Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is a metabolism- oxidative- and inflammation-related marker induced in cardiovascular diseases and is believed to represent a possible link between metabolism and cellular redox status. TXNIP is a potential biomarker in cardiovascular and ischemic diseases but also a novel identified target for preventive and curative medicine.
- TXNIP
- cardiovascular diseases marker
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases remain a major cause of death worldwide and are increasing due to the ageing population and poor eating habits. The pathological changes are originally characterized by metabolic disorders and endothelial dysfunction. Oxidative stress plays an important role and induces vascular-related gene expression, promoting local inflammatory response and cell life and death dysregulation. When oxidative stress occurs, vascular walls produce excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), which causes damage to the structure and function of endothelial cells. That enhances the inflammatory response of the vascular wall and impairs vascular function or revascularization. ROS are produced continuously during cell metabolism and are used as mediators in many biological processes. Specifically, ROS reversibly activate signaling pathways that trigger adaptation systems in the cell. Previous works have associated excessive ROS with age-related pathologies [1,2,3,4,5,6,7][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]. However, recent reviews still report that excessive ROS can lead to diseases and pathological conditions [8,9,10,11][8][9][10][11]. Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is a metabolism- oxidative- and inflammation-related marker induced in cardiovascular pathologies and could represent an emergent link between physiopathology and cardiovascular events. More precisely, TXNIP has been widely described as a pro-oxidant compound [12,13][12][13], but it is also a regulator of metabolism [14[14][15][16][17],15,16,17], a modulator of the inflammatory [18,19][18][19] or angiogenic response [20[20][21],21], and an antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic agent [22,23][22][23]. Clinically, genetic association studies have shown that polymorphisms affecting TXNIP expression are linked to hypertension and arterial stiffness and increase the risk of coronary heart disease [24,25,26][24][25][26]. Epigenetic modifications of TXNIP are also associated with risks of cardiovascular diseases [27,28][27][28]. Additionally, blood or mononuclear blood cells’ mRNA TXNIP levels have been related to coronary and heart diseases [29,30,31][29][30][31].
2. TXNIP is a Multifunctional Protein
TXNIP is a 46-kDa ubiquitously expressed protein that contains 391 amino acid residues and is encoded on chromosome 1q21.1. TXNIP is an α-arrestin protein that regulates pleiotropic biological responses [32][33][34]. TXNIP appears to perform certain functions through multiple binding partners [35], which are summarized in
.
The multiple signaling partners of TXNIP and pleiotropic effects.
| Function | Signalling Partner | References |
|---|
| Shuttle | TRX | [36,37] | [36][37] | |||||||||||||||
| HIF1a | [38] | |||||||||||||||||
| NfkB | [39,40] | [39][40] | ||||||||||||||||
| Itch | [41,42,43] | [41][42][43] | ||||||||||||||||
| Prooxydant | TRX | [13,21,32,40,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] | [13][21][32][40][44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52][53][54][55] | |||||||||||||||
| NADPH oxidase | [13,21,51,52,56,57,58] | [13][21][51][52][56][57][58] | ||||||||||||||||
| AMPK/NrF2 | [59,60,61,62] | [59][60][61][62] | ||||||||||||||||
| Redd1 | [63,64] | [63][64] | ||||||||||||||||
| Proinflammatory | NLRP3 | [13,18,21,60,65,66,67,68,69, | 13 | 70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101, | ][18 | 102, | ][21 | 103, | ] | 104,105] | [[60][65][66][67][68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75][76][77][78][79][80][81][82][83][84][85][86][87][88][89][90][91][92][93][94][95][96][97][98][99][100][101][102][103][104][105] | |||||||
| AMPK/NrF2 | [60, | [60] | 62, | [62] | 90, | [90] | 92, | [92] | 102, | [102] | 103, | [103] | 104, | [ | 106,107, | 104 | 108] | ][106][107][108] |
| NF-κB | [39,40,72,83,109,110] | [39][40][72][83][109][110] | ||||||||||||||||
| Kruppel-like factor 2 | [111] | |||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | AMPK | [92,112,113] | [92][112][113] | |||||||||||||||
| MondoA | [114,115] | [114][115] | ||||||||||||||||
| IGF1 | [116] | |||||||||||||||||
| Glut1 | [33,113,117,118, | [113][117 | 119] | [33]][118][119] | ||||||||||||||
| Glut4 | [120] | |||||||||||||||||
| ChREBP/FOXO1 | [121] | |||||||||||||||||
| Target of miRNA | miR-17, miR-17-5p | [122,123,124,125] | [122][123][124][125] | |||||||||||||||
| miR-20a, miR-20b | [126] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-25-5p | [127] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-30c-5p | [128] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-33 | [129] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-146a | [130] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-370 | [131] | |||||||||||||||||
| miR-497 | [132] |
3. TXNIP is a Novel Marker in Cardiovascular Diseases
TXNIP is a genetic, blood, peripheral blood cells, and tissue ischemia marker associated with cardiovascular diseases, as summarized in Figure 21 and in Table 2, thus making TXNIP an interesting target for prognostic and treatment.
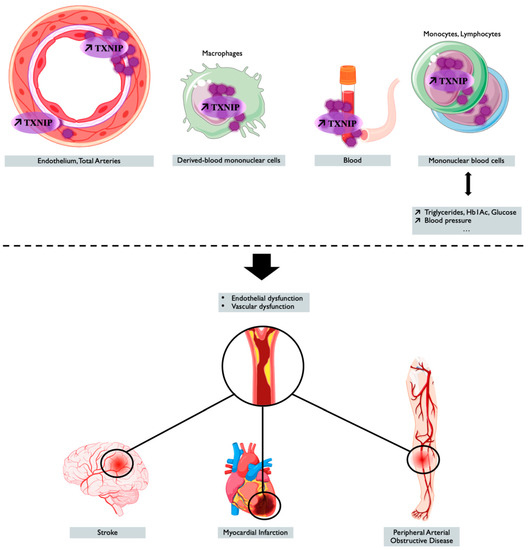
TXNIP overexpression is associated with cardiovascular outcomes and diseases. Tissue, blood levels of TXNIP, and the genetic regulation of TXNIP make it a potential marker associated with cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular event or diseases. Created with
.
