Uremic sarcopenia is a frequent condition present in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients and is characterized by reduced muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance. Uremic sarcopenia is related to an increased risk of hospitalization and all-causes mortality. This pathological condition is caused not only by advanced age but also by others factors typical of CKD patients such as metabolic acidosis, hemodialysis therapy, low-grade inflammatory status and inadequate protein-energy intake. Currently, treatments available to ameliorate uremic sarcopenia include nutritional therapy (oral nutritional supplement, inter/intradialytic parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, high protein and fiber diet and percutaneous endoscopic gastrectomy) and a personalized program of physical activity.
- uremic sarcopenia
- physical activity
1. Introduction
“Sarcopenia” is a term derived from the Greek “sarx”—meat and “penia”—loss, and it was first coined in 1988 by Irwin Rosenberg to describe the modifications that occur in the muscles during aging [1]Progressive and generalized loss of muscle strength and muscle mass (MM) is also a frequent complication in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [2][3][4]. The mechanisms involved are many and not yet fully clarified, but it is certain that they all converge towards a final process of increasing protein degradation and reducing protein synthesis, leading to a negative nitrogen balance [5]. Muscle is one of the most represented tissues in the human body. Skeletal muscles are the predominant component, while other types such as cardiac and smooth musculature are less represented. Skeletal muscle is mainly composed of proteins and it represents the “best indicator” of overall protein shift[6]. The reduction of muscle strength and mass, especially skeletal, is associated with a worsening quality of life (Qol), an increased vulnerability to adverse events such as falls, loss of personal autonomy and ultimately increased hospitalization and mortality [7].In 1931 the British neurologist Critchley Macdonald was the first, in the scientific literature, to correlate aging with the tendency to loss of skeletal MM [7]. Since then, several studies have been carried out to deepen the qualitative and quantitative changes that occur physiologically in the MM and fat mass with aging[8].Quantitative changes consist in the reduction of MM and volume, while the qualitative ones consist in the reduction of muscle strength and in physical performance. Among qualitative changes of uremic muscle should include alterations of muscle mitochondrial morphology, their protein pathways, and decreased mitochondrial respiratory function[9][10]. Moreover, the uremic condition predisposes to a capillary rarefaction altering physiological muscle function [11]. It has also been observed that aging, in addition to the loss of muscle strength and mass, is associated with increase in fat mass, especially localized in the abdominal area [12]. Many studies conducted on changes in musculature, during lifespan, are transversal. The data obtained overall indicate an estimated reduction in MM by about 1–2% per year after 50 years and muscle strength declines by 1.5% between ages 50–60, with a tendency to a further reduction of up to 3% per year, thus achieving a total loss of MM and muscle strength of about 40% from 30 to 70 years of age[8]. Longitudinal studies in geriatric populations confirmed the results of these cross-sectional studies, as discussed below. A study by Delmonico et al. [12], conducted on 1678 subjects (heterogeneous for age, sex and ethnicity), showed that from 70 years of age there is an annual reduction of the muscular area of 4.9 ± 7.4% in men and 3.2 ± 7.9% in women. Similar results were obtained by Cameron et al.[13] in a population of seventy, in which lean mass was measured with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The loss of MM was approximately 5% in five years of follow-up regardless of basal MM values. The phenomenon of aging is characterized by a primary reduction in muscle strength and subsequently occurs a reduction in MM. This could be due to the progressive infiltration of adipose tissue into the muscle [14] and the development of muscle fibrosis [15], processes that reduce muscle performance but do not result in a reduction of muscle volume.Since 2010 sarcopenia has gained more interest in the scientific community, thanks to the publication of the first consensus on the subject published by the European Working Group for Sarcopenia for Older People (EWGSOP)[16]. The criteria to be considered are three: 1—reduced MM, 2—reduced muscle strength, 3—reduced physical performance. According to the EWGSOP, the presence of criterion 1, associated with criterion 2 or 3, is required for the diagnosis of sarcopenia. Over the years, consensus has developed by different societies that agree in defining sarcopenia as a syndrome characterized by the progressive and generalized loss of MM and strength, associated with the high risk of adverse events such as physical disability, reduced Qol and death. The first consensus was revised in 2019 and the main parameter considered for the diagnosis of sarcopenia is no longer MM but muscle strength[16][17][18][19][20]. The EWGSOP1 [16] divided sarcopenia into primary, when this condition is related to age in the absence of other obvious causes, and secondary, when it is determined by other pathological conditions and not necessarily by advanced age. Secondary sarcopenia can occur in conditions of reduced physical activity (lodging, sedentary life, zero-gravity conditions), in diseases (CKD, inflammatory diseases, endocrine and malignant diseases) and under conditions of reduced intake of nutritional factors (reduced intake of nutrients, malabsorptive conditions, gastrointestinal diseases, use of anorexic drugs) [21][22]. The main difference between primary and secondary sarcopenia is that in the former the loss of MM occurs consistently and generally from the fourth to fifth decade, while in secondary sarcopenia the loss of MM is not only related to advancing age, but also to the development of pathological processes of protein degradation that are more aggressive than those that occur physiologically with aging[23]. The EWGSOP2 defined the concept of acute and chronic sarcopenia, considering the first as an acute condition present for less than six months, while the second is considered a chronic condition present for more than six months. Acute sarcopenia is often linked to an acute disease; on the contrary chronic sarcopenia is correlated with a chronic and progressive disease that induces an increased risk of mortality[20]. Experimental data showed that muscle tissue should be investigated through the execution of biopsies which permits the detection of distinct variations between primary and secondary sarcopenia [24]. In fact, primary sarcopenia is generally characterized by atrophy of both type I and type II fibers, while secondary sarcopenia, especially that associated with CKD, causes a specific reduction of type II fibers. In any case, these data need to be confirmed by further research. Secondary sarcopenia is often associated with two other well-known pathological conditions: protein-energy wasting (PEW) (present in between 18% and 75% of chronic hemodialysis (HD) patients)[25][26] and cachexia. PEW is a condition of malnutrition characterized by a reduced and inadequate protein and energy intake. It is a multifactorial condition whose diagnosis is complex and involves the integration of laboratory and anthropometric parameters. The International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM) has defined a set of criteria necessary for the diagnosis of PEW[27]. These criteria are body mass index (BMI) < 23 kg/m
; unintentional body weight loss of about 5% in 3 months or 10% in 6 months; reduction of arm circumference > 10% compared to the 50° percentile of the reference population; MM reduction of about 5% in 3 months or 10% in 6 months; albuminemia < 3.8 g/dL; total cholesterol < 2.59 mmol/L; unintentional protein intake < 0.8 g/kg per day in HD patients; unintentional energy intake < 25 kcal/kg per day. Cachexia is a condition of metabolic imbalance characterized by the loss of MM with or without loss of adipose tissue[28][29]. The Society of Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders (SCWD)[28] has proposed a series of criteria necessary for the definition and diagnosis of cachexia: albuminemia < 3.2. g/dL; hemoglobin < 12 g/dL; increment of inflammatory markers or C-reactive Protein (CRP) > 5 mg/L, interleukin (IL)-6 > 0.4 pg/mL; BMI < 20 kg/m
; unintentional loss of 5% of body weight in 12 months; appendicular skeletal muscle index, measured with DXA, <7.25 kg/m
in men and <5.45 kg/m
