowitz, M. Predictors of delayed gastric emptying in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1264–1269.
- Cassilly, D.W.; Wang, Y.R.; Friedenberg, F.K.; Nelson, D.B.; Maurer, A.H.; Parkman, H.P. Symptoms of gastroparesis: Use of the gastroparesis cardinal symptom index in symptomatic patients referred for gastric emptying scintigraphy. Digestion 2008, 78, 144–151.
- Kulich, K.R.; Madisch, A.; Pacini, F.; Piqué, J.M.; Regula, J.; Van Rensburg, C.J.; Ujszászy, L.; Carlsson, J.; Halling, K.; Wiklund, I.K. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: A six-country study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 12.
- Revicki, D.A.; Wood, M.; Wiklund, I.; Crawley, J. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Qual. Life Res. 1998, 7, 75–83.
- Wegeberg, A.L.; Brock, C.; Ejskjaer, N.; Karmisholt, J.S.; Jakobsen, P.E.; Drewes, A.M.; Brock, B.; Farmer, A.D. Gastrointestinal symptoms and cardiac vagal tone in type 1 diabetes correlates with gut transit times and motility index. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, e13885.
- Agachan, F.; Chen, T.; Pfeifer, J.; Reissman, P.; Wexner, S.D. A constipation scoring system to simplify evaluation and management of constipated patients. Dis. Colon Rectum 1996, 39, 681–685.
- Simren, M.; Palsson, O.S.; Whitehead, W.E. Update on Rome IV Criteria for Colorectal Disorders: Implications for Clinical Practice. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 15.
- Quan, C.; Talley, N.J.; Cross, S.; Jones, M.; Hammer, J.; Giles, N.; Horowitz, M. Development and validation of the Diabetes Bowel Symptom Questionnaire. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 17, 1179–1187.
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Fox, M.; Gyawali, C.P.; Roman, S.; Smout, A.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 160–174.
- Dhawan, I.; O’Connell, B.; Patel, A.; Schey, R.; Parkman, H.P.; Friedenberg, F. Utility of Esophageal High-Resolution Manometry in Clinical Practice: First, Do HRM. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 3178–3186.
- Yadlapati, R. High-resolution esophageal manometry: Interpretation in clinical practice. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 301–309.
- George, N.S.; Rangan, V.; Geng, Z.; Khan, F.; Kichler, A.; Gabbard, S.; Ganocy, S.; Fass, R. Distribution of Esophageal Motor Disorders in Diabetic Patients With Dysphagia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 890–895.
- Huang, R.J.; Chun, C.L.; Friday, K.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Manometric abnormalities in the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: A case series. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3207–3211.
- Fikree, A.; Aziz, Q.; Sifrim, D. Mechanisms underlying reflux symptoms and dysphagia in patients with joint hypermobility syndrome, with and without postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29.
- Martin-Harris, B.; Canon, C.L.; Bonilha, H.S.; Murray, J.; Davidson, K.; Lefton-Greif, M.A. Best Practices in Modified Barium Swallow Studies. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2020, 29, 1078–1093.
- Schiffer, B.L.; Kendall, K. Changes in Timing of Swallow Events in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 22–27.
- Lee, J.W.; Randall, D.R.; Evangelista, L.M.; Kuhn, M.A.; Belafsky, P.C. Subjective Assessment of Videofluoroscopic Swallow Studies. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 901–905.
- Alomari, M.; Hitawala, A.; Chadalavada, P.; Covut, F.; Al Momani, L.; Khazaaleh, S.; Gosai, F.; Al Ashi, S.; Abushahin, A.; Schneider, A. Prevalence and Predictors of Gastrointestinal Dysmotility in Patients with Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Tertiary Care Center Experience. Cureus 2020, 12, e7881.
- Abell, T.L.; Camilleri, M.; Donohoe, K.; Hasler, W.L.; Lin, H.C.; Maurer, A.H.; McCallum, R.W.; Nowak, T.; Nusynowitz, M.L.; Parkman, H.P.; et al. Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy: A joint report of the American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 753–763.