Table 2. TXNIP as a marker of cardiovascular risk and disease.
| Location | Parameter or Disease | References |
|---|
| Genetic Marker | TXNIP rs7211 variant | Arterial stiffness, obesity | [24,151] | [24][133] | |||||||||
| TXNIP rs7211- rs7212 variants | Glucose, blood pressure, coronary atherosclerosis | [24,26] | [24][26] | ||||||||||
| Various epigenetic changes | T2D | [188,189] | [134][135] | ||||||||||
| DNA methylation cg19693031 | Blood pressure, T2D, coronary artery disease | [26,27,195,196,197] | [26][27] | 28, | [28] | 190, | [136] | 191, | [ | 192,193, | 137][ | 194, | 138][139][140][141][142][143] |
| Triglycerides and/or HbA1C levels | [27,190, | [ | 191, | 136][ | 192, | 137][ | 193,198] | [27]138][139][144] | |||||
| Blood Marker | Plasma or serum levels of TXNIP | Carotid Intima Media Thickness | [30] | ||||||||||
| Stroke or heart attack | [55,199] | [55][145] | |||||||||||
| Diabetes associated macrovascular endothelial dysfunction | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Diabetes associated vascular complications | [19] | ||||||||||||
| mRNA Marker | TXNIP in peripheral blood cells | At-risk Takayasu arteritis, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, leukostasis | [80,,203] | [ | 94, | 80][ | 110, | 94 | 200,201, | ][110][146][147] | 202 | [148][149] | |
| Unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction | [29,204] | [29][150] | |||||||||||
| Diabetes associated macrovascular endothelial dysfunction | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Diabetes associated vascular complications | [19,205] | [19][151] | |||||||||||
| TXNIP in cardiac tissue | Heart attack | [55] | |||||||||||
| TXNIP in aortic tissue | At-risk Takayasu arteritis, atherosclerosis, arterial aging | [51,200,202,206] | [51][146][148][152] | ||||||||||
| Diabetes associated macrovascular endothelial dysfunction | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Diabetes associated vascular complications | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Tissue Marker | TXNIP in bonne marrow | Mobilization of cells | [202] | [148] | |||||||||
| TXNIP in Myocardiac ischemia | I/R damage (infarct size or ventricular remodeling or heart failure or atrial fibrillation) | [207,208] | [153][154] | ||||||||||
| I/R damage in diabetic hearts or survival | [64,100,109,209,210,211,212,213,214] | [64][100][109][155][156][157][158][159][160] | |||||||||||
| TXNIP in Hind limb ischemia | Reperfusion of ischemic limb, tissue-recovery, capillary density in diabetic mouse | [173,215,216] | [161][162][163] | ||||||||||
| Reperfusion of ischemic limb, tissue-recovery, capillary density in mouse with fat diet | [217,218] | [164][165] | |||||||||||
| TXNIP in cerebral ischemia | Ischemic stroke | [58,60,61,102,103,108,127,219,220,221,222,] | [58] | 223, | [60] | 224, | [ | 225,226, | 61][102][103][108][127][166][167][168][169][170][171][172][173] | 227 | [174] | ||
| Subarachnoid haemorrhage | [62,228,229,230] | [62][175][176][177] | |||||||||||
| Neonatal hypoxic-ischemia | [124,125,231] | [124][125][178] | |||||||||||
| Vascular dementia | [232] | [179] |
References
- Collins, A.R.; Lyon, C.J.; Xia, X.; Liu, J.Z.; Tangirala, R.K.; Yin, F.; Boyadjian, R.; Bikineyeva, A.; Praticò, D.; Harrison, D.G.; et al. Age-accelerated atherosclerosis correlates with failure to upregulate antioxidant genes. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, e42–e54.
- Ungvari, Z.; Kaley, G.; de Cabo, R.; Sonntag, W.E.; Csiszar, A. Mechanisms of vascular aging: New perspectives. J Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 1028–1041.
- Hebert-Schuster, M.; Cottart, C.H.; Laguillier-Morizot, C.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Golmard, J.L.; Cynober, L.; Beaudeux, J.L.; Fabre, E.E.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Catalase rs769214 SNP in elderly malnutrition and during renutrition: Is glucagon to blame? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1583–1588.
- Hebert-Schuster, M.; Fabre, E.E.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Catalase polymorphisms and metabolic diseases. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 397–402.
- Fabre, E.E.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Golmard, J.-L.; Hebert, M.; Dulcire, X.; Succari, M.; Myara, J.; Durand, D.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Gene polymorphisms of oxidative stress enzymes: Prediction of elderly renutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1504–1512.
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Diabetes, oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2709–2729.
- Nivet-Antoine, V.; Labat, C.; El Shamieh, S.; Dulcire, X.; Cottart, C.-H.; Beaudeux, J.-L.; Zannad, F.; Visvikis-Siest, S.; Benetos, A. Relationship between catalase haplotype and arterial aging. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 100–105.
- Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Saredy, J.; Wang, X.; Drummer Iv, C.; Shao, Y.; Saaoud, F.; Xu, K.; Liu, M.; Yang, W.Y.; et al. ROS systems are a new integrated network for sensing homeostasis and alarming stresses in organelle metabolic processes. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101696.
- Dubois-Deruy, E.; Peugnet, V.; Turkieh, A.; Pinet, F. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 864.
- Corkey, B.E.; Deeney, J.T. The Redox Communication Network as a Regulator of Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 567796.
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902.
- Tian, D.; Dong, J.; Jin, S.; Teng, X.; Wu, Y. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide-mediated MAPK inhibition preserves endothelial function through TXNIP signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 291–299.
- Bedarida, T.; Domingues, A.; Baron, S.; Ferreira, C.; Vibert, F.; Cottart, C.-H.; Paul, J.-L.; Escriou, V.; Bigey, P.; Gaussem, P.; et al. Reduced endothelial thioredoxin-interacting protein protects arteries from damage induced by metabolic stress in vivo. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3108–3118.
- Alhawiti, N.M.; Al Mahri, S.; Aziz, M.A.; Malik, S.S.; Mohammad, S. TXNIP in Metabolic Regulation: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Outlook. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1095–1103.
- Chaves, A.B.; Haus, J.M.; Houmard, J.A. Role of TXNIP Biology in Glucose Metabolism. Int. J. Diabetes Clin. Res. 2018, 5.