in women; reduced arm circumference; “fatigue” understood as physical and/or mental fatigue resulting from the effort or inability to continue an exercise with the same intensity, resulting in a worsening of performance; reduced appetite; unintentional reduction of energy intake < 20 kcal/kg per day; 70% reduction in usual daily energy intake[28]Sarcopenia should be considered not only as a geriatric disease, but a multidisciplinary condition. Since the first consensus on sarcopenia, published in 2010 by the EWGSOP [17], numerous studies have been performed to investigate the possible correlations of sarcopenia with CKD, especially with ESRD [30][31][32]. It has been shown that secondary uremic sarcopenia is determined by a more severe protein degradation process with respect to primary sarcopenia[33]. In primary sarcopenia, it is essential to restore a proper motor activity and an adequate Qol, thereby reducing the mortality rate. In secondary sarcopenia, where “muscle wasting” and PEW are prominent, the main goal is to reverse the process that causes sarcopenia or to restore optimal nutritional status. The latter allows patients to respond more effectively to therapeutic treatment. Further therapeutic objectives are to restore appropriate mobility and Qol and to reduce mortality and hospitalization rates. In 2019, EWGSOP2 [21] continues to define sarcopenia as a concomitant presence of altered quantity and quality of MM but, differently from the previous consensus, EWGSOP2 proposed the use of reduced muscle strength as a key criterion to identify “probable-sarcopenia”. The diagnosis of sarcopenia is confirmed by the presence of low muscle strength and low muscle quantity or quality. The stage of severe sarcopenia is reached when the patient presents a reduction in MM (quality and quantity), muscle strength and physical performance simultaneously. According to EWGSOP2, therefore, reduced MM is no longer the key element in the diagnosis of sarcopenia, but reduced muscle strength. This change is justified by the fact that reduced muscle strength is better than reduced MM in predicting adverse outcomes in sarcopenic patients[34]. Leong et al.[34], in fact, measured the prehensile force of the hand of 142,861 subjects whose age was between 35–70 years. After a follow-up of 4 years, the authors observed that the degree of prehensile strength of the hand was inversely related to all causes of mortality, cardiovascular (CV) and otherwise, and to the onset of acute myocadiac infarction and stroke. This study confirmed that the simple dynamometer measurement of the prehensile force of the hand would provide information about the patient’s prognosis, since it would relate to all causes of mortality. Thanks to the simple use of the portable manual dynamometer, muscle strength is therefore easily detectable, not only in hospital facilities, but also in other care centers. Another method for assessing muscle strength characterized by easy execution is the chair stand test as defined by the EWGSOP2. The chair stand test evaluates the muscle strength of the quadriceps group and its proper execution requires both strength and endurance from the patient. This test is adjuvant in the early diagnosis of sarcopenia[21]
2. Nutritional Therapy
Dietary interventions necessary to preserve MM and provide an adequate energy and protein load are essential for the health of HD patients and their nutritional status, especially when the processes of MM reduction are already established[35]. For CKD (stages III–V) patients, a protein intake of 0.6–0.8 g/kg body weight (b.w.)/day and an energy intake of 30–35 kcal/kg b.w./day is recommended. Despite the risk of a negative nitrogen balance, a low protein diet (LPD) is indicated for CKD, because it is related to a better metabolic status and a better control of the signs and symptoms of CKD, if compared to a diet with high protein intake [36][37]. The risk of protein restriction consists in the possibility of establishing a state of malnutrition, complicated by the reduction of MM, and therefore by sarcopenia. For this reason, it has been proposed to combine the LPD with the use of energy supplements with controlled fats and carbohydrates content[38][39] In this regard, a study by Wu et al.[39] was conducted on 109 CKD patients (stage III-IV), divided into a control group (54 patients) and an experimental group (55 patients). For a duration of 24 weeks, all participants were prescribed a diet with a controlled protein intake (CPI), comprising between 0.6–0.8 g/kg b.w./day and an energy intake of 30–35 kcal/kg b.w./day, associated with dietary counseling. Only the experimental group was required also to consume an energy supplement of 200 kcal/day (40 g of maltodextrin together with 5 g of oil creamer). The authors noted that the patients in the experimental group, thanks to the energy supplementation, had a greater adherence to the prescribed nutritional therapy and, therefore, better values for the renal function indices. Urinary protein excretion values were significantly lower respect to the control group, as well as creatinine and azotemia values, while glomerular filtration rate (GFR) values were higher. This study suggested that CKD patients in conservative therapy can successfully benefit from a diet with a CPI. At the same time, a controlled energy supplementation would ameliorate, on the one hand, the adherence to the same diet with CPI, and on the other would improve the nutritional status of the CKD patient.The LPD, with or without energy supplementation, can be used successfully especially in younger CKD patients. In fact, the protective effects of the LPD on the progression of CKD were less evident in the geriatric population. An example of this is the study of Levine et al. [40]that examined the epidemiological data from NHANES III—National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[41]. NHANES III is a cross-sectional study conducted to assess the health and nutritional status of a representative sample of the US population for ethnicity, education and comorbidity (6381 subjects aged over 50 years). From the observation of such data, the authors have evidenced that the mortality rate among the individuals with LPD was different, depending on the age of the subjects analyzed. In particular, individuals between the 50–65 years who followed a high-protein diet (HPD) had a significant increase in mortality for all causes up to a value of 74% compared to individuals of the same age but who followed a LPD. These results were opposed if the subject of the study were individuals over 66 years of age. This group, on the contrary, presented a 60% reduction in mortality rate for all causes if it consumed a LPD, while the reduction was only 28% if it consumed a diet rich in protein. This study shows that in the geriatric population higher protein intake is related to a better prognosis due to a reduced risk of mortality. The reduced protein intake in CKD patients must always take into account the possible risks of malnutrition associated with this dietary restriction, therefore the LPD must be prescribed by a multidisciplinary team that includes a nephrologist, a nutritionist expert in renal diseases and a psychologist, the latter necessary to allow the acceptance of chronic pathology and increase adherence to the prescribed dietary-nutritional treatment. It has been observed that malnutrition in CKD patients is associated with a faster progression of kidney disease, and thus a worsening of the prognosis with an increase in the mortality rate[42]. The recommendations for protein intake in ESRD patients reflect the need to ensure an adequate nutritional intake to prevent the development of comorbidities such as sarcopenia, PEW and cachexia. The recommendations of the current guidelines and consensus published so far is to take at least 1.1–1.2 g/kg b.w./day of protein for ESRD patients under HD treatment [36][43][44][45]. In HD subjects, a higher protein intake is therefore recommended compared to the one advised to the general population (0.8/kg b.w./day), especially considering the loss of amino acids and proteins that occurs during HD treatment. Moreover, in HD patients an intake of 35 kcal/kg b.w./day is recommended, taking into consideration also the age, the physical activity carried out by the patient and the hypercatabolic state induced by dialysis [36][43][44][45].In ESRD, uremic intoxication and the need to slow the progression of nephropathy are no longer the focal point of nutritional therapy, as they are treated by adequate HD therapy. The prevention and management of MM reduction thus becomes the focal point of nutritional therapy that is focused on maintaining an equal or positive nitrogen balance, so as to ensure better outcomes in patients in HD treatment. Sabatino et al. [46]have proposed an interesting algorithm that indicates the intervention times on the nutritional status, the types of intervention, and the protein-energy intake targets to be achieved in chronic HD patients. The need to further implement the protein intake in HD patients is due to the presence in this category of an increased protein catabolism and reduced synthesis that induces the development of pathological conditions such as sarcopenia. In addition, as emerged from a study of Cupisti et al.[1], often up to 50% of HD patients assume less than 1 g/kg b.w./day protein and experience a reduced energy intake, aggravating their negative nitrogen balance condition.