- Rao, S.S.; Camilleri, M.; Hasler, W.L.; Maurer, A.H.; Parkman, H.P.; Saad, R.; Scott, M.S.; Simren, M.; Soffer, E.; Szarka, L. Evaluation of gastrointestinal transit in clinical practice: Position paper of the American and European Neurogastroenterology and Motility Societies. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 8–23.
- Madsen, J.L. Scintigraphic assessment of gastrointestinal motility: A brief review of techniques and data interpretation. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 243–253.
- Thomaides, T.; Karapanayiotides, T.; Zoukos, Y.; Haeropoulos, C.; Kerezoudi, E.; Demacopoulos, N.; Floodas, G.; Papageorgiou, E.; Armakola, F.; Thomopoulos, Y.; et al. Gastric emptying after semi-solid food in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson disease. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 1055–1059.
- Loavenbruck, A.; Iturrino, J.; Singer, W.; Sletten, D.M.; Low, P.A.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Bharucha, A.E. Disturbances of gastrointestinal transit and autonomic functions in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 92–98.
- Ghoos, Y.F.; Maes, B.D.; Geypens, B.J.; Mys, G.; Hiele, M.I.; Rutgeerts, P.J.; Vantrappen, G. Measurement of gastric emptying rate of solids by means of a carbon-labeled octanoic acid breath test. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1640–1647.
- Zahn, A.; Langhans, C.D.; Hoffner, S.; Haberkorn, U.; Rating, D.; Haass, M.; Enck, P.; Stremmel, W.; Ruhl, A. Measurement of gastric emptying by 13C-octanoic acid breath test versus scintigraphy in diabetics. Z. Gastroenterol. 2003, 41, 383–390.
- Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; Nishida, H.; Yamada, M.; Koumura, A.; Sakurai, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Kimura, A.; Hozumi, I.; Araki, H.; et al. Is there delayed gastric emptying in patients with multiple system atrophy? An analysis using the (13)C-acetate breath test. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1448–1452.
- Knudsen, K.; Szwebs, M.; Hansen, A.K.; Borghammer, P. Gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease-A mini-review. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2018, 55, 18–25.
- Camilleri, M.; Bharucha, A.E.; di Lorenzo, C.; Hasler, W.L.; Prather, C.M.; Rao, S.S.; Wald, A. American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society consensus statement on intraluminal measurement of gastrointestinal and colonic motility in clinical practice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1269–1282.
- Samsom, M.; Jebbink, R.J.; Akkermans, L.M.; van Berge-Henegouwen, G.P.; Smout, A.J. Abnormalities of antroduodenal motility in type I diabetes. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 21–27.
- Patcharatrakul, T.; Gonlachanvit, S. Technique of functional and motility test: How to perform antroduodenal manometry. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 395–404.
- Penning, C.; Gielkens, H.A.; Hemelaar, M.; Lamers, C.B.; Masclee, A.A. Reproducibility of antroduodenal motility during prolonged ambulatory recording. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2001, 13, 133–141.
- Bortolotti, M.; Annese, V.; Coccia, G. Twenty-four hour ambulatory antroduodenal manometry in normal subjects (co-operative study). Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2000, 12, 231–238.
- Desipio, J.; Friedenberg, F.K.; Korimilli, A.; Richter, J.E.; Parkman, H.P.; Fisher, R.S. High-resolution solid-state manometry of the antropyloroduodenal region. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 188–195.
- Bonapace, E.S.; Maurer, A.H.; Davidoff, S.; Krevsky, B.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Whole gut transit scintigraphy in the clinical evaluation of patients with upper and lower gastrointestinal symptoms. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 2838–2847.
- Maleki, D.; Camilleri, M.; Burton, D.D.; Rath-Harvey, D.M.; Oenning, L.; Pemberton, J.H.; Low, P.A. Pilot study of pathophysiology of constipation among community diabetics. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2373–2378.