- Yoshihara, E. TXNIP/TBP-2: A Master Regulator for Glucose Homeostasis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 765.
- Li, X.; Kover, K.L.; Heruth, D.P.; Watkins, D.J.; Guo, Y.; Moore, W.V.; He, L.G.; Zang, M.; Clements, M.A.; Yan, Y. Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes high-glucose-induced macrovascular endothelial dysfunction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 291–297.
- Zhou, R.; Tardivel, A.; Thorens, B.; Choi, I.; Tschopp, J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 136–140.
- Amin, F.M.; Abdelaziz, R.R.; Hamed, M.F.; Nader, M.A.; Shehatou, G.S.G. Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates diabetes-associated vascular complications through ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117887.
- Dunn, L.L.; Buckle, A.M.; Cooke, J.P.; Ng, M.K.C. The emerging role of the thioredoxin system in angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2089–2098.
- Domingues, A.; Boisson-Vidal, C.; Marquet de Rouge, P.; Dizier, B.; Sadoine, J.; Mignon, V.; Vessières, E.; Henrion, D.; Escriou, V.; Bigey, P.; et al. Targeting endothelial thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) protects from metabolic disorder-related impairment of vascular function and post-ischemic revascularisation. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 249–264.
- Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, K.-N.; Hwang, C.Y.; Kwon, K.-S.; You, K.-H.; Choi, I. Tumor suppressor VDUP1 increases p27(kip1) stability by inhibiting JAB1. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4485–4489.
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Zhu, M.; et al. A prodrug of epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates high glucose-induced pro-angiogenic factor production by inhibiting the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis in retinal Müller cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 196, 108065.
- Alvim, R.O.; Santos, P.C.J.L.; Ferreira, N.E.; Mill, J.G.; Krieger, J.E.; Pereira, A.C. Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) rs7212 polymorphism is associated with arterial stiffness in the Brazilian general population. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2012, 26, 340–342.
- Ferreira, N.E.; Omae, S.; Pereira, A.; Rodrigues, M.V.; Miyakawa, A.A.; Campos, L.C.G.; Santos, P.C.J.L.; Dallan, L.A.; Martinez, T.L.; Santos, R.D.; et al. Thioredoxin interacting protein genetic variation is associated with diabetes and hypertension in the Brazilian general population. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 131–136.
- Wang, X.-B.; Han, Y.-D.; Zhang, S.; Cui, N.-H.; Liu, Z.-J.; Huang, Z.-L.; Li, C.; Zheng, F. Associations of polymorphisms in TXNIP and gene-environment interactions with the risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2362–2373.
- Sayols-Baixeras, S.; Subirana, I.; Lluis-Ganella, C.; Civeira, F.; Roquer, J.; Do, A.N.; Absher, D.; Cenarro, A.; Muñoz, D.; Soriano-Tárraga, C.; et al. Identification and validation of seven new loci showing differential DNA methylation related to serum lipid profile: An epigenome-wide approach. The REGICOR study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4556–4565.
- Richard, M.A.; Huan, T.; Ligthart, S.; Gondalia, R.; Jhun, M.A.; Brody, J.A.; Irvin, M.R.; Marioni, R.; Shen, J.; Tsai, P.-C.; et al. DNA Methylation Analysis Identifies Loci for Blood Pressure Regulation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 888–902.
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhong, P.; Wei, Z. Altered Expression of TXNIP in the peripheral leukocytes of patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease. Medicine 2017, 96, e9108.
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, S. Retrospective analysis of the relationship between elevated plasma levels of TXNIP and carotid intima-media thickness in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and early Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 109, 372–377.
- Szpigel, A.; Hainault, I.; Carlier, A.; Venteclef, N.; Batto, A.-F.; Hajduch, E.; Bernard, C.; Ktorza, A.; Gautier, J.-F.; Ferré, P.; et al. Lipid environment induces ER stress, TXNIP expression and inflammation in immune cells of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 399–412.
- Spindel, O.N.; World, C.; Berk, B.C. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein: Redox Dependent and Independent Regulatory Mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 587–596.
- Elgort, M.G.; O’Shea, J.M.; Jiang, Y.; Ayer, D.E. Transcriptional and Translational Downregulation of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein Is Required for Metabolic Reprogramming during G(1). Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 893–907.
- Held, M.A.; Greenfest-Allen, E.; Jachimowicz, E.; Stoeckert, C.J.; Stokes, M.P.; Wood, A.W.; Wojchowski, D.M. Phospho-proteomic discovery of novel signal transducers including thioredoxin-interacting protein as mediators of erythropoietin-dependent human erythropoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 2020, 84, 29–44.
- Hirata, C.L.; Ito, S.; Masutani, H. Thioredoxin interacting protein (Txnip) forms redox sensitive high molecular weight nucleoprotein complexes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 677, 108159.
- World, C.; Spindel, O.N.; Berk, B.C. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates TRX1 translocation to the plasma membrane in response to tumor necrosis factor-α: A key mechanism for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 transactivation by reactive oxygen species. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1890–1897.
- Hwang, J.; Suh, H.-W.; Jeon, Y.H.; Hwang, E.; Nguyen, L.T.; Yeom, J.; Lee, S.-G.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.J.; Kang, B.S.; et al. The structural basis for the negative regulation of thioredoxin by thioredoxin-interacting protein. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2958.
- Shin, D.; Jeon, J.-H.; Jeong, M.; Suh, H.-W.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-C.; Moon, O.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Chung, J.W.; Yoon, S.R.; et al. VDUP1 mediates nuclear export of HIF1alpha via CRM1-dependent pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 838–848.
- Perrone, L.; Devi, T.S.; Hosoya, K.-I.; Terasaki, T.; Singh, L.P. Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) induces inflammation through chromatin modification in retinal capillary endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 221, 262–272.
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, D.O.; Byun, J.-E.; Huy, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, T.-D.; Yoon, S.R.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor interacts with thioredoxin-interacting protein and induces NF-κB activity. Cell. Signal. 2017, 34, 110–120.
- Kelleher, Z.T.; Wang, C.; Forrester, M.T.; Foster, M.W.; Marshall, H.E. ERK-dependent proteasome degradation of Txnip regulates thioredoxin oxidoreductase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13336–13343.