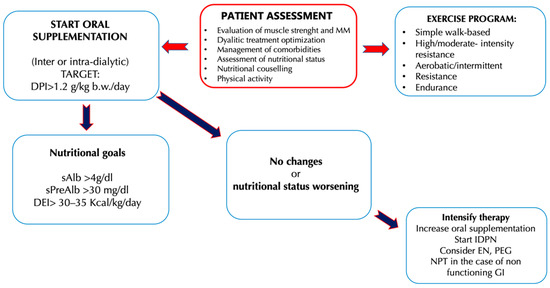 Figure 2. Clinical management of hemodialysis (HD) patients to counteract the onset and the progression of uremic sarcopenia[46]. Abbreviations: b.w., Body weight; DEI, Diet energy intake; DPI, Diet protein intake; EN, Enteral nutritional; GI, Gastrointestinal; IDPN, Intra-parenteral nutrition dialysis; MIS, Malnutrition inflammation score; MM, Muscle mass; PEG, Percutaneous endoscopic gastrectomy; SGA, Subject global assessment; TPN, Total parenteral nutrition.Several studies have been carried out to investigate the different strategies that ensure an adequate protein-energy intake in HD patients. Numerous studies have shown that, in nephropathic patients, HPD causes an accumulation of toxic compounds (derived from protein metabolism), while a LPD offers better outcomes in these patients [47] In particular, in CKD it is necessary to distinguish two categories of patient: the first (i) is represented by patients undergoing conservative therapy and the second (ii) is represented by patients in renal replacement therapy. In the first category, an HPD, defined as a diet with an intake greater than 1.2 g prot/kg/b.w. per day, is able to alter renal hemodynamics, inducing the condition of hyperfiltration [48]. Renal hyperfiltration consists in the increase in renal blood flow inducing an enhancement in intra-glomerular pressure that causes a GFR increase and the elimination of protein-derived waste nitrogen products. This cause an increase of renal parenchyma volume and body weight [94]. An HPD is also associated with an increase in urinary excretion of albumin or protein, which induces consequences both at the level of the kidney and at the level of other organs[49]. The presence and degree of albuminuria, according to current guidelines, are related to the severity of CKD and to CV mortality risk. Proteinuria induces apoptosis of renal tubular cells and alters the regeneration of podocyte cells, inducing tubular atrophy that favors the progression of kidney damage [50]. A further effect induced by an HPD is that related to metabolic acidosis. Protein metabolism is able to generate acids, derived from the metabolism of sulfide amino acids, and this phenomenon induces a decrease in bicarbonatemia worsening the picture of metabolic acidosis typical of CKD. In the literature, the phenomenon that correlates acid retention with the decline of kidney function has been described, inducing the chronic condition of metabolic acidosis[51]. This phenomenon alters protein metabolism, increases muscle catabolism and loss of muscle mass, worsens residual kidney function and, simultaneously, uremic symptoms [52]. Gaggl et al.[53] demonstrated a positive correlation between metabolic acidosis and the assumption of sodium bicarbonate in IV-stage CKD patients. In fact, they demonstrated that sodium bicarbonate oral supplementation was able to slow the decline of kidney function and improve nutritional status, with two years follow-up. HPD is also related to high phosphorus intake, mainly content in animal origin proteins and in food additives [54]. Its high blood levels help to induce the alteration of calcium-phosphorus metabolism, a very frequent condition in CKD patients [92]. The increase in phosphoremia is directly related to high levels of parathyroid hormone and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23[55] and induces an alteration of the vasal walls. The latter increases the risk of CV disease[56]. Therefore, in this patient population, the administration of HPD would not be a valid therapeutic tool since it would lead to a faster decline in kidney function. In the second category of patients, it is necessary to consider the impact of dialysis treatment on protein metabolism in order to determine the correct daily protein intake per kg of b.w. Current guidelines[57] for HD patients recommend a high protein intake, as previously mentioned, because dialytic procedure stimulates protein catabolism with high risk of MM loss. Therefore, in HD patients a high protein intake is necessary in order to avoid the establishment of PEW syndrome, induced by the loss of amino acids and proteins during the dialysis treatment. In fact, it is possible to observe in ESRD patients the phenomenon of “obesity paradox”, highlighted as a higher BMI reduces the risk of mortality[58].The HPD seems to be inversely related to the onset of the fragility state [59]. Fragility is defined as having at least three of the following five symptoms: weight loss, low physical activity, asthenia, slowing down, and fatigue. This condition is characterized by an increased susceptibility to adverse health events, leading to an enhancement incidence of hospitalization, falls and consequent fractures, disability, request for nursing assistance, and death[60][61][62]. Therefore, a diet associated with physical exercise plays a key role in the prevention and treatment of frailty [63]. All studies agree on the importance of early and regular dietary counselling to ensure a better success of nutritional therapy, especially in terms of adherence to the same [46]. Nutritional counseling must provide correct dietary nutritional information, evaluate past eating habits and identify the presence of any deficit in protein or energy intake. In addition, for patients with an energy intake less than 30 kcal/kg/day or protein intake less than 1 g/kg/day, it is necessary to provide information and tools to increase intake. Correct indication must be provided to avoid foods with high content of phosphorus, potassium and sodium and to try to avoid unnecessary fasting periods, as may occur after dialysis or in periods of acuity or hospitalization. It is therefore appropriate to reiterate the concept that a multidisciplinary team assesses the risk of uremic sarcopenia and identifies the best protein intake for each patient [1]. The therapeutic possibilities identified so far to provide a proper protein–energy intake in HD patients are manifold and include the use of oral nutritional supplements (ONS), intra-parenteral nutrition dialysis (IDPN), enteral nutrition (EN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Other useful tools proposed are specific nutritional products such as fibers and ω-3 (Table 1) [46].Table 1. Possible nutritional treatments of uremic sarcopenia in humans
Figure 2. Clinical management of hemodialysis (HD) patients to counteract the onset and the progression of uremic sarcopenia[46]. Abbreviations: b.w., Body weight; DEI, Diet energy intake; DPI, Diet protein intake; EN, Enteral nutritional; GI, Gastrointestinal; IDPN, Intra-parenteral nutrition dialysis; MIS, Malnutrition inflammation score; MM, Muscle mass; PEG, Percutaneous endoscopic gastrectomy; SGA, Subject global assessment; TPN, Total parenteral nutrition.Several studies have been carried out to investigate the different strategies that ensure an adequate protein-energy intake in HD patients. Numerous studies have shown that, in nephropathic patients, HPD causes an accumulation of toxic compounds (derived from protein metabolism), while a LPD offers better outcomes in these patients [47] In particular, in CKD it is necessary to distinguish two categories of patient: the first (i) is represented by patients undergoing conservative therapy and the second (ii) is represented by patients in renal replacement therapy. In the first category, an HPD, defined as a diet with an intake greater than 1.2 g prot/kg/b.w. per day, is able to alter renal hemodynamics, inducing the condition of hyperfiltration [48]. Renal hyperfiltration consists in the increase in renal blood flow inducing an enhancement in intra-glomerular pressure that causes a GFR increase and the elimination of protein-derived waste nitrogen products. This cause an increase of renal parenchyma volume and body weight [94]. An HPD is also associated with an increase in urinary excretion of albumin or protein, which induces consequences both at the level of the kidney and at the level of other organs[49]. The presence and degree of albuminuria, according to current guidelines, are related to the severity of CKD and to CV mortality risk. Proteinuria induces apoptosis of renal tubular cells and alters the regeneration of podocyte cells, inducing tubular atrophy that favors the progression of kidney damage [50]. A further effect induced by an HPD is that related to metabolic acidosis. Protein metabolism is able to generate acids, derived from the metabolism of sulfide amino acids, and this phenomenon induces a decrease in bicarbonatemia worsening the picture of metabolic acidosis typical of CKD. In the literature, the phenomenon that correlates acid retention with the decline of kidney function has been described, inducing the chronic condition of metabolic acidosis[51]. This phenomenon alters protein metabolism, increases muscle catabolism and loss of muscle mass, worsens residual kidney function and, simultaneously, uremic symptoms [52]. Gaggl et al.