Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Su-Jun Lee and Version 2 by Lily Guo.
Estrogen sulfotransferase (SULT1E1) is a phase II enzyme that sulfates estrogens to inactivate them and regulate their homeostasis. This enzyme is also involved in the sulfation of thyroid hormones and several marketed medicines. Though the profound action of SULT1E1 in molecular/pathological biology has been extensively studied, its genetic variants and functional studies have been comparatively rarely studied.
- estrogen sulfotransferase
- SULT1E1
1. Introduction
Human SULT1E1 cDNA was first isolated, cloned, and characterized from the liver, and its localization was mapped to human chromosome 4 [1][20]. SULT1E1 is expressed in the human embryo, and is also highly expressed in a wide range of fetal tissues, such as the liver, lung, kidney, and hormone-dependent tissues—such as the testis or endometrium—but its expression in adults with normal status is much lower than in the fetus and placenta [2][3][21,22]. The expression of SULT1E1 varies widely in the human population, although it is not known whether this is under genetic control or not [4][23]. Thus, it is possible that the variability in SULT1E1 expression results from different chemical influences.
Two agonists of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), WY14643 and IGF-1, show different regulatory effects on the SULT1E1 promoter activity. While WY14643 suppressed SULT1E1 activity, IGF-1 upregulated it, as measured by estrogen levels in endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells [5][24]. Interestingly, SULT1E1 was attenuated by both transfection with PPARγ small interfering RNA (siRNA) and exposure to GW9662, the PPARγ antagonist [6][25].
SULT1E1 regulation was observed when hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) was silenced. The significant suppression of both mRNA and protein levels of SULT1E1 occurred via Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists in HepG2 cells [7][26]. This finding confirmed that the effect of FXR on E2 was SULT1E1-dependent. In patients with obstructive cholestasis, the accumulation of bile acids (activator of FXR) led to reduced mRNA and protein expression of hepatic SULT1E1, increased serum E2 levels, and decreased serum estrone sulfate concentration [8][27]. Phosphorylated RORα takes a regulatory signal to HNF4α, and then activates the SULT1E1 promoter in human liver cells [9][28].
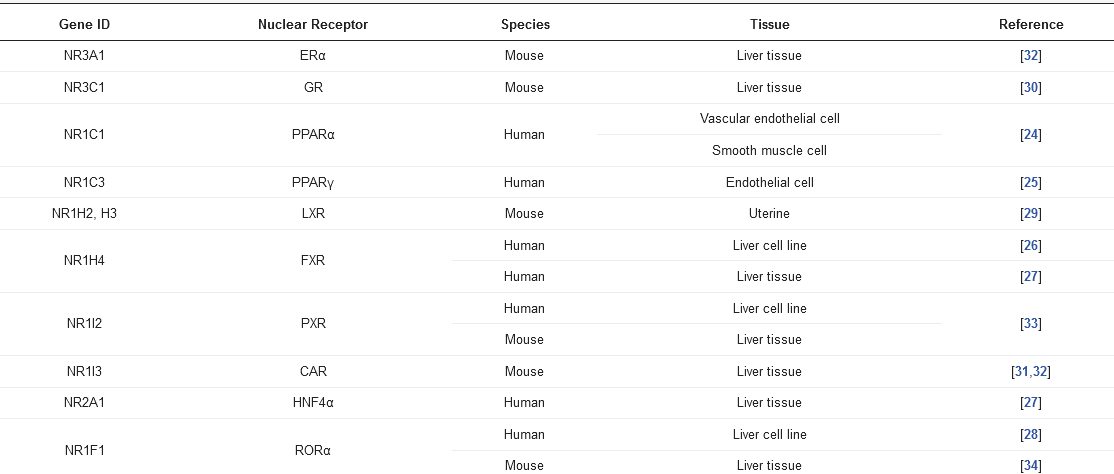
Basal expression of SULT1E1 in the liver is relatively low [10][29], but its expression and role could be impacted in response to ligands/substrates for nuclear receptors, such as the liver X receptor (LXR) [10][29], the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) [11][30], the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) [12][31], the estrogen receptor α (ERα) [13][32], the pregnane X receptor (PXR) [14][33], and the RAR-related orphan receptor α (RORα) [15][34] (Table 1).
Table 1.