- Otaki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Funayama, A.; Netsu, S.; Honda, Y.; Narumi, T.; Kadowaki, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Honda, S.; et al. HECT-Type Ubiquitin E3 Ligase ITCH Interacts with Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein and Ameliorates Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Cardiotoxicity. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002485.
- Liu, Y.; Lau, J.; Li, W.; Tempel, W.; Li, L.; Dong, A.; Narula, A.; Qin, S.; Min, J. Structural basis for the regulatory role of the PPxY motifs in the thioredoxin-interacting protein TXNIP. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 179–187.
- Patwari, P.; Higgins, L.J.; Chutkow, W.A.; Yoshioka, J.; Lee, R.T. The interaction of thioredoxin with Txnip. Evidence for formation of a mixed disulfide by disulfide exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21884–21891.
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin catalyzes the reduction of insulin disulfides by dithiothreitol and dihydrolipoamide. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9627–9632.
- Nakamura, H. Thioredoxin and its related molecules: Update 2005. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 823–828.
- Nishiyama, A.; Matsui, M.; Iwata, S.; Hirota, K.; Masutani, H.; Nakamura, H.; Takagi, Y.; Sono, H.; Gon, Y.; Yodoi, J. Identification of thioredoxin-binding protein-2/vitamin D(3) up-regulated protein 1 as a negative regulator of thioredoxin function and expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21645–21650.
- Junn, E.; Han, S.H.; Im, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Cho, E.W.; Um, H.D.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, K.W.; Han, P.L.; Rhee, S.G.; et al. Vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1 mediates oxidative stress via suppressing the thioredoxin function. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6287–6295.
- Chen, K.-S.; DeLuca, H.F. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA from HL-60 cells treated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Struct. Expr. 1994, 1219, 26–32.
- Katakam, P.V.G.; Tulbert, C.D.; Snipes, J.A.; Erdös, B.; Miller, A.W.; Busija, D.W. Impaired insulin-induced vasodilation in small coronary arteries of Zucker obese rats is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H854–H860.
- Bedarida, T.; Baron, S.; Vibert, F.; Ayer, A.; Henrion, D.; Thioulouse, E.; Marchiol, C.; Beaudeux, J.-L.; Cottart, C.-H.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Resveratrol Decreases TXNIP mRNA and Protein Nuclear Expressions with an Arterial Function Improvement in Old Mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 720–729.
- Bedarida, T.; Baron, S.; Vessières, E.; Vibert, F.; Ayer, A.; Marchiol-Fournigault, C.; Henrion, D.; Paul, J.-L.; Noble, F.; Golmard, J.-L.; et al. High-protein-low-carbohydrate diet: Deleterious metabolic and cardiovascular effects depend on age. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H649–H657.
- Nivet-Antoine, V.; Cottart, C.-H.; Lemaréchal, H.; Vamy, M.; Margaill, I.; Beaudeux, J.-L.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Borderie, D. trans-Resveratrol downregulates Txnip overexpression occurring during liver ischemia-reperfusion. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1766–1771.
- Schulze, P.C.; Yoshioka, J.; Takahashi, T.; He, Z.; King, G.L.; Lee, R.T. Hyperglycemia promotes oxidative stress through inhibition of thioredoxin function by thioredoxin-interacting protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30369–30374.
- Abdel Magied, N.; Shedid, S.M. Impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles on thioredoxin-interacting protein and asymmetric dimethylarginine as biochemical indicators of cardiovascular disorders in gamma-irradiated rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 430–442.
- Shah, A.; Xia, L.; Goldberg, H.; Lee, K.W.; Quaggin, S.E.; Fantus, I.G. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates high glucose-induced reactive oxygen species generation by mitochondria and the NADPH oxidase, Nox4, in mesangial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6835–6848.
- Zhang, C.; Abdukerim, M.; Abilailieti, M.; Tang, L.; Ling, Y.; Pan, S. The protective effects of orexin a against high glucose-induced activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in human vascular endothelial cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108052.
- Ma, M.W.; Wang, J.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Brann, D.W. NADPH Oxidase 2 Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Brain after Traumatic Brain Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6057609.
- Xu, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Xue, Y. TXNIP mediated the oxidative stress response in glomerular mesangial cells partially through AMPK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 785–792.
- Yu, J.; Wang, W.-N.; Matei, N.; Li, X.; Pang, J.-W.; Mo, J.; Chen, S.-P.; Tang, J.-P.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.H. Ezetimibe Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP Pathway after MCAO in Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4717258.
- Tian, Y.; Su, Y.; Ye, Q.; Chen, L.; Yuan, F.; Wang, Z. Silencing of TXNIP Alleviated Oxidative Stress Injury by Regulating MAPK-Nrf2 Axis in Ischemic Stroke. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 428–436.
- Xu, W.; Li, T.; Gao, L.; Zheng, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Apelin-13/APJ system attenuates early brain injury via suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress in a AMPK-dependent manner after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 247.
- Hou, X.; Yang, S.; Yin, J. Blocking the REDD1/TXNIP axis ameliorates LPS-induced vascular endothelial cell injury through repressing oxidative stress and apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C104–C110.
- Gao, C.; Wang, R.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Yin, T.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lian, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. TXNIP/Redd1 signalling and excessive autophagy: A novel mechanism of myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 645–657.
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; Hou, F.; Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, F. Mangiferin suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in perivascular adipose tissue and prevents insulin resistance in the endothelium. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1563–1575.
- Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Duan, M.; Deng, W.; Tang, Q. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101215.
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Xu, H. Fenofibrate Ameliorates Oxidative Stress-Induced Retinal Microvascular Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1395–1403.
- Sun, X.; Jiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Chen, Y. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 481, 63–70.
- Tschopp, J.; Schroder, K. NLRP3 inflammasome activation: The convergence of multiple signalling pathways on ROS production? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 210–215.
- Yeh, W.-J.; Yang, H.-Y.; Pai, M.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Chen, J.-R. Long-term administration of advanced glycation end-product stimulates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and sparking the development of renal injury. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 39, 68–76.
- Liu, D.; Yang, P.; Gao, M.; Yu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. NLRP3 activation induced by neutrophil extracellular traps sustains inflammatory response in the diabetic wound. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 565–582.
- Samra, Y.A.; Said, H.S.; Elsherbiny, N.M.; Liou, G.I.; El-Shishtawy, M.M.; Eissa, L.A. Cepharanthine and Piperine ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in rats: Role of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. Life Sci. 2016, 157, 187–199.