[53] demonstrated a positive correlation between metabolic acidosis and the assumption of sodium bicarbonate in IV-stage CKD patients. In fact, they demonstrated that sodium bicarbonate oral supplementation was able to slow the decline of kidney function and improve nutritional status, with two years follow-up. HPD is also related to high phosphorus intake, mainly content in animal origin proteins and in food additives [54]. Its high blood levels help to induce the alteration of calcium-phosphorus metabolism, a very frequent condition in CKD patients [92]. The increase in phosphoremia is directly related to high levels of parathyroid hormone and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23[55] and induces an alteration of the vasal walls. The latter increases the risk of CV disease[56]. Therefore, in this patient population, the administration of HPD would not be a valid therapeutic tool since it would lead to a faster decline in kidney function. In the second category of patients, it is necessary to consider the impact of dialysis treatment on protein metabolism in order to determine the correct daily protein intake per kg of b.w. Current guidelines[57] for HD patients recommend a high protein intake, as previously mentioned, because dialytic procedure stimulates protein catabolism with high risk of MM loss. Therefore, in HD patients a high protein intake is necessary in order to avoid the establishment of PEW syndrome, induced by the loss of amino acids and proteins during the dialysis treatment. In fact, it is possible to observe in ESRD patients the phenomenon of “obesity paradox”, highlighted as a higher BMI reduces the risk of mortality[58].The HPD seems to be inversely related to the onset of the fragility state [59]. Fragility is defined as having at least three of the following five symptoms: weight loss, low physical activity, asthenia, slowing down, and fatigue. This condition is characterized by an increased susceptibility to adverse health events, leading to an enhancement incidence of hospitalization, falls and consequent fractures, disability, request for nursing assistance, and death[60][61][62]. Therefore, a diet associated with physical exercise plays a key role in the prevention and treatment of frailty [63]. All studies agree on the importance of early and regular dietary counselling to ensure a better success of nutritional therapy, especially in terms of adherence to the same [46]. Nutritional counseling must provide correct dietary nutritional information, evaluate past eating habits and identify the presence of any deficit in protein or energy intake. In addition, for patients with an energy intake less than 30 kcal/kg/day or protein intake less than 1 g/kg/day, it is necessary to provide information and tools to increase intake. Correct indication must be provided to avoid foods with high content of phosphorus, potassium and sodium and to try to avoid unnecessary fasting periods, as may occur after dialysis or in periods of acuity or hospitalization. It is therefore appropriate to reiterate the concept that a multidisciplinary team assesses the risk of uremic sarcopenia and identifies the best protein intake for each patient [1]. The therapeutic possibilities identified so far to provide a proper protein–energy intake in HD patients are manifold and include the use of oral nutritional supplements (ONS), intra-parenteral nutrition dialysis (IDPN), enteral nutrition (EN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Other useful tools proposed are specific nutritional products such as fibers and ω-3 (Table 1) [46].Table 1. Possible nutritional treatments of uremic sarcopenia in humans
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| Significant reduction in SGA, FPG, insulin levels and HOMA-IR were detected. In addition, there was a significant enhancement in QUICKI. | ω-3 PUFA and vitamin E combined supplementation improve SGA and the metabolic profile in HD patients. | |||||
| Fiber | Krishnamurthy V.M.R. et al. [119] | 2012 | 1.105 CKD patients (stage IIIa-IV) vs. 13.438 subjects (control group) |
Two groups were divided into two subgroups according to fiber dietary intake:
|
Significant decrease in CRP was detected in CKD patients with high total fiber dietary consumption. | The high dietary fiber consumption is associated with a minor inflammation risk and mortality in CKD patients. |
| Nutritional Approaches |
Author | Year | Study Population | Nutritional Treatment | Primary Outcome | Primary End-Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONS | Caglar K. et al. [110] | 2002 | 85 malnourished CHD, HD patients | ONS assumed during each HD session, containing 16.6 g of proteins, 22.7 g of lipids and 52.8 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 475 kcal. | Significant increases in serum albumin and prealbumin levels were detected. In addition, there was a 14% increase in SGA score. |
ONS assumed during HD improves some nutritional biomarkers in malnourished HD patients. |
| Lacson Jr E. et al. [111] | 2012 | 5.227 HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL vs. 5.227 patients (control group) |
Four different intradialytic ONS were administered:
|
A reduction in mortality was found in patients treated with ONS compared to non-treated group. | ONS treatment allows a significant increase in survival of HD patients. | |
| Wu H.L. et al. [84] | 2013 | 55 CKD patients (stage III-IV) vs. 54 patients (control group) |
One daily ONS containing 0.6 g of proteins, 8.2 g of lipids, 30.9 g of carbohydrates and 1.9 g of fiber with energy content of 200 kcal. | ONS significant decreased urine protein excretion therefore, daily protein intake was lower in the ONS group. Significant decrease of creatinine and urea nitrogen levels; in addition, there was a significant increase of eGFR. | ONS has improved some blood parameters and improved the adherence to the nutritional therapy with less protein excretion. | |
| Sezer S. et al. [112] | 2014 | 32 malnourished HD patients vs. 30 patients (control group) |
ONS containing 14 g of proteins, 19.2 g of lipids and 41.3 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 400 kcal. In addition, during HD sessions was served a snack containing 14 g of proteins, 10 g of lipids and 55 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 300 kcal. |
Significant increases in serum albumin levels were detected. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dry weight of the ONS patients and a significative reduction in the dry weight of the control group. In addition, a reduction of EPO dose requirement and MIS was detected in the treated group. |
ONS treatment improves serum albumin levels and allows a lower EPO dose requirement in HD patients. | |
| Benner D. et al. [113] | 2018 | 3.374 HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL vs. 3.374 patients (control group) |
Two different ONS were used:
|
There was a 69% reduction in mortality and a 33% reduction in missed dialysis sessions. | ONS treatment allows a significant increase in survival in HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL. | |
| Leonberg-Yoo A.K. et al. [114] | 2019 | 1420 HD patients vs. 4.059 patients (control group) |
Six different intradialytic ONS were used:
|
There was a decrease of re-hospitalization within 30 days of first discharge. | ONS treatment reduces post-discharge hospital readmission rates. | |
| IDPN | Marsen T.A. et al. [115] | 2017 | 39 HD patients with PEW vs. 44 patients (control group) |
IDPN treatment three times/week containing (one dose):
|
Significant increases in serum prealbumin levels were detected. | IDPN used during HD session improves prealbumin levels. |
| Thabet A.F. et al. [116] | 2017 | 20 HD patients vs. 20 patients (control group) |
IDPN treatment three times/week. In addition, patients received EPO, iron dextran, folic acid and vitamin B 12. | Significant increases in hemoglobin and albumin levels were detected. In addition, there was a significant increase in BMI. Significant reduction in MIS was detected. |
IDPN treatment allows an improvement of refractory anemia, as it permits an increase in hemoglobin and prealbumin levels and also an increase in body weight. It also leads to a reduction in MIS. | |
| Deleaval P. et al. [60] | 2020 | 6 HD patients | Two dialysates were used during HD treatment:
|
During the HD treatment with standard dialysate a reduction in plasmatic valine was found, while with dialysate enriched in BCAA HD treatment there was an increase in plasmatic valine, isoleucine and leucine. |
The use of dialysate enriched in BCAA allows the restoration of normal plasma BCAA levels. | |
| ω-3 supplementation | Gharekhani A. et al. [117] | 2014 | 27 HD patients vs. 27 patients (control group) |
Six capsules per day of ω-3 supplementation (180 mg eicosapentaenoic acid and 120 mg docosahexaenoic acid in each capsule). | ω-3 supplementation is a significant independent predictor for the increase of serum prealbumin level after adjusting post-treatment nutritional markers. Significant decrease in ferritin levels and IL-10/IL-6 ratio was detected. |
ω-3 supplementation in HD patients permits a slight reduction of inflammation. |
| Asemi Z. et al. [118] | 2016 | 90 HD patients vs. 30 patients (control group) |
Four groups for supplementation per day:
|
Significant reduction in SGA, FPG, insulin levels and HOMA-IR were detected. In addition, there was a significant enhancement in QUICKI. | ω-3 PUFA and vitamin E combined supplementation improve SGA and the metabolic profile in HD patients. | |
| Fiber | Krishnamurthy V.M.R. et al. [119] | 2012 | 1.105 CKD patients (stage IIIa-IV) vs. 13.438 subjects (control group) |
Two groups were divided into two subgroups according to fiber dietary intake:
|
Significant decrease in CRP was detected in CKD patients with high total fiber dietary consumption. | The high dietary fiber consumption is associated with a minor inflammation risk and mortality in CKD patients. |
Abbreviations: BCAA, Branched-chain amino acid; BIA, Bioelectrical impedance analysis; BMI, Body mass index; CHD, Coronary heart disease; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; e-GFR, Estimated glomerular filtration rate; EPO, Erythropoietin; FPG, Fasting plasma glucose; HD, Hemodialysis; HOMA-IR, Homeostasis model of assessment of insulin resistance; IDPN, Intra-dialytic parenteral nutrition; IL, Interleukin; MIS, Malnutrition inflammation score; MPS, Muscle protein synthesis; ONS, Oral nutritional supplements; PUFA, Polyunsaturated fatty acids; QUICKI, Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; SGA, Subjective global assessment.
