The survival of insects depends on their ability to detect molecules present in their environment. Odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) form a family of proteins involved in chemoreception. While OBPs were initially found in olfactory appendages, recently these proteins were discovered in other chemosensory and non-chemosensory organs. OBPs can bind, solubilize and transport hydrophobic stimuli to chemoreceptors across the aqueous sensilla lymph. In addition to this broadly accepted “transporter role”, OBPs can also buffer sudden changes in odorant levels and are involved in hygro-reception. The physiological roles of OBPs expressed in other body tissues, such as mouthparts, pheromone glands, reproductive organs, digestive tract and venom glands, remain to be investigated.
- insect
- olfaction
- taste
- chemosensory functions
- non-chemosensory functions
- odorant-protein-binding assay
- Drosophila melanogaster
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
Chemoperception allows organisms to detect nutritive food and avoid toxic compounds. Moreover, chemoperception is necessary for animals to identify suitable ecological niches and mating partners. Chemoreception is mediated by chemosensory receptors that interact with a variety of semio-chemicals, (odorants, pheromones and sapid molecules), allowing their detection and eliciting an adapted behaviour. In insects, the dendrites of the sensory neurons found in olfactory and gustatory sensilla are bathed in an aqueous phase called the sensillar lymph. Therefore, volatile and non-volatile chemical compounds contacting sensory organs should be solubilized and transported across the internal aqueous phase before reaching the sensory receptors. These carrier mechanisms, called “peri-receptor events” [1], involve several families of proteins, including odorant-binding proteins (OBPs). OBPs are small soluble proteins found in high concentration in both the nasal mucus of vertebrates and the chemo-sensilla lymph of insects [2][3][4][5][6][7]. OBPs were initially discovered during the early 1980s in parallel by two research groups working on the cow [8][9][10] and on the giant moth
[11]. A large number of DNA sequences encoding OBPs were later identified in several vertebrate species, including rat [12], pig [13][14], xenopus [15], and human [16][17]. OBPs were also detected in more than one hundred insect species, such as the silk moth
[20], the turnip moth
[23], the cotton bollworm
and the oriental tobacco budworm
[24].
2. Expression Pattern of Insect OBPs
2.1. Number of OBP-Coding Genes in Insects
The number of OBP-coding genes is highly variable between insect species, ranging between 13 in some ant species [25] to >100 in several mosquitoes [26] (
).
Numbers of annotated odorant-binding proteins (OBP) genes in different insects [27][28][29].
| Species | OBP Gene Number | |
|---|---|---|
 |
D. melanogaster | 52 |
| D. simulans | 52 | |
| D. sechellia | 51 | |
| D. yakuba | 55 | |
| D. erecta | 50 | |
| D. ananassae | 50 | |
| D. pseudoobscura | 45 | |
| D. persimilis | 45 | |
| D. willistoni | 62 | |
| D. mojavensis | 43 | |
| D. virilis | 41 | |
| D. grimshaw | 46 | |
 |
Anophele gambiae | 69 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | 109 | |
| Aedes aegypti | 111 | |
 |
Tribolium castaneum | 49 |
 |
Apis mellifera | 21 |
 |
Blatella germanica | 109 |
 |
Solenopsis invicta | 18 |
 |
Bombyx mori | 44 |
2.2. Evolution of OBP Genes
Exhaustive comparative genomic analysis of OBPs gene families in 20 Arthropoda species revealed a highly dynamic evolution, with a high number of gains and losses of genes. The number of OBP members is variable and diverse across Arthropoda species, exhibiting a wide range of gene lengths and encoding different cysteine profiles. Interestingly, two OBP members (OBP73a and OBP59a) have clear orthological relationships not only in the 12 Drosophila genomes but also in almost all insect species (except in Hymenoptera). Studies in the organization in chromosome clusters of OBP genes showed that this gene family is significantly clustered across the Drosophila evolution. This conservation across ∼400 myr of evolution suggests the existence of some functional constraints maintaining the clusters [30]. Other reports revealed that OBPs were only present in the Hexapoda (insects), and absent in other arthropod subphyla including the non-hexapod pan-crustaceans, chelicerates and myriapods. Moreover, OBP genes were detected in ancestral hexapods, such as Archaeognatha, Zygentoma, and Phasmatodea. However, the origin of OBP genes is still unknown and needs further investigation [31][32].