- Koka, S.; Xia, M.; Chen, Y.; Bhat, O.M.; Yuan, X.; Boini, K.M.; Li, P.-L. Endothelial NLRP3 inflammasome activation and arterial neointima formation associated with acid sphingomyelinase during hypercholesterolemia. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 336–344.
- Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Ren, G.; Jiang, G.; Han, F. PPARα Agonist Stimulated Angiogenesis by Improving Endothelial Precursor Cell Function Via a NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2255–2266.
- Luo, B.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Ke, H.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; He, Y. NLRP3 Inflammasome as a Molecular Marker in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 519.
- Feng, H.; Gu, J.; Gou, F.; Huang, W.; Gao, C.; Chen, G.; Long, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.; et al. High Glucose and Lipopolysaccharide Prime NLRP3 Inflammasome via ROS/TXNIP Pathway in Mesangial Cells. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6973175.
- Wu, M.; Han, W.; Song, S.; Du, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, N.; Wu, H.; Shi, Y.; Duan, H. NLRP3 deficiency ameliorates renal inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 478, 115–125.
- Huang, P.-P.; Fu, J.; Liu, L.-H.; Wu, K.-F.; Liu, H.-X.; Qi, B.-M.; Liu, Y.; Qi, B.-L. Honokiol antagonizes doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte senescence by inhibiting TXNIP-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 186–194.
- An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Yang, L. Punicalagin Protects Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting Pyroptosis Based on TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1516.
- Mohamed, I.N.; Sheibani, N.; El-Remessy, A.B. Deletion of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Abrogates High Fat Diet-induced Retinal Leukostasis, Barrier Dysfunction and Microvascular Degeneration in a Mouse Obesity Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3983.
- Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Peng, W.; Zhang, B.; Guo, L. Inhibitor of RAGE and glucose-induced inflammation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: Effect and mechanism of action. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3255–3262.
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Peng, W.; Guo, L. N-acetyl cysteine inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3299–3306.
- Wang, W.; Mao, S.; Yu, H.; Wu, H.; Shan, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, G.; Liu, X. Pinellia pedatisecta lectin exerts a proinflammatory activity correlated with ROS-MAPKs/NF-κB pathways and the NLRP3 inflammasome in RAW264.7 cells accompanied by cell pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 1–12.
- Davis, B.K.; Ting, J.P.-Y. NLRP3 has a sweet tooth. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 105–106.
- Oslowski, C.M.; Hara, T.; O’Sullivan-Murphy, B.; Kanekura, K.; Lu, S.; Hara, M.; Ishigaki, S.; Zhu, L.J.; Hayashi, E.; Hui, S.T.; et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates ER stress-induced β cell death through initiation of the inflammasome. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 265–273.
- Abais, J.M.; Xia, M.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Conley, S.M.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Boini, K.M.; Li, P.-L. Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation and podocyte injury via thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) during hyperhomocysteinemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27159–27168.
- Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xian, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Aspirin alleviates endothelial gap junction dysfunction through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in LPS-induced vascular injury. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 711–723.
- Sun, J.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, X.; Gao, L. Endothelium as a Potential Target for Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6306542.
- Nyandwi, J.B.; Ko, Y.S.; Jin, H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.J. Rosmarinic acid inhibits oxLDL-induced inflammasome activation under high-glucose conditions through downregulating the p38-FOXO1-TXNIP pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114246.
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, Q.; Qin, M.-J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.-Q.; Liu, B.-L.; Wen, X.-D. Ilexgenin A inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and ameliorates endothelial dysfunction via suppression of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in an AMPK dependent manner. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 101–115.
- Tang, G.; Duan, F.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H. Metformin inhibited Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasomes activation and suppressed diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis in apoE-/- mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 119, 109410.
- Wei, H.; Bu, R.; Yang, Q.; Jia, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Exendin-4 Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis via the AMPK-TXNIP Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 8905917.
- Mai, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, D.; Ye, L.; Yu, G.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Lin, J.; Yang, T.; et al. Berberine Inhibits Nod-Like Receptor Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis via the ROS/TXNIP Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 185.
- Yamagata, K.; Hashiguchi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Tagami, M. Dietary Apigenin Reduces Induction of LOX-1 and NLRP3 Expression, Leukocyte Adhesion, and Acetylated Low-Density Lipoprotein Uptake in Human Endothelial Cells Exposed to Trimethylamine-N-Oxide. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 74, 558–565.
- Wang, D.-S.; Yan, L.-Y.; Yang, D.-Z.; Lyu, Y.; Fang, L.-H.; Wang, S.-B.; Du, G.-H. Formononetin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing the ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 759–766.
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Su, C.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, G. Cilostazol ameliorates high free fatty acid (FFA)-induced activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in human vascular endothelial cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3704–3710.
- Luo, X.; Hu, Y.; He, S.; Ye, Q.; Lv, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, X. Dulaglutide inhibits high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 671, 203–209.
- Lu, L.; Lu, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Z. Vitamin D3 Protects against Diabetic Retinopathy by Inhibiting High-Glucose-Induced Activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 8193523.
- Lian, D.; Yuan, H.; Yin, X.; Wu, Y.; He, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Puerarin inhibits hyperglycemia-induced inter-endothelial junction through suppressing endothelial Nlrp3 inflammasome activation via ROS-dependent oxidative pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 310–319.
- Qiu, H.; Liu, W.; Lan, T.; Pan, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, D. Salvianolate reduces atrial fibrillation through suppressing atrial interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad2/3 and TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in post-MI rats. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 255–265.
- Wang, W.; Wu, Q.-H.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X. Rutin protects endothelial dysfunction by disturbing Nox4 and ROS-sensitive NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 32–40.
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Li, L.; Xie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Nrf2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through regulating Trx1/TXNIP complex in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 336, 32–39.
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Curcumin attenuates glutamate neurotoxicity in the hippocampus by suppression of ER stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a manner dependent on AMPK. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 53–63.
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Gao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ma, T.; Li, G.; Zhang, X. Tilianin Protects Diabetic Retina through the Modulation of Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathways. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2020, 39, 89–99.
- Yin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.; Chang, Q.; Sun, G.; Dai, Y. Vascular endothelial cells senescence is associated with NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation via reactive oxygen species (ROS)/thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 84, 22–34.