3. Conclusions
2. Nutritional Therapy

| Nutritional Approaches |
Author | Year | Study Population | Nutritional Treatment | Primary Outcome | Primary End-Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONS | Caglar K. et al. [110] | 2002 | 85 malnourished CHD, HD patients | ONS assumed during each HD session, containing 16.6 g of proteins, 22.7 g of lipids and 52.8 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 475 kcal. | Significant increases in serum albumin and prealbumin levels were detected. In addition, there was a 14% increase in SGA score. |
ONS assumed during HD improves some nutritional biomarkers in malnourished HD patients. |
| Lacson Jr E. et al. [111] | 2012 | 5.227 HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL vs. 5.227 patients (control group) |
Four different intradialytic ONS were administered:
|
A reduction in mortality was found in patients treated with ONS compared to non-treated group. | ONS treatment allows a significant increase in survival of HD patients. | |
| Wu H.L. et al. [84] | 2013 | 55 CKD patients (stage III-IV) vs. 54 patients (control group) |
One daily ONS containing 0.6 g of proteins, 8.2 g of lipids, 30.9 g of carbohydrates and 1.9 g of fiber with energy content of 200 kcal. | ONS significant decreased urine protein excretion therefore, daily protein intake was lower in the ONS group. Significant decrease of creatinine and urea nitrogen levels; in addition, there was a significant increase of eGFR. | ONS has improved some blood parameters and improved the adherence to the nutritional therapy with less protein excretion. | |
| Sezer S. et al. [112] | 2014 | 32 malnourished HD patients vs. 30 patients (control group) |
ONS containing 14 g of proteins, 19.2 g of lipids and 41.3 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 400 kcal. In addition, during HD sessions was served a snack containing 14 g of proteins, 10 g of lipids and 55 g of carbohydrates with energy content of 300 kcal. |
Significant increases in serum albumin levels were detected. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the dry weight of the ONS patients and a significative reduction in the dry weight of the control group. In addition, a reduction of EPO dose requirement and MIS was detected in the treated group. |
ONS treatment improves serum albumin levels and allows a lower EPO dose requirement in HD patients. | |
| Benner D. et al. [113] | 2018 | 3.374 HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL vs. 3.374 patients (control group) |
Two different ONS were used:
|
There was a 69% reduction in mortality and a 33% reduction in missed dialysis sessions. | ONS treatment allows a significant increase in survival in HD patients with albumin level ≤3.5 g/dL. | |
| Leonberg-Yoo A.K. et al. [114] | 2019 | 1420 HD patients vs. 4.059 patients (control group) |
Six different intradialytic ONS were used:
|
There was a decrease of re-hospitalization within 30 days of first discharge. | ONS treatment reduces post-discharge hospital readmission rates. | |
| IDPN | Marsen T.A. et al. [115] | 2017 | 39 HD patients with PEW vs. 44 patients (control group) |
IDPN treatment three times/week containing (one dose):
|
Significant increases in serum prealbumin levels were detected. | IDPN used during HD session improves prealbumin levels. |
| Thabet A.F. et al. [116] | 2017 | 20 HD patients vs. 20 patients (control group) |
IDPN treatment three times/week. In addition, patients received EPO, iron dextran, folic acid and vitamin B 12. | Significant increases in hemoglobin and albumin levels were detected. In addition, there was a significant increase in BMI. Significant reduction in MIS was detected. |
IDPN treatment allows an improvement of refractory anemia, as it permits an increase in hemoglobin and prealbumin levels and also an increase in body weight. It also leads to a reduction in MIS. | |
| Deleaval P. et al. [60] | 2020 | 6 HD patients | Two dialysates were used during HD treatment:
|
During the HD treatment with standard dialysate a reduction in plasmatic valine was found, while with dialysate enriched in BCAA HD treatment there was an increase in plasmatic valine, isoleucine and leucine. | The use of dialysate enriched in BCAA allows the restoration of normal plasma BCAA levels. | |
| ω-3 supplementation | Gharekhani A. et al. [117] | 2014 | 27 HD patients vs. 27 patients (control group) |
Six capsules per day of ω-3 supplementation (180 mg eicosapentaenoic acid and 120 mg docosahexaenoic acid in each capsule). | ω-3 supplementation is a significant independent predictor for the increase of serum prealbumin level after adjusting post-treatment nutritional markers. Significant decrease in ferritin levels and IL-10/IL-6 ratio was detected. |
ω-3 supplementation in HD patients permits a slight reduction of inflammation. |
| Asemi Z. et al. [118] | 2016 | 90 HD patients vs. 30 patients (control group) |
Four groups for supplementation per day:
|
3. Conclusions
Sarcopenia is defined by the reduction of MM, associated with the loss of muscle strength and the reduction of physical performance. It is a frequent condition in CKD patients, especially if undergoing HD treatment. The development of sarcopenia in nephropathic patients is not associated solely with their generally advanced age. Uremic sarcopenia is mainly related to the comorbidities typical of uremia: metabolic acidosis, low-grade chronic inflammatory state, vitamin D deficiency, IR, hormonal alterations (in particular testosterone, IGF-1 and cortisol) and gut dysbiosis. These processes contribute to the development of an increased protein catabolism and of a reduced protein synthesis, resulting in a reduction of the muscle protein pool that induces a loss of MM and strength. The same hemodialytic treatment, fundamental for the patient’s survival in ESRD, causes the loss of amino acids and proteins. During and after the HD session, an increase in the processes of protein catabolism was also observed. The development of sarcopenia causes a worsening of the prognosis of CKD patients, leading not only to a worsening of Qol and of personal autonomy, but also to an increased risk of complications and mortality.For this reason, sarcopenia should be suspected and diagnosed as soon as possible in patients considered at risk. There are many tools available to investigate the presence of this disease, the choice of which is often dictated by the clinician and by diagnostic equipment availability. In reference to these latter, the most commonly used are DXA, BIA or HGS. Sarcopenia treatment is essential to improve the prognosis and survival of CKD patients. Physical exercise has been studied in several studies[64][65][66]and has provided encouraging results, but CKD patients cannot always perform it optimally, especially if they are very old and suffering from multiple comorbidities. Nutritional therapy could be a valid and effective solution in ensuring a correct protein and energy intake, which contrasts with the increased protein catabolism and the reduced protein synthesis.The possible types of nutritional therapy administration are multiple and include ONS, EN, TPN and IDPN. The assumption of supplements such as fiber or ω-3 PUFAs could also be useful in counteracting the onset and progression of sarcopenia. Studies conducted so far on different types of nutritional therapies [67][68][69][70] have provided positive results, so their use, associated with careful nutritional counselling, should be encouraged in CKD patients.Currently, it is believed that the combination of targeted and personalized physical exercise for the patient with personalized dietary-nutritional therapy[71] to ensure an adequate protein, fiber and energy intake represents the ideal approach to treat uremic sarcopenia.
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S, doi:10.1093/jn/127.5.990S.
- Giglio, J.; Kamimura, M.A.; Lamarca, F.; Rodrigues, J.; Santin, F.; Avesani, C.M. Association of Sarcopenia with Nutritional Parameters, Quality of Life, Hospitalization, and Mortality Rates of Elderly Patients on Hemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 197–207, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2017.12.003.
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Delsante, M.; Di Motta, T.; Cantarelli, C.; Pioli, S.; Grassi, G.; Batini, V.; Gregorini, M.; Fiaccadori, E. Noninvasive evaluation of muscle mass by ultrasonography of quadriceps femoris muscle in End-Stage Renal Disease patients on hemodialysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1232–1239, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2018.05.004.
- Foley, R.N.; Wang, C.; Ishani, A.; Collins, A.J.; Murray, A.M. Kidney function and sarcopenia in the United States general population: NHANES III. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 279–286, doi:10.1159/000101827.
- Stenvinkel, P.; Carrero, J.J.; von Walden, F.; Ikizler, T.A.; Nader, G.A. Muscle wasting in end-stage renal disease promulgates premature death: Established, emerging and potential novel treatment strategies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1070–1077, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfv122.
- Mitch, W.E.; Goldberg, A.L. Mechanisms of muscle wasting. The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1897–1905, doi:10.1056/NEJM199612193352507.
- Doherty, T.J. Invited review: Aging and sarcopenia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 1717–1727, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00347.2003.