2.3. Tissue Expression and Cellular Localization of OBPs
Insect OBPs were originally identified in olfactory sensilla (Vogt and Riddiford, 1981) using immuno-electron microscopy, which enable the determination of their expression patterns in the different antennal sensilla types (trichoid, basiconic and coeloconic). A comparative study conducted on three moth species, the saturniid
, the bombycid
, and the noctuid
, detected PBPs in trichoid sensilla, particularly in the extracellular sensillum lymph of the hair lumen and in the sensillum-lymph cavities. Moth PBPs were also detected in secretory organelles of the trichogen and tormogen cells, supporting the hypothesis that these cells can produce and secrete PBPs into the sensillar lymph [33].
Recently, Larter et al. focused on the ten OBPs most abundantly expressed in the Drosophila antenna. They used in situ hybridization to map their spatial distribution in the different morphological sensilla classes (
a). The expression profiles of these antennal OBPs were more precisely investigated in the basiconic sensilla subtypes using double-labelling with OBP and OR markers. The expression patterns of distinct OBP subsets in different basiconic sensilla were identified. The map reveals that ab8 and ab9 basiconic sensilla express only one abundant OBP (OBP28a), while others co-express different OBPs. Moreover, some functionally distinct basiconic sensilla contain the same subset of abundant OBPs (
b) [34]. Drosphila olfactory and gustatory sensilla house three accessory cells that surround the cell body of the sensory neurons: the thecogen, tormogen and trichogen cells which are involved in insect sensilla morphogenesis and in OBP expression in the lymph. Conversely, non-neuronal cells expressing OBPs in antennal sensilla were identified using markers labelling each accessory cell. This study revealed that OBPs can be either expressed in tormogen cells or in thecogen cells. The only exception was OBP28a, which is simultaneously expressed in both types of accessory cell [34].

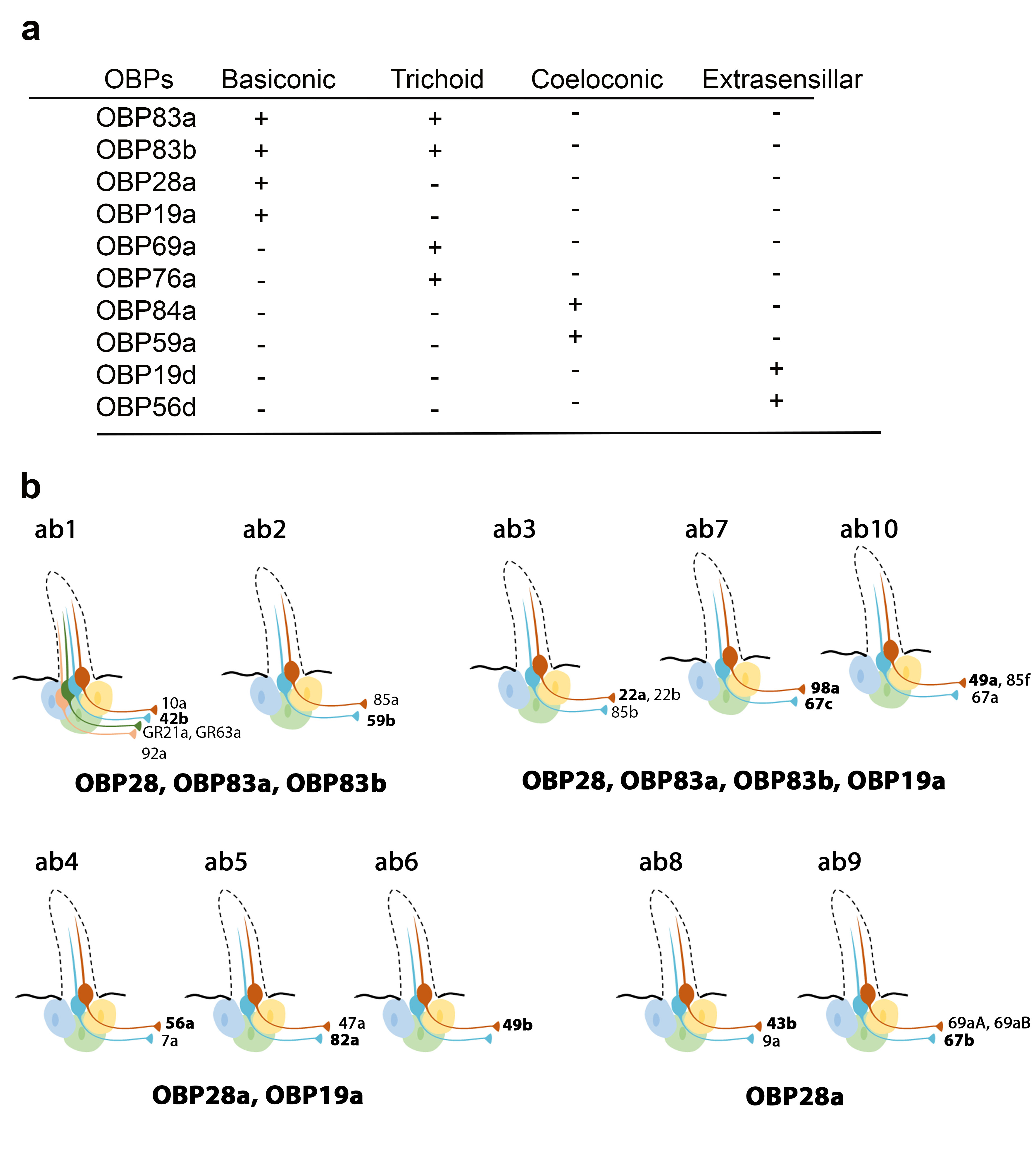
Expression patterns of the most abundant OBPs in Drosophila antennae. (
) Summary of the OBP expression patterns in the three types of antennal sensilla. OBP19d and OBP56g are expressed in epidermal cells. (
) Distribution of highly abundant OBPs expressed in Drosophila antennal basiconic sensilla. Olfactory receptor (OR) genes expressed in each olfactory receptor neuron class are indicated (all the OR genes except for GR21a and GR63a). The OR markers used for in situ hybridization for each sensilla are shown in bold [28][34].