- Dinesh, P.; Rasool, M. Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid suppresses TXNIP mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in MSU crystal stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through the upregulation of Nrf2 transcription factor and alleviates MSU crystal induced inflammation in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 44, 26–37.
- Koska, J.; Lopez, L.; D’Souza, K.; Osredkar, T.; Deer, J.; Kurtz, J.; Salbe, A.D.; Harman, S.M.; Reaven, P.D. Effect of liraglutide on dietary lipid-induced insulin resistance in humans. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 69–76.
- Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Bai, H.; Cui, W.; Guo, W.; Feng, D.; et al. Adiponectin peptide alleviates oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating AMPK/GSK-3β. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113302.
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Chang, S.; Ren, D.; Shali, S.; Li, C.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Ge, J. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 142, 65–79.
- Byon, C.H.; Han, T.; Wu, J.; Hui, S.T. Txnip ablation reduces vascular smooth muscle cell inflammation and ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 313–321.
- Wang, X.-Q.; Nigro, P.; World, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Yan, C.; Berk, B.C. Thioredoxin interacting protein promotes endothelial cell inflammation in response to disturbed flow by increasing leukocyte adhesion and repressing Kruppel-like factor 2. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 560–568.
- Andres, A.M.; Ratliff, E.P.; Sachithanantham, S.; Hui, S.T. Diminished AMPK signaling response to fasting in thioredoxin-interacting protein knockout mice. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1223–1230.
- Wu, N.; Zheng, B.; Shaywitz, A.; Dagon, Y.; Tower, C.; Bellinger, G.; Shen, C.-H.; Wen, J.; Asara, J.; McGraw, T.E.; et al. AMPK-dependent degradation of TXNIP upon energy stress leads to enhanced glucose uptake via GLUT1. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 1167–1175.
- Wilde, B.R.; Ye, Z.; Lim, T.-Y.; Ayer, D.E. Cellular acidosis triggers human MondoA transcriptional activity by driving mitochondrial ATP production. Elife 2019, 8, e40199.
- Parikh, H.; Carlsson, E.; Chutkow, W.A.; Johansson, L.E.; Storgaard, H.; Poulsen, P.; Saxena, R.; Ladd, C.; Schulze, P.C.; Mazzini, M.J.; et al. TXNIP regulates peripheral glucose metabolism in humans. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e158.
- Nagaraj, K.; Lapkina-Gendler, L.; Sarfstein, R.; Gurwitz, D.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Laron, Z.; Yakar, S.; Werner, H. Identification of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) as a downstream target for IGF1 action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1045–1050.
- Patwari, P.; Chutkow, W.A.; Cummings, K.; Verstraeten, V.L.R.M.; Lammerding, J.; Schreiter, E.R.; Lee, R.T. Thioredoxin-independent regulation of metabolism by the alpha-arrestin proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24996–25003.
- Ahn, D.; Peñaloza, H.; Wang, Z.; Wickersham, M.; Parker, D.; Patel, P.; Koller, A.; Chen, E.I.; Bueno, S.M.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; et al. Acquired resistance to innate immune clearance promotes Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 pulmonary infection. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e89704.
- Sullivan, W.J.; Mullen, P.J.; Schmid, E.W.; Flores, A.; Momcilovic, M.; Sharpley, M.S.; Jelinek, D.; Whiteley, A.E.; Maxwell, M.B.; Wilde, B.R.; et al. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Regulates Glucose Metabolism through TXNIP Destabilization. Cell 2018, 175, 117–132.e21.
- Waldhart, A.N.; Dykstra, H.; Peck, A.S.; Boguslawski, E.A.; Madaj, Z.B.; Wen, J.; Veldkamp, K.; Hollowell, M.; Zheng, B.; Cantley, L.C.; et al. Phosphorylation of TXNIP by AKT Mediates Acute Influx of Glucose in Response to Insulin. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2005–2013.
- Li, X.; Kover, K.L.; Heruth, D.P.; Watkins, D.J.; Moore, W.V.; Jackson, K.; Zang, M.; Clements, M.A.; Yan, Y. New Insight into Metformin Action: Regulation of ChREBP and FOXO1 Activities in Endothelial Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1184–1194.
- Dong, D.; Fu, N.; Yang, P. MiR-17 Downregulation by High Glucose Stabilizes Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein and Removes Thioredoxin Inhibition on ASK1 Leading to Apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 84–96.
- Liu, Y.; Lou, G.; Li, A.; Zhang, T.; Qi, J.; Ye, D.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Z. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 140–150.
- Gamdzyk, M.; Doycheva, D.M.; Kang, R.; Tang, H.; Travis, Z.D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. GW0742 activates miR-17-5p and inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3-mediated inflammation after hypoxic-ischaemic injury in rats and in PC12 cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12318–12330.
- Gamdzyk, M.; Doycheva, D.M.; Malaguit, J.; Enkhjargal, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Role of PPAR-β/δ/miR-17/TXNIP pathway in neuronal apoptosis after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury in rats. Neuropharmacology 2018, 140, 150–161.
- Chen, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. MicroRNA-20a protects human aortic endothelial cells from Ox-LDL-induced inflammation through targeting TLR4 and TXNIP signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 191–197.
- Zhang, H.-S.; Liu, M.-F.; Ji, X.-Y.; Jiang, C.-R.; Li, Z.-L.; OuYang, B. Gastrodin combined with rhynchophylline inhibits cerebral ischaemia-induced inflammasome activation via upregulating miR-21-5p and miR-331-5p. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 116935.
- Li, X.; Yao, L.; Zeng, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Yu, Q. miR-30c-5p Alleviated Pyroptosis During Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Targeting TXNIP. Inflammation 2021, 44, 217–228.
- Klein Geltink, R.I.; O’Sullivan, D.; Corrado, M.; Bremser, A.; Buck, M.D.; Buescher, J.M.; Firat, E.; Zhu, X.; Niedermann, G.; Caputa, G.; et al. Mitochondrial Priming by CD28. Cell 2017, 171, 385–397.e11.
- Wang, Y.; Ma, W.-Q.; Zhu, Y.; Han, X.-Q.; Liu, N. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Pretreated With Advanced Glycation End Product-Bovine Serum Albumin Inhibit Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 524.
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Gao, L. Circular RNA circ-BANP regulates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury through targeting the miR-370/TXNIP axis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020.