- von Haehling, S.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D. An overview of sarcopenia: Facts and numbers on prevalence and clinical impact. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2010, 1, 129–133, doi:10.1007/s13539-010-0014-2.
- Thome, T.; Salyers, Z.R.; Kumar, R.A.; Hahn, D.; Berru, F.N.; Ferreira, L.F.; Scali, S.T.; Ryan, T.E. Uremic metabolites impair skeletal muscle mitochondrial energetics through disruption of the electron transport system and matrix dehydrogenase activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C701–C713, doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00098.2019.
- Yazdi, P.G.; Moradi, H.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, P.H.; Vaziri, N.D. Skeletal muscle mitochondrial depletion and dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 532–539.
- Afsar, B.; Afsar, R.E.; Dagel, T.; Kaya, E.; Erus, S.; Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; Kanbay, M. Capillary rarefaction from the kidney point of view. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 295–301, doi:10.1093/ckj/sfx133.
- Delmonico, M.J.; Harris, T.B.; Visser, M.; Park, S.W.; Conroy, M.B.; Velasquez-Mieyer, P.; Boudreau, R.; Manini, T.M.; Nevitt, M.; Newman, A.B.; et al. Longitudinal study of muscle strength, quality, and adipose tissue infiltration. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1579–1585, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28047.
- Cameron, J.; McPhee, J.S.; Jones, D.A.; Degens, H. Five-year longitudinal changes in thigh muscle mass of septuagenarian men and women assessed with DXA and MRI. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 617–624, doi:10.1007/s40520-019-01248-w.
- Zoico, E.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V.; Sepe, A.; Olioso, D.; Pizzini, F.; Fantin, F.; Bosello, O.; Cominacini, L.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Adipose tissue infiltration in skeletal muscle of healthy elderly men: Relationships with body composition, insulin resistance, and inflammation at the systemic and tissue level. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 295–299, doi:10.1093/gerona/glp155.
- Sakkas, G.K.; Kent-Braun, J.A.; Doyle, J.W.; Shubert, T.; Gordon, P.; Johansen, K.L. Effect of diabetes mellitus on muscle size and strength in patients receiving dialysis therapy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 862–869, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.01.013.
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423, doi:10.1093/ageing/afq034.
- Muscaritoli, M.; Anker, S.D.; Argiles, J.; Aversa, Z.; Bauer, J.M.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosaeus, I.; Cederholm, T.; Costelli, P.; et al. Consensus definition of sarcopenia, cachexia and pre-cachexia: Joint document elaborated by Special Interest Groups (SIG) “cachexia-anorexia in chronic wasting diseases” and “nutrition in geriatrics”. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 154–159, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2009.12.004.
- Fielding, R.A.; Vellas, B.; Evans, W.J.; Bhasin, S.; Morley, J.E.; Newman, A.B.; Abellan van Kan, G.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Breuille, D.; et al. Sarcopenia: An undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: Prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 249–256, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2011.01.003.
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558, doi:10.1093/gerona/glu010.
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31, doi:10.1093/ageing/afy169.
- Beaudart, C.; McCloskey, E.; Bruyere, O.; Cesari, M.; Rolland, Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan, J.; Bautmans, I.; Bertiere, M.C.; et al. Sarcopenia in daily practice: Assessment and management. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 170, doi:10.1186/s12877-016-0349-4.
- Andreoli, A.; Lauro, S.; Di Daniele, N.; Sorge, R.; Celi, M.; Volpe, S.L. Effect of a moderately hypoenergetic Mediterranean diet and exercise program on body cell mass and cardiovascular risk factors in obese women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 892–897, doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602800.
- Molfino, A.; Chiappini, M.G.; Laviano, A.; Ammann, T.; Bollea, M.R.; Alegiani, F.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Muscaritoli, M. Effect of intensive nutritional counseling and support on clinical outcomes of hemodialysis patients. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1012–1015, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.01.008.
- Fahal, I.H.; Bell, G.M.; Bone, J.M.; Edwards, R.H. Physiological abnormalities of skeletal muscle in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 119–127, doi:10.1093/ndt/12.1.119.
- Domanski, M.; Ciechanowski, K. Sarcopenia: A major challenge in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 754739, doi:10.1155/2012/754739.
- Carrero, J.J.; Chmielewski, M.; Axelsson, J.; Snaedal, S.; Heimburger, O.; Barany, P.; Suliman, M.E.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Qureshi, A.R. Muscle atrophy, inflammation and clinical outcome in incident and prevalent dialysis patients. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 557–564, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2008.04.007.
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kaysen, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Price, S.R.; Wanner, C.; Wang, A.Y.; et al. Etiology of the protein-energy wasting syndrome in chronic kidney disease: A consensus statement from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 77–90, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2013.01.001.
- Dev, R. Measuring cachexia-diagnostic criteria. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2019, 8, 24–32, doi:10.21037/apm.2018.08.07.
- Pereira, R.A.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Avesani, C.M.; Carrero, J.J.; Lindholm, B.; Amparo, F.C.; Amodeo, C.; Cuppari, L.; Kamimura, M.A. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease on conservative therapy: Prevalence and association with mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1718–1725, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfv133.
- Moorthi, R.N.; Avin, K.G. Clinical relevance of sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2017, 26, 219–228, doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000318.
- Sabatino, A.; Cuppari, L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; Avesani, C.M. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease: What have we learned so far? J. Nephrol. 2020, doi:10.1007/s40620-020-00840-y.
- Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D. Sarcopenia in CKD: A roadmap from basic pathogenetic mechanisms to clinical trials. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 110–112, doi:10.1093/ckj/sfz001.
- Leong, D.P.; Teo, K.K.; Rangarajan, S.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Avezum, A., Jr.; Orlandini, A.; Seron, P.; Ahmed, S.H.; Rosengren, A.; Kelishadi, R.; et al. Prognostic value of grip strength: Findings from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. Lancet 2015, 386, 266–273, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62000-6.
- Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Di Lauro, M.; Urciuoli, S.; Pietroboni Zaitseva, A.; Wilson Jones, G.; Di Daniele, N.; Romani, A. Cardiovascular Protection of Nephropathic Male Patients by Oral Food Supplements. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 2020, 1807941, doi:10.1155/2020/1807941.
- Ikizler, T.A.; Cano, N.J.; Franch, H.; Fouque, D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Stenvinkel, P.; TerWee, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1096–1107, doi:10.1038/ki.2013.147.
- Soeters, P.B. Editorial: Ketogenic diets: What is the benefit? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 311–313, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000571.
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of protein-energy wasting in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Reconciling low protein intake with nutritional therapy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1163–1177, doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.036418.
- Wu, H.L.; Sung, J.M.; Kao, M.D.; Wang, M.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Chen, S.T. Nonprotein calorie supplement improves adherence to low-protein diet and exerts beneficial responses on renal function in chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 271–276, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2012.09.003.
- Levine, M.E.; Suarez, J.A.; Brandhorst, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Cheng, C.W.; Madia, F.; Fontana, L.; Mirisola, M.G.; Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Wan, J.; et al. Low protein intake is associated with a major reduction in IGF-1, cancer, and overall mortality in the 65 and younger but not older population. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 407–417, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.006.
- Ahluwalia, N.; Dwyer, J.; Terry, A.; Moshfegh, A.; Johnson, C. Update on NHANES Dietary Data: Focus on Collection, Release, Analytical Considerations, and Uses to Inform Public Policy. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 121–134, doi:10.3945/an.115.009258.
- Obi, Y.; Qader, H.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Latest consensus and update on protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 254–262, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000171.
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Cano, N.J.; Budde, K.; Chazot, C.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mak, R.H.; Mehrotra, R.; Raj, D.S.; Sehgal, A.R.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Diets and enteral supplements for improving outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 369–384, doi:10.1038/nrneph.2011.60.
- Cano, N.J.; Aparicio, M.; Brunori, G.; Carrero, J.J.; Cianciaruso, B.; Fiaccadori, E.; Lindholm, B.; Teplan, V.; Fouque, D.; Guarnieri, G.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Adult renal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 401–414, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2009.05.016.