The spatial and temporal expression patterns of insect OBPs have been reported in several studies, revealing that OBPs are expressed in both olfactory and taste appendages or in either chemosensory system. Gustatory OBPs have been less commonly studied than those expressed in olfactory tissues. For example, OBP57d and OBP57e are expressed in specific leg sensilla of different Drosophila species [35], while OBP49a and OBP19b are expressed in thecogen cells of
labellar sensilla [36][37]. The OBP19b protein was only detected in small and intermediate proboscis sensilla [37]. Moreover, OBP19d is not only expressed in olfactory appendages of
(antenna and maxillary palps) but also in adult gustatory organs (labellar bristles and pegs, legs, wings and in ventral and dorsal cibarial sense organs (VSCO)) [38][39] (
a,b). Two
OBPs and one
OBP were detected in the mouthparts [40], while OBP57e, OBP56g, OBP28a2 and OBP49a were identified in the legs of the oriental fruit fly
[41]. In
adults, several OBPs were exclusively identified in olfactory tissues, while others (OBP10, OBP17, OBP18, OBP22, OBP25) were identified in taste appendages (proboscis and legs) [42]. Similarly, taste-specific OBPs were identified in the labellum and tarsi in
and in the red flour beetle
[43][44]. In the desert locust
, a subset of the antennal OBP repertoire is also expressed in the maxillary and the labial palps [45]. Moreover, seven genes expressed in the labellum and tarsus of the fleshfly
were identified and show sequence similarity to insect OBP genes. Homologues of these gene products were detected in
taste tissues [46]. In the legs of the two mosquito species
and
, the identified OBP (agCP1564) shows high similarity to Drosophila OBP57e, which is specifically expressed in the tarsi [47][48] (
a). Notably, 6 OBPs (OBP1, OBP2, OBP3, OBP4, OBP7 and OBP8) were found in the antenna and legs of the onion fly
. Homology studies identified their
homologues (OBP19d, OBP83a, OBP83b, OBP56h, OBP76a, OBP69a, respectively). Unlike
,
homologues are only expressed in the fly antenna except for OBP19d, which is also expressed in Drosophila tarsi, and OBP56h, which is also expressed in Drosophila proboscis [49] (
a,b). Other studies have reported the expression of OBPs in insect legs: OBP7 in
[50], OBP10 in
[51] and OBP4, OBP6, OBP7, OBP8 in
[52]. Similarly, OBPs are expressed in the legs and wings of three species of social hymenopterans (
,
,
) [53]. Notably, three OBPs were identified in the anterior margin of the wings of
a). The differences in OBP expression between tarsi, labellum and wings might be explained by the distinct roles of OBPs in food detection and intake.