- Wang, J.; Zhao, S.-M. LncRNA-antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus promotes pyroptosis via miR-497/thioredoxin-interacting protein axis in diabetic nephropathy. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118728.
- Katsu-Jiménez, Y.; Vázquez-Calvo, C.; Maffezzini, C.; Halldin, M.; Peng, X.; Freyer, C.; Wredenberg, A.; Giménez-Cassina, A.; Wedell, A.; Arnér, E.S.J. Absence of TXNIP in Humans Leads to Lactic Acidosis and Low Serum Methionine Linked to Deficient Respiration on Pyruvate. Diabetes 2019, 68, 709–723.
- De Marinis, Y.; Cai, M.; Bompada, P.; Atac, D.; Kotova, O.; Johansson, M.E.; Garcia-Vaz, E.; Gomez, M.F.; Laakso, M.; Groop, L. Epigenetic regulation of the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) gene by hyperglycemia in kidney. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 342–353.
- Albao, D.S.; Cutiongco-de la Paz, E.M.; Mercado, M.E.; Lirio, A.; Mariano, M.; Kim, S.; Yangco, A.; Melegrito, J.; Wad-asen, K.; Gauran, I.I.; et al. Methylation changes in the peripheral blood of Filipinos with type 2 diabetes suggest spurious transcription initiation at TXNIP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 4208–4218.
- Van Greevenbroek, M.M.J.; Vermeulen, V.M.M.-J.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Evelo, C.T.; Kruijshoop, M.; Hoebee, B.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; de Bruin, T.W.A. Genetic variation in thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is associated with hypertriglyceridaemia and blood pressure in diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 498–504.
- Soriano-Tárraga, C.; Jiménez-Conde, J.; Giralt-Steinhauer, E.; Mola-Caminal, M.; Vivanco-Hidalgo, R.M.; Ois, A.; Rodríguez-Campello, A.; Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Sayols-Baixeras, S.; Elosua, R.; et al. Epigenome-wide association study identifies TXNIP gene associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and sustained hyperglycemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 609–619.
- Florath, I.; Butterbach, K.; Heiss, J.; Bewerunge-Hudler, M.; Zhang, Y.; Schöttker, B.; Brenner, H. Type 2 diabetes and leucocyte DNA methylation: An epigenome-wide association study in over 1,500 older adults. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 130–138.
- Meeks, K.A.C.; Henneman, P.; Venema, A.; Addo, J.; Bahendeka, S.; Burr, T.; Danquah, I.; Galbete, C.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Mockenhaupt, F.P.; et al. Epigenome-wide association study in whole blood on type 2 diabetes among sub-Saharan African individuals: Findings from the RODAM study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 58–70.
- Chambers, J.C.; Loh, M.; Lehne, B.; Drong, A.; Kriebel, J.; Motta, V.; Wahl, S.; Elliott, H.R.; Rota, F.; Scott, W.R.; et al. Epigenome-wide association of DNA methylation markers in peripheral blood from Indian Asians and Europeans with incident type 2 diabetes: A nested case-control study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 526–534.
- Cardona, A.; Day, F.R.; Perry, J.R.B.; Loh, M.; Chu, A.Y.; Lehne, B.; Paul, D.S.; Lotta, L.A.; Stewart, I.D.; Kerrison, N.D.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Incident Type 2 Diabetes in a British Population: EPIC-Norfolk Study. Diabetes 2019, 68, 2315–2326.
- Walaszczyk, E.; Luijten, M.; Spijkerman, A.M.W.; Bonder, M.J.; Lutgers, H.L.; Snieder, H.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V. DNA methylation markers associated with type 2 diabetes, fasting glucose and HbA1c levels: A systematic review and replication in a case-control sample of the Lifelines study. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 354–368.
- Gateva, A.T.; Assyov, Y.S.; Velikova, T.; Kamenov, Z.A. Higher levels of thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) in patients with prediabetes compared to obese normoglycemic subjects. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 734–737.
- Pfeiffer, L.; Wahl, S.; Pilling, L.C.; Reischl, E.; Sandling, J.K.; Kunze, S.; Holdt, L.M.; Kretschmer, A.; Schramm, K.; Adamski, J.; et al. DNA methylation of lipid-related genes affects blood lipid levels. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 334–342.
- Al-Hussain, F.; Iqbal, M.; Al-Quwayee, M.; Jurays, A.B.; Al-Wabel, M.; Dayes, S.; Bashir, S. The role of serum levels of thioredoxin and thioredoxin-interacting protein in stroke. J. Nat. Sci. Med. 2018, 1, 55–58.
- Tamura, N.; Maejima, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Vega, R.B.; Amiya, E.; Ito, Y.; Shiheido-Watanabe, Y.; Ashikaga, T.; Komuro, I.; Kelly, D.P.; et al. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism of the MLX Gene Is Associated with Takayasu Arteritis. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002296.
- Riahi, Y.; Kaiser, N.; Cohen, G.; Abd Elrahman, I.; Blum, G.; Shapira, O.M.; Koler, T.; Simionescu, M.; Sima, A.V.; Zarkovic, N.; et al. Foam cell-derived 4-hydroxynonenal induces endothelial cell senescence in a TXNIP-dependent manner. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1887–1899.
- Cochain, C.; Vafadarnejad, E.; Arampatzi, P.; Pelisek, J.; Winkels, H.; Ley, K.; Wolf, D.; Saliba, A.-E.; Zernecke, A. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals the Transcriptional Landscape and Heterogeneity of Aortic Macrophages in Murine Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1661–1674.
- Rong, J.; Xu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, G.; Ming, X.; He, S.; Liang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, F. Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes activation and inflammation of monocytes with DNA demethylation in coronary artery disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3560–3571.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Wei, Z.; Huang, J. Differential Expression of TXNIP Isoforms in the Peripheral Leukocytes of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 9051481.
- Pagesy, P.; Tachet, C.; Mostefa-Kara, A.; Larger, E.; Issad, T. Increased OGA Expression and Activity in Leukocytes from Patients with Diabetes: Correlation with Inflammation Markers. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 517–523.
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Yan, P.; Ren, J.; Song, M.; Li, J.; Lei, J.; Pan, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; et al. A single-cell transcriptomic landscape of primate arterial aging. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2202–2213.