- Cano, N.; Fiaccadori, E.; Tesinsky, P.; Toigo, G.; Druml, W.; Dgem; Kuhlmann, M.; Mann, H.; Horl, W.H.; Espen. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Adult renal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 295–310, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2006.01.023.
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Karupaiah, T.; Sahathevan, S.; Sadu Singh, B.K.; Khor, B.H.; Salhab, N.; Karavetian, M.; Cupisti, A.; Fiaccadori, E. Protein-energy wasting and nutritional supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 663–671, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.007.
- Cupisti, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of natural and added dietary phosphorus burden in kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 180–190, doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.12.018.
- Ko, G.J.; Obi, Y.; Tortorici, A.R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Dietary protein intake and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 77–85, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000342.
- Fouque, D.; Aparicio, M. Eleven reasons to control the protein intake of patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 383–392, doi:10.1038/ncpneph0524.
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moore, L.W.; Tortorici, A.R.; Chou, J.A.; St-Jules, D.E.; Aoun, A.; Rojas-Bautista, V.; Tschida, A.K.; Rhee, C.M.; Shah, A.A.; et al. North American experience with Low protein diet for Non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 90, doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0304-9.
- Peired, A.; Angelotti, M.L.; Ronconi, E.; la Marca, G.; Mazzinghi, B.; Sisti, A.; Lombardi, D.; Giocaliere, E.; Della Bona, M.; Villanelli, F.; et al. Proteinuria impairs podocyte regeneration by sequestering retinoic acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1756–1768, doi:10.1681/ASN.2012090950.
- Di Iorio, B.R.; Bellasi, A.; Raphael, K.L.; Santoro, D.; Aucella, F.; Garofano, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Di Lullo, L.; Capolongo, G.; Di Iorio, M.; et al. Treatment of metabolic acidosis with sodium bicarbonate delays progression of chronic kidney disease: The UBI Study. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 989–1001, doi:10.1007/s40620-019-00656-5.
- Goraya, N.; Simoni, J.; Jo, C.H.; Wesson, D.E. A comparison of treating metabolic acidosis in CKD stage 4 hypertensive kidney disease with fruits and vegetables or sodium bicarbonate. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 371–381, doi:10.2215/CJN.02430312.
- Gaggl, M.; Sliber, C.; Sunder-Plassmann, G. Effect of oral alkali supplementation on progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2014, 10, 112–120, doi:10.2174/1573402111666141231123314.
- D'Alessandro, C.; Piccoli, G.B.; Cupisti, A. The “phosphorus pyramid”: A visual tool for dietary phosphate management in dialysis and CKD patients. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 9, doi:10.1186/1471-2369-16-9.
- Scialla, J.J.; Appel, L.J.; Wolf, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Sozio, S.M.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Bazzano, L.A.; Cuevas, M.; Glenn, M.J.; et al. Plant protein intake is associated with fibroblast growth factor 23 and serum bicarbonate levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 379–388 e1, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2012.01.026.
- Foley, R.N. Phosphate levels and cardiovascular disease in the general population. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1136–1139, doi:10.2215/CJN.01660309.
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Nutrition in CKD Guideline Work Group. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006.
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. The dual roles of obesity in chronic kidney disease: A review of the current literature. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 208–216, doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000212.
- Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Goncalves, I.O.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Cesari, M.; Uchida, M.C.; Marzetti, E. Protein-Related Dietary Parameters and Frailty Status in Older Community-Dwellers across Different Frailty Instruments. Nutrients 2020, 12, 508, doi:10.3390/nu12020508.
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62167-9.
- Morley, J.E.; Vellas, B.; van Kan, G.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bauer, J.M.; Bernabei, R.; Cesari, M.; Chumlea, W.C.; Doehner, W.; Evans, J.; et al. Frailty consensus: A call to action. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 392–397, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2013.03.022.
- Scuteri, A.; Modestino, A.; Frattari, A.; Di Daniele, N.; Tesauro, M. Occurrence of hypotension in older participants. Which 24-hour ABPM parameter better correlate with? J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 804–810, doi:10.1093/gerona/glr232.
- Artaza-Artabe, I.; Saez-Lopez, P.; Sanchez-Hernandez, N.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, N.; Malafarina, V. The relationship between nutrition and frailty: Effects of protein intake, nutritional supplementation, vitamin D and exercise on muscle metabolism in the elderly. A systematic review. Maturitas 2016, 93, 89–99, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.04.009.
- Cupisti, A.; D’Alessandro, C.; Fumagalli, G.; Vigo, V.; Meola, M.; Cianchi, C.; Egidi, M.F. Nutrition and physical activity in CKD patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014, 39, 107–113, doi:10.1159/000355784.
- Naci, H.; Ioannidis, J.P. Comparative effectiveness of exercise and drug interventions on mortality outcomes: Metaepidemiological study. BMJ 2013, 347, f5577, doi:10.1136/bmj.f5577.
- Finch, C.F.; White, P.; Twomey, D.; Ullah, S. Implementing an exercise-training programme to prevent lower-limb injuries: Considerations for the development of a randomised controlled trial intervention delivery plan. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 791–796, doi:10.1136/bjsm.2010.081406.
- Leonberg-Yoo, A.K.; Wang, W.; Weiner, D.E.; Lacson, E., Jr. Oral nutritional supplements and 30-day readmission rate in hypoalbuminemic maintenance hemodialysis patients. Hemodial. Int. 2019, 23, 93–100, doi:10.1111/hdi.12694.
- Marsen, T.A.; Beer, J.; Mann, H.; German IDPN-Trial Group. Intradialytic parenteral nutrition in maintenance hemodialysis patients suffering from protein-energy wasting. Results of a multicenter, open, prospective, randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 107–117, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.016.
- Detsky, A.S.; McLaughlin, J.R.; Baker, J.P.; Johnston, N.; Whittaker, S.; Mendelson, R.A.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N. What is subjective global assessment of nutritional status? JPEN J. Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987, 11, 8–13, doi:10.1177/014860718701100108.
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Antonucci, E.; Cabassi, A.; Morabito, S.; Fiaccadori, E. Intradialytic parenteral nutrition in end-stage renal disease: Practical aspects, indications and limits. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 377–383, doi:10.1007/s40620-014-0051-6.
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Romano, L.; Marrone, G.; Noce, A.; Pujia, A.; Perrone, M.A.; Aiello, V.; Colica, C.; De Lorenzo, A. Role of Personalized Nutrition in Chronic-Degenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1707, doi:10.3390/nu11081707.
- Stenvinkel, P.; Larsson, T.E. Chronic kidney disease: A clinical model of premature aging. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 339–351, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.11.051.
- Kooman, J.P.; Kotanko, P.; Schols, A.M.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic kidney disease and premature ageing. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 732–742, doi:10.1038/nrneph.2014.185.
- Choi, Y.J. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry: Beyond Bone Mineral Density Determination. Endocrinol. Metab. (Seoul) 2016, 31, 25–30, doi:10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.25.
- Roubenoff, R.; Kehayias, J.J.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Heymsfield, S.B. Use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in body-composition studies: Not yet a “gold standard”. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993, 58, 589–591, doi:10.1093/ajcn/58.5.589.
- Chertow, G.M.; Lowrie, E.G.; Wilmore, D.W.; Gonzalez, J.; Lew, N.L.; Ling, J.; Leboff, M.S.; Gottlieb, M.N.; Huang, W.; Zebrowski, B.; et al. Nutritional assessment with bioelectrical impedance analysis in maintenance hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 75–81.
- Lauretani, F.; Russo, C.R.; Bandinelli, S.; Bartali, B.; Cavazzini, C.; Di Iorio, A.; Corsi, A.M.; Rantanen, T.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-associated changes in skeletal muscles and their effect on mobility: An operational diagnosis of sarcopenia. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2003, 95, 1851–1860, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00246.2003.
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: Association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–94, doi:10.1093/geronj/49.2.m85.
- Zha, Y.; Qian, Q. Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Nutrients 2017, 9, 208, doi:10.3390/nu9030208.
- Ikizler, T.A.; Cano, N.J.; Franch, H.; Fouque, D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Stenvinkel, P.; TerWee, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1096–1107, doi:10.1038/ki.2013.147.
- Soeters, P.B. Editorial: Ketogenic diets: What is the benefit? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 311–313, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000571.