The nuclear receptors associated with
Sult1e1 regulation.
| 11 | ||||
| SULT6B1 | ||||
| Chr 2p22.2 | ||||
| ST6B1 | ||||
| 304 (isoform 1) | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 265 (isoform 2) | ||||
| SUPl1C2P1 | ||||
| Chr 2q12.3 | SULT1C1P | pseudogene | 4 | |
| SULT1C2P2 | Chr 2q12.3 | pseudogene | ||
| SULT1D1P | Chr 4q13.3 | SULT1D1 | pseudogene | |
| SULT6B2P | Chr 12p12.1 | pseudogene |
regulation.
2. Sulfation of Estrogens and Thyroid Hormones by SULT1E1
2.1. Sulfation of Estrogens
Estrogens play fundamental roles in a variety of physiological systems. It has been widely established that estradiol (E2) exposure is one of the risk factors for breast carcinogenesis. One of the critical pathways for E2 inactivation is sulfation by SULT1E1. Estrone (E1) is synthesized by aromatization of androstenedione and is subsequently sulfated. After E1 is desulfated and subsequently turned into E2 by the 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (17β-HSD), E2 can then be sulfated through SULT1E1 [16][35]. As previously mentioned, SULT1E1 is a cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes estrogen sulfation at the 3-hydroxyl site while using PAPS as a sulfate donor (Figure 1). Moreover, this enzyme has high affinity for its substrate E2, indicating its crucial role in modulating estrogen’s action and homeostasis [17][36].
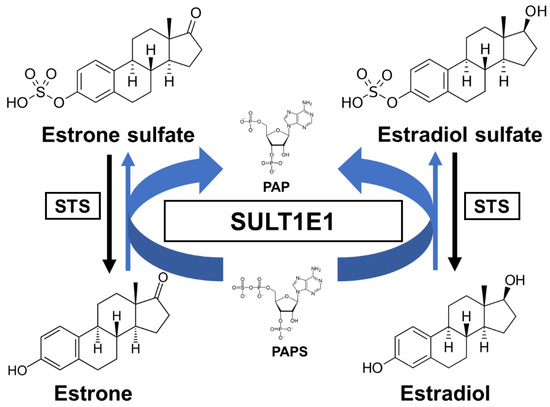
Figure 1.
A schematic sulfation pathway of estrogens. STS, steroid sulfatase; PAPS, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; PAP, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate.
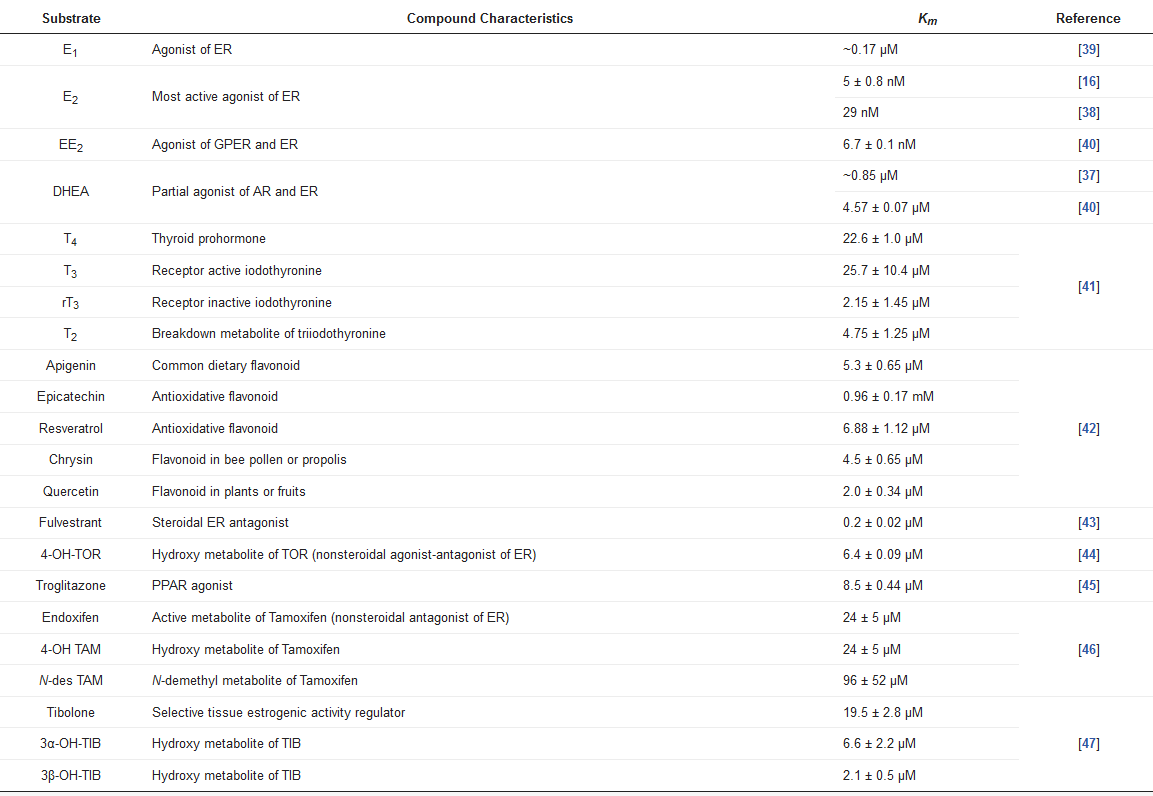
SULT1E1 has shown the distinct characteristic of having a high sulfating affinity for not only E2, but also other estrogens, such as E1 and ethinylestradiol (EE2), with nanomolar Km values (Table 2). Due to its high affinity for sulfate estrogens, SULT1E1 exhibits inhibition of substrate with increasing E2 and E1 concentrations. SULT1E1 is also used to sulfate other compounds, namely dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), pregnenolone, diethylstilbestrol (DES), and equilenin [18][19][37,38].