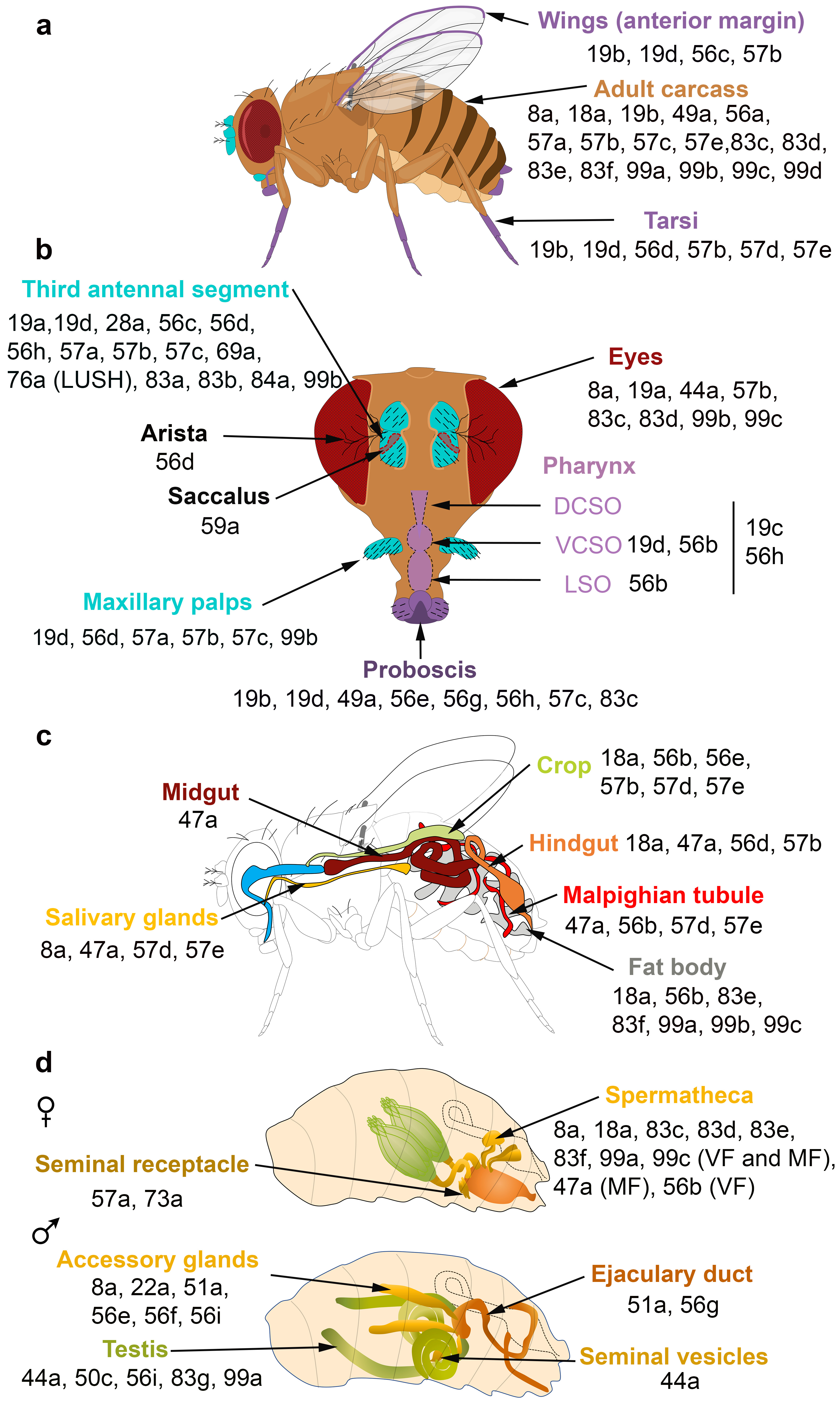
OBPs expressed in the olfactory, gustatory, digestive and reproductive organs of
. (
,
) Adult taste organs (purple) consist of the proboscis, the internal structure in the pharynx (the labral sense organ (LSO), the ventral and dorsal cibarial sense organs (VCSO and DCSO)), the leg tarsi, the anterior margin of the wings and the female genitalia. Adult olfactory organs (turquoise) consist of the antenna and the maxillary palps. OBPs expressed in each organ are indicated by their number. OBPs are found in chemosensory and non-chemosensory organs. (
) Expression patterns of OBPs in the adult digestive tract. (
) Expression patterns of OBPs in the female and male reproductive organs. The expression of OBPs in female spermatheca depends on the sexual state. Some OBPs are expressed in virgin female (VF) and mated female (MF) spermatheca, while the expression of some OBPs is mating-dependent [36][37][38][47][54][55][56][57][58][59].