- Camilleri, M.; Thorne, N.K.; Ringel, Y.; Hasler, W.L.; Kuo, B.; Esfandyari, T.; Gupta, A.; Scott, S.M.; McCallum, R.W.; Parkman, H.P.; et al. Wireless pH-motility capsule for colonic transit: Prospective comparison with radiopaque markers in chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 874–882, e233.
- van der Sijp, J.R.; Kamm, M.A.; Nightingale, J.M.; Britton, K.E.; Mather, S.J.; Morris, G.P.; Akkermans, L.M.; Lennard-Jones, J.E. Radioisotope determination of regional colonic transit in severe constipation: Comparison with radio opaque markers. Gut 1993, 34, 402–408.
- Abrahamsson, H.; Antov, S.; Bosaeus, I. Gastrointestinal and colonic segmental transit time evaluated by a single abdominal X-ray in healthy subjects and constipated patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1988, 152, 72–80.
- Metcalf, A.M.; Phillips, S.F.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; MacCarty, R.L.; Beart, R.W.; Wolff, B.G. Simplified assessment of segmental colonic transit. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 40–47.
- Sakakibara, R.; Odaka, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Liu, R.; Asahina, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamanishi, T.; Hattori, T. Colonic transit time, sphincter EMG, and rectoanal videomanometry in multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 924–929.
- Jung, H.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Moon, I.H.; Hong, Y.S. Colonic transit time in diabetic patients--comparison with healthy subjects and the effect of autonomic neuropathy. Yonsei Med. J. 2003, 44, 265–272.
- Miller, M.A.; Parkman, H.P.; Urbain, J.L.; Brown, K.L.; Donahue, D.J.; Knight, L.C.; Maurer, A.H.; Fisher, R.S. Comparison of scintigraphy and lactulose breath hydrogen test for assessment of orocecal transit: Lactulose accelerates small bowel transit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 10–18.
- Simrén, M.; Stotzer, P.O. Use and abuse of hydrogen breath tests. Gut 2006, 55, 297–303.
- Faria, M.; Pavin, E.J.; Parisi, M.C.; Lorena, S.L.; Brunetto, S.Q.; Ramos, C.D.; Pavan, C.R.; Mesquita, M.A. Delayed small intestinal transit in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes mellitus: Investigation of the relationships with clinical features, gastric emptying, psychological distress, and nutritional parameters. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 32–38.
- Davies, K.N.; King, D.; Billington, D.; Barrett, J.A. Intestinal permeability and orocaecal transit time in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 1996, 72, 164–167.
- Gabrielli, M.; Bonazzi, P.; Scarpellini, E.; Bendia, E.; Lauritano, E.C.; Fasano, A.; Ceravolo, M.G.; Capecci, M.; Rita Bentivoglio, A.; Provinciali, L.; et al. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 889–892.
- Jacobs, C.; Coss Adame, E.; Attaluri, A.; Valestin, J.; Rao, S.S. Dysmotility and proton pump inhibitor use are independent risk factors for small intestinal bacterial and/or fungal overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1103–1111.
- Rezaie, A.; Buresi, M.; Lembo, A.; Lin, H.; McCallum, R.; Rao, S.; Schmulson, M.; Valdovinos, M.; Zakko, S.; Pimentel, M. Hydrogen and Methane-Based Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Disorders: The North American Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 775–784.
- Di Stefano, M.; Quigley, E.M.M. The diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Two steps forward, one step backwards? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13494.
- Yu, D.; Cheeseman, F.; Vanner, S. Combined oro-caecal scintigraphy and lactulose hydrogen breath testing demonstrate that breath testing detects oro-caecal transit, not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with IBS. Gut 2011, 60, 334–340.
- Scott, S.M.; Carrington, E.V. The London Classification: Improving Characterization and Classification of Anorectal Function with Anorectal Manometry. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 55.
- Carrington, E.V.; Heinrich, H.; Knowles, C.H.; Fox, M.; Rao, S.; Altomare, D.F.; Bharucha, A.E.; Burgell, R.; Chey, W.D.; Chiarioni, G.; et al. The international anorectal physiology working group (IAPWG) recommendations: Standardized testing protocol and the London classification for disorders of anorectal function. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13679.