Table 2.
Substrates of SULT1E1.
| Species | RefSeq 1 | RefSeq mRNA 2 | RefSeq Protein 3 | Number of Exons 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens (human) | NC_000004.12 | NM_005420.3 | NP_005411.1 | 9 |
| Mus musculus (mouse) | NC_000071.7 | NM_023135.2 | NP_075624.2 | 8 |
| Rattus norvegicus (rat) | NC_005113.4 | NM_012883.2 | NP_037015.2 | 10 |
| Bos taurus (cow) | NC_037333.1 | NM_177488.3 | NP_803454.2 | 9 |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | NC_013683.1 | XM_002717123.2 | XP_002717169.1 | 8 |
| Sus scrofa (pig) | NC_010450.4 | NM_213992.1 | NP_999157.1 | 9 |
| Equus caballus (horse) | NC_009146.3 | NM_001081918.1 | NP_001075387.1 | 8 |
| Gene ID 1 | Locus 2 | Alias 1 | Number of Amino Acids 3 | Number of Exons 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SULT1A1 | Chr 16p11.2 | HAST1/HAST2, P-PST, PST, ST1A1, ST1A3, STP, STP1, TSPST1 | 295 (isoform a) | 13 |
| 217 (isoform b) | ||||
| SULT1A2 | Chr 16p11.2 | HAST4, P-PST, P-PST 2, ST1A2, STP2, TSPST2 | 295 (isoform 1) | 8 |
| 262 (isoform 2) | ||||
| SULT1A3 | Chr 16p11.2 | HAST, HAST3, M-PST, ST1A3, ST1A3/ST1A4, ST1A4, ST1A5, STM, TL-PST | 295 | 8 |
| SULT1A4 | Chr 16p11.2 | HAST3, M-PST, ST1A3, ST1A3/ST1A4, ST1A4, STM, TL-PST | 295 | 8 |
| SULT1B1 | Chr 4q13.3 | ST1B1, ST1B2, SULT1B2 | 296 | 10 |
| SULT1C2 | Chr 2q12.3 | ST1C1, ST1C2, SULT1C1, humSULTC2 | 296 (isoform a) | 9 |
| 307 (isoform b) | ||||
| SULT1C3 | Chr 2q12.3 | ST1C3 | 304 (isoform 1) | 10 |
| 304 (isoform 2) | ||||
| SULT1C4 | Chr 2q12.3 | SULT1C, SULT1C2 | 302 (isoform 1) | 7 |
| 227 (isoform 2) | ||||
| SULT1E1 | Chr 4q13.3 | EST, EST-1, ST1E1, STE | 294 | 9 |
| SULT2A1 | Chr 19q13.33 | DHEA-ST, DHEA-ST8, DHEAS, HST, ST2, ST2A1, ST2A3, STD, SULT2A3, hSTa | 285 | 6 |
| SULT2B1 | Chr 19q13.33 | ARCI14, HSST2 | 350 (isoform a) | 7 |
| 365 (isoform b) | ||||
| SULT4A1 | Chr 22q13.31 | BR-STL-1, BRSTL1, DJ388M5.3, NST, SULTX3, hBR-STL-1 | 284 |
SULT1E1 is also expressed in hormone-dependent tissues, such as endometrium [3][20][22,48] and placenta [2][21]. SULT1E1 is specifically expressed during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle in human endometrium [21][49]. Upregulated SULT1E1 activity in the endometrium may result in sulfating E2 after ovulation [22][50]. In addition, SULT1E1 can be induced by progestins in human Ishikawa endometrial adenocarcinoma cells [23][51].