Proteomic and transcriptional studies confirmed the expression of a subset of insect OBPs in non-sensory organs. In the honeybee, 9 of the 21 OBPs predicted by the genomic sequence were detected in the mandibular glands [60]. OBPs can be expressed in female and male reproductive organs. In
, six OBPs (especially the abundant OBP56f and OBP56g) were detected among the seminal fluid proteins transferred to females during copulation, and three of these OBPs were found in the seminal receptacle [55][61][62][63]. Similarly, OBP10 is highly abundant in the seminal fluid of the two Lepidopteran species
and
[24]. The OBPs present in seminal fluid could be carriers of oviposition deterrents. In addition, OBP22 of the mosquito
[66] and two OBPs of
[67] are also present in sperm. Proteomic analysis revealed OBP expression in mosquito ovaries and eggshell [68][69][70]. RNAseq analyses and RT-PCR data also revealed the presence of OBPs in the ovaries of the stemborer
[23]. We can hypothesize that their accumulation in the ovaries is involved in oocyte maturation. These OBPs might also bind chemo-attractant molecules, resulting in sperm attraction. Moreover, in the oriental fruit fly
, OBP44a, OBP49a, and OBP56g are highly expressed in the male testis and OBP19c is highly expressed in the female ovary [41]. Examination of the FlyAtlas expression database reveals that OBP44a, OBP50c, OBP56i, OBP83g, and OBP99a are expressed in
male testis (
d). Among the 32 OBP genes annotated in the Hessian fly
, 24 and 25 of them were found to be expressed in female and male terminal abdomens, respectively. Only OBP31 (in female) and OBP11, OBP24 and OBP32 (in male) showed relatively higher expression levels in the terminal abdomen than in the antennae [71]. Moreover, four OBPs (OBP1, OBP4, OBP8, OBP10) were identified in the
abdomen, which houses the reproductive organs. These OBPs share high sequence homology with their
analogues (OBP8, OBP56d, OBP83ef and OBP99c, respectively).
analogues are also expressed in different reproductive organs present in the abdomen (
d) [50]. In
and
, OBP expression was also detected in the abdomen [42][72]. Moreover, OBP22a, OBP51a, OBP56e, OBP56f, OBP56i are highly expressed in
male accessory glands (
d). All these data suggest that OBPs may (i) serve to bring odorants or pheromones next to the odorant receptors present in the female reproductive tract or (ii) carry male-specific molecules into female tissue to elicit a behavioral response. It is not yet known whether these OBPs are related to fertility and fecundity features.
The FlyAtlas expression database reveals that 6 OBPs are expressed in
eyes (
b). Similarly, several OBPs were identified in the eyes of the lepidopteran
[40]. Together with other proteins, these OBPs may be implicated in the complex mechanism of vision, specifically in the generation, transport and recycling of visual pigments.
In
, some OBPs are expressed in both larva and adults, while others are only expressed in adults (
). The majority of OBPs expressed in larva show similar expression patterns in adult tissues (
and
).