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of protein-energy wasting in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Reconciling low protein intake with nutritional therapy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1163–1177, doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.036418.
- Wu, H.L.; Sung, J.M.; Kao, M.D.; Wang, M.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Chen, S.T. Nonprotein calorie supplement improves adherence to low-protein diet and exerts beneficial responses on renal function in chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 271–276, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2012.09.003.
- Levine, M.E.; Suarez, J.A.; Brandhorst, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Cheng, C.W.; Madia, F.; Fontana, L.; Mirisola, M.G.; Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Wan, J.; et al. Low protein intake is associated with a major reduction in IGF-1, cancer, and overall mortality in the 65 and younger but not older population. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 407–417, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.006.
- Ahluwalia, N.; Dwyer, J.; Terry, A.; Moshfegh, A.; Johnson, C. Update on NHANES Dietary Data: Focus on Collection, Release, Analytical Considerations, and Uses to Inform Public Policy. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 121–134, doi:10.3945/an.115.009258.
- Obi, Y.; Qader, H.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Latest consensus and update on protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 254–262, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000171.
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Cano, N.J.; Budde, K.; Chazot, C.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mak, R.H.; Mehrotra, R.; Raj, D.S.; Sehgal, A.R.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Diets and enteral supplements for improving outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 369–384, doi:10.1038/nrneph.2011.60.
- Cano, N.J.; Aparicio, M.; Brunori, G.; Carrero, J.J.; Cianciaruso, B.; Fiaccadori, E.; Lindholm, B.; Teplan, V.; Fouque, D.; Guarnieri, G.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Adult renal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 401–414, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2009.05.016.
- Cano, N.; Fiaccadori, E.; Tesinsky, P.; Toigo, G.; Druml, W.; Dgem; Kuhlmann, M.; Mann, H.; Horl, W.H.; Espen. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Adult renal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 295–310, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2006.01.023.
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Karupaiah, T.; Sahathevan, S.; Sadu Singh, B.K.; Khor, B.H.; Salhab, N.; Karavetian, M.; Cupisti, A.; Fiaccadori, E. Protein-energy wasting and nutritional supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 663–671, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.007.
- Cupisti, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of natural and added dietary phosphorus burden in kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 180–190, doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.12.018.
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S, doi:10.1093/jn/127.5.990S.
- Ko, G.J.; Obi, Y.; Tortorici, A.R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Dietary protein intake and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 77–85, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000342.
- Fouque, D.; Aparicio, M. Eleven reasons to control the protein intake of patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 383–392, doi:10.1038/ncpneph0524.
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moore, L.W.; Tortorici, A.R.; Chou, J.A.; St-Jules, D.E.; Aoun, A.; Rojas-Bautista, V.; Tschida, A.K.; Rhee, C.M.; Shah, A.A.; et al. North American experience with Low protein diet for Non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 90, doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0304-9.
- Peired, A.; Angelotti, M.L.; Ronconi, E.; la Marca, G.; Mazzinghi, B.; Sisti, A.; Lombardi, D.; Giocaliere, E.; Della Bona, M.; Villanelli, F.; et al. Proteinuria impairs podocyte regeneration by sequestering retinoic acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1756–1768, doi:10.1681/ASN.2012090950.
- Di Iorio, B.R.; Bellasi, A.; Raphael, K.L.; Santoro, D.; Aucella, F.; Garofano, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Di Lullo, L.; Capolongo, G.; Di Iorio, M.; et al. Treatment of metabolic acidosis with sodium bicarbonate delays progression of chronic kidney disease: The UBI Study. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 989–1001, doi:10.1007/s40620-019-00656-5.
- Goraya, N.; Simoni, J.; Jo, C.H.; Wesson, D.E. A comparison of treating metabolic acidosis in CKD stage 4 hypertensive kidney disease with fruits and vegetables or sodium bicarbonate. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 371–381, doi:10.2215/CJN.02430312.
- Gaggl, M.; Sliber, C.; Sunder-Plassmann, G. Effect of oral alkali supplementation on progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2014, 10, 112–120, doi:10.2174/1573402111666141231123314.
- D'Alessandro, C.; Piccoli, G.B.; Cupisti, A. The “phosphorus pyramid”: A visual tool for dietary phosphate management in dialysis and CKD patients. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 9, doi:10.1186/1471-2369-16-9.
- Scialla, J.J.; Appel, L.J.; Wolf, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Sozio, S.M.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Bazzano, L.A.; Cuevas, M.; Glenn, M.J.; et al. Plant protein intake is associated with fibroblast growth factor 23 and serum bicarbonate levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 379–388 e1, doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2012.01.026.
- Foley, R.N. Phosphate levels and cardiovascular disease in the general population. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1136–1139, doi:10.2215/CJN.01660309.
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Nutrition in CKD Guideline Work Group. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006.
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. The dual roles of obesity in chronic kidney disease: A review of the current literature. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 208–216, doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000212.
- Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Goncalves, I.O.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Cesari, M.; Uchida, M.C.; Marzetti, E. Protein-Related Dietary Parameters and Frailty Status in Older Community-Dwellers across Different Frailty Instruments. Nutrients 2020, 12, 508, doi:10.3390/nu12020508.
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62167-9.
- Morley, J.E.; Vellas, B.; van Kan, G.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bauer, J.M.; Bernabei, R.; Cesari, M.; Chumlea, W.C.; Doehner, W.; Evans, J.; et al. Frailty consensus: A call to action. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 392–397, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2013.03.022.
- Scuteri, A.; Modestino, A.; Frattari, A.; Di Daniele, N.; Tesauro, M. Occurrence of hypotension in older participants. Which 24-hour ABPM parameter better correlate with? J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 804–810, doi:10.1093/gerona/glr232.
- Artaza-Artabe, I.; Saez-Lopez, P.; Sanchez-Hernandez, N.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, N.; Malafarina, V. The relationship between nutrition and frailty: Effects of protein intake, nutritional supplementation, vitamin D and exercise on muscle metabolism in the elderly. A systematic review. Maturitas 2016, 93, 89–99, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.04.009.
- Cupisti, A.; D’Alessandro, C.; Fumagalli, G.; Vigo, V.; Meola, M.; Cianchi, C.; Egidi, M.F. Nutrition and physical activity in CKD patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014, 39, 107–113, doi:10.1159/000355784.
- Naci, H.; Ioannidis, J.P. Comparative effectiveness of exercise and drug interventions on mortality outcomes: Metaepidemiological study. BMJ 2013, 347, f5577, doi:10.1136/bmj.f5577.
- Finch, C.F.; White, P.; Twomey, D.; Ullah, S. Implementing an exercise-training programme to prevent lower-limb injuries: Considerations for the development of a randomised controlled trial intervention delivery plan. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 791–796, doi:10.1136/bjsm.2010.081406.
- Leonberg-Yoo, A.K.; Wang, W.; Weiner, D.E.; Lacson, E., Jr. Oral nutritional supplements and 30-day readmission rate in hypoalbuminemic maintenance hemodialysis patients. Hemodial. Int. 2019, 23, 93–100, doi:10.1111/hdi.12694.
- Marsen, T.A.; Beer, J.; Mann, H.; German IDPN-Trial Group. Intradialytic parenteral nutrition in maintenance hemodialysis patients suffering from protein-energy wasting. Results of a multicenter, open, prospective, randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 107–117, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.016.
- Detsky, A.S.; McLaughlin, J.R.; Baker, J.P.; Johnston, N.; Whittaker, S.; Mendelson, R.A.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N. What is subjective global assessment of nutritional status? JPEN J. Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987, 11, 8–13, doi:10.1177/014860718701100108.
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Antonucci, E.; Cabassi, A.; Morabito, S.; Fiaccadori, E. Intradialytic parenteral nutrition in end-stage renal disease: Practical aspects, indications and limits. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 377–383, doi:10.1007/s40620-014-0051-6.
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Romano, L.; Marrone, G.; Noce, A.; Pujia, A.; Perrone, M.A.; Aiello, V.; Colica, C.; De Lorenzo, A. Role of Personalized Nutrition in Chronic-Degenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1707, doi:10.3390/nu11081707.