- Jeong, M.; Piao, Z.-H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.; Sun, H.-N.; Yoon, S.R.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, T.-D.; Jeon, J.-H.; et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and mobilization under stress conditions. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2495–2505.
- Jung, H.; Kim, D.O.; Byun, J.-E.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, M.J.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kang, D.-K.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, T.-D.; et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates haematopoietic stem cell ageing and rejuvenation by inhibiting p38 kinase activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13674.
- Liu, Y.; Lian, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Yi, F.; Gao, C.; Xin, C.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; et al. TXNIP mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells as a novel mechanism in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2014, 109, 415.
- Frangogiannis, N.G.; Smith, C.W.; Entman, M.L. The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 53, 31–47.
- Frangogiannis, N.G. The inflammatory response in myocardial injury, repair, and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 255–265.
- Yoshioka, J.; Chutkow, W.A.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.B.; Yan, J.; Tian, R.; Lindsey, M.L.; Feener, E.P.; Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.G.; et al. Deletion of thioredoxin-interacting protein in mice impairs mitochondrial function but protects the myocardium from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 267–279.
- Yoshioka, J.; Schulze, P.C.; Cupesi, M.; Sylvan, J.D.; MacGillivray, C.; Gannon, J.; Huang, H.; Lee, R.T. Thioredoxin-interacting protein controls cardiac hypertrophy through regulation of thioredoxin activity. Circulation 2004, 109, 2581–2586.
- Yoshioka, J.; Imahashi, K.; Gabel, S.A.; Chutkow, W.A.; Burds, A.A.; Gannon, J.; Schulze, P.C.; MacGillivray, C.; London, R.E.; Murphy, E.; et al. Targeted deletion of thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates cardiac dysfunction in response to pressure overload. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 1328–1338.
- Shen, M.; Bai, D.; Liu, B.; Lu, X.; Hou, R.; Zeng, C.; Li, N.; Fu, Z.; Li, C.; Tao, L.; et al. Dysregulated Txnip-ROS-Wnt axis contributes to the impaired ischemic heart repair in diabetic mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3735–3745.
- Hou, R.; Shen, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Xu, J.; Tao, L.; Yin, Z.; Yin, T. Thioredoxin1 Inactivation Mediates the Impairment of Ischemia-Induced Angiogenesis and Further Injury in Diabetic Myocardium. J. Vasc. Res. 2020, 57, 76–85.
- Su, H.; Ji, L.; Xing, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Qian, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H. Acute hyperglycaemia enhances oxidative stress and aggravates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury: Role of thioredoxin-interacting protein. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 181–191.
- Shaikh, I.A.; Rishi, M.T.; Youssef, M.; Selvaraju, V.; Thirunavukkarasu, M.; Ukani, G.; Lakshmanan, R.; Palesty, J.A.; Maulik, N. Overexpression of Thioredoxin1 enhances functional recovery in a mouse model of hind limb ischemia. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 216, 158–168.
- Yuan, J.; Tan, J.T.M.; Rajamani, K.; Solly, E.L.; King, E.J.; Lecce, L.; Simpson, P.J.L.; Lam, Y.T.; Jenkins, A.J.; Bursill, C.A.; et al. Fenofibrate Rescues Diabetes-Related Impairment of Ischemia-Mediated Angiogenesis by PPARα-Independent Modulation of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1040–1053.
- Ishrat, T.; Mohamed, I.N.; Pillai, B.; Soliman, S.; Fouda, A.Y.; Ergul, A.; El-Remessy, A.B.; Fagan, S.C. Thioredoxin-interacting protein: A novel target for neuroprotection in experimental thromboembolic stroke in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 766–778.
- Guo, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ding, H.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, M. Ketogenic Diet Improves Brain Ischemic Tolerance and Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Preventing Drp1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 86.
- Wang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Umbelliferone ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulating the PPAR gamma expression and suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 600, 182–187.
- Cao, G.; Jiang, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Zhou, K.; Qi, J.; Yu, B.; et al. Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1418.
- Ismael, S.; Nasoohi, S.; Yoo, A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Ishrat, T. Tissue Plasminogen Activator Promotes TXNIP-NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation after Hyperglycemic Stroke in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2495–2508.
- Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Narasimhan, P.; Sakata, H.; Chan, P.H. Induction of thioredoxin-interacting protein is mediated by oxidative stress, calcium, and glucose after brain injury in mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 440–449.
- Hua, K.; Sheng, X.; Li, T.-T.; Wang, L.-N.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Huang, Z.-J.; Ji, H. The edaravone and 3-n-butylphthalide ring-opening derivative 10b effectively attenuates cerebral ischemia injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 917–927.
- Guo, Z.-N.; Xu, L.; Hu, Q.; Matei, N.; Yang, P.; Tong, L.-S.; He, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning Attenuates Hemorrhagic Transformation Through Reactive Oxygen Species/Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein/Nod-Like Receptor Protein 3 Pathway in Hyperglycemic Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rats. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e403–e411.
- Liu, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Mu, F.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Ding, Y.; Wen, A. Z-Guggulsterone alleviated oxidative stress and inflammation through inhibiting the TXNIP/NLRP3 axis in ischemic stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107094.
- Zhao, Q.; Che, X.; Zhang, H.; Tan, G.; Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, X.; Sun, X.; He, Z. Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein Mediates Apoptosis in Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 854.
- Zhao, Q.; Che, X.; Zhang, H.; Fan, P.; Tan, G.; Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, X.; Liang, Y.; et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links endoplasmic reticulum stress to inflammatory brain injury and apoptosis after subarachnoid haemorrhage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 104.
- Liang, Y.; Che, X.; Zhao, Q.; Darwazeh, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, X.; Qin, W.; Liu, L.; et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 450, 149–158.
- Chen, D.; Dixon, B.J.; Doycheva, D.M.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; He, Y.; Guo, Z.; Nowrangi, D.; Flores, J.; et al. IRE1α inhibition decreased TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation through miR-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 32.
- Du, S.-Q.; Wang, X.-R.; Zhu, W.; Ye, Y.; Yang, J.-W.; Ma, S.-M.; Ji, C.-S.; Liu, C.-Z. Acupuncture inhibits TXNIP-associated oxidative stress and inflammation to attenuate cognitive impairment in vascular dementia rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 39–46.