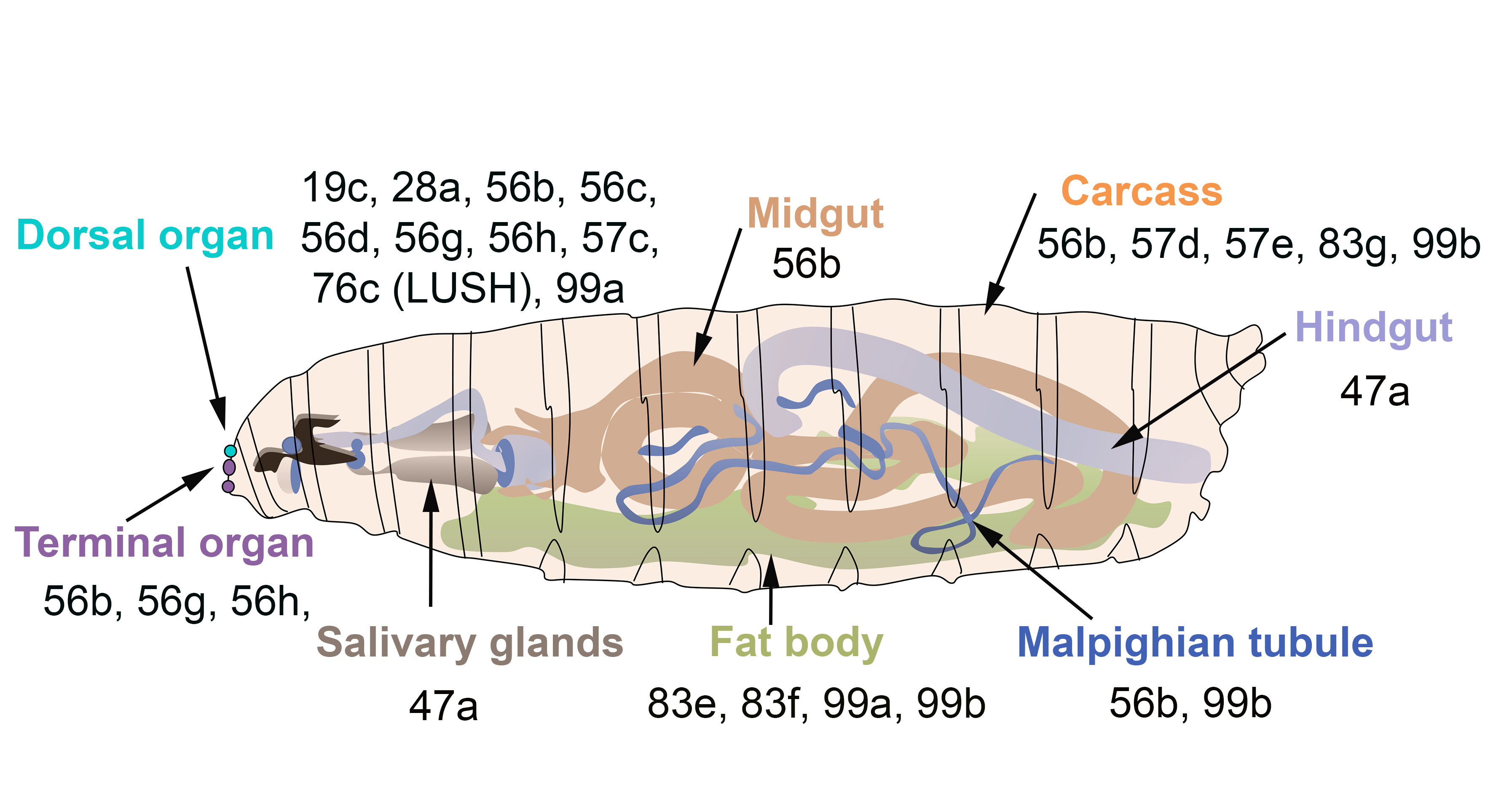
OBPs expressed in the olfactory gustatory and digestive organs of
larvae. The larval dorsal organ (turquoise) detects volatile odorants, while the larval terminal organ (purple) detects both soluble and volatile chemicals.
Surprisingly, several OBPs are expressed in the venom glands of the parasitic wasps
and
and of the honeybee
[73][74][75]. Few studies have reported the expression of OBPs in the insect digestive tract. For instance, PregOBP56a was detected in the oral disk of the blowfly
[76], while OBP56d was identified in the hindgut of
flies [54]. Fluorescent binding assays revealed that PregOBP56a binds palmitic, stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids. These data indicate that PregOBP56a might solubilize and deliver fatty acids to the midgut during feeding [76]. Similarly, the midgut of
also expresses OBPs [77]. Other studies have shown that the expression of OBPs can be altered depending on the insect’s diet. Indeed, the expression of one OBP of female
increased in the midgut, thorax and abdomen after a bloodmeal, suggesting a possible role in blood feeding [78][79]. Moreover, a diet change in
can affect gut-expressed OBPs together with other genes implicated in digestion, detoxification and nutrient acquisition. The feeding of
larvae in a host with documented resistance (
) induced the downregulation of 5 OBP genes. It is not known whether alteration of the gut OBP gene expression is directly linked to the resistance of