As an interesting effect, estrogens inhibit expression of the potent growth factor repressor transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. In addition, it was observed that MCF-7 cells expressing SULT1E1 activity did not show a decrease in ERα levels, an increase in progesterone receptor, or a decrease in transforming growth factor-β expression, suggesting the rapid sulfoconjugation of E2 by SULT1E1.
It is possible that SULT1E1 contributes to EE2 sulfation during hepatic-mediated first-pass metabolism. SULT1E1 is the high-affinity enzyme responsible for EE2 sulfation at nanomolar concentrations, so SULT1E1 plays a predominant role in the sulfation of EE2 in the intestine and liver.
2.2. Sulfation of Thyroid Hormones
Many factors serve as regulators for the effectiveness and bioavailability of receptor active thyroid hormone (T3) [24][25][52,53]. The prohormone thyroxine (T4) is predominantly secreted to regulate metabolism [26][27][54,55]. Deiodination is one of the principal and major pathways to degrade active compounds, and there are three types of deiodinase selenoproteins—iodothyronine deiodinases (D1, D2, and D3) [28][56]. These deiodinases are promotive of the reductive T4 deiodination and its metabolites (Figure 2).
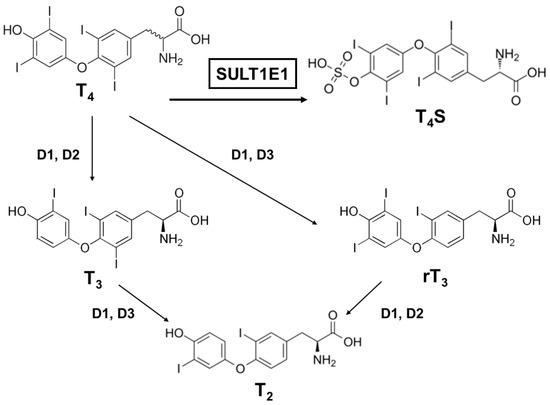
Figure 2. A schematic metabolic pathway of thyroid hormones. T4, thyroxine (prohormone); T4S, thyroxine sulfate (sulfoconjugated metabolite); T3, 3.3′,5-triiodothyronine (receptor active iodothyronine); rT3, 3.3′,5′-triiodothyronine (receptor inactive iodothyronine); T2, 3.3′-diiodothyronine.
One major modification thyroid hormones receive is sulfation, which deactivates them. Thyroxine sulfate can be detected in human fetal blood and amniotic fluid, indicating that the production of sulfoconjugates is critical in utero [29][57]. Iodothyronine sulfates (T4S, T3S, rT3S, and T2S) are generated by SULT enzymes, which are located in a variety of different tissues, and catalyze the sulfation and substitution of the hydroxyl groups of various compounds using PAPS as the sulfate donor [30][58]. Interestingly, among the SULTs, most of the SULT1 enzymes catalyze the sulfation of iodothyronines [31][32][33][34][41,59,60,61]. SULT1E1 is highly effective at catalyzing rT3 sulfation and has sulfating activity for all iodothyronines (Table 4). For rT3 sulfation especially, SULT1E1 has the highest activity among the SULT1 subfamily, even compared to SULT1A1 [32][59]. Moreover, SULT1E1 was reported as the most active enzyme that exhibited catalyzing activity for T4 sulfation [35][62].
SULT1E1 can be detected in the human endometrium and in the mouse uterus, so it might be possible that the uterus could protect the fetus from excessive thyroid hormone by inactivating pathways via SULT1E1 or D3. It is notable that the metabolites derived from D3 (rT3 and T2) are also favorable substrates of SULT1E1, suggesting that T4 and T3 are metabolized in the uterus by consecutive sulfation. The physiological roles of each iodothyronine SULT still remain too complex to be comprehended in full. Although SULT1E1 has been proven to be a potent iodothyronine SULT along with SULT1A1, it is probable that the other SULT1 enzymes contribute to iodothyronine sulfation in a tissue- or growth-dependent way [36][37][38][63,64,65].