- Lee, T.H.; Bharucha, A.E. How to Perform and Interpret a High-resolution Anorectal Manometry Test. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 46–59.
- Oblizajek, N.R.; Gandhi, S.; Sharma, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Muthyala, A.; Prichard, D.; Feuerhak, K.; Bharucha, A.E. Anorectal pressures measured with high-resolution manometry in healthy people-Normal values and asymptomatic pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13597.
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Normal values and pressure morphology for three-dimensional high-resolution anorectal manometry of asymptomatic adults: A study in 110 subjects. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 1161–1168.
- De Pablo-Fernández, E.; Passananti, V.; Zárate-López, N.; Emmanuel, A.; Warner, T. Colonic transit, high-resolution anorectal manometry and MRI defecography study of constipation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 66, 195–201.
- Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Lin, L. High-resolution Anorectal Manometry in Parkinson Disease With Defecation Disorder: A Comparison With Functional Defecation Disorder. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, 566–571.
- Sarosiek, I.; Selover, K.H.; Katz, L.A.; Semler, J.R.; Wilding, G.E.; Lackner, J.M.; Sitrin, M.D.; Kuo, B.; Chey, W.D.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. The assessment of regional gut transit times in healthy controls and patients with gastroparesis using wireless motility technology. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 313–322.
- Wang, Y.T.; Mohammed, S.D.; Farmer, A.D.; Wang, D.; Zarate, N.; Hobson, A.R.; Hellstrom, P.M.; Semler, J.R.; Kuo, B.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Regional gastrointestinal transit and pH studied in 215 healthy volunteers using the wireless motility capsule: Influence of age, gender, study country and testing protocol. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 761–772.
- Farmer, A.D.; Wegeberg, A.L.; Brock, B.; Hobson, A.R.; Mohammed, S.D.; Scott, S.M.; Bruckner-Holt, C.E.; Semler, J.R.; Hasler, W.L.; Hellstrom, P.M.; et al. Regional gastrointestinal contractility parameters using the wireless motility capsule: Inter-observer reproducibility and influence of age, gender and study country. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 391–400.
- Maqbool, S.; Parkman, H.P.; Friedenberg, F.K. Wireless capsule motility: Comparison of the SmartPill GI monitoring system with scintigraphy for measuring whole gut transit. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2167–2174.
- Kuo, B.; McCallum, R.W.; Koch, K.L.; Sitrin, M.D.; Wo, J.M.; Chey, W.D.; Hasler, W.L.; Lackner, J.M.; Katz, L.A.; Semler, J.R.; et al. Comparison of gastric emptying of a nondigestible capsule to a radio-labelled meal in healthy and gastroparetic subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 186–196.
- Rao, S.S.; Kuo, B.; McCallum, R.W.; Chey, W.D.; DiBaise, J.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Koch, K.L.; Lackner, J.M.; Miller, C.; Saad, R.; et al. Investigation of colonic and whole-gut transit with wireless motility capsule and radiopaque markers in constipation. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 537–544.
- Fraser, R.J.; Horowitz, M.; Maddox, A.F.; Harding, P.E.; Chatterton, B.E.; Dent, J. Hyperglycaemia slows gastric emptying in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1990, 33, 675–680.
- Zhou, W.; Zikos, T.A.; Clarke, J.O.; Nguyen, L.A.; Triadafilopoulos, G.; Neshatian, L. Regional Gastrointestinal Transit and Contractility Patterns Vary in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021.
- Su, A.; Gandhy, R.; Barlow, C.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Utility of the wireless motility capsule and lactulose breath testing in the evaluation of patients with Parkinson’s disease who present with functional gastrointestinal symptoms. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000132.
- Coleski, R.; Wilding, G.E.; Semler, J.R.; Hasler, W.L. Blunting of Colon Contractions in Diabetics with Gastroparesis Quantified by Wireless Motility Capsule Methods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141183.
